6 Proven Steps in Mechanical Engineering Career Roadmap
Mar 18, 2025 5 Min Read 11841 Views
(Last Updated)
In this age and time, where computer science and engineering are reigning all over, it is easy to forget about subjects that don’t involve computers.
But that doesn’t mean that the subjects are less important, in fact, they play a vital role in every industry, and one of those subjects is mechanical engineering. Many don’t know where to start and are clueless about the mechanical engineering career roadmap.
To ease that burden and to encourage your interest in the field of mechanical engineering, this blog put forth a mechanical engineering career roadmap that can help you understand the process of becoming a successful mechanical engineer. So, without any delay, let’s get started.
Table of contents
- What is the Mechanical Engineering Career Roadmap?
- Exploring the Mechanical Engineering Career Roadmap
- Building a Strong Educational Foundation
- Foundational Knowledge and Skills
- Internships and Co-op Programs
- Networking and Involvement
- Job Search and Early Career
- Optional Steps
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is mechanical engineering?
- What skills are required for a career in mechanical engineering?
- What is the scope of mechanical engineering in various industries?
- Can mechanical engineers work in research and development?
- How important is computer literacy in mechanical engineering?
What is the Mechanical Engineering Career Roadmap?
A mechanical engineering career roadmap is a strategic and structured plan that outlines the path that you have to take in your professional journey to achieve your career goals.
It’s a visual representation of the steps, milestones, and actions needed to progress and succeed in the field of mechanical engineering.
A mechanical engineering career roadmap provides clarity and direction, helping you to make informed decisions about your education, skill development, job choices, and advancement opportunities.
Exploring the Mechanical Engineering Career Roadmap
Remember one thing before starting out, this mechanical engineering career roadmap is just a guide for you to understand what and all things that need to be in your mind when you pursue it.
This is not the only way for you to become a mechanical engineer. By saying this, let us get started and buckle up to explore the mechanical engineering career roadmap.
1. Building a Strong Educational Foundation
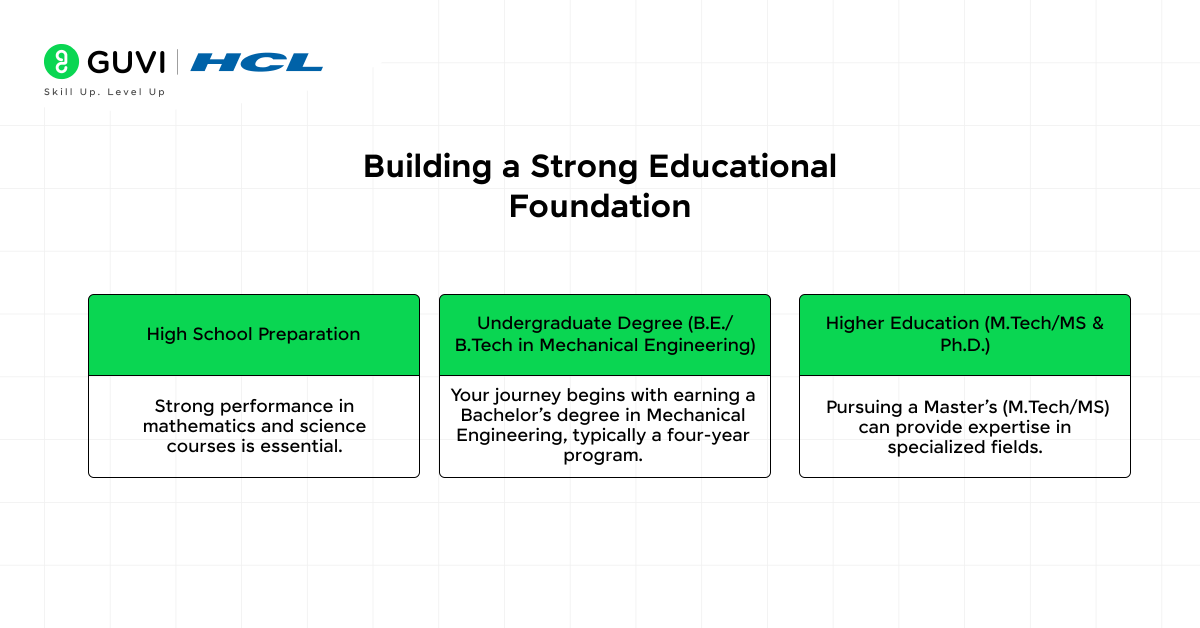
The education mentioned here refers to the process of acquiring the necessary academic foundation and qualifications to enter and excel in the field of mechanical engineering.
