
Top 10 Motion Graphics Projects for Final Year Students
Mar 18, 2025 7 Min Read 7704 Views
(Last Updated)
Motion graphics combine visual design and animation to create engaging, dynamic content for videos, ads, and presentations. For students looking to dive into this creative field, building practical projects is crucial to mastering key skills like keyframing, rigging, and 3D modeling.
In this article I will highlight and provide an in-depth guide to building 10 hands-on motion graphics projects, offering a range of difficulty levels and technical challenges to help you sharpen your animation expertise and enhance your portfolios.
Table of contents
- What is Motion Graphics?
- What Do Motion Graphics Do?
- Skills Needed for Motion Graphics
- How Motion Graphics Works
- Must-Know Tools and Software for Motion Graphics
- Top 10 Motion Graphics Projects for Students
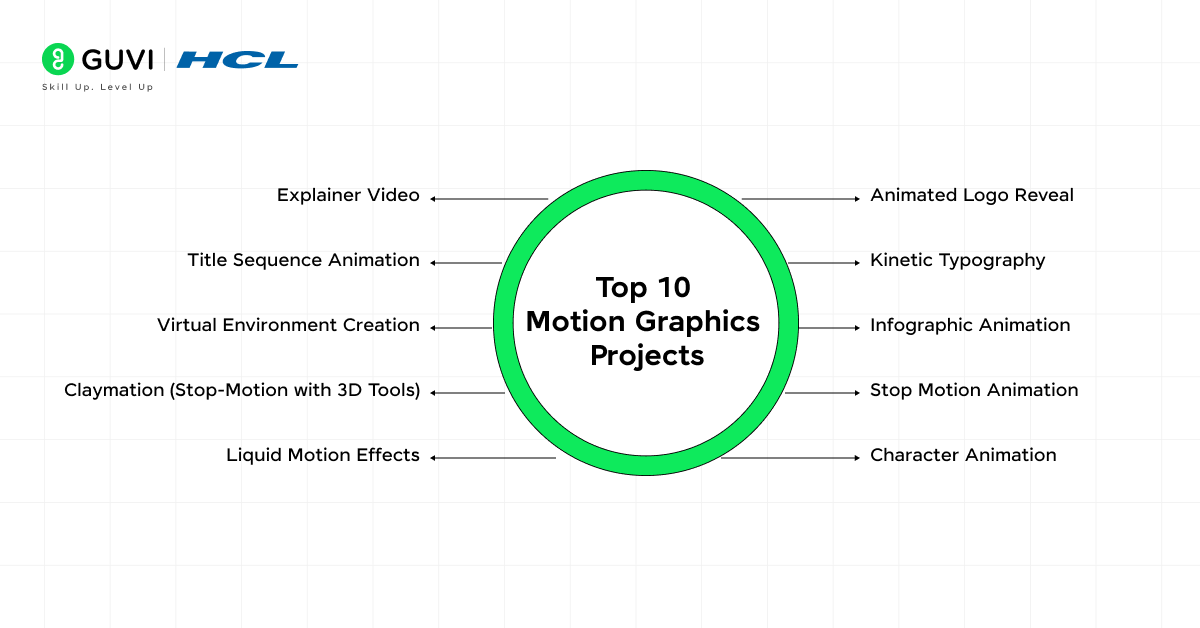
- Animated Logo Reveal
- Kinetic Typography
- Infographic Animation
- Stop Motion Animation
- Character Animation
- Explainer Video
- Title Sequence Animation
- Virtual Environment Creation
- Claymation (Stop-Motion with 3D Tools)
- Liquid Motion Effects
- Comparison Table for Motion Graphics Projects
- Takeaways…
- FAQs
- How do you plan a motion graphics project?
- What are some examples of motion graphics?
- Is VFX a motion graphic?
- What are the 3 types of motion graphics?
- Is motion graphics 2D or 3D?
What is Motion Graphics?
Motion graphics is a form of digital animation that combines graphic design elements such as shapes, text, and symbols with motion to create engaging visual content. It is widely used in industries like advertising, media production, and user interface design.
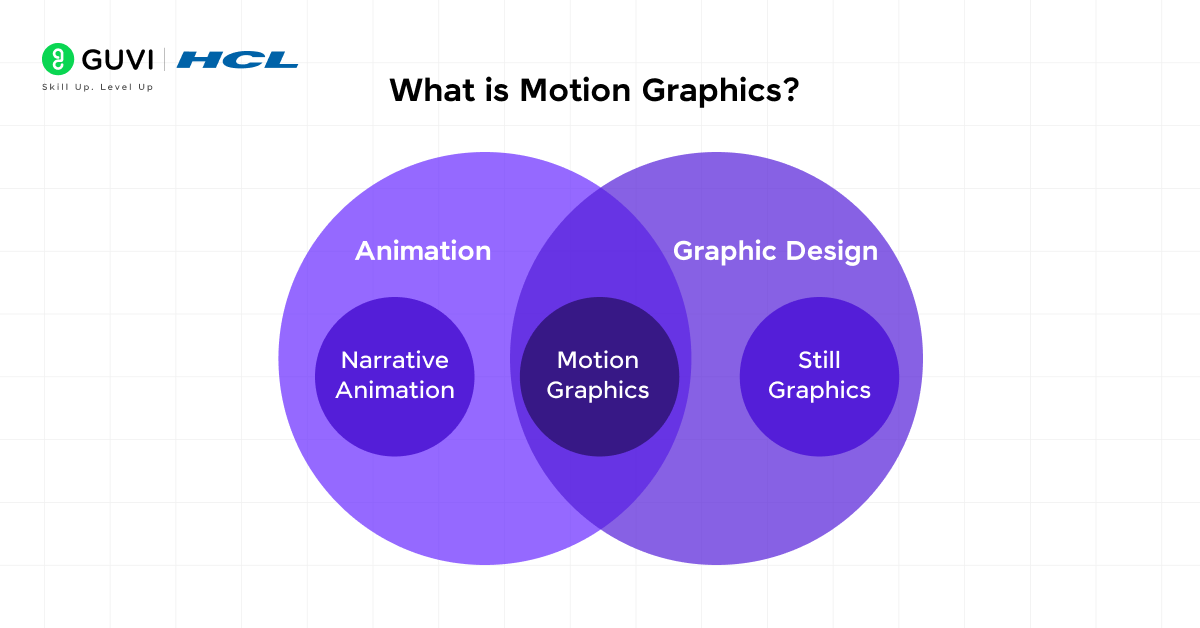
Unlike traditional animation, which often focuses on character-driven narratives, motion graphics are centered on communicating messages and enhancing storytelling through visual effects and transitions.
