
Prompt Tuning: Its Working Mechanism, Applications, and Key Aspects
Jan 21, 2026 4 Min Read 780 Views
(Last Updated)
Prompt Tuning has become one of the best methods for training the small-unit components of AI (artificial intelligence) models. Let’s understand the reason why we stated this line. In the Computer Science (CS) domain, superior product quality is not achieved through over-engineering; instead, it is ensured by breaking complex problems into small modules and designing solutions to optimize the performance of those modules.
Similarly, prompt tuning is a technique for training the AI’s small nodes to perform specific tasks more effectively, rather than modifying the entire AI brain.
In this blog, we will understand the concept of prompt tuning, how it works in the background, and other aspects. So let’s dig into our discussion.
Quick Answer:
Prompt tuning is a lightweight technique in which only a few specialized tokens are trained to guide a large AI model to produce accurate, consistent results for a specific task. It teaches the model the exact style and output you want without retraining the whole system, making it faster, cheaper, and highly effective.
Table of contents
- What is Prompt Tuning?
- Example:
- Also Read: What is Prompt Engineering?
- Note:
- Working Mechanism of Prompt Tuning Technique
- Setup Phase
- Input Construction Phase
- Forward Pass Phase
- Training or Update Phase
- Inference Phase
- Real-world Applications of Prompt Tuning
- Customer Support Chatbots
- Domain-Specific Writing Assistants
- Personalized Recommendation Systems
- Sentiment Analysis and Review Classification
- Task-Focused Content Generation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Prompt Tuning
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the main advantage of prompt tuning over full model fine-tuning?
- Can prompt tuning be used for any task type?
- Yes, it works for tasks like text classification, content generation, chatbots, and sentiment analysis.
What is Prompt Tuning?
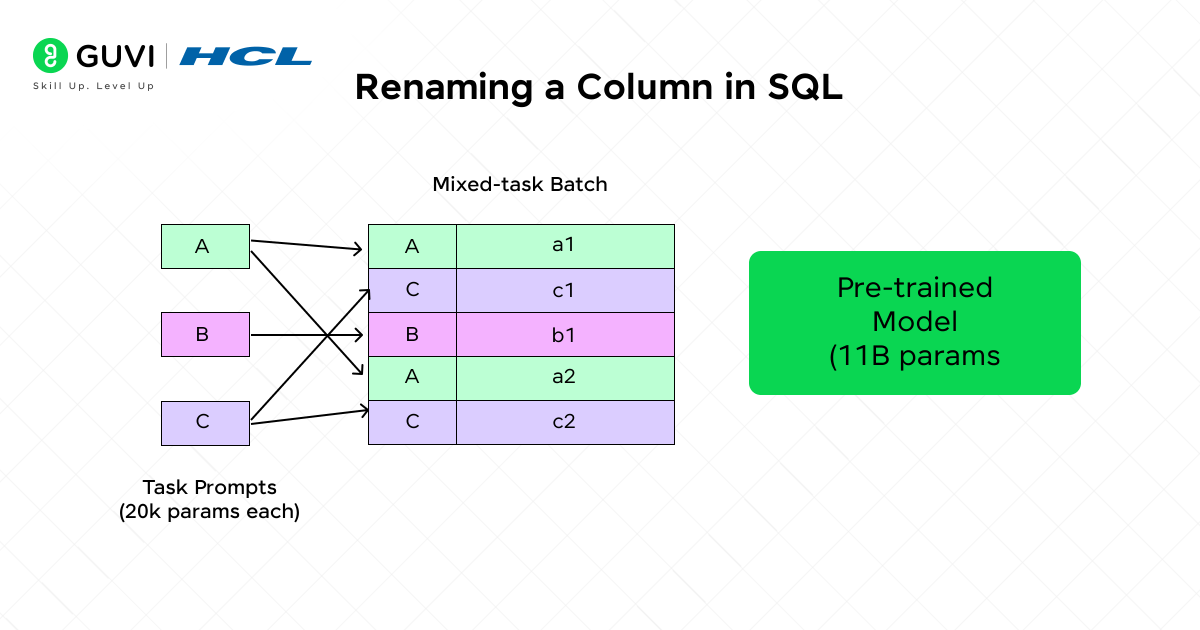
Prompt tuning is a practical approach for adapting large pre-trained models to perform tasks without requiring extensive parameter tuning. Instead of retraining the entire AI (artificial intelligence) model from scratch, we can easily integrate a trained prompt that helps the model generate the optimal result.
By adopting this approach, we can enhance the overall performance of the AI model without changing its internal layers, making it faster, cheaper, and, more importantly, consuming very little data.
Example:
Let’s say there is a website that only sells electronic products. Now, in this case, we want to instruct the AI model to write product descriptions for each electronic item listed on the platform, using a single, fixed style and format.
To perform this task, you usually would provide examples repeatedly (again and again). But with prompt tuning, you can actually train the prompt (trained prompt) to produce a crisp, concise instruction like: “Write a short, catchy, SEO-friendly electronics product description.”
After training the instruction, whenever you need it, you can use the same trained prompt, and the AI model will automatically write the most suitable product description each time without distorting the writing style.
Also Read: What is Prompt Engineering?
Note:
