What is an Algorithm? A Simple Guide for Beginners
Dec 06, 2025 5 Min Read 4108 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever followed a recipe to bake a cake or used Google Maps to find the fastest route? If so, you’ve already used an algorithm without realising it.
In simple terms, an algorithm is just a step-by-step plan or recipe for solving a problem. It’s a clear list of instructions that tells you exactly what to do next, one step at a time. In computer science, algorithms are the step-by-step instructions that programs follow to get results. In other words, any process that solves a problem by following a finite set of rules can be called an algorithm.
In this article, you’ll see practical examples from everyday life and programming, learn the qualities that make an algorithm good and get simple ways to start writing and testing your own. By the end, you’ll understand not just the definition, but how to think like someone who designs solutions. So, without further ado, let us get started!
Quick Answer:
An algorithm is a clear, step-by-step set of instructions that tells a computer (or person) how to solve a specific problem or complete a task efficiently. In short, it’s the recipe that turns input into output through logical steps.
Table of contents
- What is an Algorithm?
- Key Features of Algorithms
- Why Are Algorithms Important?
- Key Characteristics of Good Algorithms
- How to Write Your Own Algorithm?
- Everyday Examples of Algorithms
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is an algorithm in simple words?
- What are examples of algorithms in daily life?
- Why are algorithms important in computer science?
- What are the main types of algorithms?
- How can beginners learn algorithms easily?
What is an Algorithm?
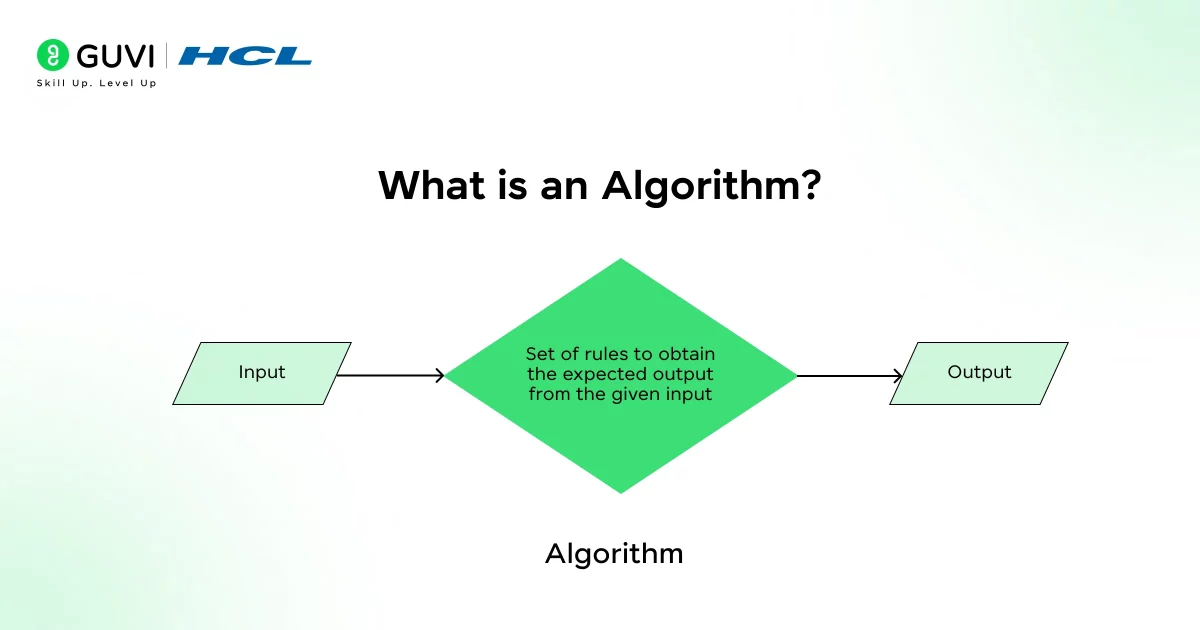
In textbook terms, an algorithm is defined as a finite, well-defined sequence of instructions designed to perform a task or solve a problem. Each step in an algorithm is unambiguous and must be executable in a clear, logical order.
The process starts with an input, follows a predictable path of operations, and results in a defined output. Algorithms are foundational in computer science because they provide a universal method for expressing how tasks should be performed, regardless of the programming language or platform used.
Key Features of Algorithms
- Step-by-Step Instructions: Every algorithm breaks a problem into small steps. Think of it as a list of orders: one step must be completed before moving to the next.
