
25 Interesting DSA Terms/Concepts Every Programmer Should Know
Nov 26, 2025 5 Min Read 1238 Views
(Last Updated)
There is one thing that every great programmer has in common: a deep understanding of DSA concepts. Data Structures and Algorithms are the secret behind every efficient program, from the search engine at Google to the recommendation system at Netflix. Whether you’re a beginner coder or preparing for interviews at the best tech companies, knowing the right terms from DSA will be important.
In this blog, we’ll break down and explain 25 relevant examples of DSA terms or concepts that every programmer should learn more about. Each concept is explained simply with some real-world context, so you can grow your problem-solving skills and write smarter, faster, general code.
Table of contents
- 25 DSA Terms and Concepts
- Array
- Linked List
- Stack
- Queue
- Hashing
- Tree
- Binary Search Tree (BST):
- Graph:
- Heap:
- Recursion:
- Dynamic Programming (DP)
- Divide and Conquer
- Sorting Algorithms
- Searching Algorithms
- HashMap / Hash Table
- Graph Traversal
- Greedy Algorithms
- Backtracking
- Bit Manipulation
- Time and Space Complexity
- Trie (Prefix Tree)
- Segment Tree
- Union-Find / Disjoint Set
- Queue Using Two Stacks
- Sliding Window Technique
- Wrapping it up:
- FAQs
- What are the most important DSA concepts for beginners?
- Are DSA concepts important beyond interviews?
- What is the best way to master DSA fast?
- What is the best resource to learn DSA?
- Which language is the best for learning DSA?
25 DSA Terms and Concepts
1. Array
The term Array is one of the most fundamental DSA concepts (Data Structure and Algorithms). An Array is basically a collection of elements (numbers, strings, or objects) that are stored in continuous memory locations. An Array allows for the access of elements in constant time (O (1) access) using an index.
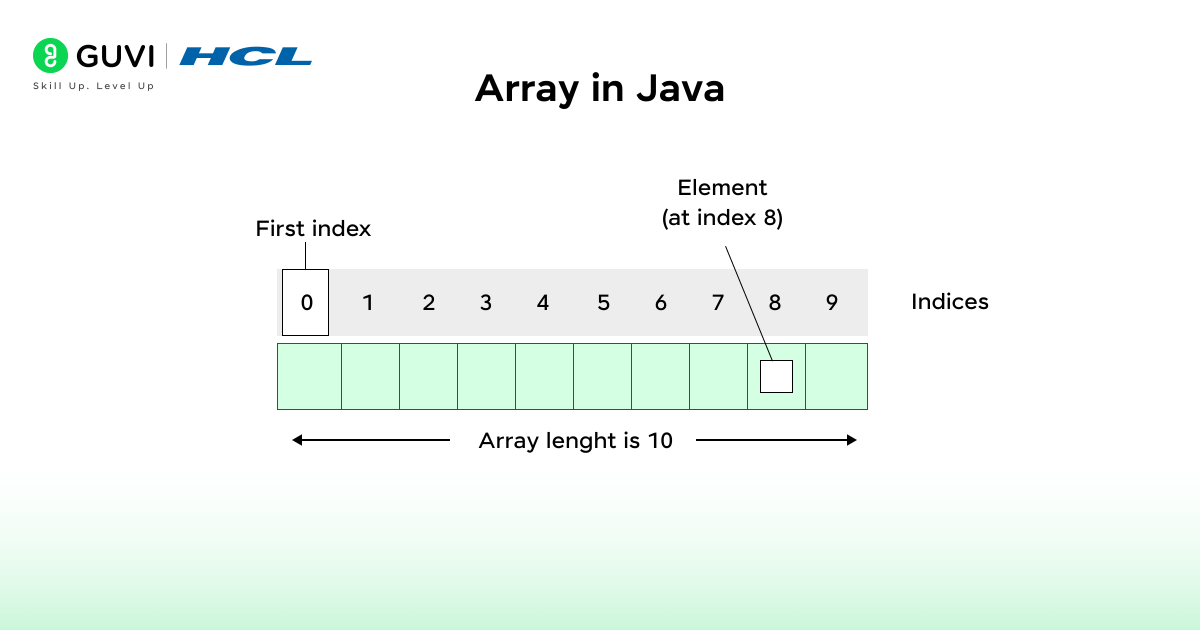
When it comes to inserting or deleting an element from an array, you have shift the other elements around to maintain the order of elements, which can be inefficient.
