
How To Become A Financial Data Scientist
Nov 19, 2025 5 Min Read 497 Views
(Last Updated)
Every second, trillions of financial transactions flow across the global economy, from stock trades and digital payments to credit approvals and crypto exchanges. This massive data hides the patterns that can predict market movements, uncover fraud, and guide billion-dollar investment decisions. The professionals who decode these insights are known as financial data scientists.
In today’s fast-paced financial world, where a single insight can define success or loss, financial data science has become the backbone of innovation. Banks use it to assess credit risks more accurately, fintech startups leverage it to personalize user experiences, and investment firms depend on it to forecast trends with precision. These applications highlight how data-driven decision-making is redefining modern finance.
In this blog, we’ll explore:
- The importance of financial data science in modern finance
- The key roles and responsibilities of a financial data scientist
- A detailed career roadmap to enter and excel in this field
- The essential skills and tools you need to master
- Real-world applications that demonstrate the impact of data science in finance
- Roles and Salary offered to a financial data scientist
By the end, you’ll gain a complete understanding of how to navigate your journey towards becoming a successful financial data scientist.
Table of contents
- Who Is A Financial Data Scientist?
- The Importance Of Financial Data Science
- Key Roles And Responsibilities of a Financial Data Scientist
- Risk Analyst
- Fraud Detection Specialist
- Portfolio Optimization Analyst
- Financial Forecaster
- Career Roadmap
- Step 1: Learn Python, R, SQL, and statistics basics
- Step 2: Understand financial concepts and markets
- Step 3: Master data visualization and machine learning techniques
- Step 4: Work on real-world financial datasets and projects
- Step 5: Build a portfolio and apply for financial data roles
- Skills And Tools You Need To Master
- Roles Offered to a Financial Data Scientist (With Salary)
- Real-World Applications
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Do I need a finance background to become a financial data scientist?
- Which programming language is most important?
- Can I work in finance without prior experience?
- How long does it take to become a financial data scientist?
- Are financial data scientist roles high-paying?
Who Is A Financial Data Scientist?
A financial data scientist is a professional who blends expertise in finance, statistics, programming, and machine learning to interpret complex financial data and generate insights that guide strategic business decisions. They act as a bridge between technical analytics and financial strategy, ensuring that data-driven insights directly translate into business value.
Unlike traditional analysts who rely mostly on historical data and manual reporting, financial data scientists use predictive modeling, AI algorithms, and automation tools to identify hidden patterns, forecast market behavior, and recommend actionable strategies.
In short, a financial data scientist turns raw, unstructured financial information into meaningful insights that help organizations make smarter, faster, and more profitable decisions.
The Importance Of Financial Data Science

Financial data science is the powerful fusion of finance, statistics, and machine learning, designed to extract meaningful and actionable insights from massive financial datasets. In an era where every transaction and market movement generates valuable data, this discipline empowers organizations to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Businesses and financial institutions leverage financial data science to:
- Detect and prevent fraudulent transactions with predictive algorithms
- Forecast stock prices and market trends using historical and real-time data
- Optimize investment portfolios for better returns and reduced risks
- Strengthen risk management strategies through advanced modeling and analytics
By transforming complex data into practical intelligence, financial data scientists enable companies to cut costs, boost profitability, and make faster, evidence-based decisions.
Key Roles And Responsibilities of a Financial Data Scientist

Financial data scientists typically take on multiple roles, each focused on solving specific financial challenges. In this section, we’ll explore four main roles that highlight how these professionals drive smarter decisions and maximize business value.
- Risk Analyst
- Fraud Detection Specialist
- Portfolio Optimization Analyst
- Financial Forecaster
1. Risk Analyst
A risk analyst uses predictive models and data analytics to identify potential threats that could impact a financial institution’s operations or profitability. Their primary goal is to assess, measure, and manage risks related to loans, investments, trading, and other financial activities. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer behavior, risk analysts help organizations make informed decisions that minimize losses and protect assets.
Example: A bank can use data to figure out which customers might not repay their loans. This helps the bank decide whether to approve the loan, set a higher interest rate, or take extra precautions to reduce potential losses.
2. Fraud Detection Specialist

A fraud detection specialist monitors financial transactions to detect unusual or suspicious patterns that could indicate fraud. Using machine learning and data analytics, they help companies prevent losses by flagging potentially fraudulent activities in real time.
Example: Spotting unusual credit card transactions, such as a sudden large purchase in a different city, so the bank can block it before any loss occurs.
3. Portfolio Optimization Analyst