- Clear Start and End: A good algorithm has a defined beginning and a definite ending point. You know when it starts (inputs are given) and when it stops (result is produced).
- Unambiguous Steps: Each instruction is precise and leaves no room for confusion. This clarity ensures that anyone (or any computer) following the algorithm will do exactly what’s intended.
- Input and Output: An algorithm takes input data (such as numbers or text), processes it through its steps, and produces an output (the solution or result). For example, a search algorithm takes in your search keywords (input) and returns matching web pages (output).
- Finite: The steps must eventually finish – an algorithm can’t run forever. It will produce the result and stop in a finite number of steps.
These characteristics make algorithms reliable guides for solving problems.
It is quite common to get confused with Data Structures and Algorithms, so if you want to know the difference between them, read the blog – Difference Between Data Structures and Algorithms
Why Are Algorithms Important?
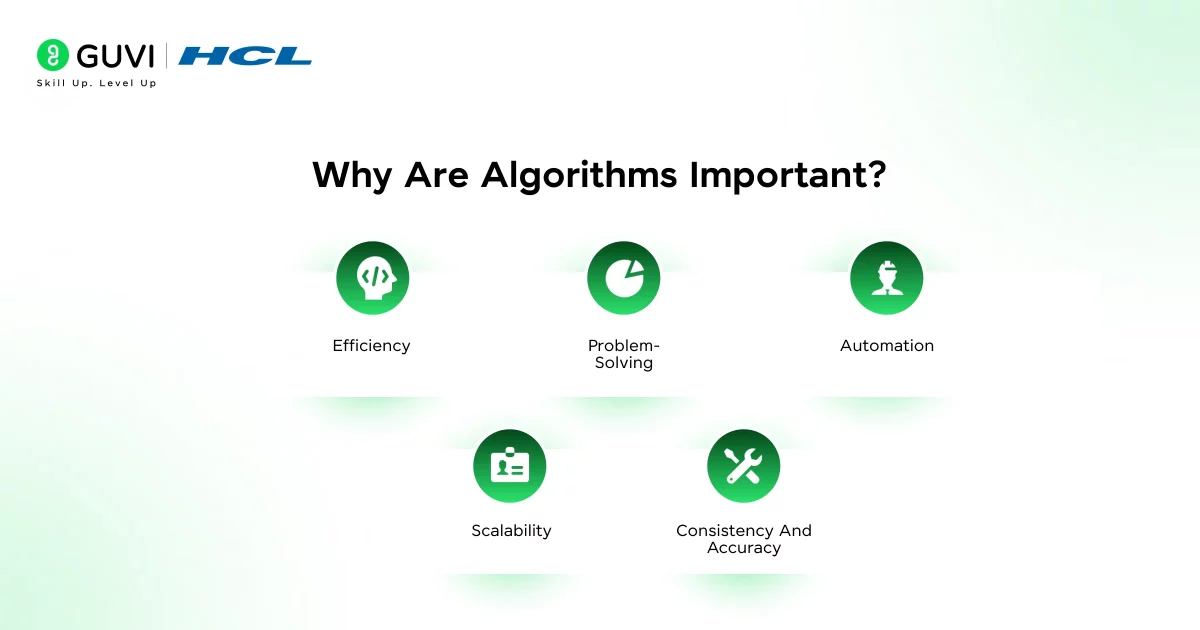
Algorithms are the backbone of problem-solving and technology. They help us systematically tackle complex tasks. Here’s why learning about algorithms matters:
- Efficiency: Well-designed algorithms make tasks faster and use resources (like time and memory) more efficiently. For example, a smart sorting algorithm can organise millions of items quickly, whereas a simple (but slow) method might take much longer.
- Problem-Solving: Algorithms provide a clear framework for solving problems step-by-step. Instead of guessing, you have a logical path to follow. This is crucial in computer programming, where you must guide the computer with precise steps.
- Automation: Many modern technologies rely on algorithms to automate decisions. Search engines, recommendation systems, and even artificial intelligence (AI) use advanced algorithms to process data and make decisions without human intervention. For instance, machine learning algorithms learn patterns from data to predict future outcomes.
- Scalability: Algorithms allow us to handle large volumes of data or tasks. As problems grow in size, good algorithms ensure that solutions remain feasible. For example, an efficient search algorithm can sift through billions of web pages quickly, which is essential for fast web browsing.
- Consistency and Accuracy: By following a fixed procedure, algorithms give consistent results every time. They eliminate human error in repetitive tasks. A calculator’s algorithm, for instance, will always compute 2+2 correctly in the same way, without mistakes.
