
Top Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers for All Levels
Feb 05, 2026 8 Min Read 2963 Views
(Last Updated)
According to a Standish Group report, over 66% of software projects either fail outright or face major challenges due to poor processes and unclear requirements. This shows why understanding the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is critical not merely for building software but also for succeeding in interviews.
SDLC provides a systematic approach to planning, designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software. Employers expect candidates to know both the theory and the practical application of SDLC. Interviewers often use these questions to check how well you can connect concepts to real-world project situations.
In this guide, we cover Software Development Life Cycle interview questions and answers across multiple levels. Mastering these software development life cycle questions will help you explain SDLC clearly. They will help you handle scenario-based challenges confidently and stand out during your interview.
Table of contents
- Beginner-Level Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers
- What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
- Why is SDLC important in software development?
- What are the common phases of SDLC?
- What happens during the planning phase of SDLC?
- What is the role of testing in the SDLC process?
- What are some SDLC models you know?
- How does the Waterfall model differ from the Agile model?
- What is the importance of documentation in SDLC?
- What challenges can occur during SDLC?
- How do maintenance activities fit into SDLC?
- Intermediate-Level Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers
- How do SDLC models affect project outcomes?
- What is the difference between verification and validation in SDLC?
- How does risk management fit into the SDLC process?
- What are functional and non-functional requirements in SDLC?
- What is the role of a feasibility study in SDLC?
- How does SDLC handle change requests?
- What is the importance of requirement traceability in SDLC?
- How do prototyping and SDLC work together?
- What metrics are commonly used to measure SDLC success?
- How does maintenance in SDLC support long-term system success?
- Advanced-Level Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers
- How do you integrate SDLC with DevOps practices?
- How is security embedded in the SDLC process?
- How do Agile and SDLC align in large-scale enterprise projects?
- What role does Continuous Integration (CI) play in SDLC?
- How do you handle performance requirements in SDLC?
- How do you apply SDLC in microservices-based architecture?
- What is the impact of automation testing on SDLC efficiency?
- How is user acceptance testing (UAT) managed in SDLC?
- How does SDLC support compliance in regulated industries?
- How do you measure technical debt in SDLC projects?
- Scenario-Based and Practical Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers For Freshers
- Your team is building a small mobile app. The client is unsure about features. How will you approach requirement gathering?
- A tester finds critical bugs just before release. What should the team do according to SDLC practices?
- You are asked to estimate the timeline for a small project. Which SDLC phase helps you with this and how?
- The client wants to add new features in the middle of development. How should this be handled?
- You are testing a web app and notice it loads slowly. In which SDLC phase should this problem have been addressed?
- Imagine you join a project in the development phase. How will you quickly understand what has been done so far?
- A project you are part of is delayed because requirements keep changing. How would SDLC help reduce this problem?
- During testing, users report usability issues with navigation. How should this feedback be handled?
- Your manager asks you to explain why deployment is not the final step of SDLC. What will you say?
- You are assigned to write test cases for a new feature. Which SDLC input will help you create them?
- Scenario-Based and Practical Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers For Experts
- A global banking system is migrating from a monolithic application to microservices. How would you adjust the SDLC to handle this migration?
- A healthcare application must comply with HIPAA regulations. How would you embed compliance in the SDLC process?
- Your company wants to implement CI/CD in a project with distributed teams across regions. How should SDLC adapt?
- A product release failed because of missed performance bottlenecks. How would you modify the SDLC to prevent this in the future?
- Your team is managing multiple vendors contributing to one project. How do you use SDLC to keep quality consistent?
- An e-commerce platform must support seasonal traffic spikes. How would you address scalability within the SDLC?
- A critical defect was missed despite multiple test cycles. How do you strengthen quality assurance in SDLC?
- How would you adapt SDLC for AI/ML-based projects where outputs are data-driven and unpredictable?
- A government project you are handling demands full transparency and audit trails. How do you design the SDLC process accordingly?
- A SaaS product has users across different countries with varied legal requirements. How do you use SDLC to handle multi-regional compliance?
- The Bottom Line
Beginner-Level Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
The Software Development Life Cycle is a structured process that guides how software is planned, built, tested, and maintained. It provides a framework for developers and stakeholders to work in an organized way.
- It covers stages like planning and software designing. It also includes coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
- The purpose is to deliver high-quality software that meets business goals.
2. Why is SDLC important in software development?
SDLC is important because it gives a clear path to follow during software creation. It reduces confusion and makes it easier to manage projects.
- It improves communication among team members and stakeholders.
- It reduces project risks and chances of missing requirements.
- It helps in delivering software on time and within budget.
