Data Analysis in Research : Types & Methods
Nov 06, 2025 3 Min Read 1682 Views
(Last Updated)
Imagine trying to solve a puzzle with thousands of scattered pieces but no picture to guide you. That’s what raw data feels like without analysis. In research, data analysis is the process that brings clarity to complexity. It helps researchers uncover patterns, validate assumptions, and make informed decisions based on evidence and not guesswork.
Whether you’re studying climate change, consumer behavior, or medical outcomes, data analysis is the bridge between observation and understanding. It’s not just about numbers—it’s about extracting value from information to support conclusions and drive action.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of data analysis in research, its types, methods, tools, challenges, and future trends.
Table of contents
- Importance of Data Science in Reasearch
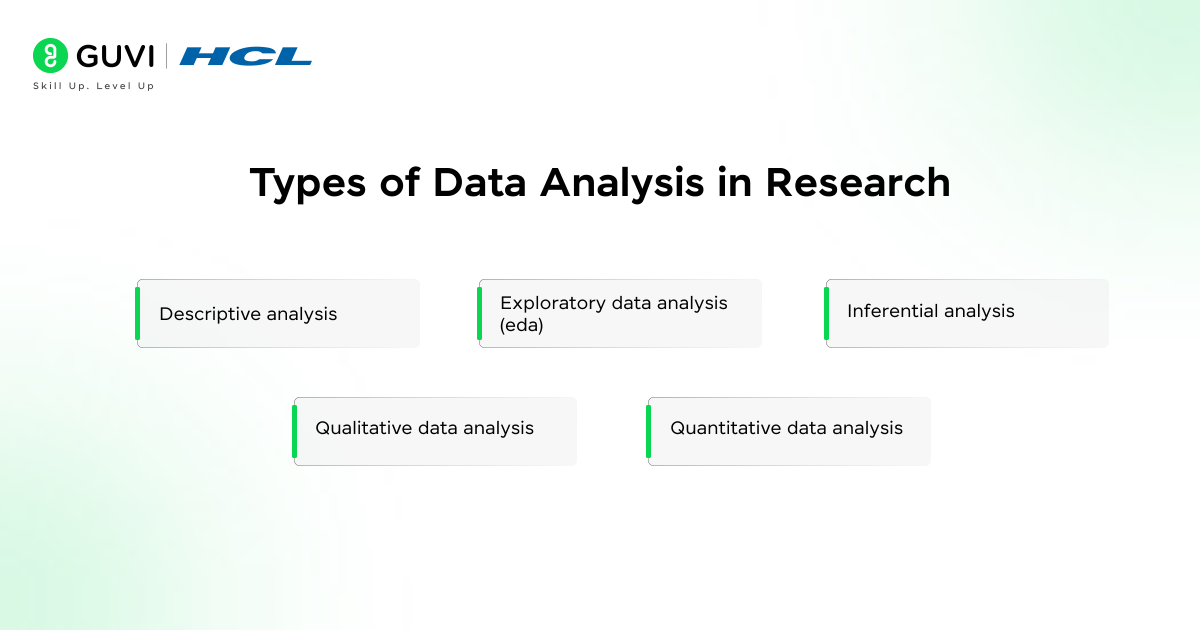
- Types of Data Analysis in Research
- 1 Descriptive Analysis
- 2 Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- 3 Inferential Analysis
- 4 Qualitative Data Analysis
- 5 Quantitative Data Analysis
- Methods Of Data Analysis
- 1 Statistical Methods
- 2 Machine Learning Methods
- Tools Used for Data Analysis
- Common Challenges in Data Analysis
- Future Trends in Data Analysis
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the difference between descriptive and inferential analysis?
- Can qualitative and quantitative analysis be used together?
- Why is exploratory data analysis important before modeling?
- What are common mistakes in data analysis?
- How does machine learning differ from traditional statistical methods?
Importance of Data Science in Reasearch
Why does data analysis matter so much in research? Because without it, even the most carefully collected data remains meaningless. Analysis transforms raw numbers and observations into insights that can guide decisions, shape policies, and fuel innovation.
