
Types of Artificial Intelligence: Explained Simply and Clearly
Aug 25, 2025 5 Min Read 1103 Views
(Last Updated)
Ever chatted with Siri, seen Netflix recommend a movie you’d watch, or wondered if robots will someday rule the world? Then you’ve already brushed against the wide spectrum of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
But here’s the thing: not all AI is created equal. There are different types of artificial intelligence, based on how powerful or capable the system is and what kind of tasks it can perform.
Whether you’re a college student exploring the tech landscape or a curious learner building foundational knowledge, understanding the types of artificial intelligence will give you more clarity about what’s happening behind the scenes and what the future might look like. Let’s break it down.
Table of contents
- What Are the Types of Artificial Intelligence?
- Types of Artificial Intelligence Based on Capabilities
- Types of Artificial Intelligence Based on Functionalities
- Summary: Side-by-Side Comparison
- Common Misconceptions About Types of Artificial Intelligence
- Misconception 1: ChatGPT is a General AI
- Misconception 2: All AI learns like humans do
- Misconception 3: AI equals robots
- Misconception 4: AI will soon become self-aware
- Misconception 5: AI is objective and unbiased
- Interactive Section
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What are the 4 main types of AI?
- What is the difference between Narrow AI and General AI?
- Is ChatGPT an example of General AI?
- Which type of AI is currently used the most?
- Will AI ever become self-aware?
What Are the Types of Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence is a broad field, and not all AI systems are created equal. Some are highly specialized and task-specific, while others aim to replicate or even surpass human cognitive abilities.
To understand this better, Artificial Intelligence is typically classified in two different ways, each offering a unique lens:
- Based on Capabilities – How intelligent and adaptable the AI is
- Based on Functionalities – How the AI behaves or operates internally
Let’s explore both in detail.
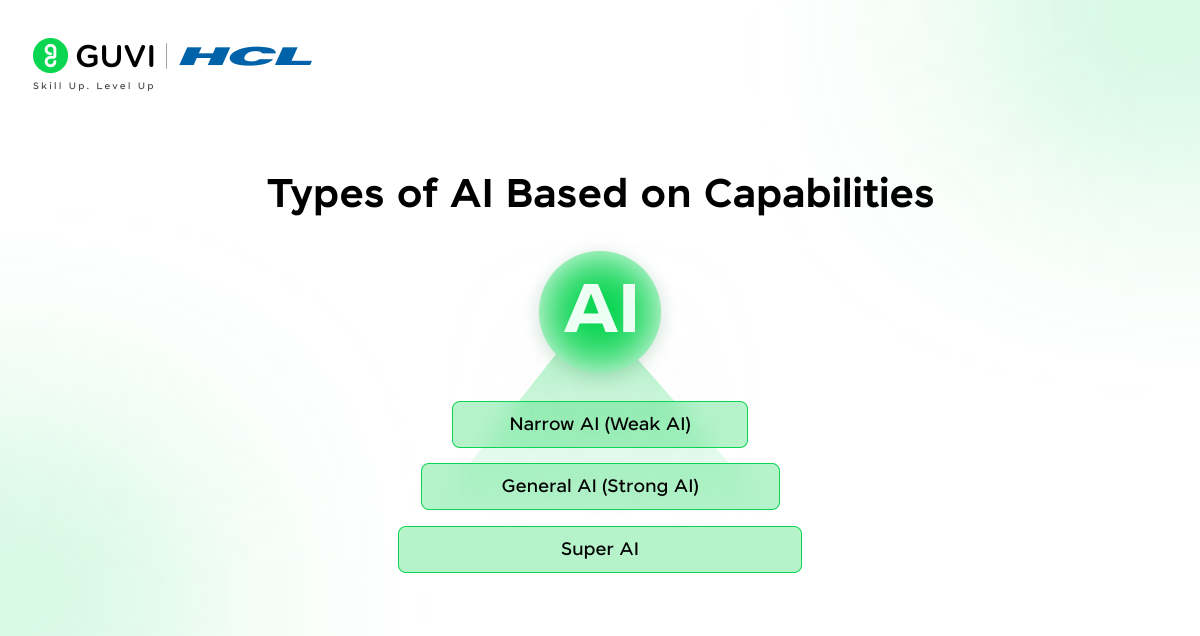
1. Types of Artificial Intelligence Based on Capabilities
This classification asks: How powerful is AI compared to human intelligence? Can it do just one thing, or is it capable of learning, adapting, and generalizing like a human?
There are three main categories here:
A. Narrow AI (Weak AI)
This is the most common and currently deployed type of AI. Narrow AI refers to systems that are designed to perform a specific task. They do that task extremely well, but that’s it. They can’t operate outside of their predefined domain or exhibit general intelligence.
Characteristics:
- Task-specific
- Trained with large datasets
- High accuracy in focused domains
- Lacks awareness or understanding
Examples:
- Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant (voice tasks)
- Netflix’s recommendation engine (content suggestions)
- Facial recognition systems.
B. General AI (Strong AI)
This is where things start to get interesting and more theoretical. General AI refers to machines that can perform any intellectual task a human can. These systems would have the ability to think, understand, and apply knowledge across different contexts, without being retrained from scratch.
