Master Data Structures and Algorithms in C: A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Dec 16, 2025 7 Min Read 1214 Views
(Last Updated)
Every second, computers across the world process trillions of operations, and behind this speed lies the power of Data Structures and Algorithms. In C, these concepts form the core of how data is stored, accessed, and modified to solve real problems efficiently. A strong understanding of arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, and trees helps in writing programs that are structured and precise. Algorithms built upon these foundations allow logical problem-solving that minimizes time and memory use.
Read the full blog to understand how mastering these concepts can elevate your coding approach.
Table of contents
- Why Data Structures and Algorithms in C Are Essential for Programmers?
- Basics of C Programming for Data Structures and Algorithms
- Data Structures in C
- Linear Data Structures
- Non-Linear Data Structures
- Abstract and Derived Data Structures
- Algorithms in C
- Types of Algorithms in C
- Searching Algorithms
- Sorting Algorithms
- Recursion-Based Algorithms
- Divide and Conquer Algorithms
- Greedy Algorithms
- Dynamic Programming Algorithms
- Graph Algorithms
- How to Learn Data Structures and Algorithms in C?
- Strengthen the Basics of C
- Understand Each Data Structure Conceptually
- Focus on Algorithm Logic
- Analyze Time and Space Complexity
- Practice Implementation Regularly
- Study Problems from Competitive Programming
- Build Projects that Combine Concepts
- Importance of Data Structures and Algorithms in C
- Building Efficient Programs
- Improving Problem-Solving Skills
- Supporting System-Level Programming
- Enabling Scalability and Optimization
- Strengthening Career and Competitive Skills
- The Bottom Line
- FAQs
- How do Data Structures and Algorithms in C improve programming efficiency?
- Is C a good language to learn Data Structures and Algorithms?
- What is the best way to practice Data Structures and Algorithms in C?
Why Data Structures and Algorithms in C Are Essential for Programmers?
Programming is more than writing code that runs. It is about creating solutions that handle data efficiently and respond quickly to user needs. Data Structures and Algorithms in C build the discipline to think in steps and manage resources wisely. C provides direct access to memory, which allows a deeper understanding of how data moves through a program.
Learning these concepts strengthens your command over problem-solving and helps you design programs that perform smoothly even under heavy computational tasks. Understanding them through C builds a disciplined programming mindset rooted in clarity and performance.
Basics of C Programming for Data Structures and Algorithms
A clear understanding of C programming builds the base for learning data structures and algorithms (DSA) effectively. C develops logical thinking and helps programmers understand how code interacts with memory and hardware. The language follows structured programming principles, which means each section of a program has a defined purpose and sequence. This makes C an ideal foundation for the DSA roadmap for programmers, helping them design efficient solutions and optimize code performance.
The following elements form the foundation of strong C programming skills:
- Syntax and Structure: Every C program follows a specific structure that includes headers, functions, and statements. The main() function marks the beginning of execution. Curly braces define code blocks, and semicolons end each statement, which keeps the logic clear.
- Data Types and Variables: C offers data types such as int, float, char, and double. Each type controls how much memory is used and what kind of data is stored. Selecting the right type improves precision and efficiency.
- Operators: Operators handle actions like arithmetic, logical comparison, and value manipulation. Arithmetic operators perform calculations. Relational and logical operators guide the program based on conditions.
- Control Statements: Control statements manage how a program flows. Conditional statements like if, else, and switch direct execution. Looping structures such as for, while, and do-while handle repeated tasks until conditions are met.
- Functions: Functions break a program into smaller parts. Each function performs a defined task, which improves organization and makes debugging easier. Parameters move data between functions to maintain clear communication in the program.
- Arrays and Pointers: Arrays store multiple elements of the same data type, which helps in managing related information. Pointers store memory addresses, which gives precise control over how data is accessed and modified. They are the foundation for advanced structures like linked lists and tree data structures, which organize data hierarchically for efficient searching, insertion, and traversal.
