
Data Analyst Roles and Responsibilities in 2025: Skills, Tools & Career Insights
Oct 10, 2025 6 Min Read 3767 Views
(Last Updated)
Data analyst roles and responsibilities in 2025 go far beyond crunching numbers. In today’s data-driven world, guesswork can’t solve problems, especially in large organizations that deal with daily truckloads of supply chain data, financial records, customer feedback, and operational metrics.
That’s where data analysis becomes a superpower.
Need a cost-saving strategy for a key client?
Trying to figure out why last month’s expenses spiked?
Looking for the best channel to upsell your newest product?
You don’t have to fly blind. You don’t have to rely on hunches.
With well-researched, real-time data at your fingertips, everything changes!
But here’s the truth: just having raw data isn’t enough.
Anyone can pull a spreadsheet. Anyone can Google a few trends and throw around assumptions.
A skilled data analyst brings structure and strategy to what others overlook.
They collect data from the right sources, such as internal systems, customer behavior, or market trends, and clean and prepare it, because raw data is often messy and incomplete. Then, they analyze patterns and trends using tools like SQL, Python, and spreadsheets, and visualize their findings with clear dashboards and reports through tools like Power BI, Tableau, or Excel.
Finally, they translate complex numbers into actionable insights so that decision-makers can move forward confidently.
In short, data analysts do more than just handle data. They guide strategy, uncover opportunities, and help businesses confidently move forward.
That’s why they are among the most in-demand professionals in today’s data-driven world. In this blog, we’ll explore who a data analyst really is, the key roles and responsibilities they handle, the skills that set them apart, and why this career is becoming one of the most sought-after in today’s tech-driven world.
By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of what it takes to thrive as a data analyst—and why this role matters more than ever.
Table of contents
- Who is a Data Analyst?
- How a Data Analyst Solves This | Data Analyst Roles and Responsibilities
- The Importance of Data Analysis in Business
- Soft and Hard Skills that make a Great Data Analyst
- Skills to master beyond tools and dashboards
- Types of Data Analysts
- Ready to Start Your Data Analytics Journey?
- In Summary
- FAQs
- What is the main role and responsibility of an analyst?
- What exactly does a data analyst do?
- What is required to be a data analyst?
- Is a data analyst an IT job?
- Is a data analyst a good role?
Who is a Data Analyst?
The primary goal of a data analyst is to bridge the gap between raw, unorganized data and actionable insights. For example, raw data that is scattered across various sources, incomplete, or full of errors can’t be directly used to make important business decisions. A data analyst’s job is to clean, organize, and interpret this data so that it can be used effectively.
Here’s an example for you to understand the data analyst role much better:
Imagine a FMCG brand wants to launch a new marketing campaign and needs to understand which of their previous campaigns worked best. They have raw data in different spreadsheets, customer feedback from surveys, social media mentions, and sales data spread across different systems. The raw data may look something like this:
- Sales data: 500, 1500, 200, 0, 3000, 100
- Customer feedback: “Not happy with the ad”, “Loved the promotion”, “Not relevant”
- Social media mentions: “Great product”, “Worst campaign ever”, “Great deal”
- Website traffic: 50,000 visits, 10,000 clicks
This data, which is from various sources, a variety of metrics, and is unorganized, can’t immediately answer questions like:
- What campaign had the highest return on investment (ROI)?
- Which customer segment responded best?
- What were the common sentiments across social media?
And this is where a data analyst comes into the picture. Now that we’ve understood what a data analyst is, let’s break down how they solve real-world problems step by step.