Let us understand the preparations, that need to go through:
a) High School Preparation:
Strong performance in mathematics and science courses is essential. Focus on subjects like calculus, algebra, geometry, and physics. These subjects form the basis for understanding complex engineering concepts.
b) Undergraduate Degree (B.E./B.Tech in Mechanical Engineering)
Your journey begins with earning a Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering, typically a four-year program that covers:
- Core subjects: Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics, Strength of Materials, and Machine Design.
- Mathematics & Physics: Foundational concepts essential for engineering applications.
- Software & Tools: Learning CAD (AutoCAD, SolidWorks, CATIA) and simulation tools (ANSYS, MATLAB).
c) Higher Education (M.Tech/MS & Ph.D.)
While a bachelor’s degree is sufficient for many jobs, pursuing a Master’s (M.Tech/MS) can provide expertise in specialized fields like:
- Robotics & Automation
- Aerospace Engineering
- Energy & Sustainability
- Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
For those inclined toward research or academia, a Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering can open doors to innovation and leadership in R&D.
2. Foundational Knowledge and Skills

Skills and knowledge development in the field of mechanical engineering is a crucial aspect of preparing for a successful career in the field. As a mechanical engineer, you’ll need a diverse set of technical and soft skills, as well as a deep understanding of engineering principles.
Here’s a breakdown of the skills and knowledge you should focus on developing:
a) Mathematical and Analytical Skills:
Build a strong foundation in advanced math, including calculus, differential equations, and linear algebra. These skills are crucial for analyzing complex engineering problems.
- Calculus and Differential Equations: Profound knowledge of calculus and differential equations to model and analyze mechanical systems.
- Linear Algebra: Understanding of linear algebra for solving complex equations and transformations.
- Statistics: Ability to apply statistical methods for data analysis and quality control in engineering projects.
b) Physics and Engineering Principles:
Deepen your understanding of physics concepts related to mechanics, heat transfer, and fluid dynamics.
- Mechanics: In-depth understanding of classical mechanics, including kinematics, dynamics, and statics.
- Thermodynamics: Knowledge of heat transfer, energy conversion, and thermodynamic cycles.
- Fluid Mechanics: Understanding of fluid behavior, fluid dynamics, and fluid properties.
- Materials Science: Familiarity with materials properties, selection, and behavior under different conditions.
c) Technical Skills:
Learn to use engineering software, including Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tools for designing and modeling, as well as simulation software for testing and analyzing mechanical systems.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Proficiency in using CAD software to create detailed designs of mechanical components and systems.
- Simulation and Analysis Tools: Ability to use software for simulating and analyzing the behavior of mechanical systems under various conditions.
- Programming: Basic programming skills in languages like Python or MATLAB can be useful for automating tasks and conducting data analysis.
