How to Choose Right Machine Learning Algorithm?
Nov 19, 2025 4 Min Read 1079 Views
(Last Updated)
All successful machine learning projects start with the same decision, surely the most important, which is to choose the right machine learning algorithm. There are dozens of models, ranging from traditional approaches like regression to contemporary ones like deep neural networks, and it becomes easy to feel overwhelmed. Each algorithm behaves differently, learns differently, and performs differently according to the data and problem you are working with.
Choosing a machine learning algorithm is not completely a technical process; it’s also a strategic one. You need to have an understanding of your data, the type of task you want to complete, and what type of predictions or insights you want to generate. The choice of algorithm could be the factor that makes or breaks your model’s success, whether you are building a recommendation engine, fraud detection system, or predicting customer churn.
As industries become more reliant on data-driven decision-making, being able to select a machine learning algorithm is one of the most in-demand skills for data science and AI professionals. This blog will walk you through the major steps, factors, and best practices, using this decision to build your confidence.
Table of contents
- Understanding the Goal: What Problem Are You Solving?
- a. Supervised Learning
- b. Unsupervised Learning
- c. Reinforcement Learning
- Know Your Data: The Foundation of Every Model
- a. Size of the Dataset
- b. Data Type
- c. Data Quality
- Consider Algorithm Complexity and Interpretability
- a. If you care about interpretability:
- b. If you care more about accuracy and performance:
- Evaluate Computational Efficiency
- a. Lightweight and Fast Algorithms
- b. Computationally Heavy Algorithms
- Check Algorithm Assumptions
- Use Model Evaluation Metrics
- Start Simple, Then Iterate
- Use Automated Tools and Frameworks
- Why Choosing the Right Machine Learning Algorithm Matters
- Final thoughts…
- FAQs
- What factors should I consider when selecting a machine learning algorithm?
- How do I know if I have selected the most suitable algorithm?
- What algorithms are best for those who are just getting started with machine learning?
- What algorithms are best for smaller datasets?
- Can I combine multiple algorithms together?
1. Understanding the Goal: What Problem Are You Solving?
Before going to the algorithms, make sure you have defined what problem you are trying to address. Most machine learning problems can be categorized into one of the following three categories:
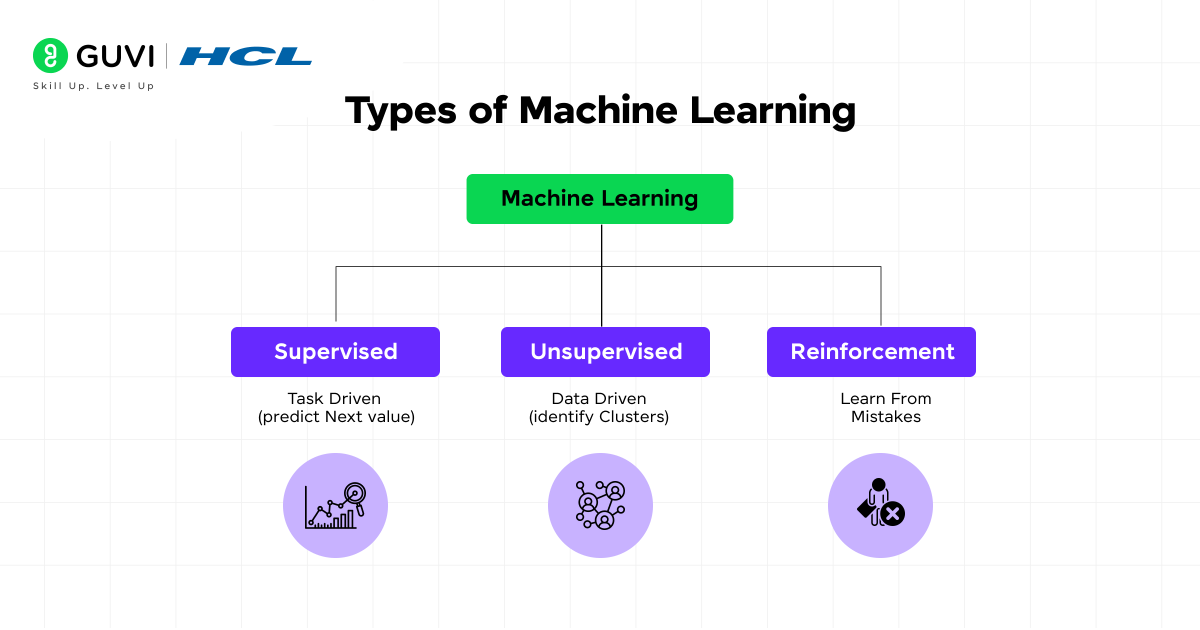
a. Supervised Learning
- Goal: Make predictions of a known outcome (or target variable) based on some input data.