How a Data Analyst Solves This | Data Analyst Roles and Responsibilities
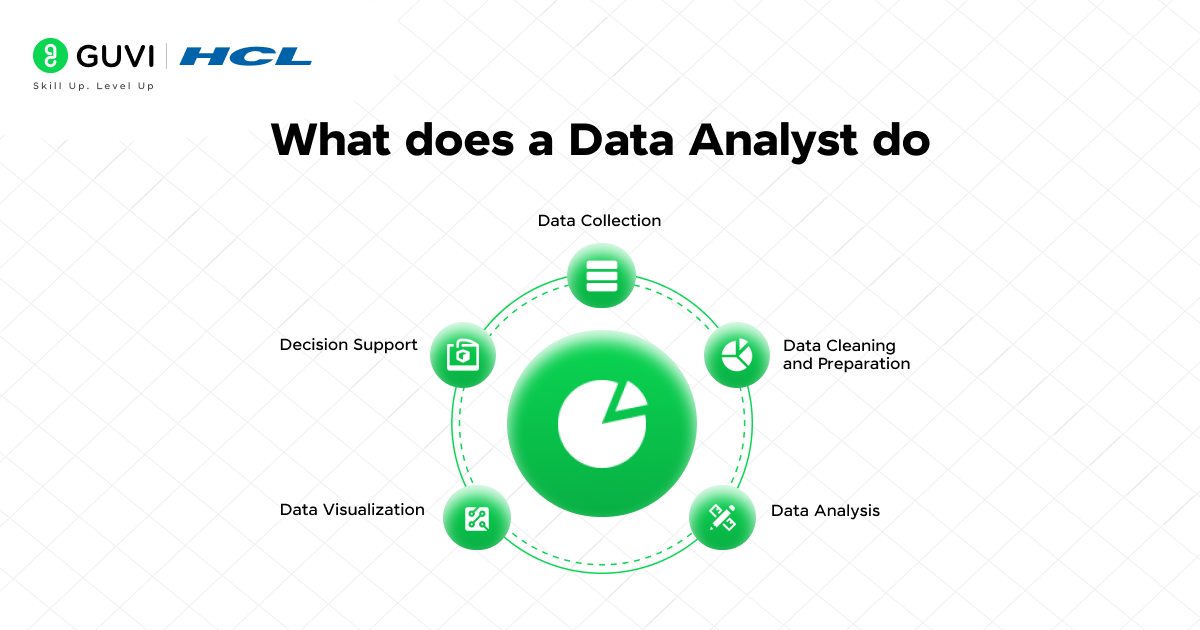
Let’s get a bit technical and dissect the role of a data analyst.
1. Data Collection
Data analysts gather relevant data from various sources like internal systems, customer behavior, market trends, and financial records. They ensure the data is comprehensive and aligned with the business goals.
2. Data Cleaning and Preparation
Data analysts clean raw data by addressing issues such as missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies. They apply techniques like imputation, normalization, and standardization to ensure that the dataset is suitable for analysis. This step often involves using Python libraries (e.g., Pandas, NumPy) to preprocess the data, remove duplicates, and convert data into a structured format.
3. Data Analysis
Leveraging analytical tools such as SQL, Python (with libraries like SciPy and Statsmodels), or R, data analysts conduct exploratory data analysis (EDA) to identify trends, correlations, and patterns within datasets. They apply statistical models and hypothesis testing to validate insights, perform regression analysis, and make data-driven predictions or classifications using machine learning algorithms.
4. Data Visualization
Data analysts use visualization tools like Power BI, Tableau, or advanced Excel techniques to create intuitive and interactive dashboards. These tools help in interpreting complex datasets through charts, graphs, and heatmaps, allowing for easy comparison of key metrics, trends, and KPIs.
5. Decision Support
The core of a data analyst’s role is to translate complex quantitative data into actionable insights. By providing clear, context-rich reports and visual presentations, data analysts support decision-making processes. They highlight key business opportunities, quantify performance, and provide recommendations for operational improvements, ensuring that executives and managers have the data-backed knowledge necessary to refine strategies.
The Importance of Data Analysis in Business
Informed decision-making, staying ahead of the competition, and minimizing risk while maximizing results, businesses are always striving for these goals. Data analysts are the key players who complete this picture.
Here’s how:
1. Staying on Track with Key Metrics
Data analysis gives businesses a clear view of what’s happening within the organization at any given time. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales trends, customer satisfaction, operational costs, and employee performance, companies can monitor progress toward goals. This continuous feedback loop allows businesses to make real-time adjustments and stay on track.
2. Spotting Growth Opportunities
Identifying an underserved market segment, recognizing product trends, or uncovering inefficiencies in existing processes—data analysis helps businesses pinpoint areas to expand, improve, or innovate. By analyzing patterns in consumer behavior, market conditions, and internal performance, businesses can capitalize on opportunities they might otherwise miss.