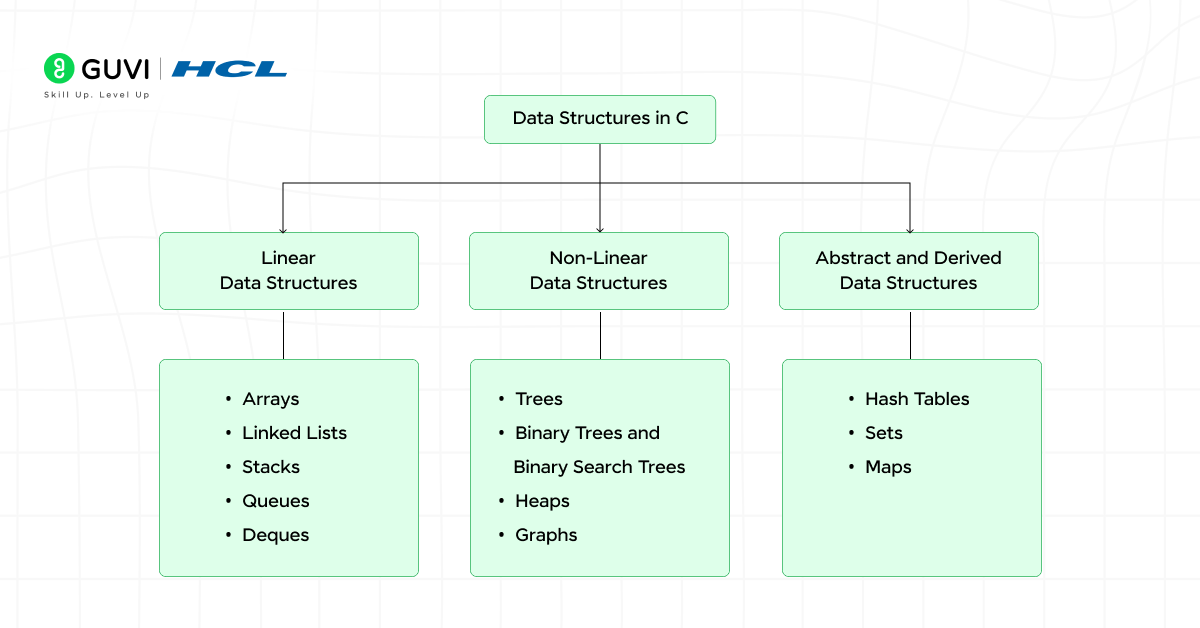
Data Structures in C
Data structures in C organize information so programs can process and manage data effectively. Each structure follows a unique pattern that supports specific operations such as searching, inserting, or deleting.
1. Linear Data Structures
Linear data structures arrange elements in a straight sequence where each element connects to its next. They are ideal for problems that require ordered data traversal or predictable processing patterns.
- Arrays: Arrays are fixed-size collections of elements stored in continuous memory locations. They allow constant-time access through index positions, which helps in searching and updating values quickly. Arrays are often used in applications that involve numerical computations, data storage tables, or fixed datasets. They also serve as the foundation for implementing more advanced structures such as matrices and strings in C. However, their static size can be a limitation when the number of elements changes during execution.
- Linked Lists: Linked lists are collections of nodes where each node contains data and a pointer to the next node. They offer flexibility because memory is allocated during runtime. Linked lists eliminate the need for shifting elements during insertion or deletion. Variants such as singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists serve different needs based on direction and accessibility. They are used in memory management systems and cases where the dataset grows or shrinks frequently.
- Stacks: Stacks follow the Last In First Out principle. The element inserted last is removed first. Stacks are used in managing function calls, parsing expressions, and controlling execution flow in recursive algorithms. They operate using two main actions: push to insert and pop to remove. Stack-based memory management in C makes recursion and backtracking easier to implement.
- Queues: Queues follow the First In First Out principle. The element inserted first is removed first. They are vital in scenarios such as process scheduling, buffering in communication systems, and managing asynchronous data flows. Variants like circular queues and priority queues extend their functionality to handle resource distribution and prioritized execution.
- Deques: Deques, or double-ended queues allow data insertion and deletion from both the front and rear. They combine the strengths of stacks and queues. Deques are useful in algorithms that need data flexibility, such as sliding window problems and caching systems.
2. Non-Linear Data Structures
Non-linear data structures represent data through hierarchical or network-based relationships. They are used in situations where one element connects to multiple others, forming complex link patterns.
- Trees: Trees store data in a parent-child format. Each node contains a value and links to its child nodes. Trees are efficient for hierarchical data representation, such as organizational charts or file directories. Operations like searching, insertion, and deletion can be optimized depending on the tree type.
- Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees:
Binary trees limit each node to two child nodes, known as the left and right children. Binary search trees maintain sorted order, which allows faster searching and insertion. Balanced forms such as AVL trees and Red-Black trees maintain structural efficiency, which keeps search operations stable even with large data. - Heaps: Heaps are specialized binary trees where each parent node follows a priority rule. A max-heap places the largest value at the root, and a min-heap keeps the smallest at the root. They are widely used in priority queues and sorting algorithms like Heap Sort. Heaps also form the basis of efficient memory allocation and job scheduling in operating systems.
- Graphs: Graphs consist of vertices and edges that define relationships between data elements. They can be directed or undirected depending on the flow of connections. Graphs represent real-world networks such as transportation systems, communication routes, and social connections. Algorithms like Breadth First Search and Depth First Search work effectively with graphs for traversal and pathfinding.
3. Abstract and Derived Data Structures
Abstract and derived data structures build upon basic structures. They focus on logical operations and data relationships rather than physical storage.
- Hash Tables: Hash tables store data in key-value pairs. A hash function converts keys into indices for fast retrieval. Collisions occur when multiple keys produce the same index, and techniques like chaining or open addressing resolve them. Hash tables are widely used in compilers and dictionary implementations because they offer near-constant time access for lookups.
- Sets: Sets maintain collections of unique elements. They automatically prevent duplicates, which makes them useful for operations that require distinct values. Sets are used in data filtering and membership testing. They are also extensively used in mathematical computations like union or intersection.
- Maps: Maps associate keys with specific values. Each key must be unique, and values can be accessed directly through their keys. Maps improve clarity in data organization by replacing numeric indices with descriptive identifiers. They are valuable in applications such as configuration management and structured storage systems.
Algorithms in C
Algorithms in C are step-by-step procedures designed to solve specific problems through a clear and logical sequence of operations. They define how data structures are used and how input is processed. They further define how output is generated. Every efficient program relies on well-structured algorithms that minimize time and memory use while leveling up accuracy. A strong understanding of algorithms helps in creating solutions that perform efficiently across different problem types.
Types of Algorithms in C

1. Searching Algorithms
Searching algorithms are used to locate a specific element within a dataset.
Key Features:
- Work with both sorted and unsorted data.
- Linear Search scans each element sequentially.
- Binary Search divides the dataset repeatedly to reduce search time.
- Operate on arrays, linked lists, and other data structures.
Top Applications:
- Database and record lookups.
- Text searching and keyword identification.
- Validation of user input in software.
- Symbol table management in compilers.
2. Sorting Algorithms
Sorting algorithms organize data in a particular order, usually ascending or descending, which improves readability and processing efficiency.
Key Features:
- Arrange data to simplify searching and comparison.
- Use methods such as Bubble Sort, Selection Sort, Insertion Sort, Merge Sort, and Quick Sort.
- Differ in time complexity based on dataset size and initial order.
- Form the foundation for data visualization and structured processing.
Top Applications:
- Statistical analysis and data visualization.
- Arranging records in databases.
- Optimizing search algorithms.
- Processing tasks in scheduling and load balancing.
3. Recursion-Based Algorithms
Recursion-based algorithms use self-calling functions to solve problems by breaking them into smaller, similar subproblems.
Key Features:
- Use base and recursive cases for termination and repetition.
- Simplify problems that involve repetitive or hierarchical patterns.
- Commonly applied to mathematical computations and structural traversal.
- Require memory management awareness to prevent stack overflow.
Top Applications:
- Computing factorials and Fibonacci sequences.
- Traversing trees and graphs.
- Backtracking in puzzles such as Sudoku or the N-Queens problem.
- File system exploration in hierarchical storage.
4. Divide and Conquer Algorithms
Divide and conquer algorithms split a complex problem into smaller subproblems, solve each one separately, and combine the results.
Key Features:
- Divide, solve, and merge approach.
- Improves efficiency on large datasets.
- Reduces overall complexity through recursive problem solving.
- Commonly used for sorting, searching, and numerical computations.
Top Applications:
- Merge Sort and Quick Sort for efficient data ordering.
- Binary Search for optimized lookup operations.
- Matrix multiplication in scientific computing.
- Image compression and signal processing.
5. Greedy Algorithms
Greedy algorithms make the most optimal choice at each step to reach the final solution.
Key Features:
- Work through locally optimal decisions that lead to a global solution.
- Easy to implement and efficient in well-defined optimization problems.
- Do not always guarantee the absolute best result, but performs well in practical use cases.
- Focus on minimizing cost or maximizing gain in each step.
Top Applications:
- Finding the shortest path using Dijkstra’s algorithm.
- Building minimum spanning trees using Kruskal’s or Prim’s algorithm.