- Examples: Predicting pricing for a house, spam detection, and credit scoring.
- Algorithms: Linear Regression, Decision Trees, Random Forest, Support Vector Machines, Gradient Boosting Machine, Neural Networks.
b. Unsupervised Learning
- Goal: Identify patterns or groupings in a data set that do not have known labels.
- Examples: Customer segmentation, anomaly detection, topic modeling.
- Algorithms: K-Mean Clustering, Hierarchical Clustering, DBSCAN, PCA (Principal Component Analysis).
c. Reinforcement Learning
- Goal: Train a model to make a sequence of decisions based on rewards and penalties.
- Examples: game-playing AI, robot movement control, dynamic pricing.
- Algorithms: Q-Learning, Deep Q-Networks (DQN), SARSA.
Once you determine if your problem is supervised, unsupervised, or reinforcement, you can narrow down your choices of algorithms.
2. Know Your Data: The Foundation of Every Model
The quality, quantity, and type of data play a huge role in choosing a machine learning algorithm. Here’s what to consider:
a. Size of the Dataset
- Small datasets: Use simpler models like Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes, or Decision Trees.
- Large datasets: Consider complex algorithms like Random Forests, Gradient Boosting, or Deep Learning models that can handle high-dimensional data.
b. Data Type
- Numerical data: Regression algorithms or neural networks.
- Categorical data: Decision Trees, Naive Bayes, or Random Forests.
- Text or language data: Natural Language Processing (NLP) models like LSTMs or Transformers.
- Images or visual data: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs).
c. Data Quality
- If your dataset has missing values, noise, or imbalances:
- Use Robust algorithms like Random Forest or XGBoost that can handle imperfections.
- Apply data preprocessing techniques like normalization, encoding, and outlier removal before training.
Download our Free eBook “Generative AI eBook” to explore practical frameworks, algorithm comparison charts, and real-world use cases.
3. Consider Algorithm Complexity and Interpretability
Not every assignment calls for the use of a deep neural network; in fact, simpler models can outperform complex models when the dataset is small and/or when having interpretable results is of importance.
a. If you care about interpretability:
Choose models that are easy to interpret and explain:
- Linear Regression
- Logistic Regression
- Decision Trees
These models are often favored in industries such as finance or healthcare, where decisions must be clear and viable.
b. If you care more about accuracy and performance:
- If you can accept less interpretability in exchange for increased performance:
- Use ensemble models, for example, Random Forest, or Gradient Boosting.
- If you are dealing with extremely large and/or complex data, I would consider Neural Networks, they’ll outperform the other models in most situations.
The “happy place” is finding the right balance between interpretable models and complex machine learning algorithms when choosing the right model.
- The term “Machine Learning” was coined way back in 1959 by Arthur Samuel!
- Naive Bayes, one of the oldest algorithms, dates back to the 1700scenturies before modern computers.
- A simple Logistic Regression model can sometimes outperform deep neural networks on clean, structured data.
- Random Forest got its name because it’s literally a “forest” of random decision trees!
4. Evaluate Computational Efficiency
Some algorithms demand massive computational resources, while others are lightweight and fast.