3. What are the common phases of SDLC?
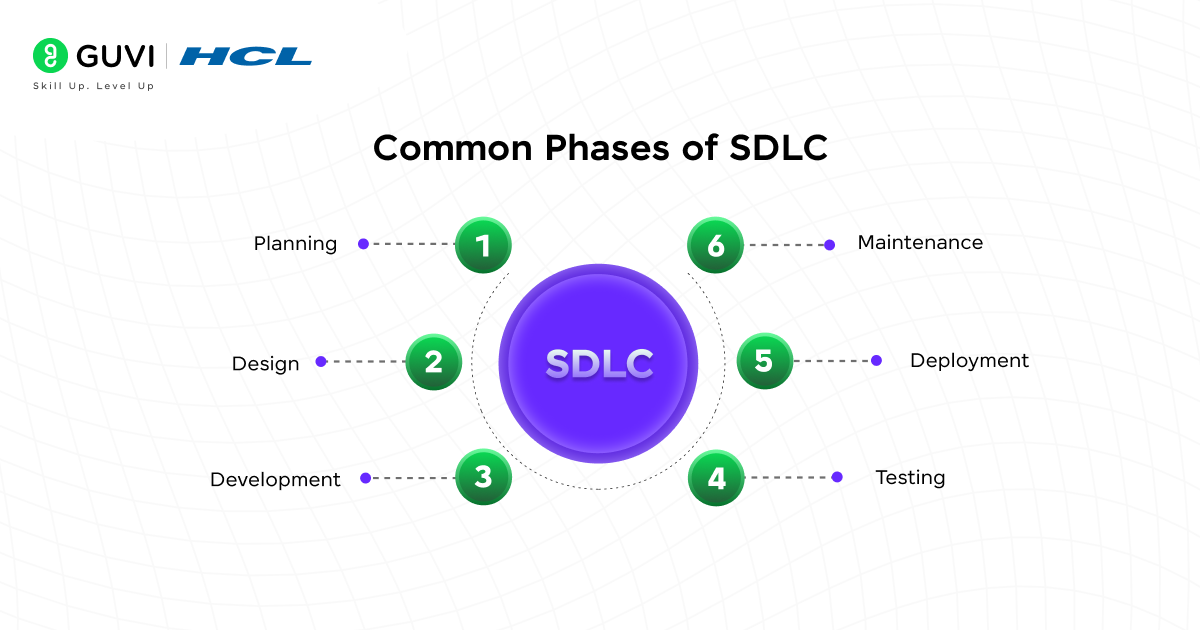
The SDLC has several standard phases. Each phase focuses on specific tasks needed to build reliable software.
- Planning: gathering requirements and defining goals.
- Design: creating architecture and design models.
- Development: writing the actual code.
- Testing: checking for defects and ensuring quality.
- Deployment: releasing the software to users.
- Maintenance: updating and improving the software after release.
4. What happens during the planning phase of SDLC?
The planning phase is about understanding what the client or business needs. The team studies the project requirements and creates a roadmap.
- Requirements are collected from stakeholders.
- Goals, scope, cost, and timeline are defined.
- A feasibility study is carried out to check technical and financial aspects.
5. What is the role of testing in the SDLC process?
Testing is essential to check if the software works correctly and is free from major defects. It ensures the product meets the expected quality.
6. What are some SDLC models you know?
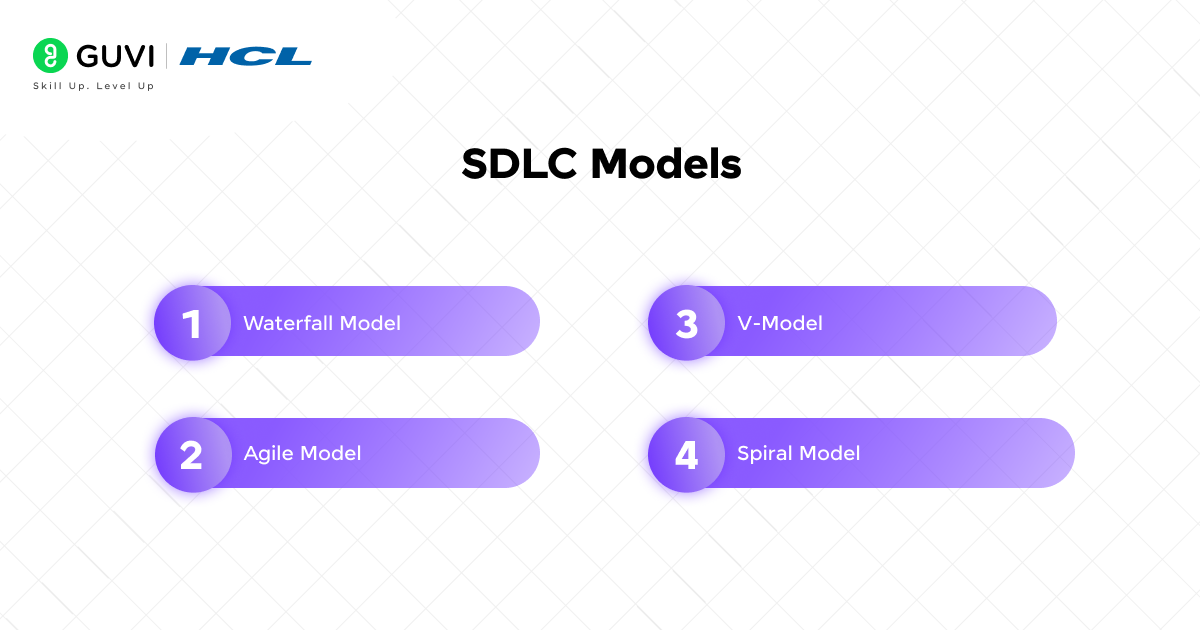
There are different SDLC models, and each has its own way of handling the process.