A portfolio optimization analyst focuses on investments in the best possible way to maximize returns while keeping risks low. They use statistical models, data analytics, and financial algorithms to decide how to distribute assets across stocks, bonds, or other investment options.
Example: A mutual fund manager uses data to decide how much money to invest in different stocks and bonds to get the best returns without taking too much risk.
4. Financial Forecaster
A financial forecaster uses historical data and machine learning models to predict future financial outcomes, such as stock prices, revenue, or market trends. Their insights help companies and investors plan strategies, make informed decisions, and stay ahead in the market.
Example: Predicting quarterly earnings for a public company.
Career Roadmap
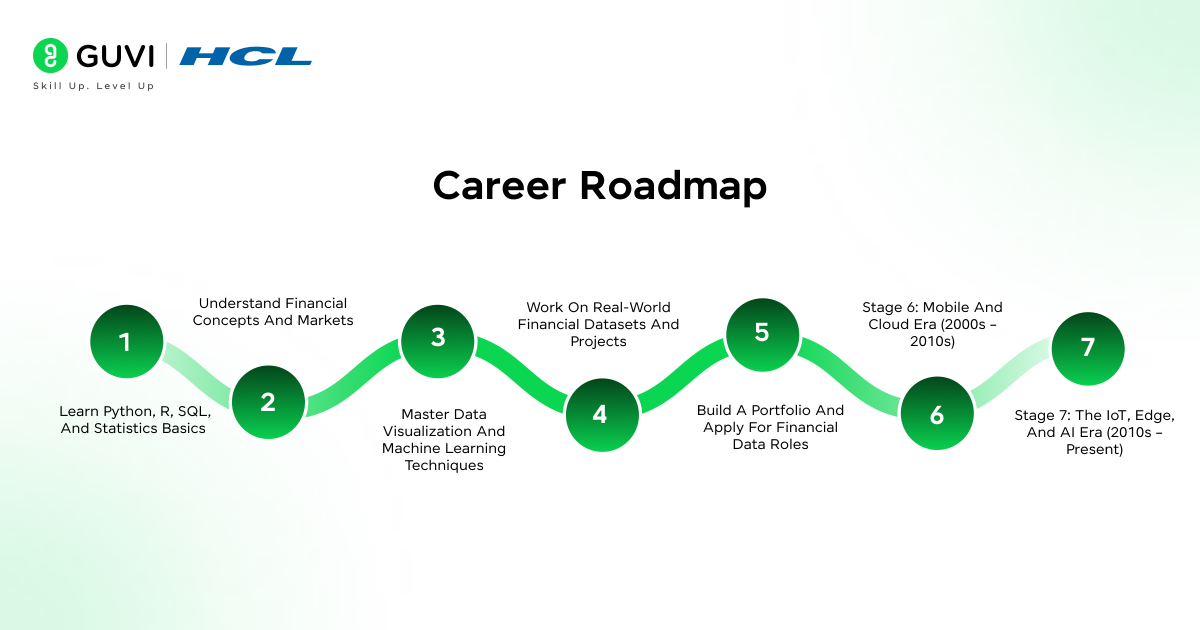
Breaking into the field of financial data science requires a mix of technical skills, financial knowledge, and hands-on experience. Here’s a clear roadmap to guide your journey from a beginner to a professional financial data scientist:
You can also strengthen your learning with HCL GUVI’s 5-day free Data Science email series, which covers Python, data analysis, visualization, and finance-related examples, perfect for beginners.
Step 1: Learn Python, R, SQL, and statistics basics
Becoming a financial data scientist starts with building a strong foundation in programming and statistics. These skills are the backbone of all data analysis and predictive modeling in finance. Without them, even the best financial knowledge cannot be applied effectively to large datasets.
Why it matters:
Financial datasets are often huge, messy, and complex. Programming languages like Python and R allow you to clean, manipulate, and analyze this data efficiently. SQL helps you extract and manage data from financial databases, which is critical for analyzing transactions, stock prices, or customer records. Meanwhile, statistics and probability give you the tools to interpret patterns, measure risk, and make data-driven predictions.
What to focus on:
- Python: Learn libraries like pandas for data manipulation, NumPy for numerical computations, Matplotlib/Seaborn for visualization, and scikit-learn for machine learning models.
- R: Ideal for statistical analysis and financial modeling, with packages like ggplot2 for visualization and caret for machine learning.
- SQL: Learn to query databases efficiently, join multiple tables, and extract meaningful insights from transactional data.
- Statistics & Probability: Understand concepts like mean, median, variance, correlation, hypothesis testing, regression, and distributions.
Step 2: Understand financial concepts and markets
Becoming a successful financial data scientist requires more than technical skills; you need a solid understanding of finance, markets, and knowing how financial systems work helps you apply data science effectively to solve real-world problems.
Why it matters:
Data without context has limited value. Understanding concepts like stocks, bonds, derivatives, risk, and investment strategies allows you to interpret data correctly and build models that make sense for businesses and investors. It also helps you communicate insights clearly to financial stakeholders.
What to focus on:
- Financial Instruments: Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, derivatives, and commodities.
- Markets & Trading: How stock exchanges work, trading mechanisms, and market trends.
- Investment Strategies: Portfolio management, asset allocation, risk-return trade-offs.
- Risk Management: Credit risk, market risk, operational risk, and liquidity risk.
Step 3: Master data visualization and machine learning techniques
Once you understand finance and have technical skills, the next step is to turn data into insights using visualization and predictive models.
Why it matters:
Raw data is difficult to interpret. Data visualization helps you communicate trends and patterns effectively, while machine learning allows you to forecast market behavior, detect fraud, and automate decision-making.
What to focus on:
- Data Visualization: Tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn, Tableau, or Power BI to create charts, dashboards, and reports.
- Machine Learning: Regression, classification, clustering, and time-series forecasting for financial prediction and risk analysis.
- Feature Engineering: Transform raw data into meaningful inputs for models.
- Model Evaluation: Use metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and RMSE to measure performance.
Step 4: Work on real-world financial datasets and projects
Having hands-on experience is crucial, and working on real datasets prepares you for the challenges you’ll face in the industry.
Why it matters:
Financial datasets are messy, incomplete, and complex. By applying your skills to real-world projects, you learn how to handle these challenges and develop practical solutions.
What to focus on:
- Project Ideas: Fraud detection, credit risk modeling, portfolio optimization, and stock price prediction.
- Tools: Python, R, SQL, Excel, Tableau, and cloud platforms like AWS or Google Cloud.
- Problem Solving: Identify business problems, clean and analyze data, build models, and present insights.
Step 5: Build a portfolio and apply for financial data roles
Your skills and projects are valuable only if you showcase them. A strong portfolio demonstrates your capability to potential employers.
Why it matters:
Employers want proof that you can apply your knowledge to solve real financial problems. A portfolio highlights your projects, analytical skills, and ability to deliver insights that drive business decisions.
What to focus on:
- Portfolio Creation: Include project descriptions, data sources, code snippets, visualizations, and results.
- Platforms: GitHub, personal websites, or Kaggle profiles.
- Resume & Applications: Highlight technical skills, financial knowledge, and completed projects relevant to the role.
- Networking: Connect with professionals on LinkedIn, attend webinars, and participate in competitions.
Skills And Tools You Need To Master