- Improves decision-making: Helps researchers draw accurate and actionable conclusions
- Validates hypotheses: Confirms or rejects assumptions with statistical evidence
- Reveals patterns: Identifies trends, correlations, and anomalies in data
- Ensures accuracy: Reduces bias and enhances reliability of results
Example – A market researcher uses survey data to identify buying patterns across age groups.
Types of Data Analysis in Research
Once you understand why analysis is essential, the next step is choosing the right type. Each type serves a different purpose—some describe data, others predict outcomes, and some explore relationships.
1.1 Descriptive Analysis
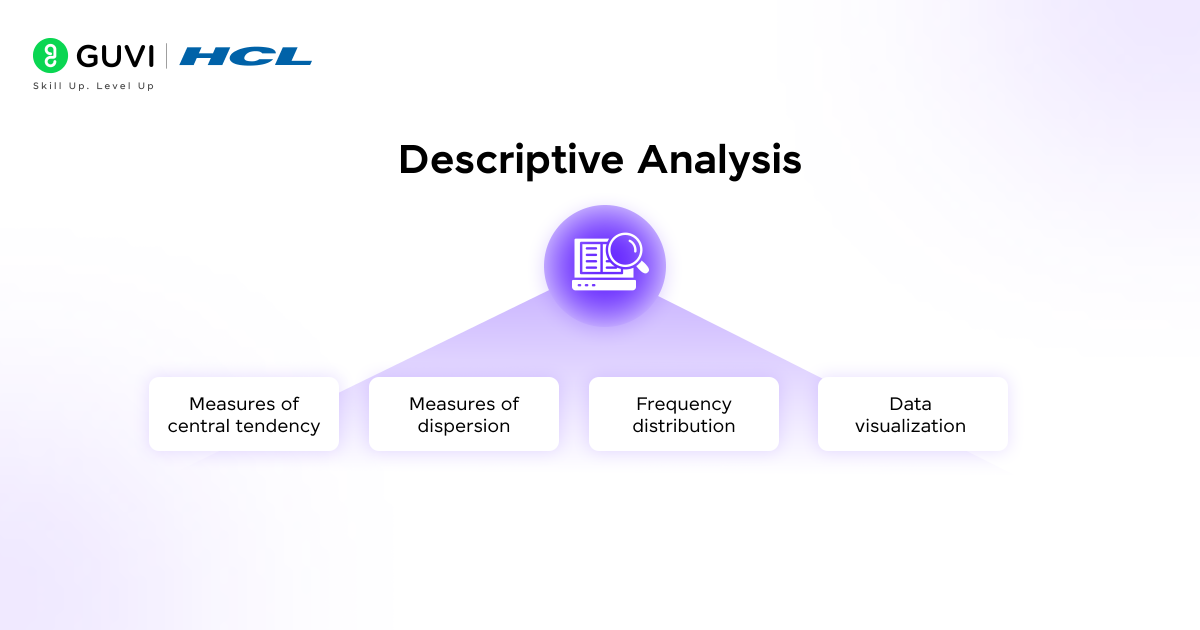
Ever wondered what the average income in a city tells us? Descriptive analysis is the starting point for understanding data. It summarizes the basic features of a dataset and answers the “what happened?” question.
- Measures of central tendency: Mean, median, and mode show the typical value
- Measures of dispersion: Range, variance, and standard deviation reveal the spread
- Frequency distribution: Highlights how often each value appears
- Data visualization: Charts and graphs make patterns easier to interpret
Example – A researcher calculates the average rainfall across five regions to compare climate patterns.
