
Technical Interview Process for Senior Developers
Feb 18, 2026 5 Min Read 606 Views
(Last Updated)
The technical interview process for senior developers checks more than coding skills. It looks at how you think about architecture, solve complex problems, and make solid engineering decisions. Hiring teams want to see your approach to scalability, system design, debugging, and handling real project responsibilities with confidence.
This guide explains what senior-level technical interviews usually involve and how you can prepare effectively. You will learn the key skills interviewers look for, the types of questions you can expect, and practical ways to show your technical depth and leadership mindset during the interview.
Quick Answer
Technical interviews for senior developers test system design, advanced coding, architecture decisions, and debugging skills. Prepare by practicing real-world designs, solving complex coding problems, and clearly explaining past project decisions to demonstrate senior-level expertise.
Table of contents
- What Is The Technical Interview Process For Senior Developers
- Technical Screening
- Deep Coding Round
- System Design Round
- Architecture Discussion
- Debugging And Optimization Round
- Behavioural And Leadership Round
- Final Hiring Manager Discussion
- How To Prepare For The Technical Interview
- Strengthen Your Core Fundamentals
- Practice System Design Consistently
- Improve Coding Problem Solving And Clarity
- Build Strong Debugging And Optimization Skills
- Prepare Real Leadership And Ownership Examples
- Interview Preparation Timeline
- 💡 Did You Know?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What Is The Most Important Round In A Senior Developer Interview?
- How Should Seniors Prepare For Technical Interviews?
- Do Companies Expect Seniors To Code Perfectly?
- How Long Does Senior Level Interview Preparation Take
What Is The Technical Interview Process For Senior Developers
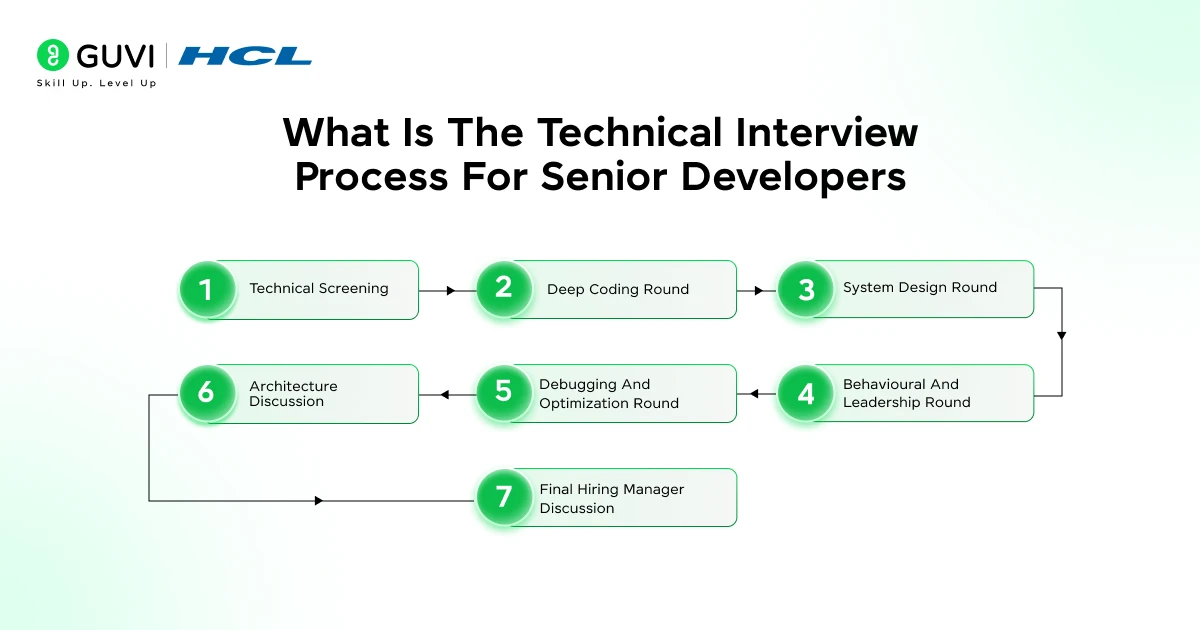
The technical interview for senior developers evaluates how well you handle complex codebases, system scalability, production failures, team leadership, and long-term engineering decisions. Companies want to know if you can own features end-to-end, improve system reliability, guide junior developers, and make thoughtful architectural choices. This section explains each stage of the senior developer technical interview process and what interviewers expect from you.
