
Top 12 Machine Learning Frameworks
Sep 09, 2025 5 Min Read 2596 Views
(Last Updated)
Building powerful AI models no longer requires starting from scratch. Machine learning frameworks provide the foundation and workflows to create models faster and with greater accuracy. In our latest blog, we reveal the best machine learning frameworks along with their strengths and best use cases. Read the full article to find the framework that fits your next project.
Table of contents
- What are Machine Learning Frameworks?
- What are ML Frameworks in Python?
- Top Machine Learning Frameworks List
- Framework Performance Comparison
- Best ML Libraries
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What are Machine Learning Frameworks?

Machine learning frameworks are structured platforms that provide tools and predefined functions to build and train models. These frameworks offer standardized workflows that make it easier to test models and adapt them for different datasets. Many frameworks also include utilities for data preprocessing and deployment. They work as a foundation that supports experimentation and production workflows in machine learning projects.
What are ML Frameworks in Python?
Machine learning frameworks in Python are software tools that provide ready-made functions and workflows to build and train models. They reduce the need to write low-level code for tasks like optimization and data handling. Popular examples include TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn. They work directly in the Python programming environment and integrate smoothly with other Python libraries such as NumPy and Pandas.
Top Machine Learning Frameworks List
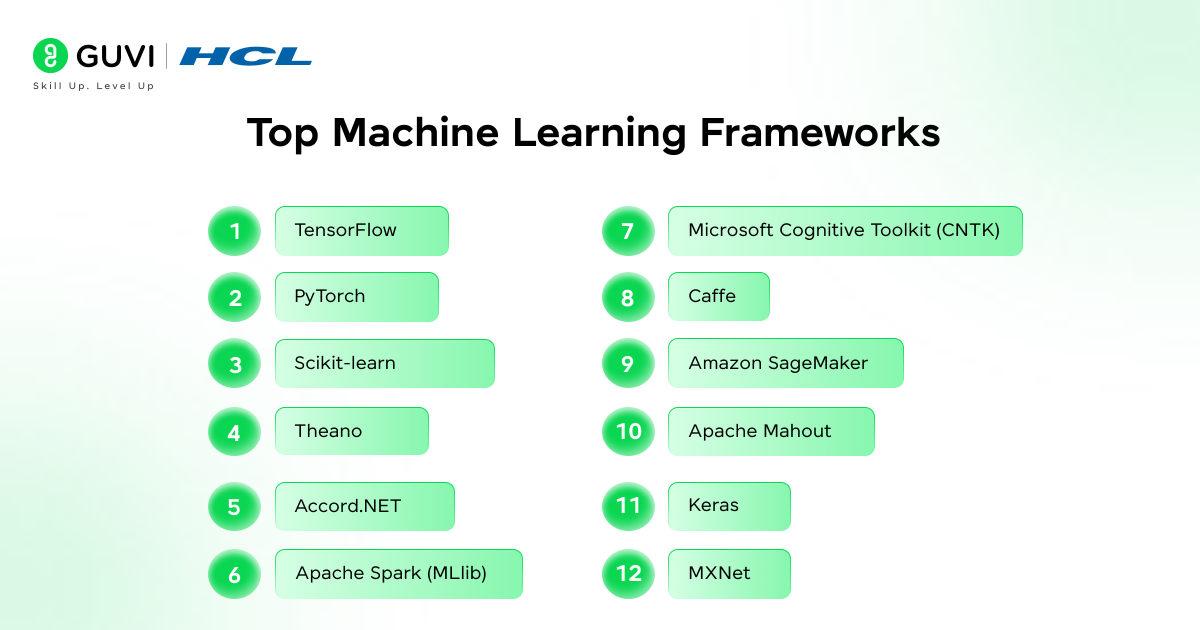
- TensorFlow
Definition: TensorFlow is a machine learning framework created by Google. It helps build and train models for a wide range of tasks. It works across platforms so you can run models on computers and in the cloud.
Top Features:
- Works with CPUs and GPUs for flexible computing. It also supports TPUs for faster training.
- Includes tools like TensorBoard for visualization and TensorFlow Lite for mobile deployment.
- Supported by a large community that shares tutorials and code.
Best Use Cases:
- Deep learning framework for image recognition and speech processing.
- Text projects such as chatbots or sentiment analysis.
- Predictive analytics in healthcare and finance.
Cons:
- It can feel complex for beginners.
- Updates sometimes create compatibility issues with older projects.
- PyTorch
Definition: PyTorch is a deep learning framework developed by Meta AI. It is known for being easy to write and run code. Developers also value its strong performance for advanced projects.
Top Features:
- Eager execution lets you run and check code step by step.
