
What is Heuristic Evaluation? An Essential Guide
Jan 16, 2025 6 Min Read 5613 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered why some websites feel effortlessly intuitive, while others leave you lost and frustrated? The secret often lies in a critical, yet frequently overlooked process known as heuristic evaluation. If you’ve heard this word, but don’t know what it means, you’ve come to the right place.
Heuristic evaluation is a method that involves evaluators examining the user interface and judging its compliance with recognized usability principles, known as heuristics. It’s a cornerstone in the world of user experience design, which helps unlock the full potential of a website’s usability.
Don’t worry. We’re going to talk about heuristic evaluation in detail for you. In this blog, we’ll explore the art and science of heuristic evaluation, what is it, why heuristic evaluation is done in UI/UX design, how to do heuristic evaluation, and all the other questions that might be bouncing in your head. So, let’s dive in.
Table of contents
- What is Heuristic Evaluation?
- How to Do a Heuristic Evaluation?
- Choose and Train Your Team
- Selecting Heuristics
- Define the Scope
- Documentation Tools
- Evaluate Independently
- Identify Issues and Prioritize
- Consolidate Findings
- Synthesize and Plan
- Difference Between Heuristic Evaluation and User Testing
- Pros and Cons of Heuristic Evaluation
- Pros of Heuristic Evaluation
- Cons of Heuristic Evaluation
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What Is Heuristic Evaluation in UX Design?
- Who Typically Performs a Heuristic Evaluation?
- Why Choose Heuristic Evaluation?
- How Does Heuristic Evaluation Differ from User Testing?
What is Heuristic Evaluation?
Let us learn from scratch. Heuristic evaluation is a methodical approach used in UI/UX design to identify usability issues within a digital product. This process involves a set of evaluators, typically usability experts, who systematically review a website or application against established usability principles, known as heuristics.
Remember how we used to have thumb rules for physics? In the world of UX design, there are certain pre-determined thumb rules to improve the usability of a website or application, which are called heuristics. These heuristics serve as a framework to pinpoint areas where the user experience may falter.
In simpler terms, think of heuristic evaluation as a health check-up for a website or app, conducted by seasoned UX doctors. These experts use a checklist of key usability principles to examine the product.
The goal of heuristic evaluation is to ensure that a website or app is intuitive, user-friendly, and effective in its functionality, in addition to being visually appealing, so that users can navigate it smoothly, accomplish their tasks with ease, and enjoy their digital experience.
As we proceed to the next phase, make sure you understand the fundamentals of UI/UX, which includes heuristic analysis, journey maps, testing, etc. If you want to explore more about it, join GUVI’s UI/UX Course with placement assistance. You’ll also learn about the tools used in UI/UX which are AdobeXd, Illustrator, Photoshop, Figma, and many more. Build some amazing real-time projects to get hands-on experience. Also, if you want to explore Figma through a Self-paced course, try GUVI’s Figma certification course.
Also Read | Must Do Practices in UI/UX Design
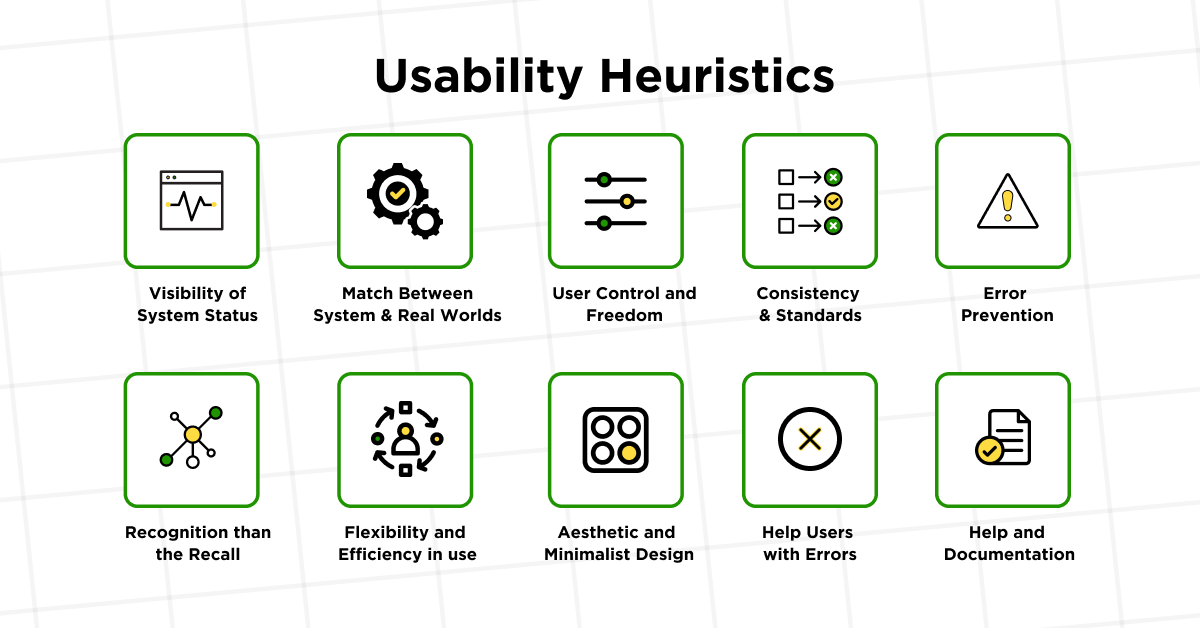
The concept of heuristic evaluation was popularized by Jakob Nielsen and Rolf Molich in the early 1990s. They identified a set of heuristics that are commonly used for this type of evaluation. But what are these heuristics, or thumb-rules of human-computer interaction? Here are the ten usability heuristics given by Nielsen, explained briefly:
- Visibility of System Status: Always keep users in the loop with clear, timely feedback about what the system is doing. This transparency builds user trust and understanding.