- Waterfall model: follows a step-by-step sequence where one phase must finish before moving to the next.
- Agile model: works in small cycles, focusing on flexibility and quick feedback.
- V-Model: emphasizes testing alongside each development phase.
- Spiral model: combines iterative development with risk analysis.
7. How does the Waterfall model differ from the Agile model?
Here is how the Waterfall model differs from the Agile model:
| Factor | Waterfall Model | Agile Model |
| Process Flow | Linear, sequential | Iterative, incremental |
| Phase Progression | One phase must finish before the next begins | Work divided into short iterations (sprints) |
| Flexibility | Rigid, difficult to accommodate changes | Flexible, adapts to feedback and changing requirements |
| Delivery Approach | Small, working parts are delivered frequently | Small, working parts delivered frequently |
| Feedback Cycle | Limited, occurs after project completion | Continuous, incorporated throughout development |
8. What is the importance of documentation in SDLC?
Documentation provides a record of requirements, design, and processes. It helps teams work more efficiently and supports future maintenance.
- Makes it easier for new team members to understand the system.
- Helps during troubleshooting and updates.
- Reduces misunderstandings between software developers and stakeholders.
9. What challenges can occur during SDLC?
Several challenges can arise that slow down or complicate the project.
- Requirements may be unclear or change frequently.
- Communication gaps between developers and clients can cause errors.
- Limited testing resources may lead to missed defects.
10. How do maintenance activities fit into SDLC?
Maintenance is the last but ongoing phase. After deployment, the software needs updates to stay useful.
- Fixing bugs that appear after release.
- Adding new features requested by users.
- Updating the system to match new technologies or security needs.
Intermediate-Level Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers
11. How do SDLC models affect project outcomes?
The choice of the SDLC model influences timelines and risk handling. A wrong model may cause delays or wasted resources.
- Waterfall works best for projects with fixed requirements.
- Agile fits projects that need adaptability and fast feedback.
- Spiral helps manage high-risk projects by combining iterations with risk analysis.
12. What is the difference between verification and validation in SDLC?
Verification and validation are both quality assurance activities, but serve different purposes.
Here’s the comparison:
| Factor | Verification | Validation |
| Focus | Checks if the product is built correctly | Checks if the right product is built |
| Activity type | Process-oriented | Product-oriented |
| Timing | Performed during design and development | Performed during testing and acceptance |
| Question answered | “Are we building the product right?” | “Are we building the right product?” |
13. How does risk management fit into the SDLC process?
Risk management identifies and handles potential problems that could impact the project.
- Risks are usually identified during planning and design.
- High-impact risks are tracked, and mitigation plans are created.
- Regular reviews are done during development and testing to keep risks under control.
14. What are functional and non-functional requirements in SDLC?
Requirements are grouped into functional and non-functional categories. Both are important to ensure the system works as expected.
Here’s the breakdown:
| Requirement Type | Description | Examples |
| Functional | Describes what the system should do | Login, payment processing, data entry |
| Non-functional | Describes how the system should perform | Security, performance, reliability, scalability |
15. What is the role of a feasibility study in SDLC?
A feasibility study checks if the project is worth pursuing before development begins. It looks at different aspects of the project.
- Technical feasibility: Can the required technology support the project?
- Economic feasibility: Is the project affordable and financially viable?
- Operational feasibility: Will the solution work well within the organization?
16. How does SDLC handle change requests?
Change requests are common and need a structured approach so the project is not disrupted.
- Requests are logged and analyzed for impact on cost, schedule, and scope.
- The project manager and stakeholders review and approve changes.
- Approved changes are integrated into the system with updated documentation.
17. What is the importance of requirement traceability in SDLC?
Requirement traceability ensures every requirement is addressed throughout the SDLC.
- It links requirements with design, development, and testing activities.
- Helps confirm that no requirement is overlooked.
- Makes it easier to manage changes since each requirement’s impact is tracked.
18. How do prototyping and SDLC work together?
Prototyping is often used within SDLC to improve requirement gathering and design.
- A prototype is a simplified version of the system created early in the cycle.
- It helps users visualize features before actual development.
- Feedback from prototypes reduces misunderstandings and rework.