3. Internships and Co-op Programs
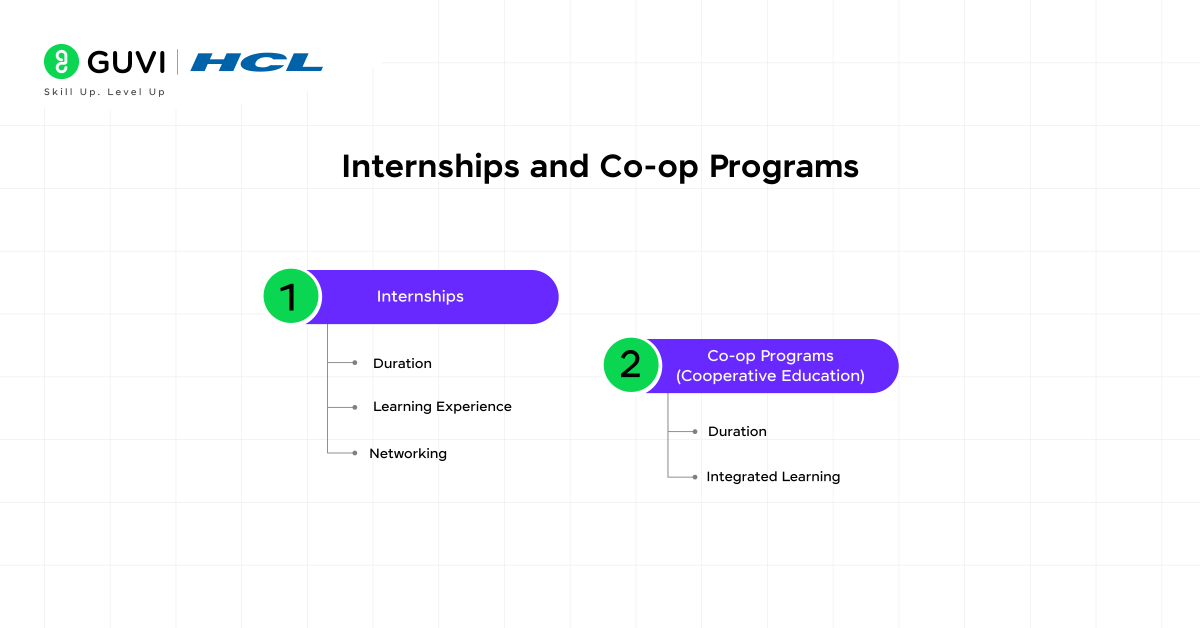
Internships and co-op programs are invaluable opportunities for you to gain real-world experience and bridge the gap between academic learning and practical application.
Here’s a closer look at internships and co-op programs:
a) Internships:
- Duration: Internships typically last for a few months, often during summer breaks, but can also be part-time during the academic year.
- Learning Experience: Interns gain insights into the daily operations of an engineering team, work culture, and industry practices. They also interact with professionals in the field, learning from their expertise.
- Networking: Internships allow you to build a professional network, which can be helpful for future job opportunities and career advice.
b) Co-op Programs (Cooperative Education)
- Duration: Co-op programs are more structured and can last several months to a year or more. They usually alternate between academic semesters and work terms.
- Integrated Learning: Co-op programs provide a deeper integration of academic learning with practical experience. Students apply what they learn in the classroom directly to their work assignments.
4. Networking and Involvement

Networking and involvement within the mechanical engineering field are essential for building meaningful connections, staying updated on industry trends, and opening doors to new opportunities.
Engaging with professionals, attending events, and participating in engineering communities can greatly enhance your career prospects. Here’s a closer look at the importance of networking and involvement:
a) Building a Professional Network:
- Industry Contacts: Networking allows you to connect with professionals who can provide insights, advice, and potential job leads.
- Mentorship: Building relationships with experienced engineers can offer guidance and mentorship as you navigate your career.
- Collaboration: Networking can lead to collaboration on projects, research, or initiatives that expand your skills and knowledge.
b) Learning and Knowledge Sharing:
- Industry Insights: Engaging with others in your field helps you stay informed about the latest industry developments, technological advancements, and best practices.
- Learning from Peers: Sharing experiences and challenges with fellow engineers can provide new perspectives and solutions to common problems.
- Conferences and Events: Attending workshops, seminars, and conferences exposes you to cutting-edge research, innovations, and thought leadership.
c) Career Opportunities:
- Hidden Job Market: Many job openings are never publicly advertised; networking can help you tap into this hidden job market.
- Referrals: Recommendations from professionals you’ve connected with can increase your chances of being considered for job positions.
- Recruitment: Companies often prefer hiring candidates with referrals from their trusted network.
d) Personal Branding:
- Visibility: Active participation in networking events and discussions can increase your visibility within the engineering community.
- Sharing Expertise: Presenting at events or contributing to discussions allows you to showcase your knowledge and establish yourself as an industry expert.