TIP: Tech companies heavily test candidates on algorithms during their hiring process (e.g., Google’s hiring process often includes algorithm challenges). This shows how crucial algorithmic thinking is for solving real-world engineering problems.
If you want to read more about how DSA paves the way for effective coding and its use cases, consider reading HCL GUVI’s Free Ebook: The Complete Data Structures and Algorithms Handbook, which covers the key concepts of Data Structures and Algorithms, including essential concepts, problem-solving techniques, and real MNC questions
Key Characteristics of Good Algorithms

Whether you’re writing an algorithm yourself or using one, it’s helpful to know what makes an algorithm good. A well-designed algorithm should have the following properties:
- Clarity and Precision: Each step must be unambiguous. A person (or computer) following the algorithm should know exactly what to do. If an algorithm has vague or confusing instructions, it can’t reliably solve the problem.
- Efficiency: A good algorithm solves the problem using the least possible time and resources. That means it doesn’t do any unnecessary work. For example, a well-optimized search algorithm can find information much faster than a naive one, saving time for the user and energy for the computer.
- Definiteness: Every step of the algorithm has a clear purpose and leads toward the goal. There should be no guesswork. If the same algorithm is given the same input again, it should always follow the same steps and yield the same result (deterministic).
- Finiteness: A good algorithm will always come to an end after a finite number of steps. It shouldn’t loop forever; eventually, it must produce an answer or outcome.
- Generality, While not always needed for beginners, algorithms often aim to handle a class of problems, not just one specific instance. For example, a sorting algorithm should work for any list of numbers, not just one fixed list.
These characteristics ensure that algorithms are reliable and useful. In practice, when engineers write algorithms, they test them to check these qualities. If an algorithm isn’t efficient or doesn’t always end with a correct result, it’s refined until it does.
How to Write Your Own Algorithm?

Thinking about algorithms is not just theoretical – you can actually create your own algorithms to solve problems. Writing an algorithm usually involves these steps:
- Understand and Define the Problem: First, be crystal clear on what you’re trying to solve. What is the goal? What should the algorithm accomplish? Identify the inputs you have and the outputs you expect.
- Outline Inputs and Outputs: Specify what data the algorithm starts with (input) and what it should produce (output). This focus keeps the algorithm on track. For a sorting task: input = an unsorted list of numbers; output = a sorted list.
- Break Down the Steps: Write the step-by-step instructions in simple language. Each step should move you closer to the answer. Avoid unnecessary complexity. For example, a basic sorting algorithm might say: (a) start at the first number, (b) compare it to the next one, (c) swap if they’re out of order, (d) move to the next pair, and so on until the list is sorted. Using plain words or pseudocode (informal code-like language) is fine at this stage.
- Test Your Algorithm: Run through your algorithm with different examples (inputs) to see if it works. Check for mistakes or any steps that might go wrong. For example, if you wrote an algorithm to add two numbers, test it with positive, negative, and zero values to ensure it always gives the correct sum.
- Optimise and Refine: If you notice your algorithm is too slow or uses too much memory, look for improvements. Can any steps be combined? Can you find a shortcut? Often, there are multiple ways to solve the same problem, so choosing the most efficient path is important.
By following these steps, you can design algorithms for simple tasks and gradually tackle more complex ones. Remember, an algorithm is just a plan – writing it down carefully is the first step toward implementing it in code.