1.2 Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
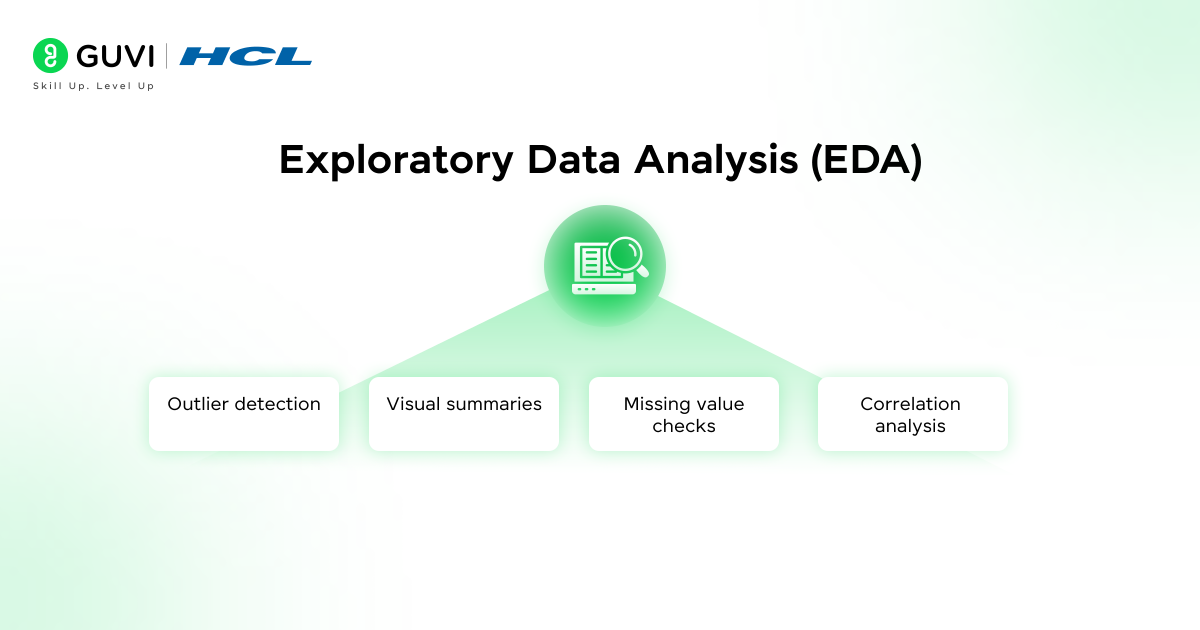
Before diving into models, researchers often explore their data to spot trends or anomalies. EDA is like detective work—it helps you understand the shape and structure of your data.
- Outlier detection: Identifies unusual or extreme values
- Visual summaries: Box plots, histograms, and scatter plots reveal structure
- Missing value checks: Ensures data completeness and reliability
- Correlation analysis: Examines relationships between variables
Example – A box plot of student scores reveals a cluster of low performers.
1.3 Inferential Analysis
What if you could predict population behavior using just a sample? Inferential analysis lets researchers generalize findings and test hypotheses with statistical confidence.
- Hypothesis testing: t-tests, chi-square, and ANOVA validate assumptions
- Confidence intervals: Estimate population parameters with precision
- Regression analysis: Models relationships between variables
- Sampling techniques: Ensure representative data for valid inference
Example – A clinical trial uses sample data to predict drug effectiveness.
1.4 Qualitative Data Analysis
Not all data comes in numbers. When researchers work with interviews, open-ended surveys, or observations, qualitative analysis helps uncover meaning, emotion, and context.
- Thematic analysis: Identifies recurring ideas or patterns
- Content analysis: Categorizes and quantifies textual data
- Narrative analysis: Explores stories and personal experiences
- Coding frameworks: Organizes qualitative data for interpretation
Example – A researcher analyzes transcripts to understand student stress during exams.
1.5 Quantitative Data Analysis
If your research involves measurable variables and statistical rigor, quantitative analysis is the go-to approach. It helps test theories, quantify relationships, and forecast outcomes.
- Descriptive statistics: Summarize numerical data
- Inferential statistics: Generalize findings from samples
- Predictive modeling: Forecast future trends
- Mathematical simulations: Model complex systems
Example – A survey reveals a strong link between education and income levels.