Characteristics:
- Human-level cognition
- Ability to reason, plan, and solve problems
- Self-learning across domains
- Can transfer knowledge across tasks
Why it’s important:
If achieved, General AI could transform industries and societies. It could handle complex, multi-domain problems, like designing a product, running a business, and teaching a class, all within the same framework.
C. Super AI
Now we’re crossing into futuristic and philosophical territory. Super AI is a hypothetical system that surpasses human intelligence in all aspects, including creativity, problem-solving, reasoning, emotional intelligence, and more.
Characteristics:
- Performs better than humans in all cognitive functions
- Possesses consciousness, emotions, and self-awareness
- Can make independent decisions, potentially without human intervention
Why it matters:
Super AI raises ethical questions and existential risks. What happens when machines can outthink humans in every way? How do we ensure they act in our interest?
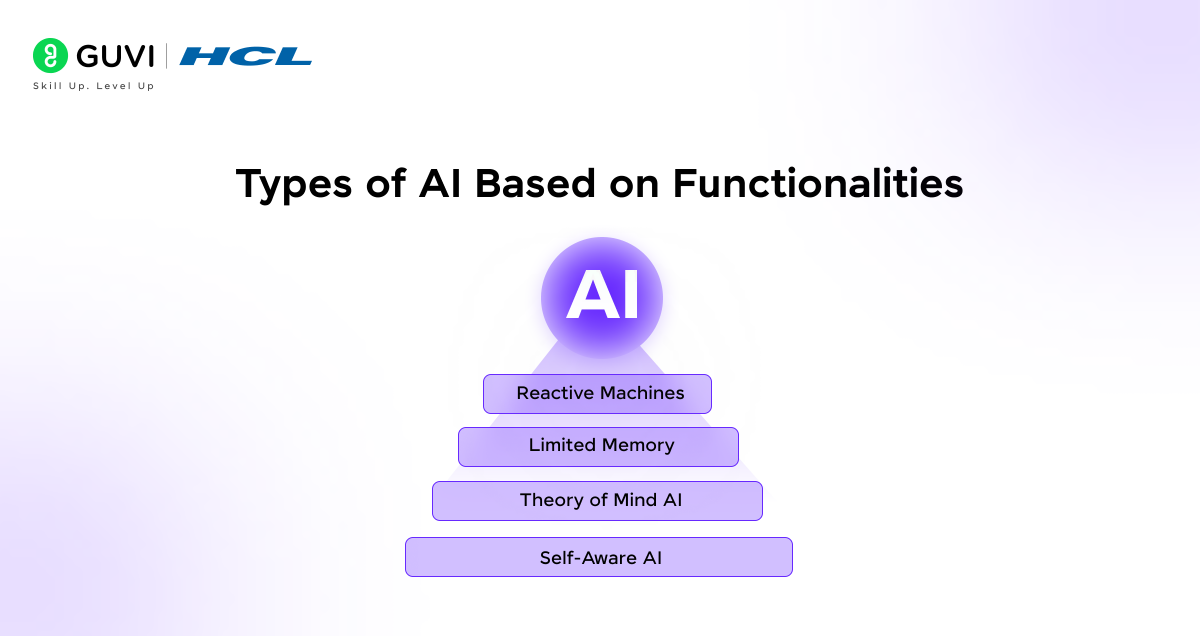
2. Types of Artificial Intelligence Based on Functionalities
This classification focuses on how an AI system works internally, its architecture, memory, learning ability, and behavioral traits.
There are four categories here:
A. Reactive Machines
These are the simplest form of AI systems. They don’t store past experiences or learn from them. They simply react to current inputs based on pre-defined rules.
Characteristics:
- No memory
- No ability to learn
- Performs one task with high precision
- Completely reactive, not proactive
Example:
- IBM’s Deep Blue, the chess-playing AI that defeated world champion Garry Kasparov in 1997. It could evaluate moves but had no memory of past games or strategic learning.
B. Limited Memory
Most current AI systems fall under this category. They can learn from past data and use it to make better decisions, but only within a limited scope.
Characteristics:
- Can access past data temporarily
- Continuously improves with more data
- Requires regular training updates
Examples:
- Self-driving cars: They use data from recent movements and environmental factors to make real-time decisions.
- Chatbots: Learn from past conversations to better respond.
- Email spam filters: Learn which types of emails users mark as spam.
C. Theory of Mind AI
This is a future-facing type of AI still in the research phase. It refers to systems that can understand emotions, intentions, beliefs, and mental states.
In short, machines that “get” humans.
Characteristics:
- Social awareness
- Emotional intelligence
- Empathetic response capability
- Can model human decision-making
D. Self-Aware AI
The most advanced and controversial form of AI. These systems would be fully conscious and have a sense of self, able to perceive and understand their existence, just like humans do.
Characteristics:
- Self-awareness and introspection
- Emotions and consciousness
- Autonomy at a human level or beyond
Why It’s Controversial:
If a machine becomes self-aware, it may develop its own goals. How do we regulate or coexist with such entities? This dives into philosophy, ethics, and even law.