- Match Between System and the Real World: Speak the user’s language, using familiar terms and concepts rather than technical jargon. Align your design with real-world conventions for intuitive understanding.
- User Control and Freedom: Users make mistakes; provide them with an ’emergency exit’ to undo actions easily. This feature enhances user comfort and control over the application.
- Consistency and Standards: Maintain consistency in language, layout, and design across your platform. Users shouldn’t have to guess whether different terms or actions mean the same thing.
- Error Prevention: A well-thought-out design prevents problems from occurring. Implement checks for common errors and offer confirmation options before users commit to an action.
- Recognition Rather Than Recall: Design your interface so that users don’t have to remember information from one part to another. Visible elements and actions reduce cognitive strain.
- Flexibility and Efficiency of Use: Cater to both new and experienced users by offering shortcuts. This flexibility enhances efficiency and allows users to tailor frequent actions to their needs.
- Aesthetic and Minimalist Design: Clutter-free and minimalist design focuses user attention on what’s necessary. Avoid irrelevant information that can dilute the user’s focus and decision-making process.
- Help Users Recognize, Diagnose, and Recover from Errors: Error messages should be in plain language, clearly indicating the issue and suggesting constructive solutions. This approach reduces user frustration during problem-solving.
- Help and Documentation: While it’s ideal for systems to be intuitive, sometimes additional help is necessary. Provide easy-to-find, task-focused support with clear, step-by-step instructions.
These were to give you a brief idea. You can read about them in detail here. These are not the only set of heuristics followed in the industry. But, if you’re a beginner or working towards enhancing the user experience for your product, then Nielsen’s heuristics are the most trusted, commonly used, and strongly suggested heuristics by experts.
Also Read |Most Important UI/UX Design Principles You Can’t-Miss
How to Do a Heuristic Evaluation?
Now that you’re aware of what is heuristic evaluation and what is it used for, the next question that naturally pops up is how to perform a heuristic evaluation. There are several key steps involved in this process.
Here’s a step-by-step process about how to do a heuristic evaluation:
1. Choose and Train Your Team
First things first, gather your crew of evaluators. Ideally, you want a mix of experts – some seasoned in UX design, others maybe fresh with new perspectives. Ideally, a heuristic evaluation should be conducted by a group of 3-5 UX experts.
Each evaluator brings a unique perspective, increasing the likelihood of identifying a wide range of usability issues. They should be well aware of the product and user goals in advance.
Also Read | How to Become a UI/UX Designer in India
2. Selecting Heuristics
While there are many sets of heuristics, Jakob Nielsen’s 10 usability heuristics are widely recommended. They cover essential aspects like system visibility, error prevention, and user control. A common set of heuristics will ensure that the team is on the same page and consistent with the guidelines of evaluation.

3. Define the Scope
Define what exactly you’re evaluating. You need to focus on specific aspects like a particular task, section of the site, user group, or device type. A narrower scope allows for a more detailed evaluation, which helps save time, and resources while ensuring high efficiency and focused results.
4. Documentation Tools
Use tools like a heuristic evaluation workbook, spreadsheets, or digital whiteboards, whichever you’re comfortable with, for evaluators to record their observations. This would ensure better flow, clarity, and uniformity when you need to combine and find the overall result of the evaluation.
Also Find Out Top 11 UI/UX Design Tools for 2025
5. Evaluate Independently
The purpose of getting the review from multiple members is to get diverse perspectives to achieve maximum efficacy. Each team member should evaluate the interface independently to avoid bias. Familiarize yourself with the product and then look for design elements that violate the chosen heuristics.
6. Identify Issues and Prioritize
Once the evaluators have their observations in place, we need to find out the issues in the usability experience. You have to focus on how the design aligns or conflicts with each heuristic.
Now, mark those usability issues according to their severity, such as critical, minor, or normal issues. This helps in prioritizing which issues need immediate attention, as well as the ones that can be attended to later.

7. Consolidate Findings
Now, you have to consolidate and discuss the findings of all the evaluations. Just remove the duplicate issues and again categorize the different issues based on the severity.