Methods Of Data Analysis

Once you’ve chosen the type of analysis, the next step is selecting the right method. Methods vary based on your research goals, data format, and available tools.
2.1 Statistical Methods
Statistical methods form the backbone of most research analysis. They help summarize data, test hypotheses, and identify relationships.
- Descriptive statistics: Mean, median, mode, and standard deviation
- Inferential statistics: Hypothesis testing and confidence intervals
- Multivariate analysis: Examines multiple variables simultaneously
- Time series analysis: Tracks changes over time
Example – A researcher compares test scores across three schools using ANOVA.
2.2 Machine Learning Methods
When datasets grow large and complex, machine learning methods offer scalable, predictive solutions. These algorithms adapt and improve as they process more data.
- Classification: Assigns categories (e.g., spam vs. non-spam)
- Clustering: Groups similar data points
- Regression models: Predict numerical outcomes
- Dimensionality reduction: Simplifies complex data
Example – A real estate analyst uses regression models to predict housing prices.
Grab HCL GUVI’s free Python eBook to master Python for data analysis with beginner-friendly examples and projects.
Tools Used for Data Analysis

Choosing the right tool can make or break your analysis workflow. Researchers rely on a mix of programming languages, statistical software, and visualization platforms.
- Excel: Ideal for basic statistical analysis and visualization
- Python: Offers libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib
- R: Powerful for statistical modeling and data visualization
- SPSS: Commonly used in social science research
- Tableau: Great for interactive dashboards and visual storytelling
Example – A data analyst uses Python and Pandas to clean and analyze survey responses.
Common Challenges in Data Analysis
Even with the right tools and methods, researchers face challenges that can compromise accuracy and reliability. Addressing these issues is key to producing valid results.
- Missing or incomplete data: Leads to biased or misleading conclusions
- Sampling bias: Reduces generalizability and skews results
- Overfitting in models: Makes predictions too specific to training data
- Misuse of statistical tests: Invalidates findings and interpretations
Example – A health survey excludes rural populations, misrepresenting national trends.
Future Trends in Data Analysis
As technology evolves, data analysis is becoming faster, smarter, and more collaborative. Researchers are adopting advanced tools and techniques to handle larger datasets and generate real-time insights.
- AI-powered analysis: Automates complex tasks and improves accuracy
- Real-time dashboards: Enable instant decision-making and monitoring
- Automated data cleaning: Reduces manual effort and improves data quality
- Cloud integration: Enhances scalability and team collaboration
Example – Researchers use cloud platforms to analyze global climate data in real time.
Join HCL GUVI’s free 5-day Data Science Email Course to learn how to analyze, visualize, and apply data effectively.
Conclusion
Data analysis is the foundation of credible, impactful research. It transforms raw observations into structured insights, helping researchers validate theories, uncover trends, and make informed decisions. Whether you’re working with survey responses, lab results, or interview transcripts, choosing the right type and method of analysis ensures your findings are both accurate and meaningful.
Master data analysis with HCL GUVI’s Data Science Course — a comprehensive program covering Python, SQL, Machine Learning, and Data Visualization. Learn from industry experts, work on real-world projects, and gain mentorship to build a strong career in data science.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between descriptive and inferential analysis?
Descriptive analysis summarizes data to show what happened, while inferential analysis uses sample data to make predictions or generalizations about a population.
2. Can qualitative and quantitative analysis be used together?
Yes, combining both methods provides a richer understanding by integrating numerical trends with contextual insights.
3. Why is exploratory data analysis important before modeling?
EDA helps detect patterns, outliers, and data quality issues, ensuring models are built on reliable foundations.
4. What are common mistakes in data analysis?
Using biased samples, ignoring missing data, misapplying statistical tests, and overfitting models are frequent errors that compromise results.
5. How does machine learning differ from traditional statistical methods?
Machine learning focuses on pattern recognition and prediction using algorithms, while statistical methods emphasize hypothesis testing and inference.



































Did you enjoy this article?