
Design Thinking and Prototyping in UI/UX: A Comprehensive Guide
Jan 16, 2025 5 Min Read 5010 Views
(Last Updated)
Design thinking is a user-centric approach to problem-solving that emphasizes empathy and experimentation. It is a process that can be divided into five phases: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test.
In this guide, we will focus on the fourth stage of design thinking: prototyping. We will explore what prototypes are, why they are important, different types of prototypes, and best practices for creating prototypes in UI/UX design.
So let’s get started with design thinking and prototyping in ui/ux.
Table of contents
- What is Design Thinking?
- The Essence of Design Thinking and Prototyping in UI/UX
- The Value of Prototyping in the Design Process
- Exploring Different Types of Prototypes
- Low-Fidelity Prototypes
- Medium-Fidelity Prototypes
- High-Fidelity Prototypes
- Prototyping Techniques and Tools
- A) Paper Prototyping
- B) Digital Prototyping
- C) 3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping
- The Iterative Nature of Prototyping
- The Benefits of Design Thinking and Prototyping in UI/UX
- Concluding Thoughts...
- What is a prototype in design thinking?
- What is design thinking in UI UX?
- Is design thinking a UX framework?
- What is the main goal of design thinking?
What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is an ideology and a process used to solve complex problems in a user-centric way. It places the user front and center, focusing heavily on empathy. Unlike traditional problem-solving approaches that fixate on obstacles and limitations, design thinking encourages experimentation, iteration, and thinking outside the box.

The design thinking process consists of five phases: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. These steps are not strictly linear, and each phase brings discoveries to light. Prototyping is the fourth stage in the design thinking process and is based on everything learned in the previous stages.
Prototypes are tangible representations of ideas, concepts, and solutions that enable designers to visualize, test, and refine their designs before investing time and resources into development.
As we proceed to the next phase, make sure you understand the fundamentals of UI/UX, which includes heuristic analysis, journey maps, testing, etc. If you want to explore more about it, join GUVI’s UI/UX Course with Placement Assistance. You’ll also learn about the tools used in UI/UX which are AdobeXD, Illustrator, Photoshop, Figma, and many more. Build some amazing real-time projects to get hands-on experience.
Also, if you want to explore Figma through a Self-paced course, try GUVI’s Figma certification course.
Also Read: Balancing Between Creativity and Functionality in UI/UX Design Projects [2024]
The Essence of Design Thinking and Prototyping in UI/UX
Design thinking prototypes hold immense significance in the UI/UX design process. They act as a means of communication, allowing designers to effectively convey their ideas to stakeholders, team members, and end-users.
By creating a physical or digital representation of their concept, designers ensure a shared understanding of the desired outcome and align everyone involved in the design process.
Furthermore, prototypes serve as a platform for exploration and experimentation. They allow designers to generate multiple iterations, test different possibilities, and experiment with various design elements.
Prototyping encourages creativity by providing designers with the freedom to explore unconventional solutions and think outside the box.
Also Read Rapid Prototyping in UI/UX Designing: All You Should Know in 2024
The Value of Prototyping in the Design Process
Prototyping plays a critical role in the overall design process by uncovering potential design flaws and challenges early on. By creating prototypes and subjecting them to testing and evaluation, designers can identify and address issues before investing significant time and resources into developing a final product.
This iterative approach reduces the risk of costly mistakes and increases the likelihood of creating a successful design. Additionally, prototypes enable designers to gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and end-users.
By presenting a prototype, designers can elicit reactions, preferences, and suggestions. This user-centered feedback is invaluable in refining and improving the design, ensuring that it meets the needs and expectations of its intended users.
Prototyping also promotes collaboration and interdisciplinary teamwork. By creating physical or digital prototypes, designers can engage stakeholders, engineers, marketers, and other relevant parties in the design process.
This collaborative approach encourages diverse perspectives, fosters innovation, and enhances the overall quality of the design.
Find Out UI/UX Best Practices: Creating Exceptional Digital Experiences
Exploring Different Types of Prototypes
Prototypes come in various forms and levels of fidelity, each serving a specific purpose and offering unique advantages in the design process. Let’s explore three common types of prototypes: low-fidelity, medium-fidelity, and high-fidelity.
1. Low-Fidelity Prototypes
- Low-fidelity prototypes are basic, simplified representations of a design concept.
- They are often created using inexpensive and readily available materials such as paper, cardboard, or foam.

