
Array Data Structures and Algorithms in Java: How to Create and Use Them
Mar 06, 2026 6 Min Read 1623 Views
(Last Updated)
Arrays are among the most essential data structures in Java, and knowing how to use them is essential to writing efficient algorithms. Whether you are storing a list of student scores, keeping track of inventory data, or building dynamic programs, arrays are the basis of problem-solving in programming.
In this blog post, we will be covering everything you need to know about Array Data Structures and Algorithms in Java what an array is, how it works, the different types of arrays, operations you can perform on an array, the advantages and limitations of using arrays, and the algorithms that can be applied to arrays.
Table of contents
- What is an Array in Java?
- Why Are Array Data Structures and Algorithms Important?
- Types of Arrays in Java
- One-Dimensional Array
- Multi-Dimensional Array
- How to Declare, Initialize, and Access Arrays in Java
- Declaring an Array
- Initializing an Array
- Accessing and Updating Elements
- Finding Array Length
- Traversing Arrays Using Loops
- Arrays of Objects in Java
- Passing Arrays to Methods
- Returning Arrays from Methods
- Common Algorithms Using Arrays in Java
- Searching An Element (Linear Search)
- Sorting an Array
- Finding the Maximum and Minimum Element
- Reversing an Array
- Advantages of Arrays in Java
- Disadvantages of Arrays in Java
- Conclusion:
- FAQs
- What is an array in Java?
- What are the benefits of using arrays?
- Can an array hold different data types?
- What are the differences between an array and an ArrayList?
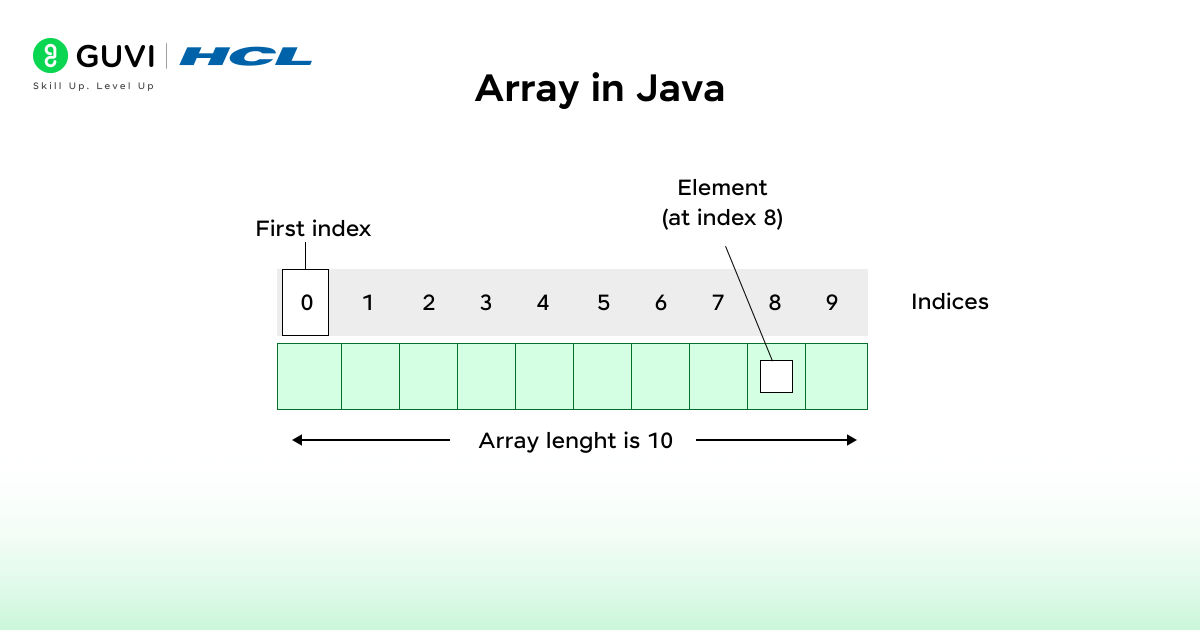
What is an Array in Java?
An array in Java is a collection of elements of the same data type stored in contiguous memory locations. It allows you to store multiple values in a single variable rather than declaring separate variables for each value.