3. A Clear Roadmap for Strategic Decision-Making
Data analysis eliminates guesswork from business strategy. Insights into past successes and failures help inform forecasts and projections, allowing businesses to make decisions with confidence. Instead of shooting in the dark, companies can take a structured approach to decision-making, investing resources where they’re most likely to yield returns, ensuring they “sow” wisely and “reap” the benefits.
4. Improving Operational Efficiencies and Minimizing Risk
From supply chain optimization to reducing downtime and improving employee workflows, data-driven insights make it easier to pinpoint and address inefficiencies. Predictive analytics, for example, can forecast market trends or potential disruptions, giving companies a head start in mitigating risks.
5. Enhancing Customer Experience and Loyalty
Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal brand advocates, and retaining existing customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. Data analysis helps businesses track customer preferences, feedback, and pain points, allowing them to improve customer satisfaction and foster long-term loyalty.
6. Maximizing ROI on Marketing Campaigns
Marketing without data analysis is like fishing without a net. With data, businesses can track the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, measure engagement rates, and optimize strategies to maximize return on investment (ROI).
7. Supporting Better Financial Management
A clearer understanding of cash flow, profitability, and financial risks leads to better budgeting, forecasting, and decision-making. With a skilled data analyst beside them, no business would leave money on the table.
In short, data analysts help businesses navigate through complexities, drive smarter decisions, and unlock growth opportunities while minimizing risks. Their work is crucial for staying competitive and efficient in today’s fast-paced business world.
Soft and Hard Skills that make a Great Data Analyst
To excel as a data analyst in 2025, professionals must possess a balanced blend of technical (hard) skills and interpersonal (soft) skills. Here are a few skills that truly set standout data analysts apart in organizations today:
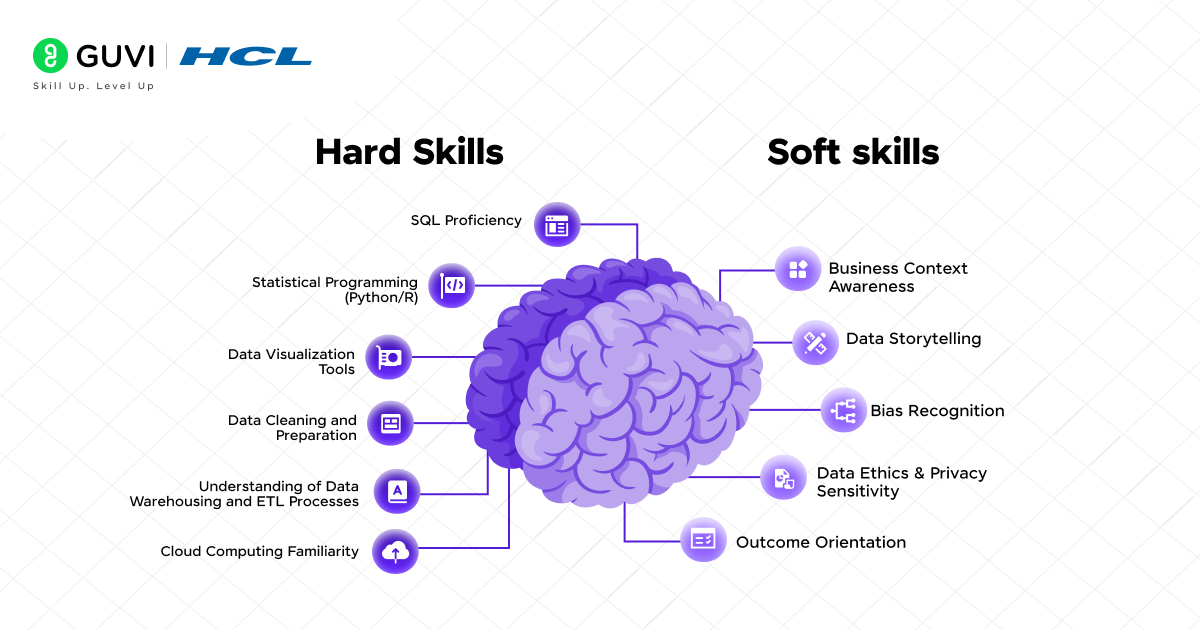
1. SQL Proficiency
Essential for querying and managing relational databases, enabling efficient data extraction and manipulation.