For example:
| int marks[] = {90, 85, 78, 92, 88}; |
Arrays are used to store lists of items like marks, prices, or sensor data.
2. Linked List
A Linked List is a linear data structure where each element is called a node, and contains the data and a pointer to the next node. Linked List nodes are not stored in contiguous memory like an array, allowing for dynamic memory allocation of the linked list.
elements in constant time (O (1) access) using an index.
Advantages:
- Easier insertion and deletion (no need to shift elements).
- More efficient for structures that are growing and shrinking.
Disadvantages:
- Slower access time (O(n)) as the data must be traversed.
Use case: Undo features, playlist management (MP3 player), and dynamic memory in operating systems.
3. Stack
A stack is a linear data structure that uses the LIFO (Last In, First Out) method. Think of stacking plates: the last plate you put down will be the first one you remove.
- Operations:
- Push: add an element.
- Pop: remove the top element.
- Peek: see the top element without removing it.
- Applications:
- Managing function calls (recursion).
- Evaluating expressions (converting infix to postfix).
- Backtracking when browsing the internet.
Example:
| stack = [] stack.append(10) stack.pop() |
Also Explore: 5 Best Reasons to Learn Data Structures and Algorithms [DSA]
4. Queue
A Queue operates according to the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle. The first element added to a Queue is the first one removed.
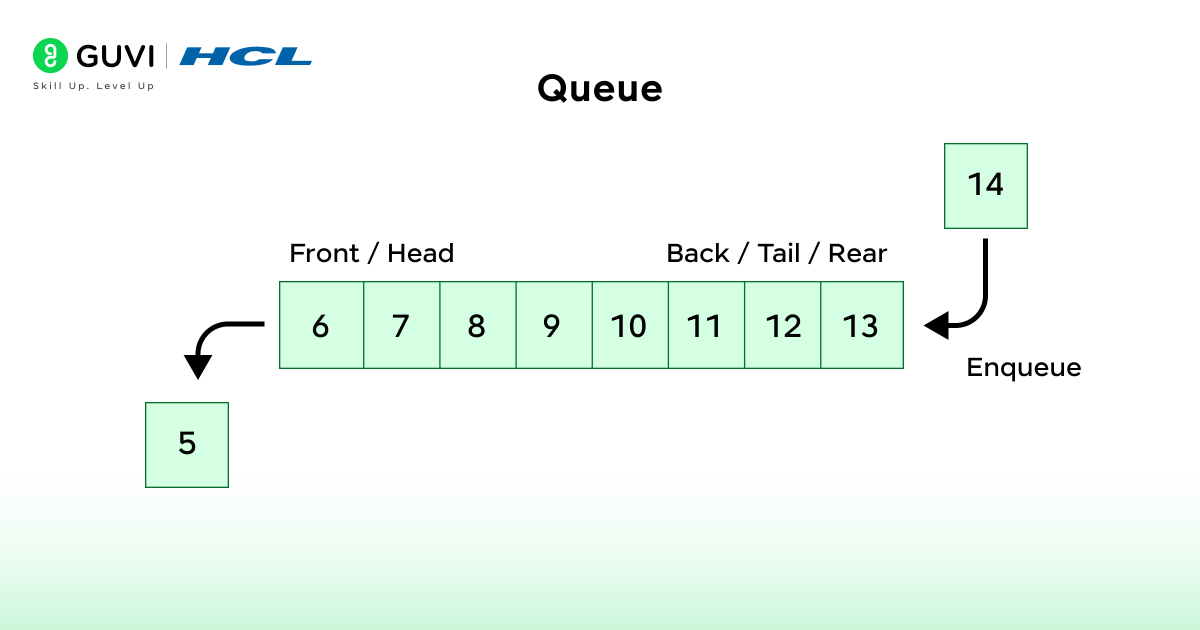
- Operations:
- Enqueue: Add an element to the end of queue
- Dequeue: Remove from the front.
