
Top 10 Types of Regression in Machine Learning You Must Know
Sep 12, 2025 6 Min Read 2243 Views
(Last Updated)
When you think about machine learning, you probably imagine powerful algorithms that are predicting the stock market, recommending what you should binge on Netflix, or helping doctors identify diseases. Behind many of the smart applications we use, there is one simple concept known as regression.
Regression in machine learning includes more than simply drawing a straight line on a graph. It is a family of methods that can describe relationships between variables, predict values, and derive information and insight from data. It is common to think about regression when estimating housing value, determining the likelihood of customer churn, predicting sales, or estimating customer lifetime value, and regression is often the first thing that comes to a data scientist’s mind.
In this blog, we will discuss the different types of regression in machine learning, how they work, when to use them, their pros and cons, and provide real-world examples. By the end of this blog, you will have a solid understanding of regression models in machine learning and how they fit into today’s data-driven world.
Table of contents
- What is Regression in Machine Learning?
- Why Regression Matters in Machine Learning?
- Types of Regression in Machine Learning
- Linear Regression in Machine Learning
- Logistic Regression in Machine Learning
- Polynomial Regression in Machine Learning
- Ridge Regression in Machine Learning
- Lasso Regression in Machine Learning
- ElasticNet Regression in Machine Learning
- Stepwise Regression in Machine Learning
- Bayesian Regression in Machine Learning
- Quantile Regression in Machine Learning
- Support Vector Regression in Machine Learning
- Applications of Regression in Machine Learning
- Business and Finance
- Healthcare
- Marketing
- Technology and AI
- Environment and Agriculture
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Regression Models
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
- Final Thoughts
- FAQs
- Is regression only useful in technical fields like AI and data science?
- Do I need to know advanced math to understand regression models?
- When should I use linear regression?
- What is the use of logistic regression if it’s a classification algorithm?
What is Regression in Machine Learning?
Regression in machine learning is a type of supervised learning algorithm. Meaning, the model is trained with the dataset containing known inputs (features) and the known outputs (labels). The main goal of regression is to learn the relationship between given inputs and outputs so that the model can predict the future values accurately.
Unlike classification, which involves categorizing data into categories (for example, putting data into a “spam” and “not spam” category, or putting a pet into “cat” or “dog”), regression is used where the outcome is a number. In other words, regression deals with continuous values.
For example:
- Predicting how much a house will be sold for based on its size, location and the number of rooms.
- Predicting what the temperature will be tomorrow using past weather data.
- Forecasting the number of sales of a product for the following month.
In these examples, the answer is not a label like “yes” or “no,” but is a number (e.g. ₹75,00,000 for the house, 32°C for tomorrow’s temperature, or maybe 15,000 units of sales).
Therefore, regression models in machine learning are fundamentally about identifying patterns in numbers and these will then be used to predict the future. Regression helps answer questions like “How much?” or “How many?” or “What will it be?”
Why Regression Matters in Machine Learning?
You might be thinking: with so many algorithms out there, why pay particular attention to regression models in machine learning? Here are some reasons:
- Foundation for ML: Many of the complex models you will run into are based on the foundations of regression.
- Interpretability: Regression is a measure of “how much” each component contributes to the outcome.
- Wide-ranging Uses: AI-driven applications, marketing, finance, and healthcare all make use of regression models.
- Flexibility: Depending on the available regression methodologies, you can model either linear data in a simple linear manner or fit a complex nonlinear structure.
Regression may seem trivial, but it has some interesting facts about it. Did you know that regression is over 200 years old? It was first published by Sir Francis Galton while studying heredity. Even though it is an old concept, linear regression is still today the most popular algorithm, in both statistics and machine learning.
Types of Regression in Machine Learning
1. Linear Regression in Machine Learning
Linear regression is probably the most common algorithm used for predictive analytics. It tries to understand a straight-line relationship between the inputs (features) and outputs (target). Let’s say, it is estimating how much the output value changes when the input changes.
The general formula for linear regression is:
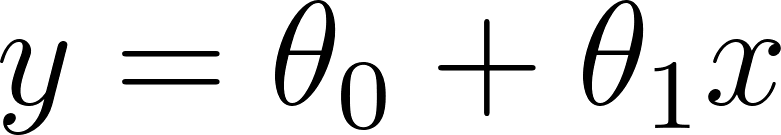
Where:
- y = the predicted output
- x = the input feature
- θ = the coefficient or weight that shows the influence of x on y
- b = the bias or intercept, representing the base value when x = 0
Linear regression is simple to implement and to interpret, which is why it is often the first approach for beginners. However, it may occasionally overfit or underperform if in fact, the data has very strong nonlinear patterns.