a. Lightweight and Fast Algorithms
- Logistic Regression
- Naive Bayes
- K-Nearest Neighbours (KNN) for small datasets
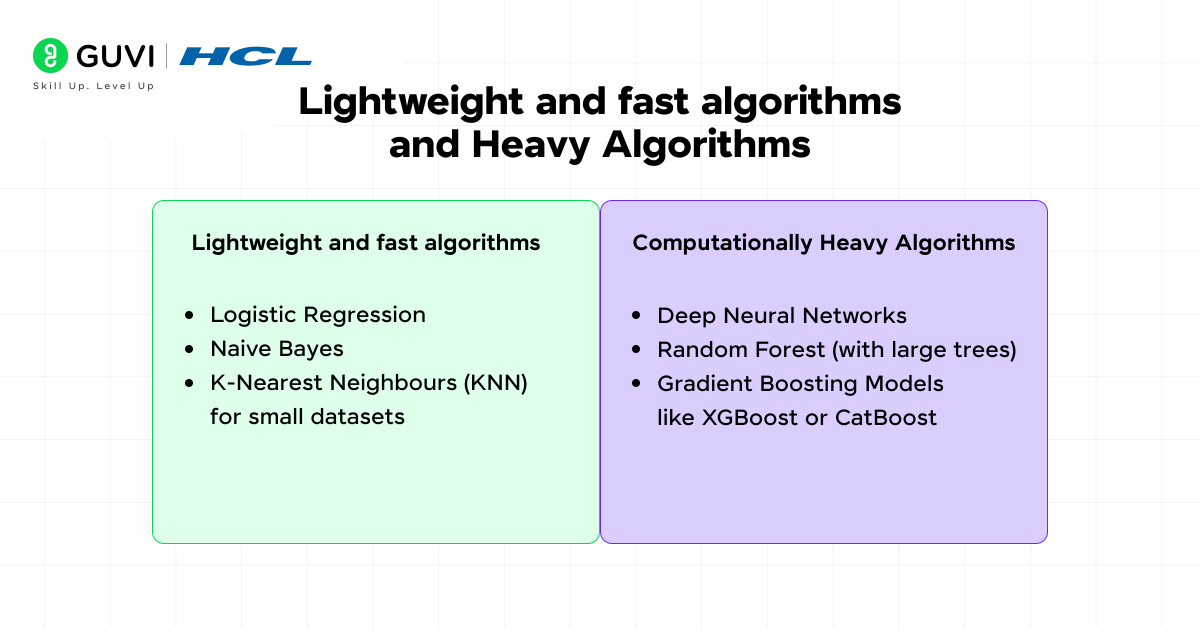
b. Computationally Heavy Algorithms
- Deep Neural Networks
- Random Forest (with large trees)
- Gradient Boosting Models like XGBoost or CatBoost
When working with limited hardware or real-time systems, go for simpler models. For cloud-based or large-scale data projects, complex models are worth the investment.
Are you interested in knowing the actual process that data scientists go through when picking algorithms, in the real world? Then don’t just rely on theory; instead, experience it with HCL GUVI’s Free 5-Day AI & ML Email Course. Learn step-by-step through hands-on projects, expert insights, and real datasets.
5. Check Algorithm Assumptions
Every machine learning algorithm makes underlying assumptions about data distribution and relationships. Ignoring them can lead to poor performance.
| Algorithm | Key Assumption |
| Linear Regression | Linear relationship between input and output |
| Logistic Regression | Independent features |
| Naive Bayes | Features are conditionally independent |
| SVM | Data is linearly separable (for linear kernel) |
| K-Means | Spherical clusters of similar size |
If your data violates these assumptions, consider non-linear or tree-based algorithms that don’t rely on strict statistical rules.
6. Use Model Evaluation Metrics
Once you shortlist a few algorithms, use evaluation metrics to compare their real-world performance.
| Problem Type | Key Metrics |
| Classification | Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F1-Score, ROC-AUC |
| Regression | Mean Squared Error (MSE), R² Score, Mean Absolute Error (MAE) |
| Clustering | Silhouette Score, Davies–Bouldin Index |
You can use tools like cross-validation to ensure your model performs consistently across different data subsets. This systematic testing helps in choosing a machine learning algorithm that generalizes well.
7. Start Simple, Then Iterate
A common mistake is starting with highly complex models from the beginning. The best practice is:
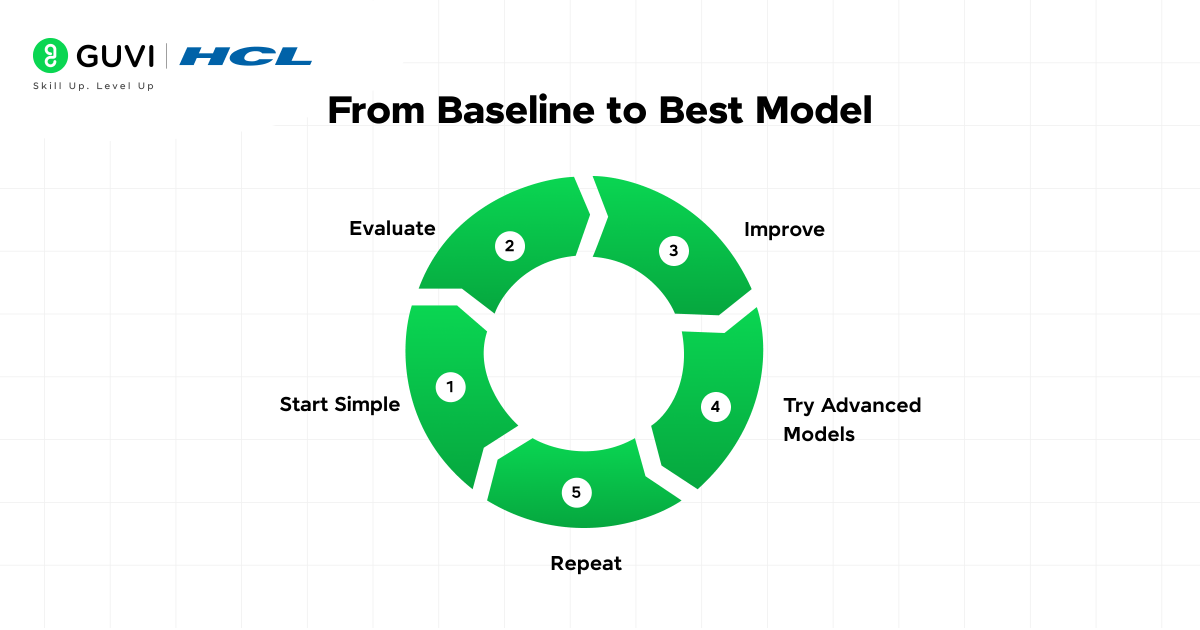
- Start with a baseline model, simple algorithms like Logistic Regression or Decision Trees.