1. Technical Screening
2. Deep Coding Round
3. System Design Round
4. Architecture Discussion
5. Debugging And Optimization Round
6. Behavioural And Leadership Round
7. Final Hiring Manager Discussion
1. Technical Screening
The technical screening round checks whether you meet the core expectations for a senior role. Interviewers focus on your real engineering experience, clarity in communication, and ability to explain complex technical decisions. You will be asked about your past project architecture, major challenges you solved, and how you think about fundamental engineering principles.
• Experience with distributed systems, microservices, or event-driven architectures
• Ability to explain trade-offs when choosing tools or technologies
• Comfort discussing scaling strategies for high traffic systems
Example: Reviewing how you improved performance in a legacy codebase
Tips: Keep your answers direct and impact-focused
Advice: Highlight measurable results whenever possible
2. Deep Coding Round
The deep coding round checks whether you can write clean, maintainable, and optimized code while explaining your thought process clearly. The technical interview for Senior developers must balance problem-solving, clarity, and production-ready standards.
• Writing efficient and readable code under constraints
• Choosing the right data structures for each scenario
• Explaining time and space complexity clearly
Example: Implementing a graph traversal with optimized space usage
Tips: Think aloud to show your reasoning
Advice: Prioritize correctness first, then optimize
3. System Design Round
The system design round is one of the most important parts of the technical interview for senior developers. It checks your ability to design scalable, reliable, and maintainable systems that work under real-world traffic and load.
• Designing APIs, databases, caching layers, and microservices
• Making choices between consistency, availability, and latency
• Planning for scalability, reliability, and monitoring
Example: Designing a chat system or video streaming platform
Tips: Start with requirements and constraints before presenting the architecture
Advice: Always mention failure handling and observability
4. Architecture Discussion
This round tests how well you make long-term architectural decisions. Interviewers want to see if you understand design patterns, refactoring strategies, and how to evolve a large codebase responsibly over time.
• Selecting patterns such as CQRS, event sourcing, or the repository pattern
• Designing clean and modular architecture
• Managing long-term code quality and technical debt
Example: Explaining why you migrated from a monolithic to a microservice architecture
Tips: Use real data or outcomes to support your decisions
Advice: Highlight collaboration with DevOps, QA, and product teams
5. Debugging And Optimization Round
Debugging is a core skill for senior developers because you handle production incidents and performance bottlenecks. This round checks how you troubleshoot issues logically and calmly.
• Finding hidden bugs in large codebases
• Optimizing performance in high-load systems
• Diagnosing memory leaks, latency spikes, or failures
Example: Finding a race condition in a multi-threaded environment
Tips: Reproduce the issue before troubleshooting
Advice: Break down the problem into smaller testable steps
6. Behavioural And Leadership Round
Senior developers must mentor teams, collaborate across departments, and deliver high-impact work. This round checks your communication, teamwork, ownership, and leadership qualities.
• Handling conflicts and communication gaps
• Managing deadlines and delivering key features
• Mentoring junior developers effectively
Example: Explaining how you led a team through a critical production outage
Tips: Use real experiences, not hypothetical ones
Advice: Show ownership, accountability, and clear decision-making.
7. Final Hiring Manager Discussion
The hiring manager checks cultural fit, long-term potential, and whether your leadership style matches the team’s needs. This is where your mindset, ownership, and overall engineering maturity matter most.