- Resource allocation and scheduling tasks.
- Data compression with Huffman coding.
6. Dynamic Programming Algorithms
Dynamic programming algorithms solve problems by storing intermediate results and reusing them to avoid repeated calculations.
Key Features:
- Break problems into overlapping subproblems.
- Store solutions in tables or arrays for reuse.
- Reduce time complexity compared to recursion.
- Useful for optimization problems and sequential decision-making.
Top Applications:
- Shortest path algorithms, such as Floyd-Warshall.
- Knapsack problem and resource allocation tasks.
- Sequence alignment in bioinformatics.
- Predictive modeling and decision-making algorithms.
7. Graph Algorithms
Graph algorithms process and analyze data represented in the form of nodes and edges. They help understand relationships, connections, and network structures.
Key Features:
- Represent relationships between entities in a network.
- Use traversal techniques such as Depth First Search and Breadth First Search.
- Include shortest path and minimum spanning tree algorithms.
- Handle both directed and undirected graphs.
Top Applications:
- Network routing and traffic optimization.
- Social media connection analysis.
- Circuit design and dependency resolution.
- Web page ranking and link analysis.
Take your programming skills beyond logic and loops! Join our AI Software Development Course to bridge your understanding of Data Structures and Algorithms with the intelligence of real-world AI systems. This course helps you learn how efficient data handling, algorithmic thinking, and automation power modern AI applications, all under expert mentorship and guided learning paths.
How to Learn Data Structures and Algorithms in C?
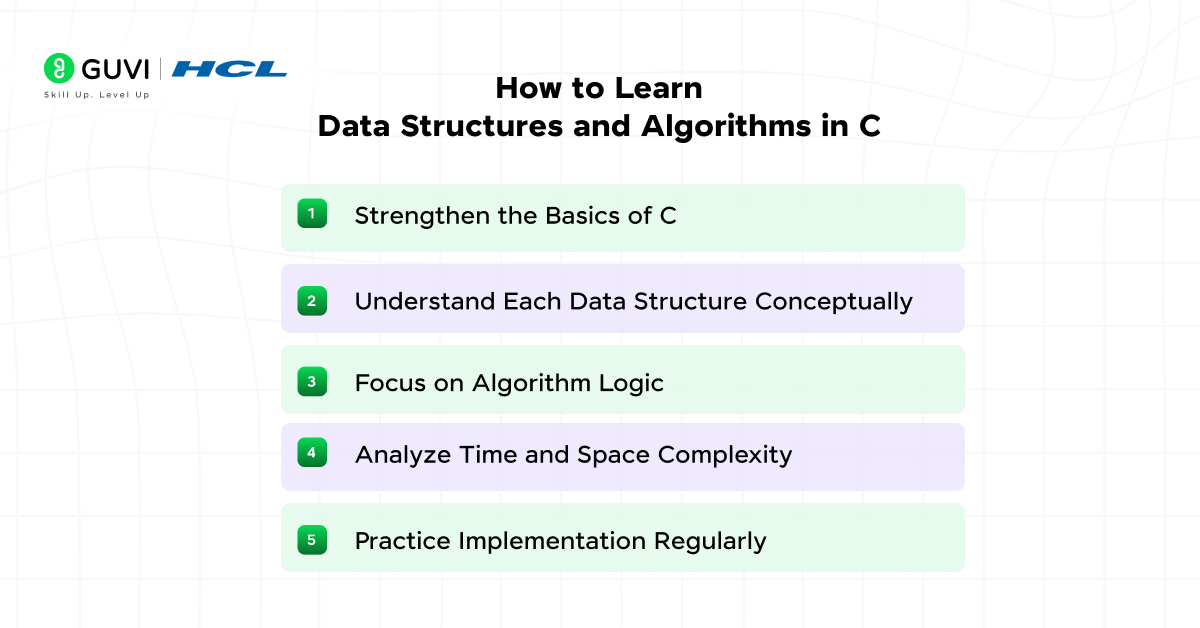
1. Strengthen the Basics of C
A clear understanding of C fundamentals is the first step. Learn about data types, operators, control statements, loops, and functions. Practice writing small programs that use arrays, pointers, and memory allocation. These concepts form the base on which data structures are built. Strong command over syntax and logical flow makes it easier to move into more complex topics.