- Evaluate the performance on validation data.
- Iterate with more advanced algorithms if the baseline isn’t sufficient.
- Fine-tune hyperparameters (like learning rate, depth, etc.) to boost accuracy.
This iterative approach ensures you don’t overcomplicate solutions that a simpler model could handle efficiently.
8. Use Automated Tools and Frameworks
Modern machine learning (ML) platforms have made the task of determining a machine learning algorithm significantly easier through automation.
- AutoML (automated machine learning) tools (e.g. Google Cloud AutoML, H2O.ai, Auto-sklearn) will automatically test algorithms with the data and suggest the best algorithms to use.
- ML libraries, such as scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch, offer quick experimentation options.
- Visualization tools (e.g., MLflow, Weights & Biases) help compare results systematically.
Automation does not replace the need for understanding, but can shorten the time taken to test and support decisions made by practitioners.
Why Choosing the Right Machine Learning Algorithm Matters
Here are the reasons why it is important:
- Accuracy and performance: The right algorithm improves the accuracy of the model and allows for reliable and accurate predictions.
- Efficiency: The right and optimized algorithms can reduce the time and resources required for computation.
- Better insights: A proper selection helps discover hidden trends and patterns in the dataset.
- Scalability: By properly choosing the model is more adaptable to larger and complex datasets.
- Interpretability: Some algorithms are better suited for making a decision easier to interpret, which is important in compliance, finance, and healthcare, which have regulatory or advisory implications.
If you’ve made it this far, you already think like a machine learning professional. Why not take the next step? The HCL GUVI AI & ML course, co-designed with IIT-M Pravartak which will help you turn curiosity into an actual career. Real projects. Expert mentors. Industry-ready skills. Enroll today and start building your ML future.
Final thoughts…
Finding success with machine learning is about much more than just picking the fanciest algorithm. It is a lot more about picking an appropriate algorithm to address a specific goal. You can choose the right machine learning algorithm with confidence by matching the type of problem you’re solving, the nature of your data, and your expectations of performance.
Keep in mind that the best model is the one that appropriately utilizes your data and drives the insights you seek while solving your organization’s problem.
So, take a breath, understand your problem, experiment with purpose, and let the data direct the decision, because choosing machine learning algorithm is really an art, based on science!
FAQs
1. What factors should I consider when selecting a machine learning algorithm?
You should consider your data’s type, its size, the type of problem you are attempting to solve, and how accurate you need your model to be. The goal is to make an informed choice weighing tradeoffs such that you achieve the simplicity you would prefer against the desired performance.
2. How do I know if I have selected the most suitable algorithm?
The simplest way to find out is to run an experiment. Evaluate and compare some metrics such as accuracy, precision, or recall. If your chosen algorithm produces good results with the unseen data, you will know you made a good choice.
3. What algorithms are best for those who are just getting started with machine learning?
It is best to start simple. You could use simple models to understand the basics of model development such as Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, or Decision Trees.
4. What algorithms are best for smaller datasets?
Using lighter models like Naïve Bayes or KNN or SVM is ideal as they would work well with limited records.
5. Can I combine multiple algorithms together?
Definitely, the ensemble models like Random Forest and XGBoost combine models to increase accuracy.





























Did you enjoy this article?