What Do Motion Graphics Do?
Motion graphics bring static visuals to life, enabling designers to communicate ideas dynamically. It enhances user experience (UX) by making data, instructions, or abstract concepts easier to understand through animation.
For instance, motion graphics are used in infographics, explainer videos, logo animations, and advertisements to capture attention and convey complex messages effectively.
Skills Needed for Motion Graphics
To excel in motion graphics and build good value projects, you need to know about the combination of technical and creative skills needed for the task, let’s look at them:
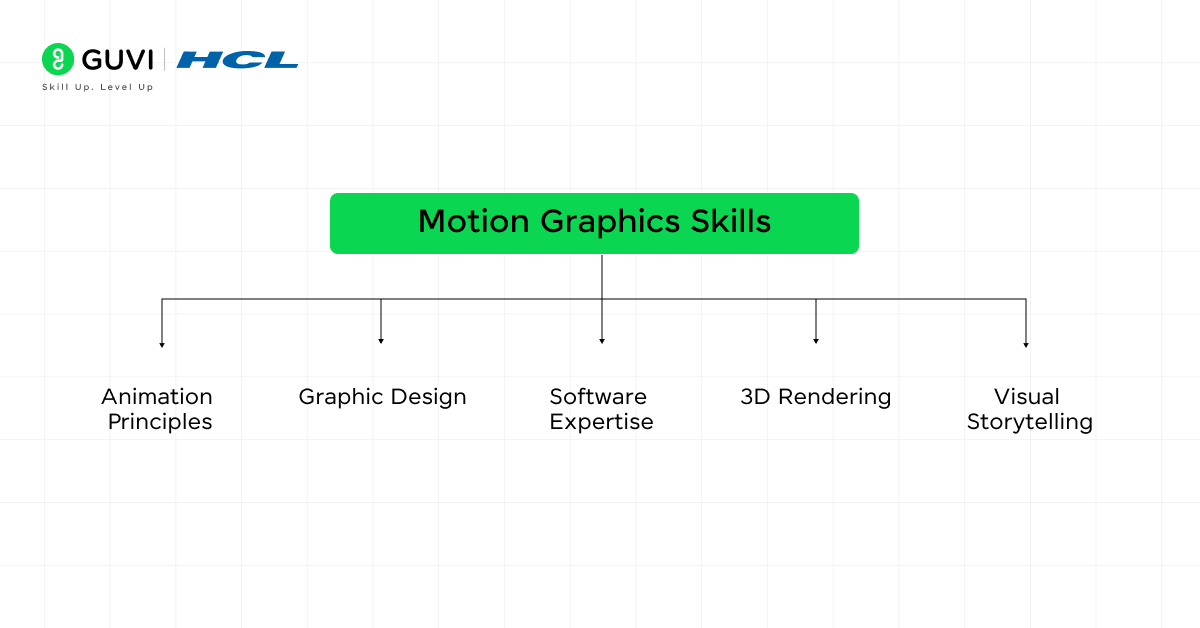
| Skill | Description |
| Animation Principles | Understanding keyframing, easing, and timing to create smooth, natural animations. |
| Graphic Design | Proficiency in typography, color theory, and composition to design visually appealing content. |
| Software Expertise | Mastery of tools like Adobe After Effects, Blender, and Cinema 4D for designing and animating graphics. |
| 3D Rendering | Knowledge of creating 3D environments and models for advanced motion graphics. |
| Visual Storytelling | Ability to translate ideas into compelling visuals that enhance the narrative or message being conveyed. |
How Motion Graphics Works
You need to understand the general motion graphics workflow to determine the work and time needed before starting your project so that you can have a plan of action ready.
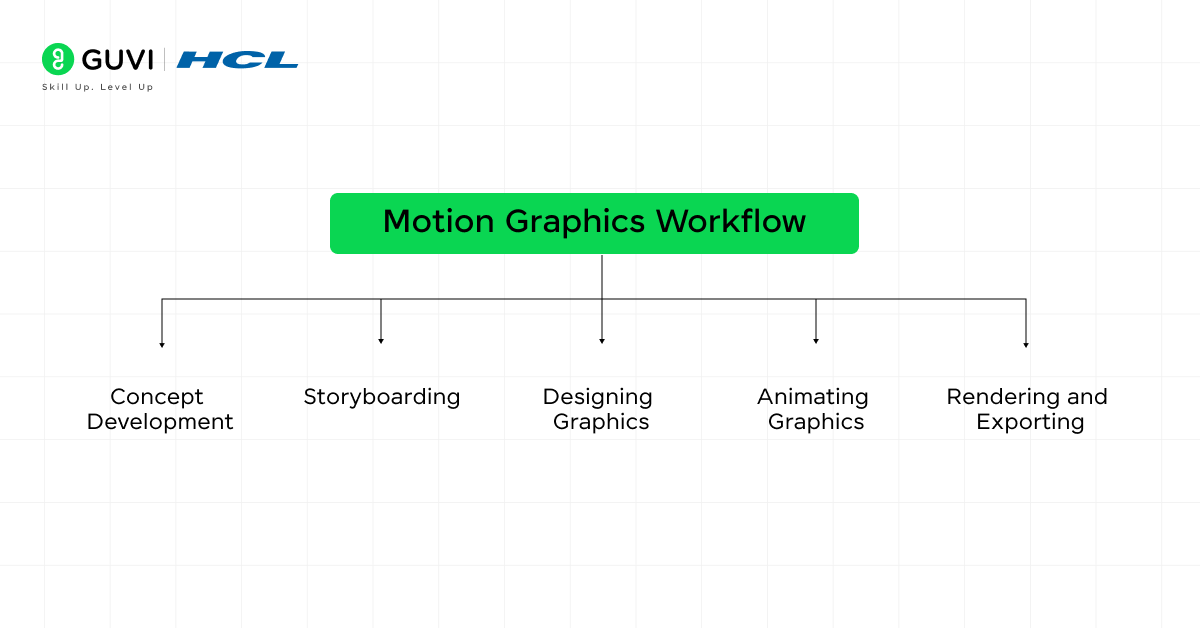
Technical Workflow
The motion graphics workflow generally follows these steps:
- Concept Development: Define the message or story to be conveyed through the animation. This involves brainstorming ideas and sketching out concepts.
- Storyboarding: A storyboard is created to map out the sequence of animations. It helps in visualizing how the graphics will move and interact over time.
- Designing Graphics: Using tools like Adobe Illustrator or Photoshop, the designer creates static elements such as logos, shapes, or text.