Summary: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Based on Capabilities | What It Means | Example |
| Narrow AI | Task-specific AI | Siri, ChatGPT |
| General AI | Human-level multitasking AI | Not yet developed |
| Super AI | Exceeds human intelligence | Sci-fi concepts |
| Based on Functionalities | What It Means | Example |
| Reactive Machines | Respond to specific input, no memory | IBM Deep Blue |
| Limited Memory | Use historical data to make decisions | Self-driving cars |
| Theory of Mind | Understand human emotions and intentions | Still in research phase |
| Self-Aware AI | Fully conscious and autonomous | Not yet created |
The term “Artificial Intelligence”, was coined back in 1956 by John McCarthy at a conference at Dartmouth College. That’s older than the Internet.
Common Misconceptions About Types of Artificial Intelligence
AI’s portrayal in movies, media, and even marketing has created a lot of confusion. Let’s bust a few myths.
Misconception 1: ChatGPT is a General AI
It’s not. It might seem smart; it can write essays, poems, and code, but it doesn’t “understand” anything. It can’t reason, feel, or generalize like a human. It’s trained on patterns and probabilities.
Reality: ChatGPT is a very advanced form of Narrow AI with a massive training dataset.
Misconception 2: All AI learns like humans do
Some AIs don’t learn at all. Reactive Machines, for instance, follow pre-programmed logic and don’t store data. Even limited-memory systems can’t evolve past their training without human input.
Reality: AI learns only what it’s trained or programmed to learn,no more, no less.
Misconception 3: AI equals robots
This is a big one. People often associate AI with humanoid robots. But most AI is software.
- Google Maps? AI.
- Amazon product suggestions? AI.
- Grammarly correcting your email? AI.
Reality: AI is the “brain.” A robot is just one potential “body” AI can operate in.
Misconception 4: AI will soon become self-aware
We’re nowhere close. While progress in NLP (Natural Language Processing) and robotics is impressive, we don’t yet understand consciousness well enough to replicate it in machines.
Reality: Even Theory of Mind AI is in early research stages. Self-aware AI is more science fiction than science, at least for now.
Misconception 5: AI is objective and unbiased
Not true. AI reflects the data it’s trained on. If that data is biased (which it often is), the AI will mirror those biases, sometimes in ways that can harm people.
Reality: Human oversight is essential to monitor AI outputs and ensure fairness.
Interactive Section
Let’s see how well you’ve understood the topic. Pick the correct answers:
1. Which type of AI can perform a single task but does it extremely well?
A. Super AI
B. General AI
C. Narrow AI
D. Theory of Mind
Answer: C. Narrow AI
2. Which of the following is an example of Limited Memory AI?
A. Google Translate
B. A chess-playing machine with no learning
C. Self-driving car
D. Super AI
Answer: C. Self-driving car
3. Which type of AI understands human emotions and social behavior?
A. Reactive Machine
B. Limited Memory
C. Theory of Mind
D. Narrow AI
Answer: C. Theory of Mind
If you’re serious about mastering artificial intelligence and want to apply it in real-world scenarios, don’t miss the chance to enroll in HCL GUVI’s Intel & IITM Pravartak Certified Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning course. Endorsed with Intel certification, this course adds a globally recognized credential to your resume, a powerful edge that sets you apart in the competitive AI job market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of AI is evolving fast, but at its core, it’s all about levels, how intelligent, how independent, and how adaptable these systems are.
- Most of what we see today is Narrow AI and Limited Memory AI
- General AI and beyond are still part of ongoing research
- Understanding the types of AI helps you decode what the tech is, and what it isn’t
Now that you’ve got a grip on the different types, go ahead and observe the tech around you. You’ll start seeing these classifications play out in real life. And that, right there, is how you move from passive consumer to smart learner.
FAQs
1. What are the 4 main types of AI?
The four main types are Reactive Machines, Limited Memory, Theory of Mind, and Self-Aware AI. Reactive and Limited Memory AI are in use today, while the other two remain experimental or hypothetical. Each type represents a deeper level of intelligence and awareness in machines.
2. What is the difference between Narrow AI and General AI?
Narrow AI is task-specific; it can perform one job really well, like translating text or recommending songs. General AI, on the other hand, would mimic human intelligence across different tasks and adapt without retraining. As of now, only Narrow AI exists in the real world.
3. Is ChatGPT an example of General AI?
No, ChatGPT is a form of advanced Narrow AI. It generates text based on patterns in data but doesn’t truly understand or reason like a human. It can’t think independently or solve problems outside of its training.
4. Which type of AI is currently used the most?
Limited Memory AI is the most widely used today in real-world applications. It powers technologies like self-driving cars, recommendation engines, and fraud detection systems. These systems learn from past data but within a limited scope.
5. Will AI ever become self-aware?
Self-aware AI is still a theoretical concept with no working examples. While it’s a popular theme in science fiction, current technology hasn’t come close to creating conscious machines. Whether it ever will is still an open question in science and ethics.





























Did you enjoy this article?