19. What metrics are commonly used to measure SDLC success?
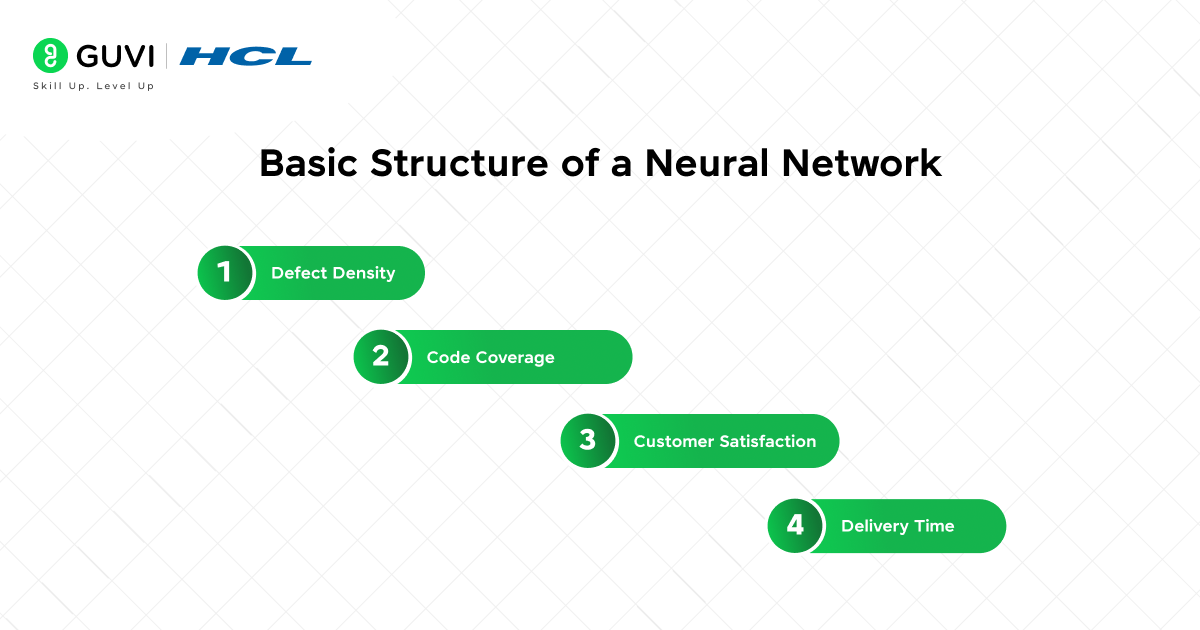
Metrics help evaluate project quality and efficiency.
- Defect density– number of defects per unit of code.
- Code coverage– percentage of code tested.
- Customer satisfaction– feedback from end users.
- Delivery time– adherence to project schedule.
20. How does maintenance in SDLC support long-term system success?
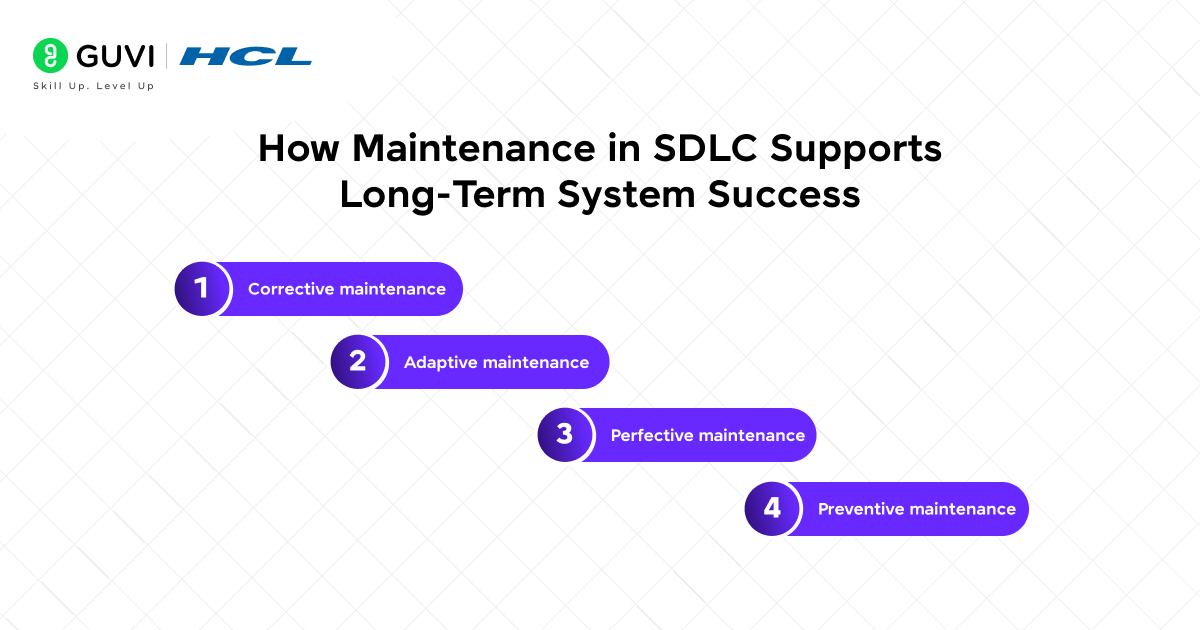
Maintenance ensures software continues to function effectively after release.