- Applications:
- CPU task scheduling.
- Customer service systems.
- Handling print jobs.
- Types:
- Circular Queue
- Priority Queue
- Double-ended Queue (Deque)
5. Hashing
Hashing is one of the most efficient DSA concepts used to store and return data in constant time. The hash function takes the input (the key) and converts it to a numeric index (hash value), which is the location where the data will be stored.
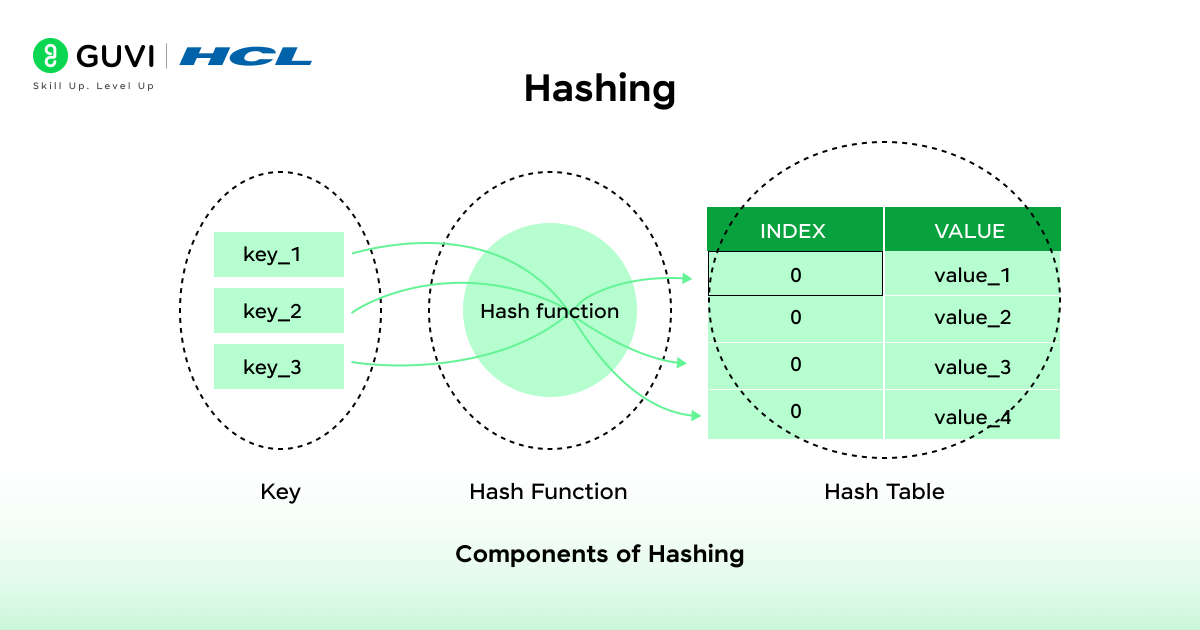
Example:
A good example of how commonly hashing is used as part of DSA is in Python, which internally uses hashing to store key-value pairs in dictionaries.
| student = {“name”: “Amit”, “age”: 22} |
Applications:
- Password encryption.
- Database indexing.
- Caching mechanisms such as Redis or Memcached.
6. Tree
A Tree is a hierarchical data structure representing nodes connected by edges. The node at the very top is called the root node, and a node that has no children is called a leaf node.
Why trees? They allow for efficient searching and sorting, and representation of hierarchical data.
- Applications:
- Structure of the HTML DOM.
- Organization of files in operating systems.
- Indexing in Databases (B-trees, B+ trees).
Also Read: Is DSA Important for Placement in 2025?
7. Binary Search Tree (BST):
A BST is a type of tree where each node has its left child with smaller values and its right child with larger values.
- Advantages:
- Searches are quicker (O(log n)), as these are faster than using a linear search.
- Insertion and deletion are simple.
- Applications:
- To search databases.
- Autosuggest and dictionary-like systems.
- Organizing data in sorted order.