For example, instead of writing:
| int num1 = 10; int num2 = 20; int num3 = 30; |
You can store all the values in a single array
| int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30}; |
Why Are Array Data Structures and Algorithms Important?
Arrays are one of the most important data structures in Java as they form the basis for many other data structures such as stacks, queues and lists. They are a simple and fast way to store and handle data, hence they are an important concept when learning about algorithms.
Imagine having to keep track of marks for 100 students without arrays. You would have to create 100 separate variables to hold those values! Using arrays, you can group all those values into one data structure and reference any one of those values instantly using its index.
This is why arrays are important:
1. Foundation for Other Structures
Arrays are the building blocks that many complex data structures can be built from, such as lists, stacks, queues and matrices. It would be difficult to design and manipulate advanced data structures without arrays.
2. Core of Algorithm Design
The majority of algorithms will use an array in Java, from algorithms that sort to algorithms that search. For example Binary Search, which takes advantage of the ordered nature of an array, searches for an element quickly, Merge Sort and Quick Sort sort by manipulating values of an array.
3. Speed and Efficiency
One amazing fact about arrays is that accessing an element in an array is constant time (O(1)) because an array stores data in contiguous memory. This makes arrays very fast and a good choice when you need performance.
4. Real-World Use
Arrays are also everywhere; they are used for everything from storing readings from sensors or financial information, representing pixels in an image, or representing the feature value of training data when working on a machine learning project.
Also Explore: 5 Best Reasons to Learn Data Structures and Algorithms [DSA]
Types of Arrays in Java
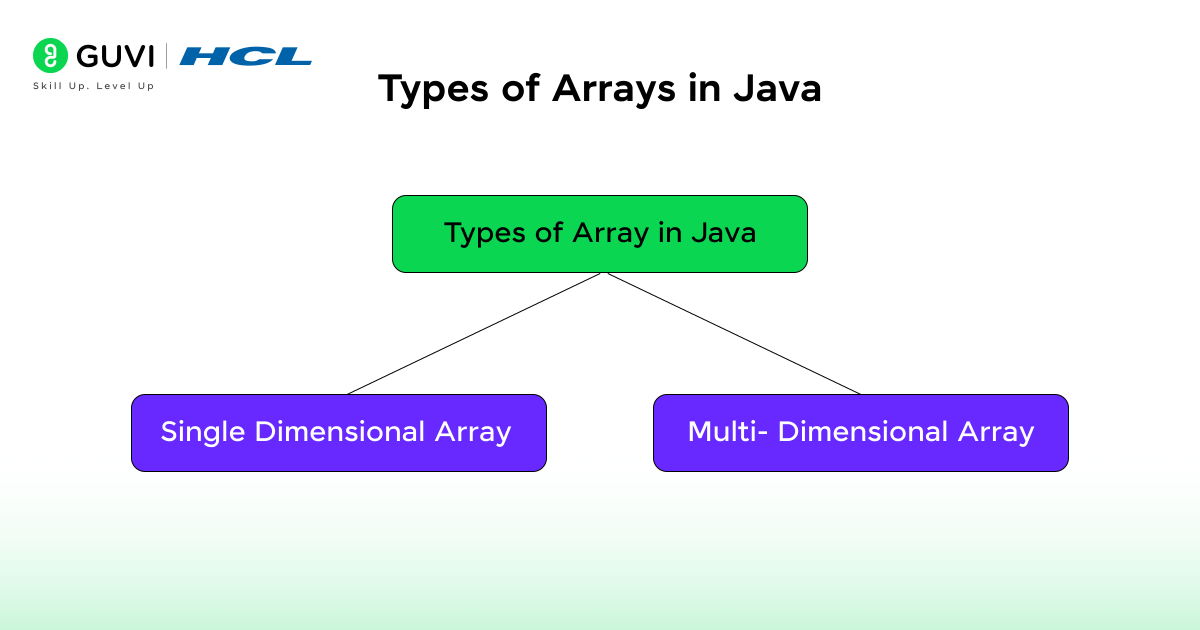
1. One-Dimensional Array
This is the simplest form of an array, which stores data in a single line
For example:
| int[] marks = {85, 90, 78, 92}; |
2. Multi-Dimensional Array
It is an array of arrays, as the name suggests. It is often used to represent matrices or tables.
| For example: int[][] matrix = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9} }; |
Also Read: Is DSA Important for Placement in 2025?