2. Logistic Regression in Machine Learning
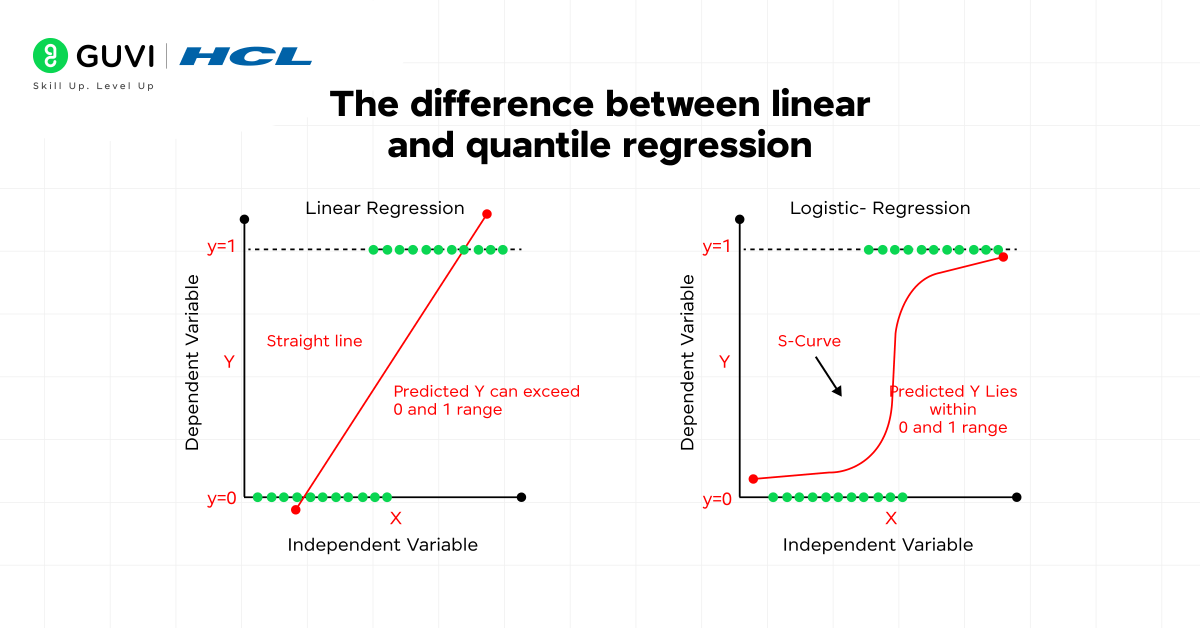
Logistic regression is a classification algorithm that predicts the probability of an event. It is most commonly used for binary classification, where the target variable has two possible outcomes (e.g., yes/no, 0/1, spam/not spam).
Whereas most regression predicts a continuous value, logistic regression predicts a categorical value by using the sigmoid (logistic) function to transform any real value to the probability of an event from 0 to 1.
Sigmoid Function:
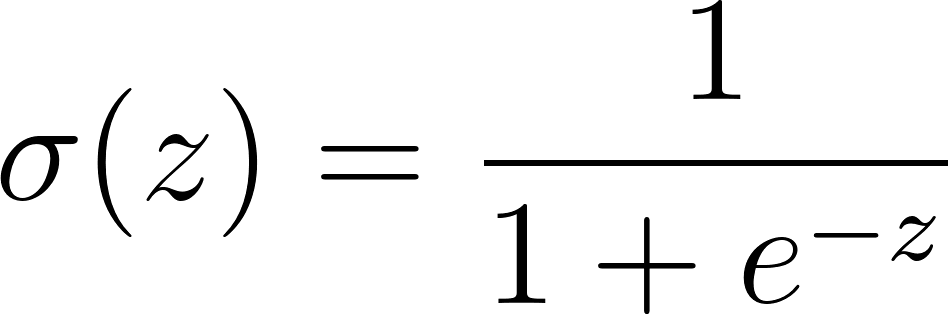
Here,
- σ(z) = predicted probability
- e = mathematical constant (Euler’s number ≈ 2.718)
- z = linear function of inputs
If the probability is greater than 0.5, the output is classified as class 1; otherwise, it is classified as class 0.