2. Statistical Programming (Python/R)
Utilized for data analysis, statistical modeling, and machine learning tasks. Python, with libraries like Pandas and NumPy, is particularly popular.
3. Data Visualization Tools
Proficiency in tools such as Tableau, Power BI, or Matplotlib to create clear and insightful visual representations of data.
4. Data Cleaning and Preparation
Skills in identifying and correcting data inconsistencies, handling missing values, and preparing datasets for analysis.
5. Understanding of Data Warehousing and ETL Processes
Knowledge of Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes and data warehousing concepts to manage and integrate large datasets.
6. Cloud Computing Familiarity
Experience with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for data storage and processing.
Skills to master beyond tools and dashboards
- Business Context Awareness
A great data analyst understands how data maps to business goals. They connect metrics to money, impact, or risk. It’s not just about turning raw data into spreadsheets; it’s about interpreting what those numbers mean for the bottom line. That could mean reducing churn, improving efficiency, or driving revenue. - Data Storytelling
Not everyone in the organization, especially stakeholders, can connect the dots and make sense of the reports you provide. Insights must be structured into a clear, engaging narrative.
Visuals alone aren’t enough; context and clarity are key. You’re telling a story that drives action, not just presenting figures. - Bias Recognition
Spotting human and data bias protects decision quality. For example, relying only on past customer data might ignore changing user behavior or exclude underrepresented groups.
Great analysts challenge assumptions and ask: “Is this data truly representative, or are we just seeing what we want to see?” - Data Ethics & Privacy Sensitivity
Great analysts know where the ethical and legal lines lie. If you’re building a customer segmentation model, for example, you must ensure personal identifiers are anonymized and that usage complies with data protection laws like GDPR. Just because you can analyze something doesn’t mean you should. - Outcome Orientation
Analysts focus on results, not just reports. Every insight must tie back to business outcomes such as growth, savings, retention, or risk reduction. It’s about impact over impressiveness and clarity over complexity.
While many of these skills are developed on the job, building them early can give you a strong edge in a market full of dashboard-pushers and spreadsheet jockeys.
Types of Data Analysts
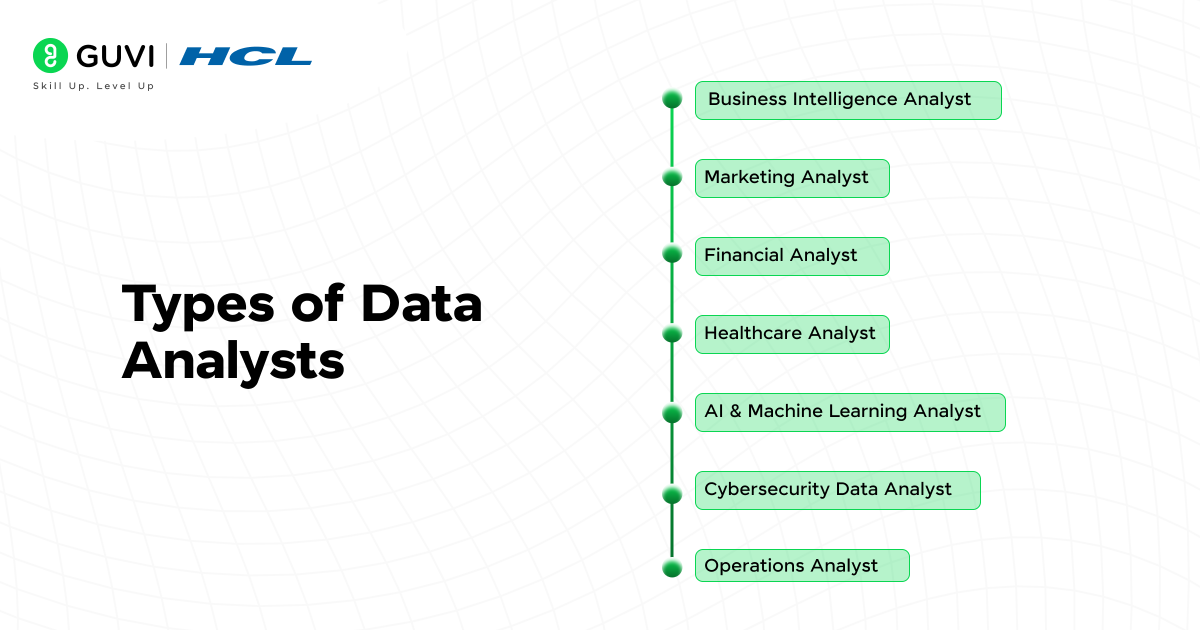
| Role | Focus | Industries | Role in Organization |
| Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst | Transforming data into actionable business insights. | Corporate strategy, e-commerce, and manufacturing | Analyzes data to drive business strategy and decisions. |
| Marketing Analyst | Analyzing consumer behavior and marketing campaign performance. | Tech, finance, autonomous systems, and AI marketing | Optimizes marketing efforts through data-driven insights. |
| Financial Analyst | Analyzing financial data to guide business decisions. | Banking, fintech, investment firms, insurance | Manages financial data to guide investment decisions. |
| Healthcare Analyst | Analyzing patient data and healthcare trends to improve outcomes. | Hospitals, insurance, biotech, pharmaceuticals | Provides insights to improve healthcare services and costs. |