• Sharing long-term engineering vision
• Aligning technical decisions with business goals
• Demonstrating proactive problem-solving
Example: Describing how you improved engineering processes in a previous team
Tips: Show genuine interest in the team’s mission
Advice: Highlight adaptability and growth mindset
How To Prepare For The Technical Interview
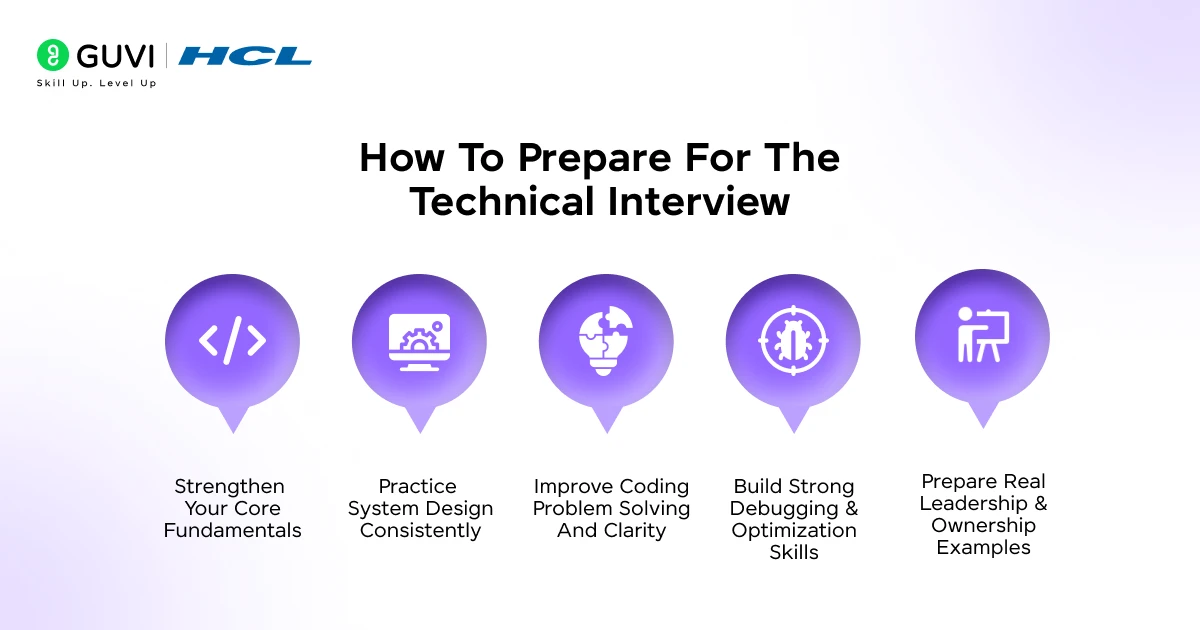
Preparing for the technical interview for senior developers requires covering fundamentals, system design, coding depth, debugging skills, and leadership readiness. In this section, we will look at the key areas you need to prepare, including:
- Strengthen Your Core Fundamentals
- Practice System Design Consistently
- Improve Coding Problem Solving And Clarity
- Build Strong Debugging And Optimization Skills
- Prepare Real Leadership And Ownership Examples
1. Strengthen Your Core Fundamentals
Strong fundamentals help you approach complex interview questions with clarity and confidence. This step ensures that you understand the base concepts behind every engineering decision.
Syllabus To Cover
• Data structures and algorithm patterns
• Database fundamentals and indexing
• Concurrency, multithreading, async workflows
• Networking basics such as latency, throughput, load
• Data structures and algorithms that support efficient solutions
• Database concepts, including indexing and transactions
• Concurrency and async communication
Example: Explaining how you improved API performance using caching and indexing
Tips: Review topics you have used in real projects
Advice: Keep explanations practical and direct
2. Practice System Design Consistently
System design is a major part of senior interviews and reflects how you think about scalability, reliability, and long-term architecture. Practicing different system patterns helps you build confidence.
Syllabus To Cover
• High-level architecture components
• Databases, caching, queues, load balancing
• Scalability, consistency, latency trade-offs
• Failure handling and observability
• Identifying requirements and constraints
• Planning data flow and component communication
• Ensuring reliability, monitoring, and scale
Example: Designing a notification system for millions of users
Tips: Start from the basics before scaling the system
Advice: Always explain trade-offs behind your choices
3. Improve Coding Problem Solving And Clarity
Coding rounds test how well you think, structure solutions, and write maintainable code. Clear communication is just as important as the final answer.
Syllabus To Cover
• Graphs, trees, arrays, and dynamic programming
• Problem-solving strategies and patterns
• Clean code structure and readability
• Time and space complexity reasoning
• Choosing the right data structure for each scenario
• Writing efficient and clean code
• Explaining complexity clearly
Example: Choosing BFS over DFS for a shortest path problem
Tips: Think aloud to show your reasoning process
Advice: Solve for correctness first, then optimize
4. Build Strong Debugging And Optimization Skills
Debugging showcases your ability to handle real-world issues that arise in production. Interviewers value calm, structured, and logical problem-solving.