- Animating Graphics: The static elements are imported into motion software (e.g., Adobe After Effects), where keyframing, transitions, and effects are applied to animate the design.
- Rendering and Exporting: Once the animation is finalized, the project is rendered and exported in appropriate formats for distribution.
Must-Know Tools and Software for Motion Graphics
Motion graphics designers use various tools depending on the complexity of the project. Below is a comparison of key motion graphics software:

| Software | Key Features | Best For | Ease of Use |
| Adobe After Effects | Keyframing, effects, 3D layers, expressions | 2D/3D animation, VFX | Moderate |
| Blender | 3D modeling, rigging, rendering, physics simulation | 3D animation, motion tracking | Difficult |
| Cinema 4D | Procedural animation, 3D modeling, motion tracking | 3D motion graphics, visual effects | Moderate |
| Adobe Animate | Vector-based animation, interactivity | Web animations, game design | Easy |
Top 10 Motion Graphics Projects for Students
Now that we have learned about all that we need before building motion graphics projects, let’s discuss the projects I have hand-picked for you so that you can start building this very instant given that you have the skills we discussed in the previous section.
Do you feel like you don’t have the skills or you’re not ready to build a career in motion graphics and VFX? Then I have a great learning learning resource for you.
The Adobe Certified VFX Career Program with AI Integration by GUVI offers a cutting-edge curriculum combining traditional visual effects (VFX) techniques with the latest generative AI technologies.
Designed for aspiring VFX artists and tech enthusiasts, this course covers tools like Adobe After Effects, AI-driven animation, and 3D modeling. Students benefit from hands-on projects, real-world applications, and expert mentorship to gain proficiency in both VFX and AI. Ideal for those looking to enhance their creative and technical skills in the evolving VFX industry.
1. Animated Logo Reveal
Description: In this project, students take a static company or personal logo and animate its components to create an engaging reveal sequence. Animated logo reveals are commonly used for brand intros in videos, websites, and advertisements.
Key Learning Outcome:
- Keyframing: You will learn to apply keyframes to manipulate scale, position, opacity, and rotation over time, making the logo appear as though it “comes to life.”
- Transitions: Techniques such as motion blur, easing (to smooth the animation), and fade-in/fade-out effects are essential in making the animation feel fluid and professional.
- Layering: Understanding how to layer different elements (e.g., text, shapes, and images) and applying different animation properties to each layer allows for more complex and dynamic animations.
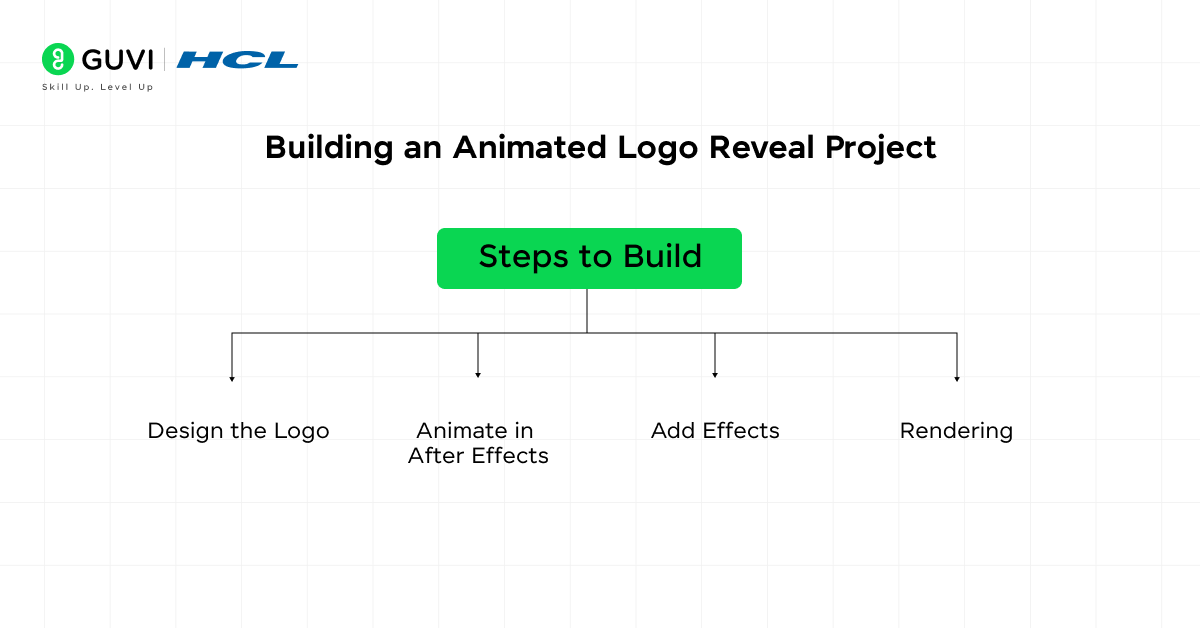
Steps to Build:
- Design the Logo: Create or import a vector-based logo in Illustrator.
- Animate in After Effects: Import the logo into After Effects, separate its components (e.g., text, icons), and animate each part using keyframes.
- Add Effects: Use motion blur, light streaks, or other effects to enhance the animation.
- Rendering: Export the animation in a high-resolution format for use in videos or presentations.
Tools: Adobe After Effects, Blender.
2. Kinetic Typography
Description: Kinetic typography involves animating text to communicate a message or narrate a story. This project helps students master the art of using motion to enhance typography for music videos, promotional content, or animated advertisements.
Key Learning Outcome:
- Text Layer Manipulation: Learn how to manipulate text layers by animating properties like tracking (space between letters), kerning (space between individual letters), and leading (line spacing).
- Audio Synchronization: Synchronizing the movement of the text with audio (e.g., voiceover or music) requires a strong understanding of timing and pacing.
- Animation Curves: Utilize animation curves to create smooth, organic movements for the text, giving it a natural rhythm and flow.