- Comes with libraries like TorchVision for images and TorchText for language tasks.
- Integrates well with Python for a smooth workflow.
Best Use Cases:
- Deep learning framework for computer vision and image classification.
- Research projects that need frequent adjustments.
- Reinforcement learning experiments.
Cons:
- Production deployment options are not as broad as TensorFlow.
- Large models can require powerful hardware.
- Scikit-learn
Definition: Scikit-learn is primarily a library, but it is also a Python machine learning framework that focuses on traditional algorithms. It is known for its simple interface and clear documentation.
Top Features:
- Provides algorithms for classification and regression. It also supports clustering methods.
- Bestows tools for cleaning and preparing data.
- Works well with Python libraries like NumPy and Pandas.
Best Use Cases:
- Creating models with smaller datasets.
- Learning core machine learning methods in an educational setting.
- Quick prototypes for analytics and business reporting.
Cons:
- Not designed for deep learning projects.
- Theano
Definition: Theano is a Python machine learning framework built for numerical computation. It was one of the first tools to make deep learning practical with GPU acceleration.
Top Features:
- Speeds up calculations by optimizing mathematical expressions.
- Runs on both CPUs and GPUs.
- Works closely with NumPy for handling arrays and matrices.
Best Use Cases:
- Deep learning research.
- Academic projects focused on numerical performance.
- Building models where training speed is important.
Cons:
- No longer actively maintained.
- Lacks many features found in modern frameworks.
- Accord.NET
Definition: Accord.NET is a machine learning framework for the .NET platform. It combines statistical methods with image and signal processing tools.
Top Features:
- Offers algorithms for classification and clustering.
- Supports image and audio processing.
- Works directly in C# and other .NET languages.
Best Use Cases:
- Computer vision in .NET applications.
- Audio analysis and speech recognition.
- Building machine learning into desktop software.
Cons:
- Smaller user base than Python frameworks.
- Fewer tutorials and learning resources.
- Apache Spark
Definition: Apache Spark is a distributed computing system with a machine learning library called MLlib. It is designed to process large amounts of data across many machines.
Top Features:
- Runs tasks in parallel to speed up processing.
- MLlib supports algorithms for classification and regression.
- Works with many storage systems such as Hadoop and Amazon S3.
Best Use Cases:
- Training models with huge datasets.
- Real-time recommendation engines.
- Large-scale business analytics.
Cons:
- Needs a distributed environment to run efficiently.
- Steeper learning curve for those new to big data tools.
- Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit
Definition: Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit is also called CNTK. It is a deep learning framework from Microsoft. It focuses on high performance and scalability.
Top Features:
- Trains models across multiple GPUs at once.
- Works with both Python and C++.
- Optimized for deep neural network training.
Best Use Cases:
- Speech recognition projects.
- Large-scale image classification.
- Neural networks that need heavy computation.
Cons:
- Smaller community than TensorFlow or PyTorch.
- Documentation can feel limited for new users.
- Caffe
Definition: Caffe is a deep learning framework built for image processing speed. It was developed by the Berkeley Vision and Learning Center.
Top Features:
- Highly optimized for convolutional neural networks.
- Trains and tests image models quickly.
- Uses configuration files to define models without coding everything.
Best Use Cases:
- Object detection in images.
- Academic research in computer vision.
- Fast prototyping for vision-based models.
Cons:
- Not flexible for non-image tasks.
- Slower community activity compared to newer tools.
- Amazon SageMaker
Definition: Amazon SageMaker is a cloud-based machine learning framework and service from AWS. It helps build and deploy models without managing servers.
Top Features:
- Offers ready-to-use algorithms.
- Connects easily with AWS storage and data tools.
- Adjusts resources automatically to match workloads.
Best Use Cases:
- Deploying models at scale in production.
- Training large datasets in the cloud.
- Creating full ML workflows without in-house infrastructure.
Cons:
- Costs can rise quickly with heavy use.
- Works best for teams already using AWS.
- Apache Mahout
Definition: Apache Mahout is an open source machine learning framework for scalable data analysis. It is designed to run on big data systems like Hadoop.
Top Features:
- Provides algorithms for clustering and classification.
- Optimized for processing large datasets.
- Integrates with Hadoop and Spark.
Best Use Cases:
- Large-scale recommendation engines.
- Grouping data into clusters for business analysis.
- Predictive modeling on enterprise datasets.
Cons:
- Narrower range of algorithms compared to other frameworks.
- Requires knowledge of big data platforms.
- Keras
Definition: Keras is a high-level deep learning framework that works with TensorFlow as a backend. It focuses on making model building quick and simple.