How to Declare, Initialize, and Access Arrays in Java
1. Declaring an Array
To use an array, you must first declare it. The declaration tells Java the data type and that it will store multiple values.
You can declare an array in two ways:
| // Method 1 int arr[]; // Method 2 (preferred) int[] arr; |
Here, you’re just declaring a variable arr that will hold an array of integers, but no memory is allocated yet.
Note: The declaration only defines the type; you still need to allocate memory before storing values.
2. Initializing an Array
After declaring, you can initialize the array using the keyword new as shown in the example below.
| int[] arr = new int[5]; |
This allocates space for five integers in memory.
By default, Java initializes:
- Numeric arrays with 0
- Boolean arrays with false
- Reference arrays (like objects) with null
You can also assign values manually:
| arr[0] = 10; arr[1] = 20; arr[2] = 30; arr[3] = 40; arr[4] = 50; |
Or use array literals ( the simple way)
| int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; |
- The size of this array specifies the length of the newly created array.
- You don’t have to write the new int[] in current versions of Java.
3. Accessing and Updating Elements
You can access array elements using their index:
| System.out.println(arr[2]); // prints 30 |
You can also update elements:
| arr[2] = 99; System.out.println(arr[2]); // prints 99 |
Remember, if you try to access an index outside the array length, Java will throw an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
4. Finding Array Length
The length of an array can be accessed using the .length property:
int size = arr.length;
System.out.println(“Array size: ” + size);
5. Traversing Arrays Using Loops
You can print or manipulate all array elements using a for loop or an enhanced for loop.
For example:
| class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(“Element at index ” + i + “: ” + arr[i]); } } } |
Output:

Download HCL GUVI’s free Data Structures & Algorithms eBook and start mastering problem-solving skills that every top developer needs!
Arrays of Objects in Java
Arrays can contain items of any type, not just primitive types. You can also create arrays of objects, for example, I’ll create an array of Student objects with a Student class.
| class Student { int rollNo; String name; Student(int rollNo, String name) { this.rollNo = rollNo; this.name = name; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Student[] students = new Student[3]; students[0] = new Student(1, “Aman”); students[1] = new Student(2, “Visha”); students[2] = new Student(3, “Mandeep”); for (int i = 0; i < students.length; i++) { System.out.println(“Roll No: ” + students[i].rollNo + “, Name: ” + students[i].name); } } } |
Output:
| Roll No: 1, Name: Aman Roll No: 2, Name: Visha Roll No: 3, Name: Mandeep |
- Arrays in Java are objects, not just simple data containers!
- The length of an array in Java is fixed once created — you can’t resize it later.
- Java automatically initializes array elements: 0 for numbers, false for booleans, and null for objects.
- Arrays were among the first data structures introduced in programming languages!
- The famous Binary Search algorithm works efficiently because of arrays’ indexed structure.
Passing Arrays to Methods
Arrays can be passed as arguments to methods in Java, just like regular variables.
| public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {3, 5, 7, 9}; printSum(nums); } static void printSum(int[] arr) { int sum = 0; for (int n : arr) sum += n; System.out.println(“Sum of array elements: ” + sum); } } |
Output:
| Sum of array elements: 24 |
Returning Arrays from Methods
Just like you can pass arrays to methods, you can also return arrays from them.
| class Main { static int[] createArray() { return new int[]{10, 20, 30}; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] result = createArray(); for (int val : result) System.out.print(val + ” “); } } |
Output:
| 10 20 30 |
Also Read: Best DSA Roadmap Beginners Should Know 2025
Common Algorithms Using Arrays in Java
Arrays are the basis for many algorithms in Java. Let’s see a few frequently used ones.
1. Searching An Element (Linear Search)
If the array is not sorted, then use Linear Search to find an element.
| int[] arr = {10, 25, 30, 40, 50}; int key = 30; boolean found = false; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { if (arr[i] == key) { System.out.println(“Element found at index: ” + i); found = true; break; } } if (!found) System.out.println(“Element not found!”); |
2. Sorting an Array
Sorting helps in organizing elements in ascending or descending order.