2. Understand Each Data Structure Conceptually
Study one data structure at a time. Learn how it stores data, how elements are inserted or deleted, and how memory is managed. Start with arrays and linked lists, then move to stacks, queues, trees, and graphs. Try implementing each structure manually in C rather than relying on predefined libraries. This helps in understanding internal working and pointer manipulation.
3. Focus on Algorithm Logic
Algorithms define how data is processed. Learn to write algorithms before coding them. Understand how they handle input, decision-making, and output generation. Start with basic searching and sorting algorithms, then move toward recursive, greedy, and dynamic programming approaches. This forms a solid DSA roadmap that helps you progress from foundational algorithmic thinking to advanced problem-solving techniques through structured learning and analysis.
4. Analyze Time and Space Complexity
Study the Big O notation to evaluate performance. Learn how to measure how fast an algorithm runs and how much memory it uses. Comparing complexities such as O(n), O(log n), and O(n²) builds awareness of efficiency. This analysis helps in choosing the right method for a specific problem.
5. Practice Implementation Regularly
Consistent coding practice reinforces understanding. Write C programs that apply each data structure and algorithm to real-world scenarios. Examples include implementing a queue for task scheduling or using a tree for searching operations. Practicing through projects and exercises improves logical consistency and debugging skills.
6. Study Problems from Competitive Programming
Competitive programming platforms help apply theoretical knowledge in time-bound environments. Solving problems based on sorting, recursion, and graph traversal builds confidence and enhances speed. This practical experience sharpens problem-solving skills and encourages creative approaches to algorithm design.
7. Build Projects that Combine Concepts
Integrating multiple data structures and algorithms in a single project develops practical knowledge. Create systems such as a file directory manager, pathfinding simulator, or mini-database. Projects like these help connect theory with real application and showcase problem-solving ability through structured design.
Importance of Data Structures and Algorithms in C
1. Building Efficient Programs
Data structures and algorithms allow programs to process information with minimal time and space. Choosing the right structure, such as arrays for fixed-size data or linked lists for flexible storage, helps in managing data efficiently. Well-designed algorithms further improve performance by reducing unnecessary computations.
2. Improving Problem-Solving Skills
Understanding data structures and algorithms helps programmers think logically. Each structure and algorithm teaches a unique way of approaching a problem. Arrays teach sequential organization, trees encourage hierarchical thinking, and graphs develop relationship-based problem-solving skills.
3. Supporting System-Level Programming
C is widely used in system-level programming such as operating systems, embedded software, and compilers. Efficient use of data structures ensures proper memory handling and predictable performance. Algorithms manage tasks like scheduling and process control. This balance between structure and logic is vital for systems that need stability and accuracy.
4. Enabling Scalability and Optimization
Well-structured programs scale better as data grows. A properly chosen algorithm can handle large datasets without loss of performance. Sorting and indexing methods help applications manage expanding information efficiently. Optimization through algorithm design guarantees that programs remain responsive even under heavy computational loads.
5. Strengthening Career and Competitive Skills
Data structures and algorithms are key areas tested in technical interviews and programming competitions. Mastering them improves both coding and reasoning ability. They prepare programmers for real-world problem-solving where performance and accuracy matter equally.
Master the logic that powers every efficient program! Enroll in our Data Structures and Algorithms using Java Course to strengthen your coding foundation, understand core algorithmic principles, and build confidence for technical interviews. Designed by industry experts, this course helps you think like a problem solver while coding like a pro.
The Bottom Line
Mastering Data Structures and Algorithms in C constructs the foundation for writing structured and logical programs. It sharpens analytical thinking and strengthens coding discipline. Decoding how data structures manage storage and how algorithms process information helps in creating solutions that perform with speed and precision. Consistent practice and real-world implementation make C a powerful language for mastering computational thinking and professional programming growth.
FAQs
1. How do Data Structures and Algorithms in C improve programming efficiency?
Data Structures and Algorithms in C improve efficiency by organizing data and optimizing processing speed. They reduce memory waste and execution time, which helps programs run faster and more reliably.
2. Is C a good language to learn Data Structures and Algorithms?
Yes, C is one of the best languages to learn Data Structures and Algorithms because it provides direct control over memory and low-level data management. It helps learners understand how data moves and is stored in memory, which builds a stronger foundation for mastering complex algorithmic logic.
3. What is the best way to practice Data Structures and Algorithms in C?
Start by learning the basics of C programming and then implement core structures like arrays, stacks, and linked lists manually. Gradually work on sorting, searching, and recursive algorithms.
























Did you enjoy this article?