- Low-fidelity prototypes are quick and easy to produce, allowing designers to generate multiple iterations rapidly.
- These prototypes are useful in the early stages of the design process, where the focus is on exploring different ideas and gathering initial feedback.
- Low-fidelity prototypes help designers test the overall concept, basic functionality, and user interactions.
- They are particularly effective for identifying major design flaws and gathering broad feedback on the overall user experience.
2. Medium-Fidelity Prototypes
- Medium-fidelity prototypes offer a higher level of detail and functionality compared to low-fidelity prototypes.
- They are created using more advanced prototyping tools and materials, such as digital wireframing software, 3D modeling, or interactive mockups.
- Medium-fidelity prototypes provide a closer approximation of the final product’s look, feel, and interactions.
- These prototypes are suitable for testing specific features, gathering more detailed user feedback, and evaluating the feasibility of technical aspects.
- Medium-fidelity prototypes allow designers to refine the visual design, test specific interactions, and assess the overall user experience more realistically.
3. High-Fidelity Prototypes
- High-fidelity prototypes are the most advanced and realistic representations of a design concept.
- They closely resemble the final product in terms of visual design, functionality, and user interactions.
- High-fidelity prototypes are often created using specialized software tools, coding, or even physical manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing.
- These prototypes are ideal for conducting comprehensive user testing, gathering detailed feedback, and evaluating the design’s final look and feel.
- High-fidelity prototypes enable designers to simulate complex interactions, test usability, and assess the overall user experience with a high level of accuracy.
- By understanding the different types of prototypes and their purposes, designers can strategically choose the appropriate fidelity level based on their specific design goals, timeline, and available resources.
- Each type of prototype contributes to the iterative design process and helps designers make informed decisions to create innovative and user-centered solutions.
Also Explore: Prototyping With Figma: 8 Important Tips You Shouldn’t Miss
Prototyping Techniques and Tools
To effectively create prototypes in UI/UX design, designers can employ various techniques and tools that cater to different fidelity levels and design needs. Let’s explore some popular prototyping techniques and tools:
A) Paper Prototyping
Paper prototyping is a low-fidelity prototyping technique that involves creating physical, hand-drawn representations of a design concept.
It is a quick and inexpensive way to visualize ideas and gather feedback early in the design process. Designers can sketch out screens, interfaces, or even entire user flows on paper to simulate the user experience.
By using simple materials like paper, sticky notes, and markers, designers can easily iterate and make changes based on feedback. Paper prototypes are particularly effective for testing and refining user interactions and workflows.
Also Explore: 8 Best UI/UX Prototyping Tools
B) Digital Prototyping
Digital prototyping involves using software tools to create interactive and realistic representations of a design concept. With the advancement of technology, there are numerous digital prototyping tools available that allow designers to create dynamic interfaces, simulate user interactions, and test the functionality of a product.
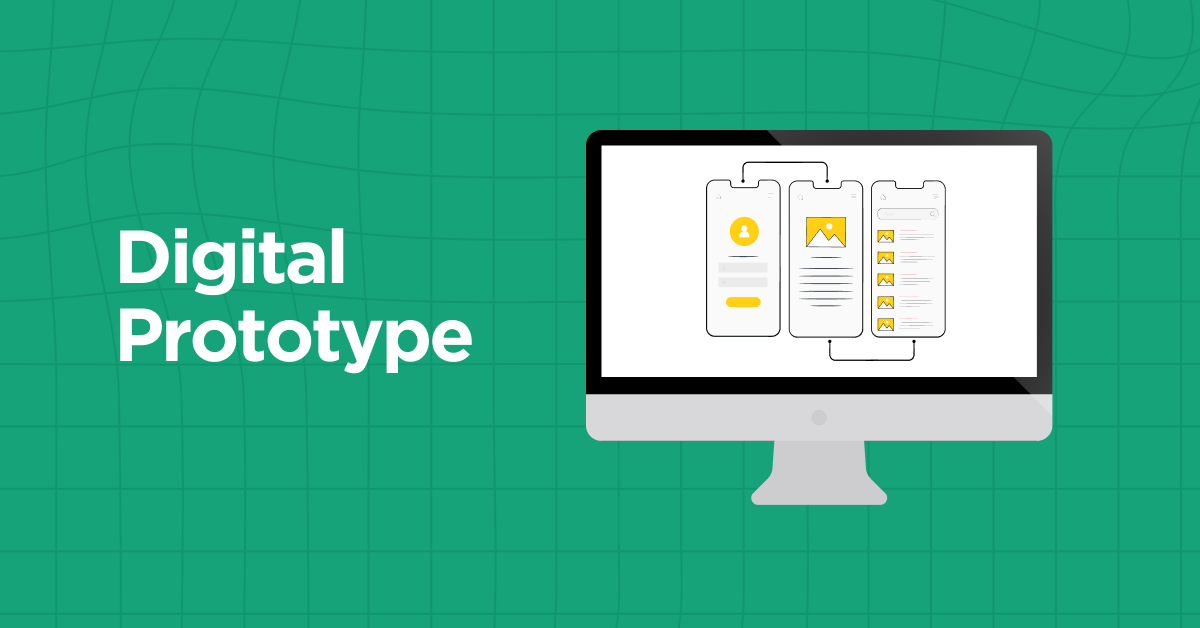
These tools often provide pre-built components, animations, and interaction patterns, enabling designers to create high-fidelity prototypes without the need for coding.
Digital prototyping allows for more realistic user testing and provides a clearer understanding of how the final product will look and function.
C) 3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping
3D printing and rapid prototyping are revolutionary techniques that have transformed the manufacturing industry. With 3D printing, designers can create physical prototypes by building layer upon layer of material, bringing their digital designs to life.
This technique allows for the creation of complex and intricate shapes that would be challenging to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. Rapid prototyping, on the other hand, involves using computer-aided design (CAD) software and CNC machines to quickly fabricate physical prototypes from various materials.
Both 3D printing and rapid prototyping enable designers to validate the form, fit, and function of a product before mass production. These techniques have significantly reduced the time and cost required to create prototypes, making them accessible to a wider range of designers and businesses.
By leveraging these prototyping techniques and tools, UI/UX designers can effectively bring their design concepts to life, gather valuable feedback, and refine their designs based on user insights.
Must Read: Motion Graphics in UI/UX: Enhancing User Experience with Dynamic Visuals
The Iterative Nature of Prototyping
Prototyping is inherently an iterative process, involving the creation of multiple versions of a design and refining them through feedback and testing.
Unlike traditional linear design processes, where ideas are refined sequentially, prototyping embraces an iterative mindset that encourages constant iteration and improvement. Each prototype serves as a learning opportunity, providing valuable insights that inform the subsequent iterations.