Trained Prompt = It is not plain text like we often type to get the desired results on platforms such as ChatGPT or Perplexity. A trained prompt is built from complex, specialized hidden tokens, which are vectors (numbers) stored in the model.
So when we say the prompts are trained in reality, these vectors are actually getting trained and updated.
For better comprehension: This particular prompt –> “Write a short, catchy electronics description,” is not just a text, it is actually a small set of learnable numbers like: [P1, P2, P3, P4 …]. Here, the “P tokens” are trained and manipulated according to the requirements and objectives.
Working Mechanism of Prompt Tuning Technique
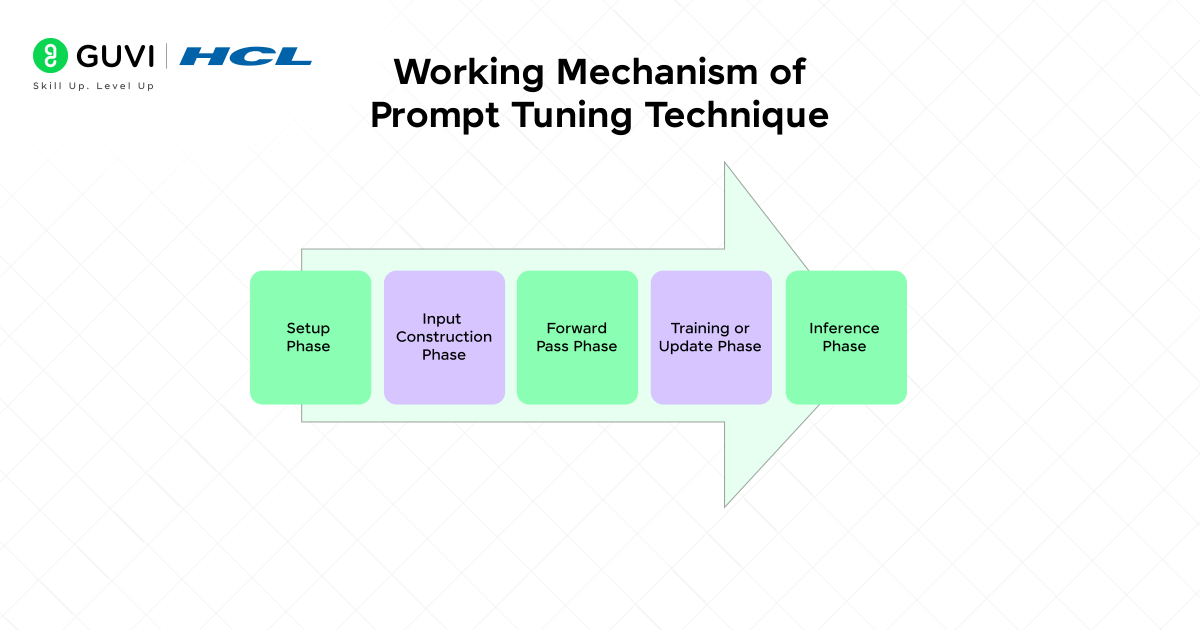
The working mechanism of prompt tuning comprises five main phases, which we list below in sequence to help you better understand it.
1. Setup Phase
In this phase, the pretrained model and tokenizer are loaded, but the model is kept completely frozen so none of its original knowledge gets changed. Along with this, a small set of learnable vectors called soft prompt embeddings is created.
These soft prompts are placed at the beginning of every input and are the only part that will be trained. This setup makes prompt tuning very efficient because we work with a tiny number of parameters instead of retraining the whole model.
2. Input Construction Phase
In this phase, the input text is first turned into tokens and then into embeddings using the model’s existing embedding layer. After that, the soft prompt embeddings are added in front of these token embeddings. This creates one combined input sequence that contains both the learned prompts and the actual text.
Positional encodings are applied so the model understands the correct order of everything. This step ensures that the model always sees the soft prompts first, which helps guide the model during learning.
3. Forward Pass Phase
In this phase, the full combined sequence—soft prompts plus text embeddings—is passed through the Transformer model. The model processes this input exactly the way it normally does, moving through its attention layers and feed-forward layers.
Even though the model is frozen, the soft prompts still influence how it pays attention to different parts of the input. Over time, this shaping effect helps the model adjust its responses to better match the task without changing any of its original weights.
4. Training or Update Phase
In this phase, the model’s output is compared with the correct answer using a loss function. Backpropagation is then used to calculate how far the output is from the expected result. But because the model’s parameters are frozen, the only part that receives updates is the soft prompt embeddings.
After many steps, these prompts learn meaningful patterns that guide the model toward the task, allowing the frozen model to behave almost like it was fine-tuned.
5. Inference Phase
In this phase, the trained soft prompts are added to new, unseen inputs in the same way they were added during training. The model processes this combined input and produces results that reflect the knowledge learned by the soft prompts.
Since the main model remains unchanged and only a small prompt file is reused, this makes inference fast, lightweight, and easy to deploy for any task or application.
Real-world Applications of Prompt Tuning
1. Customer Support Chatbots