Note: Although logistic regression is primarily used for classification tasks, it is often grouped with regression algorithms because it relies on regression-like concepts, such as fitting a linear equation to input features and estimating coefficients.
3. Polynomial Regression in Machine Learning
Sometimes, data does not fit well with a straight line (like in linear regression). Polynomial Regression is an extension of linear regression that adds powers of the input variable to the model. This helps in capturing curved or nonlinear relationships between variables.
Equation:
Y = β₀ + β₁X + β₂X² + β₃X³ + … + βₙXⁿ + ε
Here:
- X = input (independent variable)
- Y = output (dependent variable)
- β₀, β₁, …, βₙ = coefficients (weights)
- ε =error term
Imagine predicting house prices. The relationship between price and size may not be straight; at first, prices rise slowly, then sharply as size increases. Polynomial regression can model this curved growth pattern better than a straight line.
4. Ridge Regression in Machine Learning
One major issue with linear regression is overfitting, especially when we have many features. Ridge regression in machine learning helps solve this by adding a penalty term (regularization) to the regression equation.
Syntax (cost function):
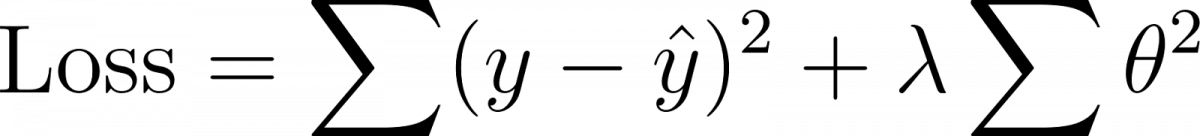
Here, λ (lambda) controls the penalty. Larger values shrink coefficients, reducing model complexity.
Example: Predicting movie ratings from multiple features (genre, actors, budget, runtime) where too many correlated features may overfit.
5. Lasso Regression in Machine Learning
The loss function in Lasso regression combines two parts: the error term and the penalty term. The error term,, measures how far the model’s predictions are from the actual values, just like in linear regression. The penalty term,λ∑∣βj∣, adds a cost for having large coefficients. This penalty encourages the model to shrink some coefficients to zero, which means Lasso can automatically remove irrelevant features. In short, Lasso regression helps improve accuracy, prevents overfitting, and performs feature selection at the same time.
Syntax (cost function):
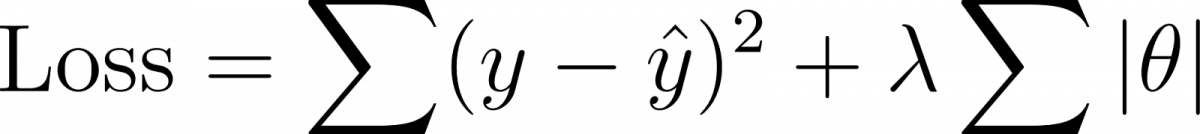
Where:
- |θ| = absolute value of coefficients
6. ElasticNet Regression in Machine Learning
ElasticNet combines both Lasso (L1) and Ridge (L2) penalties, making it effective when dealing with datasets that have many features.
Syntax (cost function):
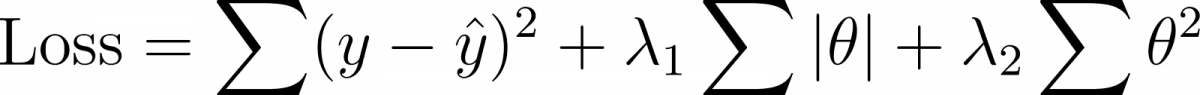
Where:
- λ₁ = weight for L1 penalty (like Lasso)
- λ₂ = weight for L2 penalty (like Ridge)
7. Stepwise Regression in Machine Learning
Stepwise regression is an iterative technique for constructing regression models. Instead of fitting all of the variables, it adds or deletes predictors based on their statistical significance (for example: p-values or AIC).
The three stepwise methods to create a predictive model are:
- Forward selection – begin with none and build up by adding significant predictors.
- Backward elimination – begin with all, and delete the least predictive.
- Hybrid (stepwise) – begin with all, and delete the least predictive.
(No single formula, but it still uses linear regression equations with selected variables.)