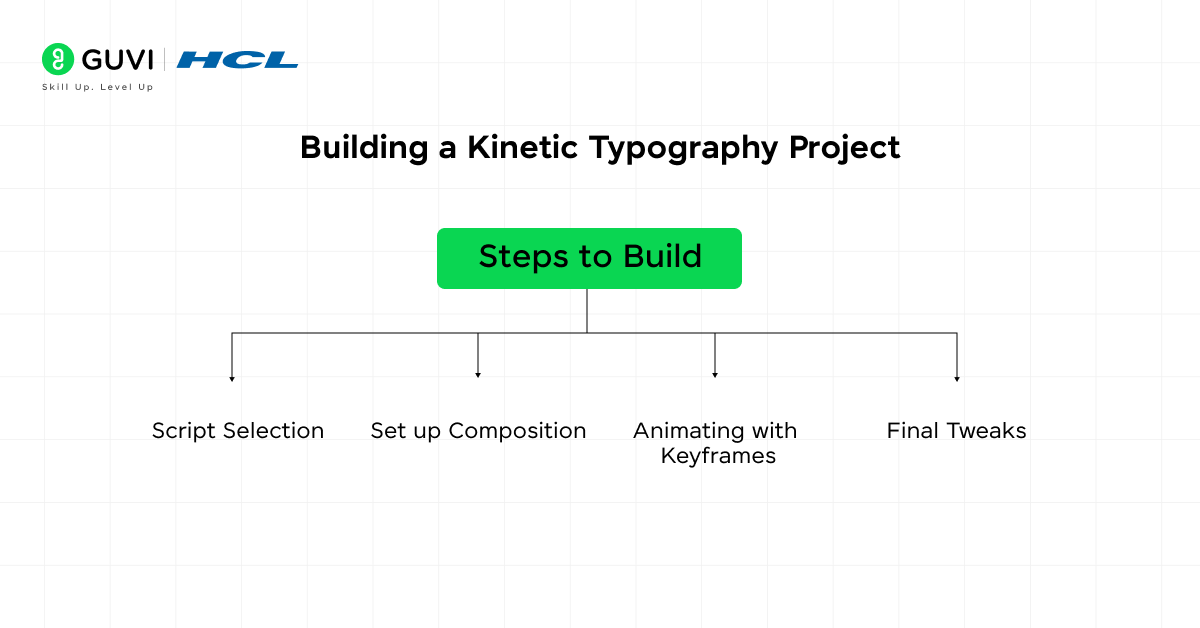
Steps to Build:
- Script Selection: Choose a script, voiceover, or lyric to animate.
- Set up Composition: Set up a composition in After Effects, add text, and break it into separate layers if needed.
- Animating with Keyframes: Animate the text properties (scale, position, opacity, etc.) in sync with the audio. Use easing functions for smooth movements.
- Final Tweaks: Add effects like glow or motion blur to enhance the overall look.
Tools: Adobe After Effects, Adobe Animate.
3. Infographic Animation
Description: Infographic animations take static infographics (graphs, charts, and icons) and add movement to make the data visually engaging. This type of project is often used in corporate presentations, educational videos, and news media to present data dynamically.
Key Learning Outcome:
- Data Visualization: Learn how to visualize complex data through animated graphs and charts.
- Masking and Layering: Masking techniques are crucial for revealing data points progressively, guiding the viewer’s attention.
- Smooth Transitions: Master smooth transitions between different sections of the infographic (e.g., bar charts morphing into pie charts) to keep the viewer engaged.
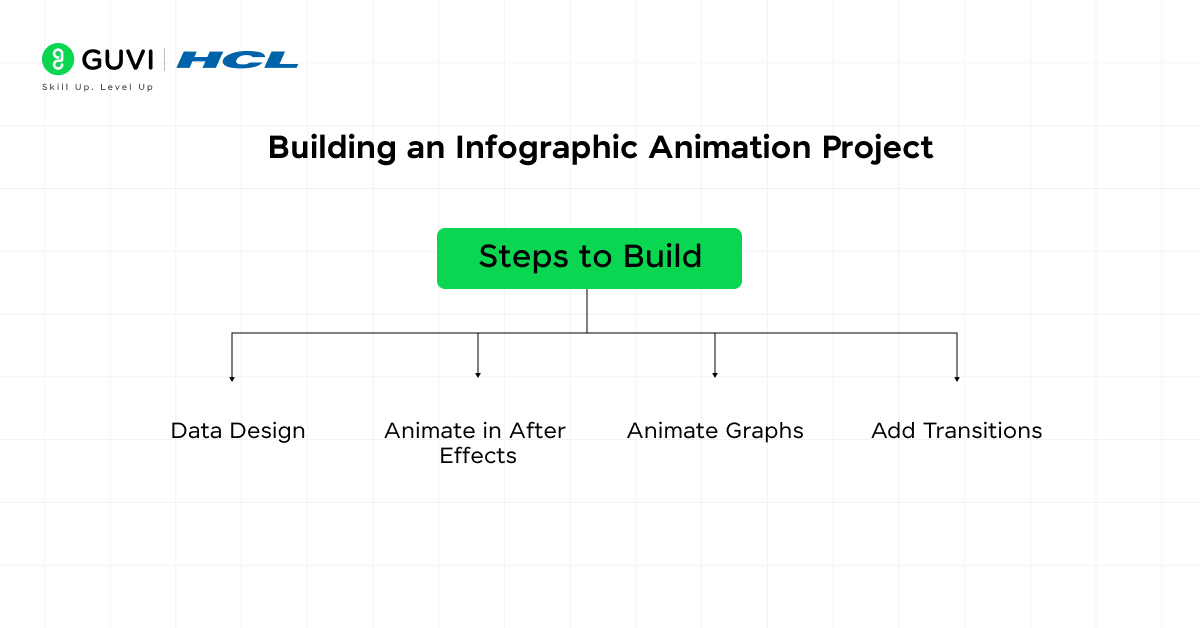
Steps to Build:
- Data Design: Use design software like Illustrator to create the static version of the infographic.
- Animate in After Effects: Import the elements into After Effects and animate individual components (bars, lines, text) to reveal data dynamically.
- Animate Graphs: Animate graphs by using scaling techniques or by creating shape-layer animations to progressively reveal information.
- Add Transitions: Smoothly transition between different types of graphs or sections using motion paths or masking techniques.
Tools: After Effects, PowerPoint with animations.
4. Stop Motion Animation
Description: Stop motion animation involves creating a series of photographs of objects that are moved incrementally to simulate motion. This technique can be used with physical objects (e.g., clay models, paper cutouts) or digital assets. It is a popular method for creating short films or promotional content.
Key Learning Outcome:
- Frame-by-Frame Animation: Understanding how to animate incrementally to create the illusion of continuous motion.
- Timing and Framerate: The student will learn how different framerates (e.g., 12 FPS, 24 FPS) affect the smoothness and realism of the animation.
- Lighting and Composition: Learn to maintain consistent lighting and composition for each frame to avoid flickering or inconsistency in the animation.