Everyday Examples of Algorithms
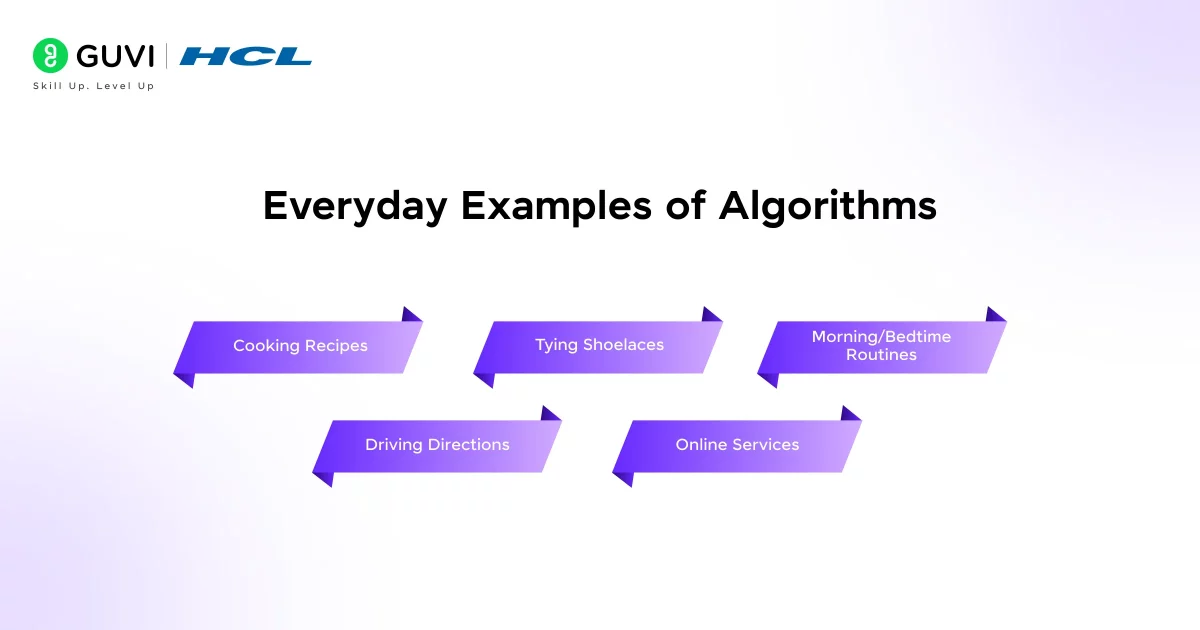
Algorithms aren’t just for computers – they exist in daily life all around us. Whenever you follow a fixed process with clear steps, you’re following an algorithm. Here are some concrete examples:
- Cooking Recipes: As mentioned, a recipe is a classic everyday algorithm. It lists ingredients and precise instructions that reliably produce a dish.
- Tying Shoelaces: Believe it or not, tying your shoes is an algorithm. You perform a fixed series of moves (make loops, cross them, pull through) in the same order each time to get a bow.
- Morning/Bedtime Routines: Your daily routines are algorithms. Whether getting ready for school or preparing for bed, you follow steps (brush teeth, set alarm, etc.) in sequence. Each action leads you closer to the goal of being ready for the day or night.
- Driving Directions: When you drive to a destination, you use an algorithm. You may follow a GPS’s step-by-step navigation to reach your goal efficiently.
- Online Services: Many apps and websites use algorithms behind the scenes. For instance, Google Search runs search algorithms to find and rank the most relevant pages for your query. Shopping sites use recommendation algorithms to suggest products based on what you’ve viewed or bought.
These examples illustrate how algorithms make complex tasks easier by breaking them down into simple steps.
If you’re serious about mastering DSA in software development and want to apply it in real-world scenarios, don’t miss the chance to enrol in HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak and MongoDB Certified Online AI Software Development Course. Endorsed with NSDC certification, this course adds a globally recognised credential to your resume, a powerful edge that sets you apart in the competitive job market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an algorithm is simply a clear, step-by-step set of instructions for solving a problem. By learning how algorithms work and how to write them, you’re learning to think logically. You start to see solutions as sequences of steps, and you gain tools to solve complex problems systematically.
As we’ve seen, every algorithm has inputs, clear instructions, and produces an output. We start by clearly defining the problem, break it down into steps, and then test and improve our solution. Remember: even something as simple as getting dressed in the morning is following an algorithm you created for yourself! So next time you follow any step-by-step guide, give a thought – you’re using an algorithm.
FAQs
1. What is an algorithm in simple words?
An algorithm is a set of clear, step-by-step instructions used to solve a problem or complete a task. It’s like a recipe that tells a computer what to do, in what order.
2. What are examples of algorithms in daily life?
Everyday examples include following a cooking recipe, using GPS navigation, sorting your playlist alphabetically, or deciding what to wear based on the weather.
3. Why are algorithms important in computer science?
Algorithms are the foundation of all computer programs. They make problem-solving faster, more efficient, and help computers perform tasks accurately and automatically.
4. What are the main types of algorithms?
Common types include sorting algorithms (like Bubble Sort), searching algorithms (like Binary Search), and pathfinding algorithms (like Dijkstra’s). Each solves a specific kind of problem.
5. How can beginners learn algorithms easily?
Start with simple examples, write them out step by step, and test them manually or in code. Practice solving small problems and gradually move to more complex ones.
























Did you enjoy this article?