Example: Building a credit scoring model from financial indicators, ensuring that only the most predictive financial indicators are reflected in your model.
8. Bayesian Regression in Machine Learning
Bayesian Regression is a type of regression using Bayesian inference based on bayes’ theorem, rather than simply estimating fixed values for the model coefficients. While linear regression produces a single ‘best fit’ line, Bayesian regression treats the model parameters as distributions, rather than single values.
With Bayesian regression, we start with a prior belief (what we believe the parameters to be), and with more data, we update the prior to produce a posterior distribution. This makes Bayesian regression extremely useful when there is uncertainty in data or prior knowledge is available.
9. Quantile Regression in Machine Learning
Most regression models, such as linear regression, are designed to estimate the mean (or average) of the target variable. However, averages are not always informative because we may want to know how the outcomes behave at other points in the distribution.
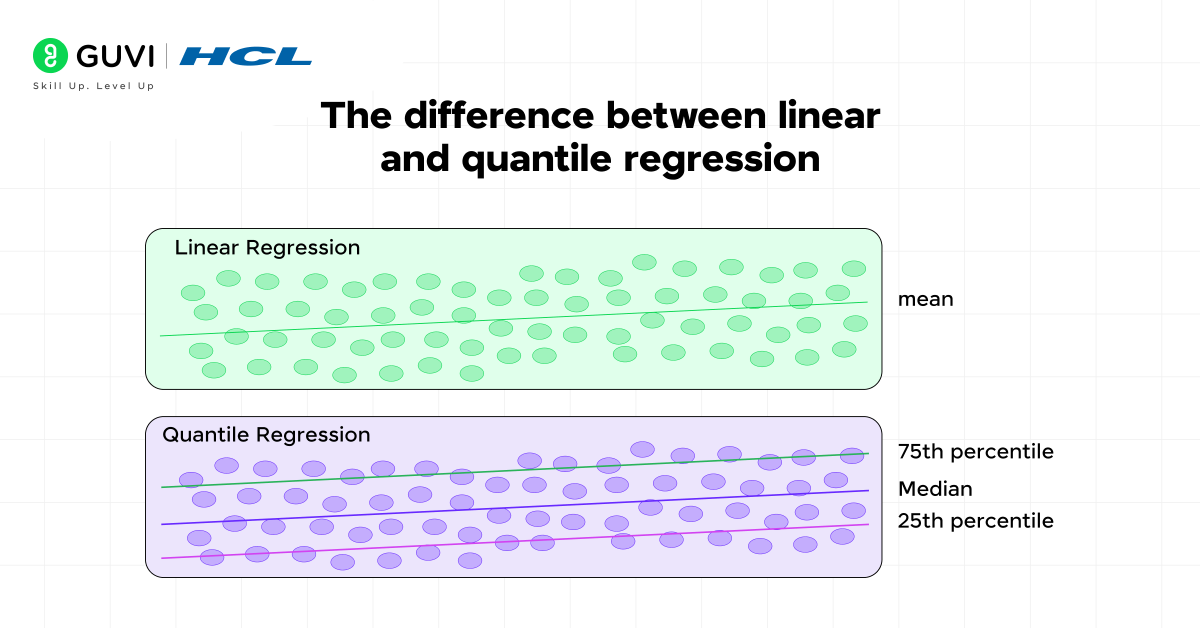
Quantile Regression helps address this issue because it estimates a quantile (e.g. the 25th, 50th/median, or 90th percentiles), rather than just estimating the mean. As a result, quantile regression is extremely useful for assessing datasets that are skewed, have outliers, or have unequal distributions.
Example: Suppose you are predicting the price of houses. A simple regression might give you an estimate of the average price, but a buyer or seller may be interested in the lower-end (25th percentile) or higher-end (90th percentile) values of the price. Quantile regression allows us to capture these variations in the data!
10. Support Vector Regression in Machine Learning
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are known for classification, of course! But SVMs can also be adapted for regression and are called Support Vector Regression (SVR).
In SVR, instead of predicting exact outcomes, you try to fit the data within a margin of tolerance (epsilon), while being as flat as possible.
How does it work?
- In regression, we want to fit a line (or curve) as closely to the data as possible.
- In SVR, instead of trying to hit every data point exactly, we fit the line within a margin of tolerance (ε).
- This margin means:
- If a prediction is within the margin, we don’t mind so much (it’s ‘good enough’).