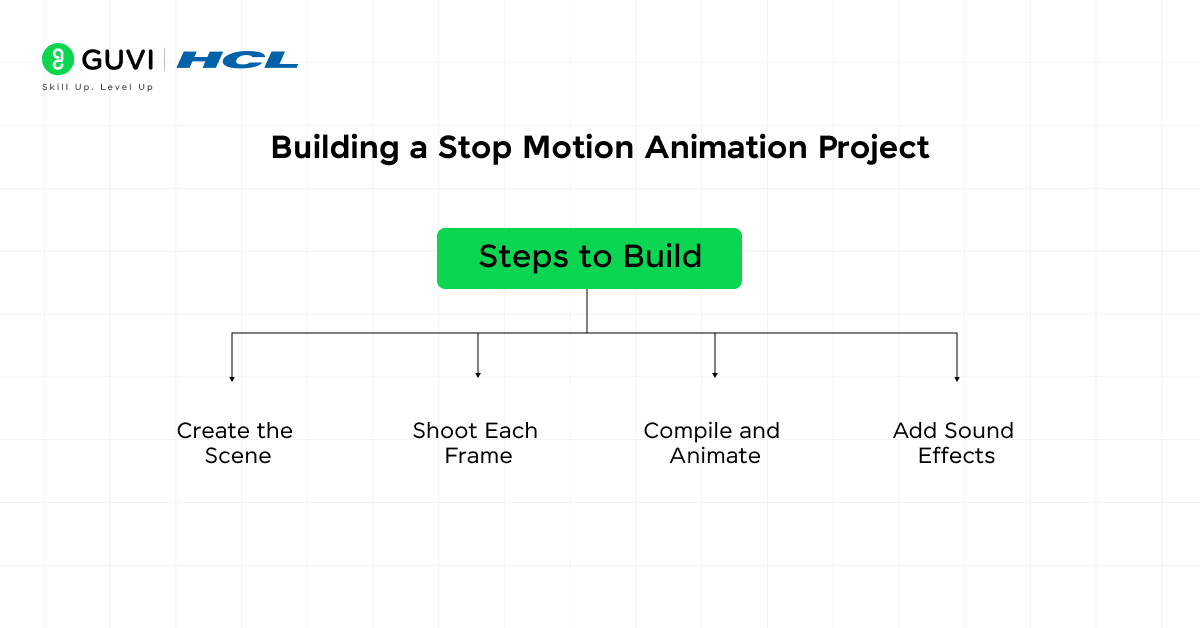
Steps to Build:
- Create the Scene: Arrange the objects you want to animate in a well-lit area, making sure that each object is moveable frame by frame.
- Shoot Each Frame: Move the object slightly, take a photo, and repeat the process. Use a tripod to ensure consistency.
- Compile and Animate: Use software like Stop Motion Studio to compile the photos into a continuous animation sequence.
- Add Sound Effects: Incorporate sound effects or background music to enhance the animation.
Tools: Stop Motion Studio, Blender.
5. Character Animation
Description: Character animation projects allow students to design and animate 2D or 3D characters, giving them life and movement. It is widely used in film, television, and video games. This project helps students understand the principles of human motion, rigging, and keyframing for character animation.
Key Learning Outcome:
- Rigging: Learn to rig a character, which involves creating a skeleton or bone structure that can be manipulated to move the character’s limbs and body.
- Keyframing for Motion: Develop skills in using keyframes to animate walk cycles, facial expressions, and gestures.
- Secondary Motion: Master secondary motion principles (e.g., hair or clothing following the character’s main movement) to add realism.
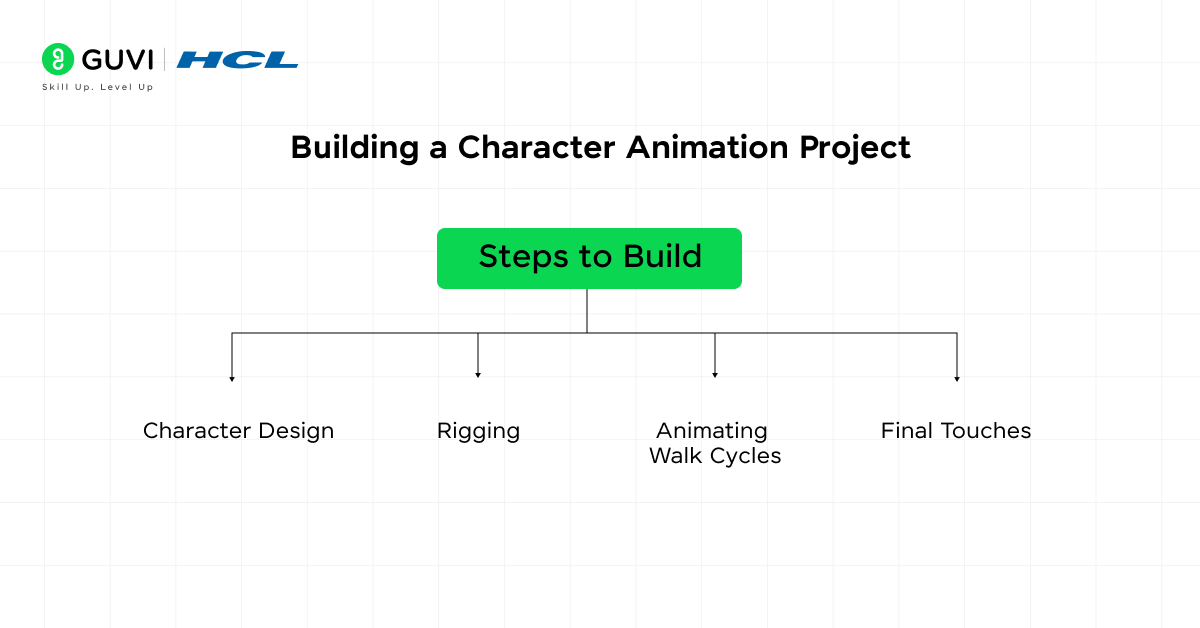
Steps to Build:
- Character Design: Use software like Adobe Illustrator or Photoshop to design a 2D character, or Blender/Cinema 4D for 3D characters.
- Rigging: Rig the character by adding a skeleton that can be manipulated. Apply inverse kinematics (IK) for realistic movement.
- Animating Walk Cycles: Animate the character performing actions like walking, running, or jumping using keyframes.
- Final Touches: Apply secondary motion, facial expressions, and texture effects to enhance realism.
Tools: Blender, Cinema 4D.
6. Explainer Video
Description: Explainer videos are short, informative videos designed to simplify complex topics through motion graphics. These are commonly used in marketing, education, and product demos.
Key Learning Outcome:
- Narrative Structure: Learn how to craft a simple, clear narrative that guides the viewer through the subject matter.
- Scene Transitions: Explore various transition effects (e.g., wipes, cuts, morphing) to create a seamless flow between scenes.