Know About: 12 Important UX Designer Skills That You Should Know
8. Synthesize and Plan
Now, focus on the issue resolution based on the severity of the issues. This step often involves further user testing and research. Regular check-ins ensure that your product stays user-friendly and adapts to changing user needs and expectations. It’s a cycle. As your product evolves, so should your evaluations.
This was the general process followed during any heuristic evaluation. However, you have to keep a few things in mind:
1. Complement with User Research: Heuristic evaluations cannot replace user research. They should be used in conjunction with actual user testing to design effective user experiences.
2. Context Matters: Not all heuristic violations are definitive problems. Consider the context and user needs before deciding on changes.
3. Developing UX Instincts: Regular practice of heuristic evaluations can help develop strong UX instincts, enabling designers to quickly identify potential usability issues.
Also, Explore 10 Important UI/UX Testing Tools For UI/UX Designers
Difference Between Heuristic Evaluation and User Testing
We saw while doing a heuristic evaluation, we need user testing as well. But if we’re doing heuristic evaluation to find and fix usability issues, then why do we need to do user testing? Well, they might be often used interchangeably, but there are major differences between them.
Heuristic evaluation is an expert-driven process where UX professionals assess a product’s interface against established usability principles, such as Nielsen’s 10 usability heuristics. It’s a cost-effective, quick method that relies on the expertise of evaluators to predict potential usability issues without involving actual users. This approach is ideal for early-stage design checks, focusing on aligning the product with recognized usability standards.
In contrast, user testing is a user-centric approach that involves real users interacting with the product in a controlled environment. This method provides direct insights into user flow, user behavior, preferences, and challenges, offering a realistic view of how users experience the product, hence mostly implemented at the final stage or post-product development.
One is based on principles (where the approach remains static and generalized), and the other is based on real-time observations (which offer a more specific, diverse, and dynamic outlook). While more resource-intensive, user testing is invaluable for obtaining authentic feedback and understanding the product’s performance in real-world scenarios. Any day, heuristic evaluation is not a replacement for user testing.
Also Read | Importance of A/B Testing in UI/UX Design
Pros and Cons of Heuristic Evaluation
Now that we’re aware of what is heuristic evaluation, let’s look at the extent of its efficacy and significance and understand whether there are any pitfalls associated with this process.
Pros of Heuristic Evaluation
- Rapid Usability Feedback: Efficiently identifies major usability flaws in a short time frame.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Requires fewer resources than comprehensive user testing.
- Expert-Led Analysis: Utilizes the deep expertise of UX professionals for a detailed evaluation.
- Comprehensive Interface Assessment: Broadly assesses a range of UI elements against established usability principles.
- Design Stage Versatility: Applicable at various stages, from early prototypes to completed designs.
- Issue Prioritization: Aids in identifying and ranking critical design issues for prioritization.
- Heuristic Diversity: Adaptable to different sets of heuristics for specialized domain evaluations.
- Strategic Design Insights: Offers strategic insights into design improvements and UX strategy.
Cons of Heuristic Evaluation
- User Experience Gap: This may not capture real user experiences and their unique challenges.
- Evaluator Bias: Potential for bias based on individual evaluators’ experiences and perspectives.
- Contextual Limitations: Less effective in understanding the full context of user interactions.
- Subtlety Oversight: Risk of missing nuanced usability issues that users might face.
- Complement to User Testing: This cannot completely replace the insights from actual user testing.
Kickstart your UI/UX journey by enrolling in GUVI’s UI/UX Course where you will master technologies like AdobeXd, Illustrator, and Figma, and build interesting real-life UI/UX projects.
Alternatively, if you would like to explore Figma through a Self-paced course, try GUVI’s Figma certification course.
Conclusion
Heuristic evaluation is an effective tool for all UX designers and product developers out there as you’re dealing with the basics of experience design and usability determined by the experts. It would help you analyze and eliminate any critical issues at the beginning stages, which can be a major game changer for your digital product.
So, just employ heuristic evaluation in your review process to serve the best user experience and interactions with your users. Remember, it’s an iterative process. Define your scope, combine the evaluations, and work on the flagged issues in a phased manner to get the most out of your heuristic evaluations. And you’re all set to go!
Also Read: Top UI/UX Design Trends: Embracing Innovation in 2025
FAQs
-
Heuristic evaluation is a method used in UX design where experts evaluate a product’s user interface against a set of established usability principles, known as heuristics. This process helps in identifying usability issues that could affect user experience.
-
Heuristic evaluations are typically performed by UX professionals or usability experts. These individuals use their expertise in UX principles and design to assess and identify potential usability issues in a product’s interface.
-
Many UX designers choose heuristic evaluation because it offers rapid identification of major usability issues, cost-effectiveness compared to extensive user testing, expert insights into the user interface, and the ability to apply the evaluation at various stages of the design process.
-
Heuristic evaluation differs from user testing in that it is an expert-driven process focusing on compliance with usability principles, whereas user testing involves real users interacting with the product. Heuristic evaluation provides quick, expert insights, while user testing offers direct feedback on how actual users experience the product.

















Did you enjoy this article?