- Corrective maintenance: fixing errors found after deployment.
- Adaptive maintenance: updating software to work with new environments.
- Perfective maintenance: adding enhancements or improving performance.
- Preventive maintenance: making changes to reduce future risks.
Advanced-Level Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers
21. How do you integrate SDLC with DevOps practices?
DevOps brings automation and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) into the SDLC. It reduces delays between development and operations.
- Automated builds and deployments shorten release cycles.
- Continuous testing integrates quality checks throughout development.
- Monitoring tools support quick detection of issues in production.
- Collaboration between developers, testers, and operations improves reliability.
22. How is security embedded in the SDLC process?
Security should be part of every SDLC phase, not added at the end. This approach is called Security Development Life Cycle (SecSDLC).
- Threat modeling is done during design.
- Code reviews and static analysis tools detect vulnerabilities during development.
- Penetration testing and vulnerability scans strengthen security before deployment.
- Regular updates and monitoring help maintain secure systems after release.
23. How do Agile and SDLC align in large-scale enterprise projects?
Agile works with SDLC by using iterative cycles but scaling it across multiple teams can be complex.
- Frameworks like SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) or LeSS (Large-Scale Scrum) are applied.
- Requirements are broken into epics, features, and user stories.
- Integration points are managed across teams to prevent conflicts.
- Regular reviews ensure alignment with business goals.
24. What role does Continuous Integration (CI) play in SDLC?
Continuous Integration is key to maintaining code quality and stability in the development phase.
- Developers frequently merge their code changes into a shared repository.
- Automated build tools run unit tests to detect defects early.
- CI reduces integration problems that occur when features are developed separately.
- It supports faster delivery of working software.
25. How do you handle performance requirements in SDLC?
Performance is a non-functional aspect but critical for user satisfaction. It is integrated into design and testing.
- Load testing simulates user demand.
- Stress testing checks system limits under extreme conditions.
- Scalability analysis ensures the system can handle growth.
- Monitoring tools measure response time and throughput after deployment.
26. How do you apply SDLC in microservices-based architecture?
Microservices require modifications to traditional SDLC since the system is divided into independent services.
- Each microservice can have its own SDLC pipeline.
- APIs and service contracts are carefully defined.
- Continuous deployment pipelines manage frequent updates.
- Independent testing of services is followed by integration testing across services.
27. What is the impact of automation testing on SDLC efficiency?
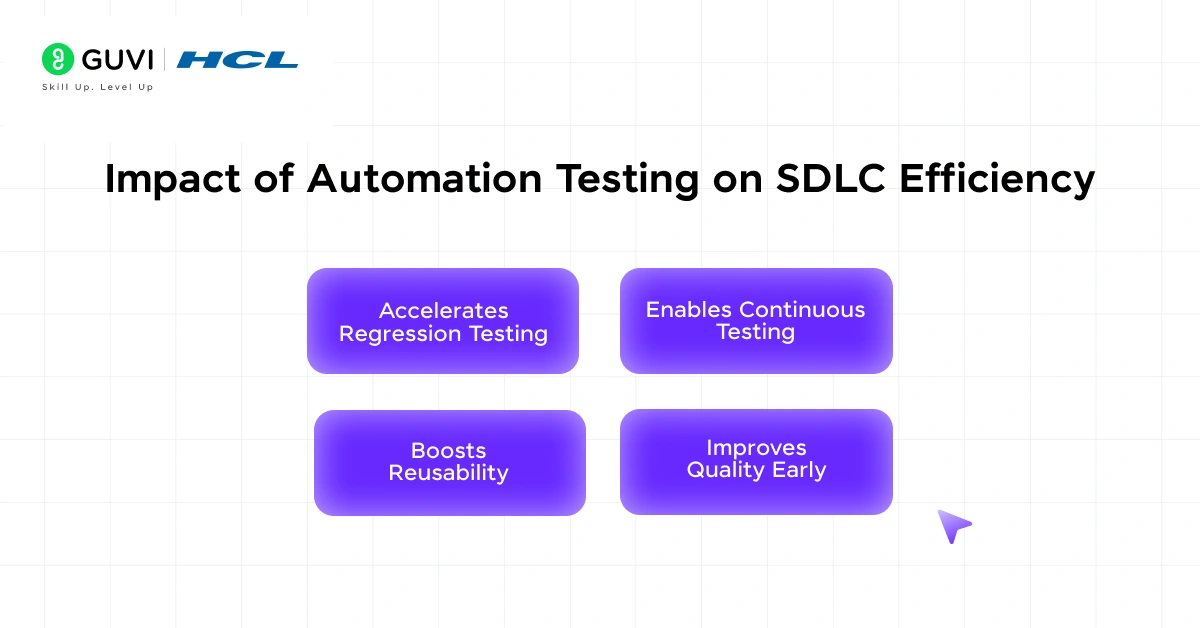
Automation testing accelerates SDLC by reducing manual effort and improving consistency.