- Minimalist Design: Develop the skill of presenting information using minimal, yet effective design elements.
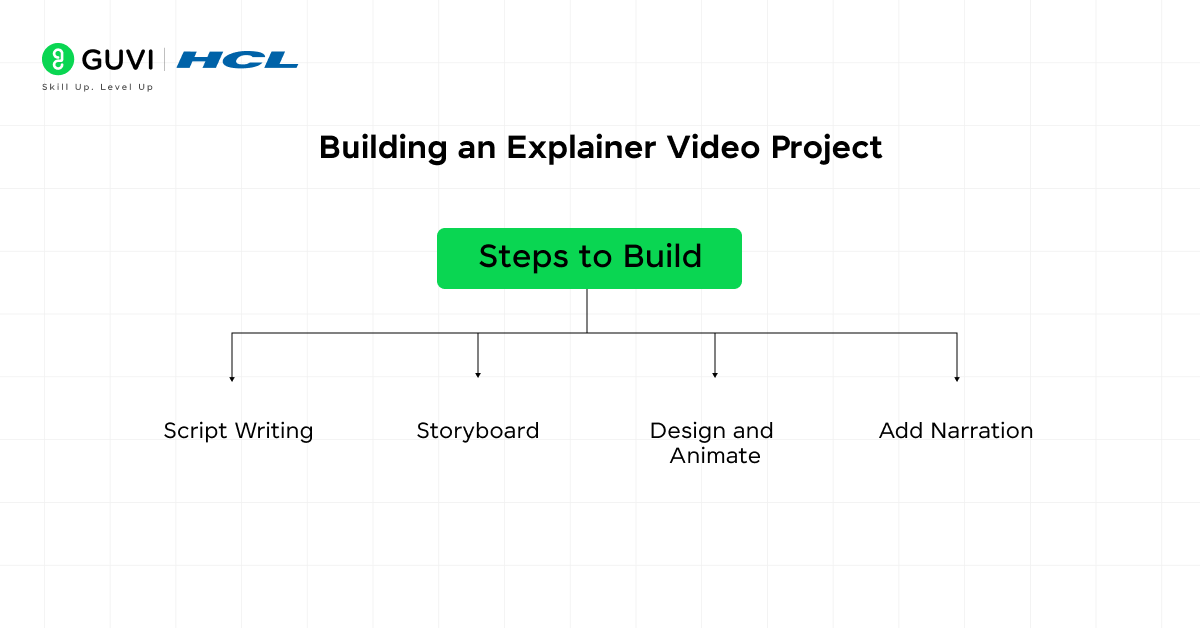
Steps to Build:
- Script Writing: Create a script outlining the key points to cover.
- Storyboard: Sketch out the key visual elements of each scene in the storyboard.
- Design and Animate: Use After Effects to design and animate the visuals that accompany the script.
- Add Narration: Record or add voiceovers to explain the concepts in sync with the animations.
Tools: Adobe After Effects, Powtoon.
7. Title Sequence Animation
Description: In this project, students design and animate an opening title sequence for a fictional film or series. Title sequences are essential in setting the mood, tone, and visual identity of a production.
Key Learning Outcome:
- Typography in Motion: Learn to animate text (typography) in creative ways to captivate viewers while delivering essential information (e.g., actor names, production titles).
- Cinematic Techniques: Master the use of camera angles, light leaks, and motion blur to create a cinematic feel.
- Mood Setting: Understand how color grading and animation pacing impact the emotional tone of the title sequence.
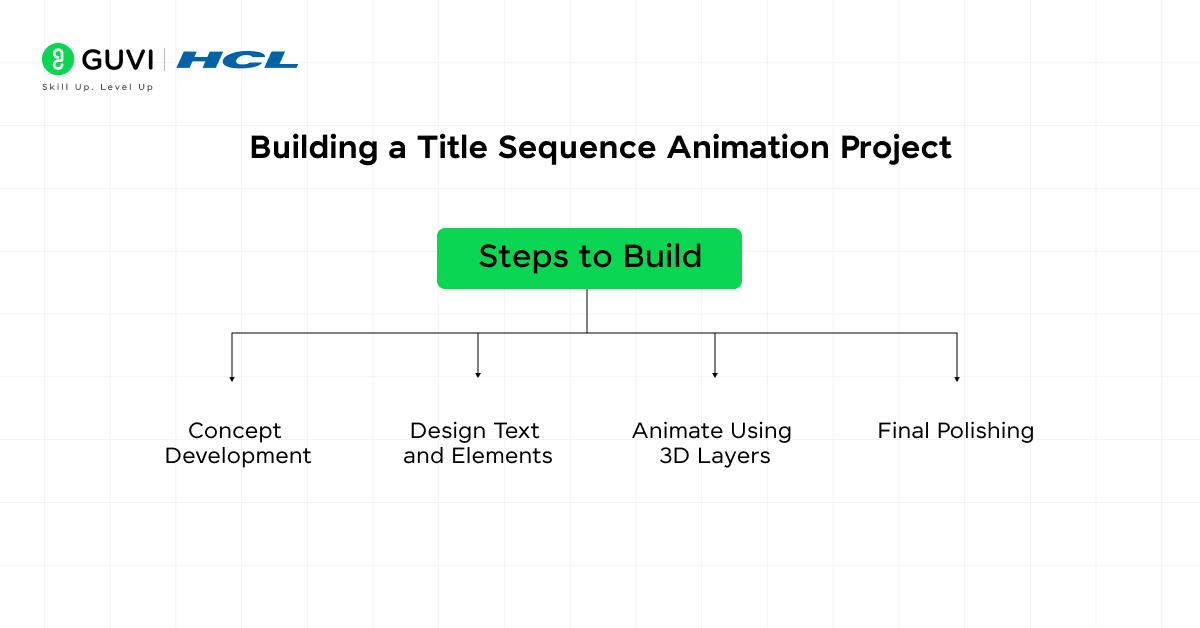
Steps to Build:
- Concept Development: Choose a theme or concept for the title sequence.
- Design Text and Elements: Use After Effects to create title text and accompanying visual elements.
- Animate Using 3D Layers: Use 3D layers and cameras to create depth and parallax effects.
- Final Polishing: Add motion blur, lighting effects, and color grading to complete the cinematic look.
Tools: Adobe After Effects, Final Cut Pro.
8. Virtual Environment Creation
Description: In this project, students are tasked with building and animating a 3D virtual environment, often used in games, architectural visualizations, and simulations. This includes creating terrains, lighting, textures, and animating objects within a 3D space.
Key Learning Outcome:
- 3D Modeling: Understand the creation of landscapes using 3D modeling software like Blender. You’ll learn to shape terrains, add objects, and place camera angles for a visually appealing scene.