8. Graph:
A Graph outlines a set of vertices (nodes) connected by edges. The Graph is one of the most versatile terms in DSA, as it can be used to model relationships of data.
- Types:
- Directed Graph has edges that are directed (like a one-way road). An Undirected Graph does not have direction (has roles, like friendships).
- Weighted Graph, where the edges have weights associated with them (like the distance between 2 cities).
- Applications:
- Social networks (friends/followers).
- GPS and path finding.
- Recommendation systems.
9. Heap:
A Heap is a special binary tree that follows the heap property:
- MaxHeap, where the parent node is greater than or equal to the children.
- MinHeap, where a parent node is smaller than or equal to its children.

Use cases:
- Priority queues.
- Finding the k smallest/largest elements in an array.
- Memory management systems.
10. Recursion:
Recursion is the process in which a function calls itself to arrive at a smaller version of the same problem.
Recursion occurs when a function calls itself to solve a smaller instance of the same problem.
Every recursive function has:
- Base case: When to stop recursion.
- Recursive case: The smaller subproblem.
Example:
| def factorial(n): if n == 0: return 1 return n * factorial(n-1) |
Also Read: Best DSA Roadmap Beginners Should Know 2025
Applications:
- Tree traversal
- Divide and conquer algorithms.
- Solving puzzles like the Tower of Hanoi.
11. Dynamic Programming (DP)
Dynamic Programming enhances recursive algorithms by caching the results of previously solved subproblems (memoization or tabulation). This tree-shaking property avoids the computation of the same results numerous times, leading to better overall performance.
- Example: Fibonacci numbers, rather than solving fib(3) multiple times, we use DP to save it once.
- Applications:
- Shortest-path algorithms.
- Resource allocation problems.
- Optimization for machine learning models.
12. Divide and Conquer
Divide and Conquer technique that separates a large problem into smaller subproblems, solves the subproblems independently, and then merges the solutions. Examples of divide and conquer algorithms include:

- Merge Sort (divide an array – sort – and merge)
- Quick Sort (divide, sort, then merge sublists).
Advantages:
- Simplifying complex problems.
- Enhanced performance when applied to large datasets
13. Sorting Algorithms
Sorting is a key DSA concept that takes a “no order” dataset (an unsorted dated table) and organizes the elements in either ascending or descending order. Sorting algorithms would include:
- Bubble Sort: Simple, but slow.
- Merge Sort: Stable, efficient.
- Quick Sort: Fast average case.
- Heap Sort: Utilizes the heap property.
Applications:
- Optimizing database queries.
- Data visualization and analytics.
- Ranking and filtering systems.
Also, Explore About 10 Best Data Structures and Algorithms Courses [2025]
14. Searching Algorithms
Searching algorithms denote the operation to find and return an element in a dataset. Common examples of searching algorithms include:
- Linear Search: Checking every element – O(n).
- Binary Search: Divide and conquer – O(log n).
Applications:
- Search engines.
- Online shopping filtering.
- Autocomplete features.
15. HashMap / Hash Table
A HashMap or Hash Table is a hashing implementation that stores key-value pairs.
- Benefits:
- Constant time insertion and lookup.
- Efficient memory usage.
- Applications:
- Caching.
- Database indexing.
- Language compilers (for symbol tables).
16. Graph Traversal
Graph traversal is visiting all the nodes in a systemized way.
There are two main algorithms:
- BFS (Breadth-First Search): This visits each neighbor of a current node before going to the next level.
- DFS (Depth-First Search): This goes to the deepest node before “backing up” and finds the others.
Applications:
- Web crawlers.
- Finding a path in a game.
- Routing network packets.
17. Greedy Algorithms
Greedy algorithms make the optimal choice at each step, aiming for a global optimum.
Example:
- Coin change problem.
- Kruskal’s and Prim’s algorithms for the minimum spanning tree.
Pros: Simple and fast.
Cons: Doesn’t always guarantee the best solution.
Applications:
- Data compression (Huffman coding).
- Scheduling and resource allocation.
Download HCL GUVI’s free Data Structures & Algorithms eBook and start mastering problem-solving skills that every top developer needs!