Large language models (LLMs) can be trained with prompt tuning to provide accurate and polite responses that are tailored to a specific company. A small soft prompt is trained so that the chatbot recognizes the products, tone, and support style of the company, instead of retraining the whole model. It allows enterprises to tailor customer service robots to their customers at a fraction of the cost and with less effort.
2. Domain-Specific Writing Assistants

The healthcare, finance, education, and law industries require very specific writing styles. With prompt tuning, a model can be taught the rules, vocabulary, and tone of a certain domain by using only a small data sample.
This produces writing assistants that are faithful, reliable, and conform to industry standards without the risk of the main model losing its knowledge.
3. Personalized Recommendation Systems

By tuning prompts, companies can get models to offer better recommendations, be it books, products, or learning paths. User behavior and preferences can be used to train the soft prompt so that the model can become a more personalized and relevant suggester, while the main model remains intact.
4. Sentiment Analysis and Review Classification

Prompt tuning helps a model better understand and identify customer reviews, social media posts, or feedback. A soft prompt can be made to recognize positive, negative, or neutral sentiments on a particular domain, like restaurants, hotels, or apps, by being trained on a certain dataset, which enhances accuracy without a lot of computations.
5. Task-Focused Content Generation

With the help of prompt tuning, models can be made to produce content that is specifically tailored to certain requirements, such as product descriptions, blog introductions, marketing taglines, or technical summaries.
It is a cheap way for businesses to generate a large amount of content that is consistent across different channels by training small prompts that instruct the model on the style, keywords, structure, and tone they use.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Prompt Tuning
| S.No | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1 | Only trains small prompts, so it’s fast and uses less memory. | It may not work well for very complex tasks. |
| 2 | Saves storage as soft prompts are tiny (a few KBs). | Sensitive to prompt length and how they are initialized. |
| 3 | Can switch between tasks quickly by swapping prompts. | Prompts usually work only for the model they were trained on. |
| 4 | Keeps the original model knowledge safe. | Hard to understand exactly what the prompts learned. |
| 5 | Cost-effective compared to full model fine-tuning. | Performance can drop if the training data is small or noisy. |
You can train just 20–100 soft prompt vectors to make a 175-billion-parameter model perform a new task—without changing a single weight in the model!
Do you know that top product-based companies across the world, such as Google, Meta, Microsoft, and OpenAI, are now literally in a race to hire the best AI talent? If you aspire to be part of these top global tech brands, you need an ed-tech partner you can trust. And HCL GUVI, a leading upskilling platform, provides you with reliability through its Intel & IITM Pravartak Certified Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning Course. Join this comprehensive program and become a certified AI / ML expert.
Conclusion
To sum up, prompt tuning is an excellent and convenient method for adapting large language models (LLMs) to targeted tasks; hence, it does not require retraining the entire model. Essentially, the AI is led to carry out a particular task with precision and efficiency by the mere training of a few soft prompts.
As a result, the technology employed in conversational agents, content creation, and user-tailored suggestions becomes more versatile, less costly, and simpler to implement, thus demonstrating that little changes still have the power to bring about great achievements in AI integration.
FAQs
What is the main advantage of prompt tuning over full model fine-tuning?
It trains only a small set of soft prompts, keeping the main model frozen, making it faster and cheaper.
Can prompt tuning be used for any task type?
Yes, it works for tasks like text classification, content generation, chatbots, and sentiment analysis.
Yes, it works for tasks like text classification, content generation, chatbots, and sentiment analysis.
Soft prompts are small vectors that can be prepended to new inputs, making deployment lightweight.




























Did you enjoy this article?