- Regression testing is automated for faster feedback.
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines enables continuous testing.
- Test scripts can be reused across multiple cycles.
- Early defect detection reduces overall project cost.
28. How is user acceptance testing (UAT) managed in SDLC?
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) validates whether the software meets real-world business needs before its final release. During UAT, end users or clients execute predefined test cases within a staging environment that mimics the production setting. The process specifically checks usability, business workflows, and the enforcement of business rules. Any feedback gathered during UAT is logged as change requests or bug reports, which are addressed by the development team. Only after successful UAT approval can the software proceed to deployment.
29. How does SDLC support compliance in regulated industries?
Industries like healthcare and aviation require strict compliance with regulations.
- SDLC includes compliance checks during requirements gathering.
- Documentation is maintained for audits and certifications.
- Testing covers regulatory standards such as HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI-DSS.
- Deployment and maintenance phases include monitoring for compliance drift.
30. How do you measure technical debt in SDLC projects?
Technical debt represents shortcuts in design or coding that lead to future maintenance costs.
- Static code analysis tools track code complexity and violations.
- Defect backlog size is monitored for recurring patterns.
- Code review processes highlight areas needing refactoring.
- Teams prioritize reducing technical debt during maintenance to avoid future risks.
Scenario-Based and Practical Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers For Freshers
31. Your team is building a small mobile app. The client is unsure about features. How will you approach requirement gathering?
Freshers should explain how to deal with unclear requirements.
- Start with basic interviews or workshops to capture initial ideas.
- Suggest creating prototypes or mock-ups for client feedback.
- Document the requirements clearly and keep them flexible for changes.
Also Read: Is Software Development Hard?
32. A tester finds critical bugs just before release. What should the team do according to SDLC practices?
This question checks practical problem-solving.
- Stop deployment until the issues are resolved.
- Log the defects properly and prioritize fixes.
- Retest the fixes and run regression tests before approving release.
33. You are asked to estimate the timeline for a small project. Which SDLC phase helps you with this and how?
Freshers should connect planning with estimation.
- The planning phase provides scope, requirements, and feasibility.
- Use that information to create effort estimation.
- Break down tasks into smaller modules for better time prediction.
34. The client wants to add new features in the middle of development. How should this be handled?
This checks how you think about change management.
- Record the new request and analyze its impact on cost and schedule.
- Discuss changes with stakeholders and update documentation.
- Apply the approved changes to the design and development cycle.
35. You are testing a web app and notice it loads slowly. In which SDLC phase should this problem have been addressed?
This question links performance with SDLC stages.
- Performance issues should be considered during design through proper architecture.
- They should also be validated during testing with performance and load tests.
- Ignoring performance early can lead to costly fixes later.
36. Imagine you join a project in the development phase. How will you quickly understand what has been done so far?
Freshers are expected to show awareness of documentation and traceability.
- Review requirement documents and design specifications.
- Check version control systems for the current code.
- Go through test cases to see how features are expected to work.
37. A project you are part of is delayed because requirements keep changing. How would SDLC help reduce this problem?
This is about controlling scope creep.
- Proper requirement analysis during planning reduces changes later.
- Requirement traceability helps track which modules are impacted by changes.
- Formal change request processes prevent uncontrolled updates.
38. During testing, users report usability issues with navigation. How should this feedback be handled?
This connects SDLC with user experience.
- Log the feedback as defects or improvement requests.
- Review the design documents to see if usability guidelines were missed.
- Implement changes. Retest and include them in the updated release cycle.
39. Your manager asks you to explain why deployment is not the final step of SDLC. What will you say?
This tests knowledge of the maintenance phase.
- Deployment releases the software, but issues may appear afterward.
- Maintenance involves bug fixes, upgrades, and security patches.
- Without maintenance, software becomes outdated or unreliable.
40. You are assigned to write test cases for a new feature. Which SDLC input will help you create them?
Freshers should show practical application of documentation.
- Requirement documents specify what the feature should do.
- Design documents explain workflows and data structures.
- These inputs guide functional and edge case test design.
Scenario-Based and Practical Software Development Life Cycle Interview Questions and Answers For Experts
41. A global banking system is migrating from a monolithic application to microservices. How would you adjust the SDLC to handle this migration?