- If it falls outside the margin, the model adapts to reduce that error.
So SVR is less strict and instead pays attention to flatness (simplicity) ignoring all the minuscule deviations.
Applications of Regression in Machine Learning
1. Business and Finance
- Stock Price Prediction: Regression variations (support vector regression and polynomial regression) are used to predict stock price movements.
- Sales Forecasting: Businesses rely on regression models to determine potential revenue based on advertising, industry movements, and seasonality.
- Risk Assessment: Logistic regression is used in the credit decision-making process and fraud detection.
2. Healthcare
- Disease Prediction: Logistic regression in machine learning assists with classification problems in determining if a patient is at-risk of acquiring a health condition (diabetes, heart disease, etc.)
- Drug Effectiveness: Quantile regression can model how different people respond to drugs.
- Medical Imaging: Bayesian regression helps users include uncertainty when analyzing scans.
3. Marketing
- Customer Churn Prediction: Logistic regression can help predict if customers will continue to use your service.
- Advertising Effectiveness: By using regression models, ROI can be estimated from various marketing campaigns.
- Recommendation Systems: Regression can help predict user ratings of products or content.
4. Technology and AI
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Regression models can be used to predict sentiment scores in text.
- Computer vision: Regression can provide bounding box estimates for detecting objects.
- Speech Recognition: Regression can help predict acoustic event patterns in audio signals.
5. Environment and Agriculture
- Forecasting Weather: Bayesian regression and polynomial regression are applied to climate models.
- Predicting Crop Yields: Regression can help farmers predict crop yields based on a variety of parameters, such as soil content, rainfall, and fertilizer use.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Regression Models
Advantages:
- Regression models such as linear regression are transparent and easy to interpret, which allows easier explanation of predictions.
- Good for predicting continuous values (e.g., sales, prices, demand).
- Performs well with relatively small datasets compared to deep learning.
- Trainability and implementation is fast.
- Many types (linear, logistic, ridge, lasso etc.) are there to cover different types of problems.
- A starting point for more sophisticated machine learning and statistical models.
Disadvantages:
- Assumptions may be unrealistic; models such as linear regressions assume linear relationships that do not actually exist in the data.
- Sensitive to outliers, any extreme values will disproportionately affect your predictions.
- Does generally works well with data that is not highly non-linear, unless transformed (like polynomial regression).
- Complex models such as polynomial or stepwise regressions may fit noise, rather than the patterns you want.
- Multicollinearity, or highly correlated features, will decrease the reliability of the model.
- On very complex datasets, a simple model may (and probably will) be a worse predictor than an advanced algorithm such as a decision tree or neural network.
If regression sparked your curiosity, it’s just the beginning. With HCL GUVI’s Advanced AI & Machine Learning Course, co-designed with industry leaders, you’ll master hands-on skills in Python, Deep Learning, NLP, Generative AI, and MLOps. Gain real-world experience through projects, mentorship, and job-ready training to turn your learning into a career advantage.
Final Thoughts
Regression in machine learning can sound simple. However, it is one of the most powerful and most often used techniques. Whether it is linear regression, which models relationships in a straight line or support vector regression, which deals with a level of non-linearity, each type of regression comes with its own strengths for certain problems. Knowing when and how to use regression algorithms in machine learning is where the real secret lies.
If you are working with feature selection, then Lasso may assist you. If you have uncertainty to deal with, then Bayesian regression is available. If you would like robustness in having non-linear data, then support vector regression yields a separation margin from classes.
FAQs
1. Is regression only useful in technical fields like AI and data science?
No, regression can be used in many other areas apart from AI and data science, it can be used in marketing, finance, healthcare, agriculture and so on.
2. Do I need to know advanced math to understand regression models?
Not in the beginning of your learning process. A basic understanding of algebra and functions are enough for you to get started. Later on when you learn deeper, you should be able to understand concepts like linear algebra, statistics, and calculus.
3. When should I use linear regression?
Use linear regression when your data shows a linear relationship between input variables and the output, and when the assumptions of normality, linearity, and homoscedasticity are satisfied.
4. What is the use of logistic regression if it’s a classification algorithm?
Despite its name, logistic regression is used for binary classification problems. It calculates the probability of an event occurring using a sigmoid function.




























Did you enjoy this article?