5. Job Search and Early Career

Job search involves finding and securing your first job, applying your academic knowledge to practical projects, and building a strong foundation for your future career growth.
Here’s a guide to navigating the job search and early career phase as a mechanical engineer:
a) Resume and Portfolio Preparation:
- Craft a well-structured resume that highlights your education, relevant coursework, projects, internships, technical skills, and any awards or honors.
- Create an online portfolio or personal website showcasing your projects, design work, and any other engineering-related accomplishments.
b) Job Search Strategies:
- Online Job Boards: Use platforms like LinkedIn, Indeed, Glassdoor, and specialized engineering job boards to search for job openings.
- Company Websites: Visit the careers sections of engineering firms, manufacturing companies, and technology companies you’re interested in.
- Career Fairs: Attend job fairs, both on-campus and industry-specific, to connect with potential employers and learn about job opportunities.
- Networking: Leverage your professional network to learn about hidden job openings and gain insights into different companies.
c) Application Process:
- Tailor your resume and cover letter for each job application to highlight how your skills match the job requirements.
- Highlight relevant experiences and projects that showcase your technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and teamwork.
6. Optional Steps
Optional steps in the mechanical engineering career roadmap refer to the additional choices you can make to enhance your skills, knowledge, and opportunities in your career beyond the core education and job requirements.
These steps can help you specialize in certain areas, stand out in a competitive job market, and further your professional growth. Here are some optional steps to consider:
a) Advanced Degrees:
- Pursuing a master’s or Ph.D. degree in mechanical engineering or a related field can provide specialized knowledge, research opportunities, and a deeper understanding of advanced concepts.
- Advanced degrees are particularly valuable if you’re interested in academia, research, or specialized engineering roles.
b) Specialized Certifications:
- Depending on your career path, consider obtaining certifications that demonstrate your expertise in specific areas. For example, certifications in CAD software, project management, or specialized engineering fields can boost your credentials.
- Certifications related to specific industries, such as aerospace, automotive, or energy, can make you more competitive in those sectors.
c) Research and Publications:
- Engage in research projects related to your interests in mechanical engineering. Publishing research papers in conferences or journals can enhance your reputation and contribute to the field’s knowledge base.
Whether you’re just starting or looking to advance your career, strategic planning, skill development, and professional networking are key to long-term success.
If you want to learn about the CAD tools required for mechanical engineering, consider enrolling in GUVI’s CAD for Mechanical Engineers Course where you will master technologies including AutoCAD, Solidworks, CATIA, Ansys, GD & T, etc, and build interesting real-life mechanical projects and industry-grade certificate.
Conclusion
As we conclude this exploration of the mechanical engineering career roadmap, it becomes clear that mechanical engineering requires a strategic blend of foundational knowledge, skills, and a thorough understanding of basic education.
A career in mechanical engineering offers endless opportunities for growth and innovation. By focusing on education, hands-on experience, technical expertise, and continuous learning, you can establish yourself as a leading engineer in your field.
FAQs
Mechanical engineering is a branch of engineering that focuses on designing, analyzing, and manufacturing mechanical systems, devices, and processes to meet a variety of industrial and consumer needs.
Essential skills include proficiency in mathematics, physics, computer-aided design (CAD) software, problem-solving, critical thinking, communication, technical writing, and a strong understanding of mechanical principles.
Mechanical engineers work across industries, such as automotive, aerospace, energy, manufacturing, robotics, biomedical, and consumer electronics, contributing to product design, testing, quality control, research, and development.
Yes, mechanical engineers contribute significantly to research and development by designing experimental setups, testing prototypes, and refining product designs to meet specific goals.
Computer literacy is crucial. Mechanical engineers use software for design, simulation, and analysis. Proficiency in CAD software, programming languages, and simulation tools is highly beneficial.























![A Complete Look on Mechanical Engineer's Salary in India [2025] 16 Feature image - A Complete Look on Mechanical Engineer’s Salary in India](https://www.guvi.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Feature-image-A-Complete-Look-on-Mechanical-Engineers-Salary-in-India.webp)

Did you enjoy this article?