- Lighting and Texturing: Focus on realistic lighting (ambient, directional, and point lights) and apply textures to give surfaces like water, rocks, and foliage realistic appearances.
- Camera Movements: Learn to animate camera movements to simulate fly-throughs or character perspectives in the 3D world.
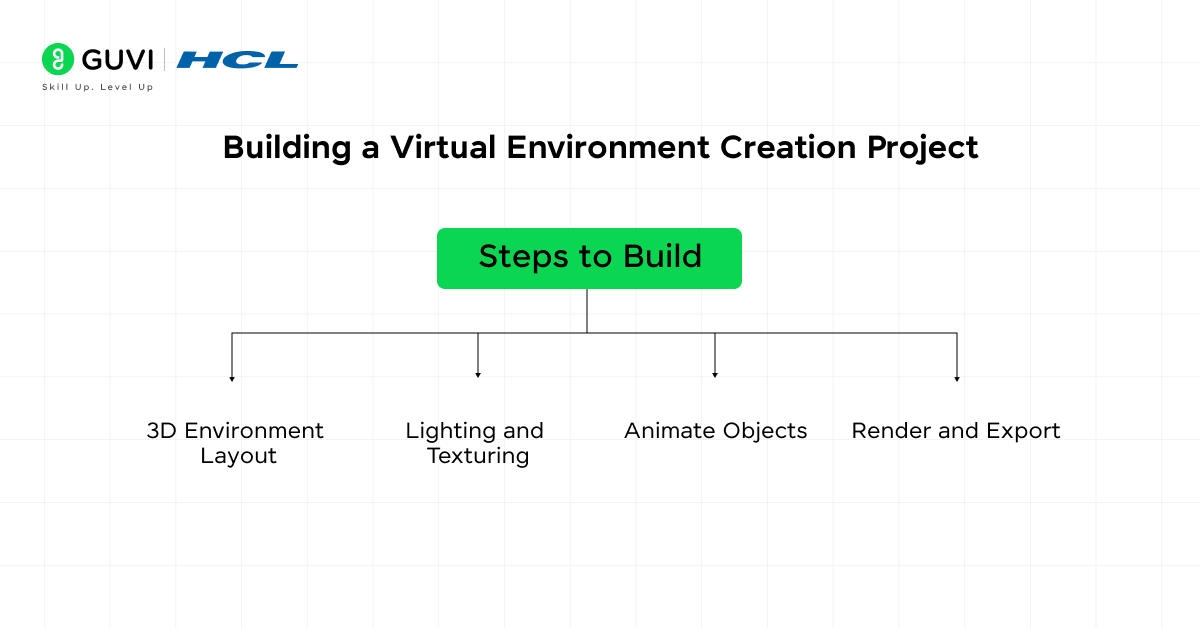
Steps to Build:
- 3D Environment Layout: Start by designing the 3D layout in Blender or Cinema 4D, using height maps or manual modeling to create terrain.
- Texturing and Shading: Apply textures to the surfaces using UV mapping techniques. Add realistic shading to enhance depth.
- Animate Objects: Use keyframes to animate moving elements in the environment, such as trees swaying or water flowing.
- Render and Export: Optimize your project for rendering. Ensure the environment is ready for interactive or visual outputs by selecting appropriate rendering settings.
Tools: Blender, Cinema 4D, Unreal Engine.
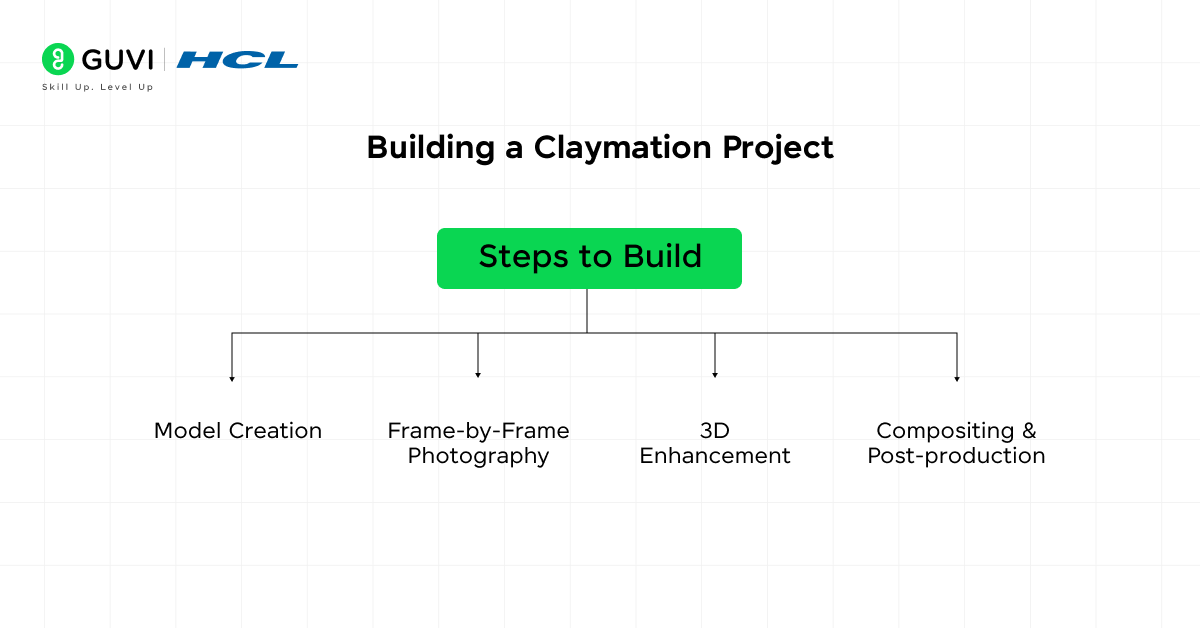
9. Claymation (Stop-Motion with 3D Tools)
Description: This project blends traditional claymation (stop-motion animation with clay models) and modern 3D tools. Students will create characters and objects out of clay, photograph them in small incremental movements, and then enhance the animation using 3D modeling software. This approach is often used in creative storytelling or playful commercials.
Key Learning Outcome:
- Stop-motion Animation: Learn the art of stop-motion by physically manipulating clay models and photographing each frame to simulate motion.
- 3D Enhancement: Use Blender or Maya to add lighting, textures, and smooth animations, giving your clay models a more polished and realistic appearance.
- Compositing: Integrate the 3D-enhanced models with backgrounds and other assets using Adobe After Effects.
Steps to Build:
- Model Creation: Sculpt the clay models for your characters and objects.