18. Backtracking
Backtracking is a problem-solving method that tries all possibilities and “backs up” when it hits a wall.
Example:
- Solving a Sudoku. After filling in the numbers and the move did not work (the player has to backtrack).
Applications:
- Pathfinding (maze solving).
- Combinatorial problems (N-Queens).
- Game AI logic.
19. Bit Manipulation
Bit manipulation involves directly operating on binary representations of numbers.
Common operations:
- AND (&)
- OR (|)
- XOR (^)
- Left and Right Shift
Applications:
- Cryptography
- Data compression
- Competitive programming problems.
20. Time and Space Complexity
All algorithms come at a cost: Time Complexity (How fast) and Space Complexity (How much memory).
Notation: Big-O (O(n), O(log n), O(n²))
Examples:
- Binary Search → O(log n)
- Bubble Sort → O(n²)
These concepts help you determine which algorithm is best for solving the problem at hand.
21. Trie (Prefix Tree)
A Trie is a tree-like structure used to represent strings.
- Example: Autocomplete applications try to guess words for the user as they type.
- Advantages:
- Fast to search for prefixes.
- More space-efficient structure than a list of words.
- Applications:
- Spell-checking.
- IP routing.
- Boggle / Scrabble or similar games.
22. Segment Tree
A Segment Tree breaks an array up into segments so that range queries can be calculated more efficiently (sum or min of a subarray).
- Time complexity: O(log n) to update the tree and O(log n) to query data in the tree.
- Applications:
- Stock price analysis.
- Competitive programming.
- Range minimum/maximum problems.
23. Union-Find / Disjoint Set
This data structure and algorithm concept allows for keeping track of elements that have been divided into distinct sets without overlap.
- Operations:
- Find: Which set does an element belong to?
- Union: Combine two sets.
- Applications:
- Kruskal’s algorithm.
- Check if two nodes are connected in a network.
- Determine if a graph contains a cycle.
24. Queue Using Two Stacks
This is a nifty implementation technique that utilizes the functionality of each structure.
An implementation path would be:
- One stack for the enqueue operations.
- One stack for the dequeue operations (which will reverse the order).
Purpose:
- Understand how different structures can be interchanged.
- Experience an interview-level DSA algorithmic problem to facilitate logical reasoning.
25. Sliding Window Technique
A Sliding Window is a technique that places a subset (window) over some data to move forward, looking for results quickly without having to do the full computation every time.
- Example:
- Find the maximum sum of k consecutive integers in an array.
- Applications:
- String pattern matching.
- Data streams.
- Real-time analytics.
If you’re serious about mastering these 25 essential DSA concepts, start practicing today! Also enroll in HCL GUVI’s AI & Software Development, co-created with IIT-M Pravartak, and learn through real-world coding challenges, expert mentorship, and hands-on projects.
Wrapping it up:
Learning these 25 fascinating DSA (Data Structures and Algorithms) terms and concepts provides you with the capability to write efficient, optimized, and scalable code. Each of these concepts will build your logical thinking and allow you to solve programming problems in real life.
Whether you are preparing for an interview, building pet projects, or just improving your problem-solving mindset, you will be a confident and capable developer by understanding these DSA (Data Structures and Algorithms) concepts.
I hope this blog helps you learn the most important DSA terms that every programmer should know about. Keep coding, keep practicing, and remember that great programmers do not remember algorithms; they understand how to build them!!
FAQs
1. What are the most important DSA concepts for beginners?
Begin with arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, and trees before discussing recursion and dynamic programming.
2. Are DSA concepts important beyond interviews?
Yes, they are key in writing scalable software that can optimize real-world applications.
3. What is the best way to master DSA fast?
Try to practice daily, learn patterns (like two-pointer and sliding window), and also try to solve various problems.
4. What is the best resource to learn DSA?
Free platforms like GUVI or LeetCode have great beginner-to-advanced content.
5. Which language is the best for learning DSA?
C++ and Java are considered the most popular because they both offer the best efficiency. Python will also work well for understanding logic.
























Did you enjoy this article?