| AI & Machine Learning Analyst | Analyzing AI models and datasets for machine learning accuracy. | Tech, finance, autonomous systems, AI marketing | Optimizes AI and machine learning systems. |
| Cybersecurity Data Analyst | Using data analysis to detect and prevent cyber threats. | Government, banking, IT security, cloud | Analyzes data to secure systems from cyber threats. |
| Operations Analyst | Analyzing processes to enhance operational efficiency. | Manufacturing, logistics, retail, supply chain | Identifies inefficiencies and optimizes operations. |
| Product Analyst | Evaluating product performance and user behavior. | Tech, consumer goods, SaaS | Guides product strategy with data-backed insights. |
Ready to Start Your Data Analytics Journey?
If you’re eager to step into this exciting field, consider enrolling in HCL GUVI’s Data Science Course. With in-depth modules covering everything from data wrangling to machine learning, this course is designed to equip you with the skills needed to thrive in a data-driven world. If you’re a beginner or looking to deepen your knowledge, this comprehensive program will provide hands-on experience and prepare you for a successful career as a data analyst. Explore HCL GUVI’s Data Science Course
In Summary
Before you jump into creating your resume, portfolio, or diving into platforms like LinkedIn or Naukri, it’s important to know the massive opportunities ahead.
The data analytics sector in India is set to reach a staggering $16 billion by 2025, which means a surge in job openings across key industries such as IT, finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and government. Leading companies like Oracle, Qualcomm, Bajaj Finance, and Wipro are already on the lookout for skilled data analysts, with hundreds of positions available as of early 2025.
The future is bright for data analysts, and as businesses increasingly rely on data to make smarter decisions, your opportunity to shape the future of industries is within reach.
If you’re just starting or looking to make a career shift, now is the perfect time to dive into the world of data analysis.
FAQs
1. What is the main role and responsibility of an analyst?
An analyst collects, processes, and interprets data to help businesses make informed decisions. They identify trends, generate reports, and provide actionable insights to improve operations and performance.
2. What exactly does a data analyst do?
A data analyst gathers, cleans, and analyzes data to uncover patterns and trends. They use statistical methods to make predictions, create reports, and assist businesses in making data-driven decisions.
3. What is required to be a data analyst?
To be a data analyst, you need strong analytical skills, proficiency in tools like Excel, SQL, and data visualization software, along with knowledge of statistics and business operations.
4. Is a data analyst an IT job?
While data analysts work with technology, their primary focus is on interpreting data and providing business insights, not IT infrastructure. It involves a mix of analytical and business skills.
5. Is a data analyst a good role?
Yes, being a data analyst is a good role with strong demand. It offers competitive salaries, opportunities for growth, and the chance to work with cutting-edge data technologies.



































Did you enjoy this article?