- Frame-by-Frame Photography: Move the models slightly and take a series of photographs for animation.
- 3D Enhancement: Import the photographs into Blender or Maya to add lighting, and textures, and smooth out the movements.
- Compositing & Post-production: Use Adobe After Effects to blend the animation with the background and add final effects.
Tools: Blender, Maya, Adobe After Effects.
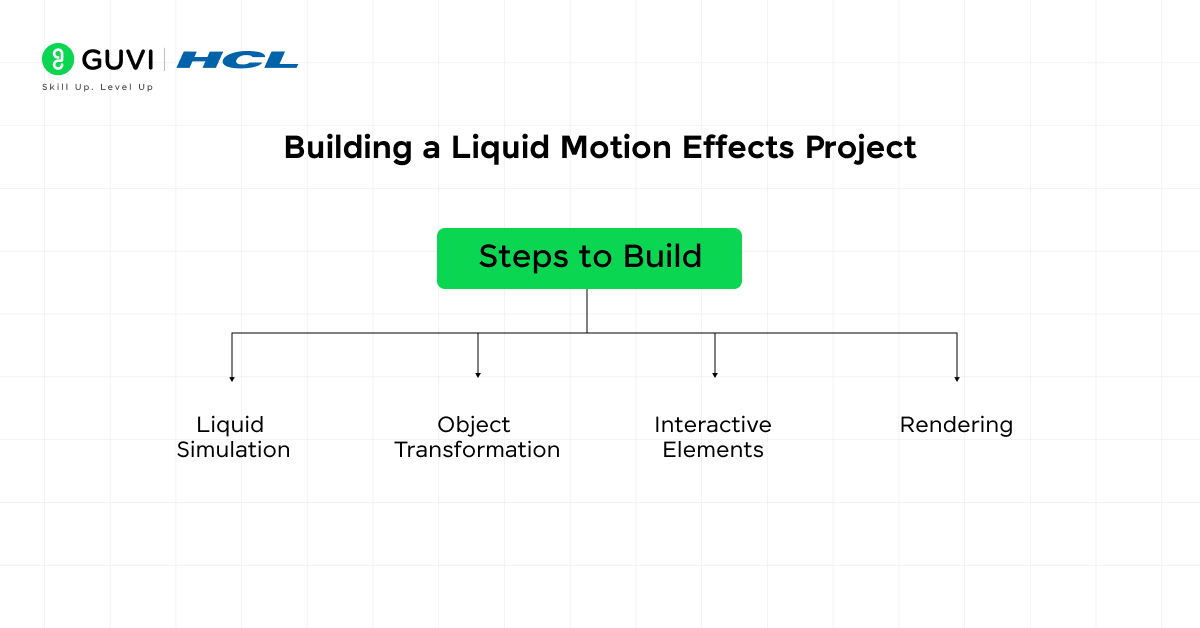
10. Liquid Motion Effects
Description: Liquid motion effects mimic the fluidity and flow of water or other liquids. This project is ideal for creating dynamic logo reveals, seamless transitions, or adding fluid-like interactions to UI/UX designs. You will explore how to simulate liquid behavior using physics-based animation software.
Key Learning Outcome:
- Fluid Dynamics: Understand the principles of liquid simulation using Blender’s or Houdini’s physics engine to create realistic water flow or splashes.
- Morphing Effects: Learn to morph objects into liquid-like forms, which are often used in logo reveals or website animations.
- Interactive Elements: Develop interactive animations for web pages or apps where user actions (e.g., scrolling or clicking) trigger fluid-like effects.
Steps to Build:
- Liquid Simulation: Use Blender or Houdini to create a liquid simulation based on real-world physics.
- Object Transformation: Morph solid shapes into fluid forms, such as transforming a logo into a splash of water.
- Interactive Elements: Integrate the liquid effects into a webpage or app, making them respond to user inputs.
- Rendering: Optimize your simulation for high-quality rendering with smooth transitions.
Tools: Blender, Houdini, After Effects.
Comparison Table for Motion Graphics Projects
| Project Name | Key Learning Outcomes | Tools | Difficulty Level | Time to Complete |
| Animated Logo Reveal | Keyframing, Layering, Transitions | After Effects, Blender | Beginner | 1-2 Days |
| Kinetic Typography | Text Layer Animation, Audio Sync | After Effects, Animate | Beginner | 2 Days |
| Infographic Animation | Data Visualization, Masking, Transitions | After Effects | Intermediate | 3 Days |
| Stop Motion Animation | Frame-by-Frame Animation, Lighting, Composition | Stop Motion Studio | Intermediate | 4-5 Days |
| Character Animation | Rigging, Walk Cycles, Secondary Motion | Blender, Cinema 4D | Advanced | 1-2 Weeks |
| Explainer Video | Narrative Structure, Minimalist Design, Audio Sync | After Effects, Powtoon | Beginner | 3-4 Days |
| Title Sequence Animation | Cinematic Techniques, Text Animation, Mood Setting | After Effects, Final Cut Pro | Advanced | 1 Week |
| Virtual Environment Creation | 3D Modeling, Lighting, Texturing, Camera Movements | Blender, Unreal Engine | Advanced | 2-3 Weeks |
| Claymation Animation | Stop-motion Techniques, 3D Enhancement, Compositing | Blender, Maya, After Effects | Intermediate | 4-5 Days |
| Liquid Motion Effects | Fluid Dynamics, Morphing Effects, Interactive Elements | Blender, Houdini, After Effects | Intermediate | 3-4 Days |
Takeaways…
These 10 motion graphics projects are excellent starting points for students to explore and enhance their motion design skills. Each project focuses on a different aspect of motion graphics, from 2D animations to complex 3D environments.
By building these projects, you will gain technical expertise in various animation techniques, including keyframing, rigging, compositing, and 3D modeling, which are fundamental skills in today’s multimedia and entertainment industries.
I hope this guide sets you on the path of building your first motion graphics project, do let us know what you thought of these projects in the comments section below.
FAQs
Start by defining the project goals, script, and storyboard. Then, gather assets, choose software, and create an animation timeline for production.
Examples include animated logos, explainer videos, infographics, and title sequences in films.
No, VFX involves creating realistic effects in live-action scenes, while motion graphics focus on animated design elements.
The three types are explainer videos, infographics, and logo animations.
Motion graphics can be both 2D and 3D, depending on the project’s requirements.























![10 Unique Keras Project Ideas [With Source Code] 17 Keras Project Ideas](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Feature-Image.png)




Did you enjoy this article?