Top Features:
- Easy-to-read API for creating models.
- Supports convolutional and recurrent neural networks.
- Runs seamlessly with TensorFlow.
Best Use Cases:
- Learning deep learning concepts.
- Quickly testing new model ideas.
- Building prototypes for research and education.
Cons:
- Relies on other frameworks to run.
- Limited flexibility for very specialized models.
- MXNet
Definition: MXNet is a deep learning framework supported by the Apache Software Foundation. It is constructed for efficiency and scaling across multiple machines.
Top Features:
- Supports both symbolic and imperative programming.
- Runs on many CPUs and GPUs.
- Works well for distributed computing setups.
Best Use Cases:
- Training deep learning models across large clusters.
- Cloud-based AI services.
- Projects that need a mix of programming styles.
Cons:
- Smaller community than TensorFlow or PyTorch.
- Can feel complex for beginners.
Framework Performance Comparison
| Framework | Speed | Scalability | Ease of Learning | Community Support |
| TensorFlow | High on GPUs and TPUs | Strong cloud and multi-device support | Moderate learning curve | Very large and active |
| PyTorch | Fast with GPUs | Good for research scaling | Easier than TensorFlow | Large and growing |
| Scikit-learn | Fast on small datasets | Limited for large-scale tasks | Very easy | Large in classical ML |
| Theano | High with GPU optimization | Moderate | Moderate | Small, minimal updates |
| Accord.NET | Moderate | Limited | Easy for .NET developers | Small |
| Apache Spark (MLlib) | High with cluster setups | Excellent on big data | Steep learning curve | Large in big data field |
| Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK) | High on multi-GPU setups | Strong | Moderate | Medium-sized |
| Caffe | Very fast for image tasks | Limited beyond CNNs | Moderate | Medium-sized |
| Amazon SageMaker | High in managed environments | Excellent with AWS | Easy for AWS users | Large in AWS ecosystem |
| Apache Mahout | High on big data frameworks | Strong for distributed tasks | Steep | Medium in enterprise use |
| Keras | Moderate | Good via TensorFlow backend | Very easy | Large beginner-friendly |
| MXNet | High on distributed setups | Excellent | Steep | Medium-sized |
Find out how to turn your knowledge of the top machine learning frameworks into career-focused skills with our Intel®-certified AI/ML course. With an industry-aligned curriculum, practical hands-on training, native language support, and access to a global network of 80,000+ learners, you will gain the expertise to select, implement, and optimize ML frameworks for impactful AI solutions in 2025 and beyond.
Best ML Libraries
While machine learning frameworks provide the overall structure for building and deploying models, libraries focus on delivering specific algorithms and utilities that can be used within those frameworks. They allow developers to add powerful methods to their workflows without coding them from scratch. Choosing the right library can speed up experimentation and improve model performance.
- Scikit-learn: Well-suited for classical algorithms such as regression and clustering.
- XGBoost: Popular for high-speed as well as high-accuracy gradient boosting.
- LightGBM: Designed for fast training on large datasets with lower memory use.
- CatBoost: Works well with categorical data and requires less preprocessing.
- H2O.ai: Presents machine learning and AutoML features for quick model creation.
Conclusion
The right machine learning framework can speed up development and make deployment smoother. Each option in the above machine learning frameworks list has its own strengths. The ultimate choice depends on:
- Your project goals
- Dataset size
- Team expertise
- Environment where the model will run
Pairing frameworks with the right deployment tools guarantees that your models can move from testing to production without unnecessary complexity. Thus, no matter if you are building a small prototype or a large-scale AI system, the right combination of framework, library, and deployment tool can make all the difference in delivering results effectively.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between machine learning and deep learning?
Machine learning focuses on algorithms that learn patterns from data to make predictions or decisions. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers to process more complex patterns, usually in large datasets.
2. Do I need to know programming to work with machine learning?
Basic programming skills are essential for most machine learning tasks. Python is the most common language due to its ease of use and extensive ML libraries. Some platforms offer low-code or no-code solutions, but deeper customizations require coding knowledge.
3. How important is data quality in machine learning projects?
Data quality is critical because models learn patterns directly from the data they are trained on. Poor-quality data can lead to inaccurate predictions and unreliable results.
4. Can machine learning models work in real time?
Yes, with the right setup, models can process and respond to data in real time. This is common in applications like fraud detection and recommendation systems.
5. What hardware is best for training machine learning models?
The choice depends on the complexity of the model and dataset size. CPUs work for smaller models. On the other side, GPUs or TPUs are preferred for deep learning tasks due to faster processing.




























Did you enjoy this article?