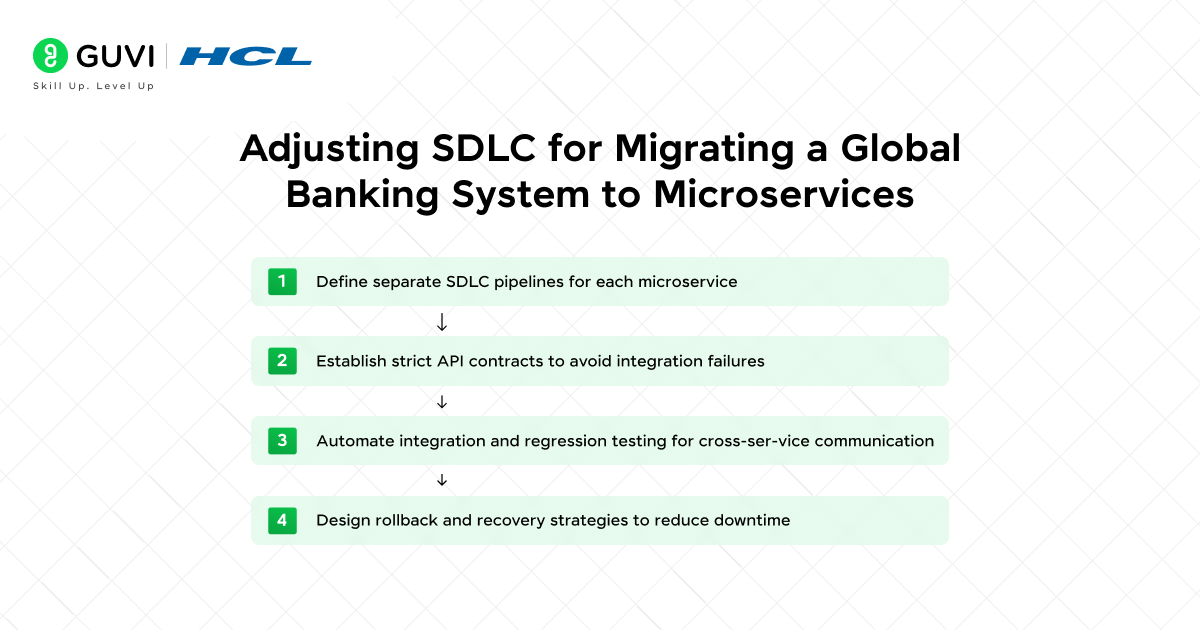
Migrating to microservices demands a shift in the SDLC toward decentralized ownership, where each service evolves independently yet aligns with a shared ecosystem. Emphasizing early-stage observability, embedded security, and CI/CD automation becomes crucial. The SDLC must also account for system-wide coordination through standardized practices, ensuring agility without sacrificing control, a balance critical in the high-stakes environment of global banking.
42. A healthcare application must comply with HIPAA regulations. How would you embed compliance in the SDLC process?
Compliance cannot be a one-time check; it should be integrated throughout.
- Add regulatory reviews during requirements gathering.
- Use static analysis and automated scans for security compliance.
- Maintain auditable documentation at every milestone.
- Perform compliance-driven testing before production release.
43. Your company wants to implement CI/CD in a project with distributed teams across regions. How should SDLC adapt?
Distributed teams face integration delays, communication gaps, and code conflicts. The SDLC should evolve to synchronize its work.
- Use centralized version control and automated pipelines.
- Schedule frequent integration jobs to reduce conflicts.
- Add common dashboards for build, test, and deployment visibility.
- Apply staggered test cycles to make use of global time zones.
44. A product release failed because of missed performance bottlenecks. How would you modify the SDLC to prevent this in the future?
Performance issues often occur when design and testing overlook scalability. To prevent future failures, performance must be treated as a formal requirement.
- Add performance acceptance criteria in the requirement documentation.
- Conduct design reviews with performance in mind.
- Automate load and stress testing as part of CI/CD.
- Deploy pre-production monitoring to simulate real traffic.
45. Your team is managing multiple vendors contributing to one project. How do you use SDLC to keep quality consistent?
When managing multiple vendors contributing to a single project, ensuring consistent quality becomes crucial due to the inherent risks around integration and standardization. Leveraging the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) framework helps enforce uniform practices across all vendors.
To begin with, coding guidelines should be established and rigorously followed, with adherence verified through structured code reviews. Each vendor is also required to submit unit test reports alongside their deliverables, which helps maintain baseline quality standards.
Shared staging environments should be provided to facilitate integrated testing across all modules. Finally, organizing joint User Acceptance Testing (UAT) sessions enables full end-to-end workflow validation, ensuring that the entire solution meets the project’s requirements cohesively.
46. An e-commerce platform must support seasonal traffic spikes. How would you address scalability within the SDLC?
Scalability planning starts early and must be validated before deployment. If ignored, the system may crash during peak usage.
- Capture scalability as a key requirement.
- Design architectures with horizontal scaling options.
- Simulate peak demand in testing environments.
- Deploy auto-scaling and monitoring for live traffic.
47. A critical defect was missed despite multiple test cycles. How do you strengthen quality assurance in SDLC?
Such defects point to gaps in test coverage or weak traceability. Strengthening QA means tightening the link between requirements and testing.
- Expand requirement-to-test mapping using traceability matrices.
- Introduce exploratory testing sessions.