Syllabus To Cover
• Reading logs and tracing failures
• Identifying bottlenecks in high-load systems
• Memory leaks, latency spikes, and timeout issues
• Optimizing code and improving performance
• Fixing hidden bugs in complex code
• Diagnosing failures under high load
• Identifying memory and performance issues
Example: Finding a race condition in a multithreaded module
Tips: Reproduce the issue before exploring solutions
Advice: Break down the failure into smaller checks
5. Prepare Real Leadership And Ownership Examples
Senior developers must show leadership, teamwork, and ownership. Preparing structured examples helps you communicate your experience effectively.
Syllabus To Cover
• Mentoring and guiding junior developers
• Leading high-pressure releases or migrations
• Handling outages and production issues
• Cross-functional collaboration with product and DevOps
• Handling conflicts and communication challenges
• Delivering high-impact features under deadlines
• Guiding juniors with clear mentorship
Example: Leading your team through a critical production outage
Tips: Use real examples from your career
Advice: Highlight measurable results and team impact
Interview Preparation Timeline

Syllabus To Cover
• Core fundamentals, coding, system design, debugging, and leadership skills
Timeline Overview
Week 1–2: Core Fundamentals
Strengthen data structures, algorithms, databases, and concurrency.
Practice explaining concepts with examples from real projects.
Week 3–4: Coding Skills
Work on graphs, trees, arrays, and dynamic programming.
Focus on writing clean, efficient code and communicating your approach clearly.
Week 5–6: System Design Foundations
Learn scalable architectures, caching, queues, and load balancing.
Understand reliability, latency, and design trade-offs.
Week 7–8: System Design Deep Dive
Design end-to-end systems and justify your decisions confidently.
Focus on scalability, storage, APIs, and fault tolerance.
Week 9–10: Debugging and Optimization
Trace failures, identify bottlenecks, and improve performance.
Practice debugging under pressure using real-world scenarios.
Week 11–12: Leadership and Ownership
Prepare stories showing mentoring, leading releases, and managing outages.
Highlight measurable improvements and team impact.
Week 13: Mock Interviews and Final Prep
Do mock sessions, revise weak areas, and polish communication.
Outcome:
Following this plan builds strong technical, problem-solving, and leadership skills, preparing you to successfully land a senior developer role.
To strengthen your coding, system design, and real-world project experience, HCL GUVI’s Full Stack Development Course is an ideal choice. It covers front-end, back-end, databases, and full-stack fundamentals with hands-on projects, mentor guidance, and interview support, which is perfect for preparing for senior developer roles.
💡 Did You Know?
- Interviewers often assess senior candidates more on decision making under pressure than coding speed.
- Many senior-level rejections happen because candidates cannot clearly justify their system design choices.
- Sharing real examples of improving system performance or leading a project is more impactful than memorized definitions.
Conclusion
The technical interview process for senior developers evaluates your ability to design scalable systems, solve problems efficiently, and make confident engineering decisions. Strong fundamentals, clear thinking, and real project experience are valued far more than memorized solutions. Preparing strategically helps you approach interviews with clarity and confidence.
To take your preparation to the next level, practice system design consistently, refine your architecture knowledge, and simulate real interview scenarios. Review your past projects to highlight measurable impact and outcomes, and focus on communicating your decisions effectively to impress interviewers.
FAQs
1. What Is The Most Important Round In A Senior Developer Interview?
The system design round is usually the most critical because it reveals your ability to build scalable, reliable, and high quality systems.
2. How Should Seniors Prepare For Technical Interviews?
Focus on system design, code optimization, debugging, and reviewing real project challenges from your experience.
3. Do Companies Expect Seniors To Code Perfectly?
They expect clean, structured, and efficient code but value clear reasoning more than perfection.
4. How Long Does Senior Level Interview Preparation Take
Most candidates need 6 to 10 weeks to revise design concepts, practice coding, and prepare strong project explanations.




































Did you enjoy this article?