Example using Bubble Sort:
| int[] arr = {5, 2, 9, 1, 5, 6}; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length – 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < arr.length – i – 1; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = temp; } } } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); |
Output:
| [1, 2, 5, 5, 6, 9] |
You can also use the built-in method:
| Arrays.sort(arr); |
3. Finding the Maximum and Minimum Element
| int[] arr = {12, 45, 23, 78, 56}; int max = arr[0]; int min = arr[0]; for (int num : arr) { if (num > max) max = num; if (num < min) min = num; } System.out.println(“Max: ” + max); System.out.println(“Min: ” + min); |
4. Reversing an Array
| int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; for (int i = arr.length – 1; i >= 0; i–) { System.out.print(arr[i] + ” “); } |
Output:
| 50 40 30 20 10 |
Also, Explore About 10 Best Data Structures and Algorithms Courses [2025]
Advantages of Arrays in Java
Arrays are critical to Array Data Structures and Algorithms in Java because of their simplicity, speed, and organization. Below are four reasons they can be so helpful:
- Fast Access: You can access elements in an array in constant time (O(1)) at an index. This means it doesn’t matter if you are accessing the first element or the one hundredth element; your access speed is always the same, which makes them a great fit for search and sorting algorithms.
- Memory Efficient: Arrays keep all elements in contiguous memory locations. Thus, memory consumption is efficient and access is quicker than other structures that don’t reside in a contiguous fashion (e.g., linked lists).
- Easy to Use: Arrays make data management and iteration much easier. For example, you can loop through the elements, update element values directly, and systematically operate with all elements, such as sum, average, sort, etc.
- Building Blocks for Complex Structures: The majority of other data structures (e.g., stacks, queues, heaps, etc.) are built on an array or similar constructs. Learning and mastering arrays is the first step in preparing to learn about more advanced data structures and algorithms in Java.
Disadvantages of Arrays in Java
While arrays are simple and quick, there are some weaknesses developers should be aware of:
- Fixed Size: Once an array has been created, it cannot be resized. In order to accommodate for more elements, developers must construct a new array and duplicate the current data.
- Same Data Type Only: An array can only hold elements of the same data type and cannot hold integers, strings, and booleans together in the same array.
- Costly Insertions and Deletions: Adding or removing elements (especially in the middle) requires shifting other elements, making these operations slower (O(n)).
- No Built-in Flexibility: Arrays are more restrictive, with less built-in flexibility, especially compared. Unlike a collection like ArrayList, arrays cannot auto-resize and have no methods to aid with sorting or searching, while in Java, the developer must develop sorting and searching themselves, or rely on the class helpers Arrays.
Take your next step with HCL GUVI’s AI Software Development, co-created with IIT-M Pravartak, and learn through hands-on coding, real-world projects, and mentor guidance.
Conclusion:
Arrays may seem easy, but they are truly the backbone of programming in Java. From efficient data storage to powering some of the most complicated algorithms, arrays do a lot of heavy lifting behind the scenes.
Once you grasp how arrays work, how to create, access, and manipulate arrays, you’re not just learning syntax; you’re actually programming your brain to think like a programmer. This vital foundation will make it much easier to learn about complex data structures such as linked lists, trees, and graphs.
I really hope this blog post was able to teach you the basics of arrays in Java – what they are, how they work, and why they are so important in programming.
FAQs
1. What is an array in Java?
An array in Java is a data structure that holds multiple values of the same type in one variable. An array’s values can be accessed by an index.
2. What are the benefits of using arrays?
Arrays provide fast access to data, easy iteration, and a great way to organize large amounts of data. Arrays are also the basis for many advanced data structures.
3. Can an array hold different data types?
No. Java arrays are homogeneous all elements in an array must be of the same type.
4. What are the differences between an array and an ArrayList?
Arrays are fixed in size, while ArrayLists can resize dynamically as needed.
























Did you enjoy this article?