- Automate regression suites for recurring checks.
- Perform defect root cause analysis to refine strategies.
48. How would you adapt SDLC for AI/ML-based projects where outputs are data-driven and unpredictable?
Traditional SDLC phases need modification for AI/ML, since data drives results instead of fixed logic. The cycle must handle model training and continuous improvement.
- Add explicit phases for data collection and preprocessing.
- Include model training and validation in development and testing.
- Monitor metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall continuously.
- Integrate retraining cycles in the maintenance phase.
49. A government project you are handling demands full transparency and audit trails. How do you design the SDLC process accordingly?
Government systems often face strict audit requirements. The SDLC should be designed for traceability and accountability.
- Record approvals and change logs at each stage.
- Store all deliverables in secured repositories.
- Generate automated reports for testing, defects, and releases.
- Conduct periodic compliance audits alongside project milestones.
50. A SaaS product has users across different countries with varied legal requirements. How do you use SDLC to handle multi-regional compliance?
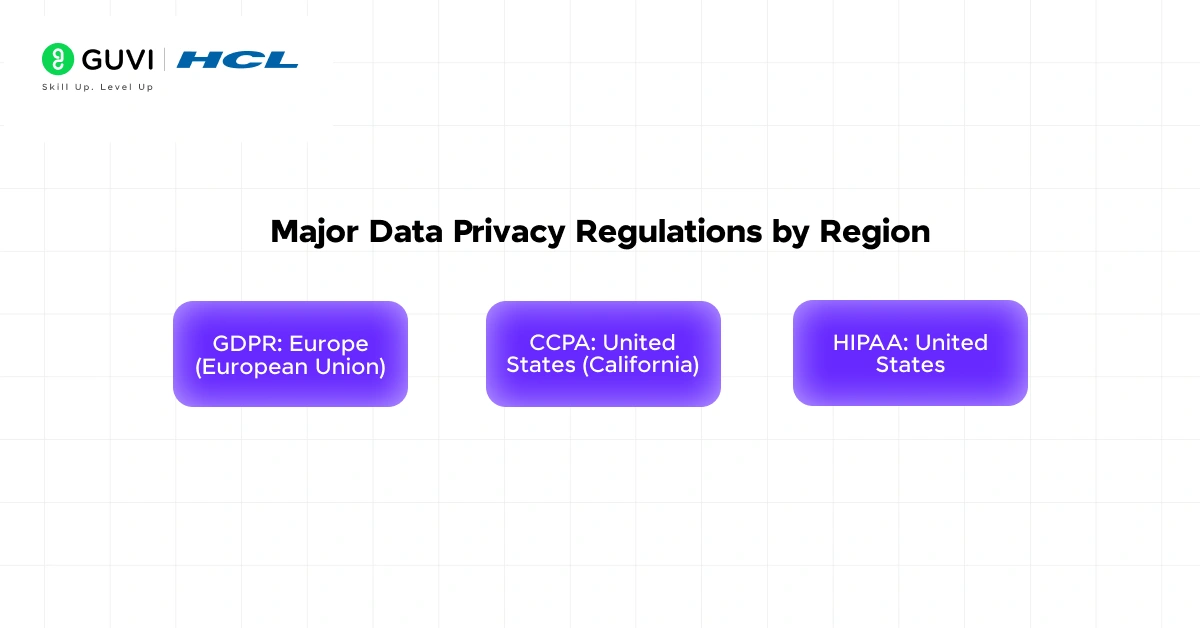
Multi-region products face different laws, such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in the U.S. The SDLC must handle these variations through modularity.
- Gather region-specific compliance requirements.
- Design modular features to adapt for local laws.
- Test deployments against GDPR, CCPA, and similar frameworks.
- Maintain region-specific pipelines for controlled releases.
Take your career to the next level with our AI software development course, certified by MongoDB and IITM Pravartak. This self-paced, career-focused program offers hands-on projects, hackathons, real-world system design, and a 4-day offline industry immersion, along with flexible weekend live sessions and lifetime access to recordings. Backed by globally recognized certifications, expert mentorship, 1:1 mock interviews, and personalized placement assistance, you’ll gain both technical expertise and professional confidence. Plus, with AI-powered learning through ZenGPT, practice platforms like CodeKata, WebKata, and SQLKata, rewards, forums, and the support of HCL GUVI’s 1.86M+ learner community, you’ll graduate with industry-ready skills, a strong portfolio, and the credibility to stand out in today’s competitive tech landscape.
The Bottom Line
Comprehending the Software Development Life Cycle is important for building strong interview responses and for dealing with real project challenges with confidence. These software development life cycle interview questions cover every level from basics to advanced practices.
It will help you explain concepts clearly and apply structured methods in practical scenarios. With this preparation, you will be able to present yourself as someone who not only knows SDLC theory but can also apply it effectively in professional environments.



































Did you enjoy this article?