The iterative nature of prototyping allows designers to explore different ideas, identify flaws, and make necessary adjustments throughout the design journey. It also promotes collaboration and encourages a culture of experimentation and innovation.
Also Find Out About Wireframe vs. Mockup vs. Prototype: Top Differences [2024]
The Benefits of Design Thinking and Prototyping in UI/UX
Prototyping offers a multitude of benefits throughout the UI/UX design process. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
- Visualizing Ideas: Prototypes provide a tangible representation of abstract concepts, making ideas more concrete and easier to understand. They enable designers to communicate their vision effectively to stakeholders, clients, and team members.
- Gathering Feedback: Prototypes serve as conversation starters, allowing designers to collect valuable feedback and insights from users, stakeholders, and experts. By involving others in the feedback process, designers can uncover valuable perspectives and identify areas for improvement.
- Testing and Validation: Prototypes facilitate early testing and validation of design ideas. By creating and testing prototypes, designers can identify usability issues, evaluate user preferences, and validate assumptions before investing significant time and resources into development.

- Iterative Refinement: Prototyping enables designers to iterate and refine their designs based on user feedback and testing results. It allows for rapid experimentation, quick adjustments, and incremental improvements, leading to better design outcomes.
- Risk Reduction: Prototyping helps mitigate risks associated with design decisions. By testing ideas early, designers can identify and address potential flaws or usability issues, reducing the likelihood of costly errors or redesigns in later stages.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Prototypes serve as a powerful tool for aligning stakeholders and facilitating collaboration. By visualizing ideas in a tangible form, prototypes help stakeholders grasp the design intent, provide more informed feedback, and foster a shared understanding.
- Inspiring Creativity: Prototyping encourages designers to think creatively and explore unconventional ideas. It provides the freedom to experiment, take risks, and push the boundaries of innovation, ultimately leading to more imaginative and groundbreaking solutions.
By leveraging the benefits of prototyping in UI/UX design thinking, designers can enhance their design process, create more user-centered solutions, and deliver exceptional user experiences.
Also Explore: Minimalism in UI/UX Design: Role and Importance for Design Career
Kickstart your UI/UX journey by enrolling in GUVI’s UI/UX Course where you will master technologies like AdobeXd, Illustrator, and Figma, and build interesting real-life UI/UX projects.
Alternatively, if you would like to explore Figma through a Self-paced course, try GUVI’s Figma certification course.
Concluding Thoughts…
Design thinking prototypes are invaluable tools in the UI/UX design process. They enable designers to visualize, test, and refine their concepts before investing time and resources into development.
By employing various prototyping techniques and tools, designers can effectively communicate their ideas, gather feedback, and iterate on their designs.
The iterative nature of prototyping promotes collaboration, experimentation, and innovation, leading to more successful design outcomes.
By embracing the benefits of prototyping in UI/UX design thinking, designers can create user-centered solutions that delight and engage users.
Also Explore: Journey Mapping in Design Thinking: Important Things to Do [2024]
A prototype in design thinking is a preliminary model or version of a product, allowing designers to visualize and test ideas before final implementation.
Design thinking in UI/UX refers to a problem-solving approach that prioritizes user needs, involving empathy, ideation, and prototyping to create user-centric solutions.
Yes, design thinking is considered a UX framework, emphasizing user-centricity, creativity, and iterative problem-solving in the design process.
The main goal of design thinking is to solve complex problems by focusing on human needs, fostering creativity, and iterating through prototyping to arrive at innovative solutions.

















Did you enjoy this article?