To become a successful financial data scientist, you need a balanced mix of financial understanding, programming expertise, and analytical tools. These skills enable you to work with complex datasets, extract meaningful insights, and turn them into actionable business strategies.
Essential skills:
- Finance knowledge: statements, investment principles, market mechanics
- Programming: Python, R, SQL
- Statistics & Machine Learning: regression, classification, clustering, time-series analysis
- Data Visualization: Tableau, Power BI, Matplotlib
- Big Data & Cloud Tools: Hadoop, Spark
Tools:
- Python & R: statistical modeling and machine learning
- SQL & Excel: querying and structured data management
- Tableau / Power BI: interactive dashboards
- Hadoop / Spark: big data processing
Roles Offered to a Financial Data Scientist (With Salary)
The financial data science domain offers a wide range of roles, blending analytical, technical, and financial expertise. Salaries depend on your experience, skill set, and the complexity of the projects you handle. Here are some of the top roles and their average salary ranges:
Financial Data Scientist: ₹6–10 LPA (freshers) | ₹15–28 LPA (experienced) — Analyzes complex financial datasets, builds predictive models, and supports data-driven investment decisions.
Reference – Glassdoor
Quantitative Analyst (Quant): ₹8–12 LPA (freshers) | ₹20–35 LPA (experienced) — Uses statistical and mathematical models to forecast market trends and evaluate risk.
Reference – Glassdoor
Risk Analyst: ₹5–9 LPA (freshers) | ₹12–20 LPA (experienced) — Assesses financial risks, credit exposure, and investment viability using analytical tools and models.
Reference – Glassdoor
Financial Analyst (Data-Driven): ₹4–8 LPA (freshers) | ₹10–18 LPA (experienced) — Leverages data insights to evaluate company performance, prepare forecasts, and optimize portfolio strategies.
Reference – Glassdoor
Data Engineer (Finance Domain): ₹7–12 LPA (freshers) | ₹15–25 LPA (experienced) — Designs and maintains large-scale data pipelines and systems that support financial analytics.
Reference – Glassdoor
Machine Learning Engineer (Finance): ₹9–14 LPA (freshers) | ₹20–30 LPA (experienced) — Develops algorithms for fraud detection, credit scoring, and financial forecasting.
Reference – Glassdoor
Business Intelligence Analyst (Finance): ₹6–10 LPA (freshers) | ₹14–22 LPA (experienced) — Builds dashboards and visualization tools that help finance teams track KPIs and performance metrics.
Reference – Glassdoor
Real-World Applications
Financial data scientists apply their skills in:
- Fraud detection in banking and fintech
- Algorithmic trading and stock prediction
- Portfolio management and investment analysis
- Credit scoring and lending decisions
- Risk management for insurance and financial services
For a deeper understanding, the Data Science eBook provides a beginner-friendly roadmap covering Python, data handling, visualization, and machine learning with finance examples and exercises.
Conclusion
Becoming a financial data scientist requires a mix of finance knowledge, programming, statistics, and machine learning. Understanding the key roles, following a structured career roadmap, mastering relevant skills, and applying them in real-world scenarios will help you succeed in this high-demand field.
Join HCL GUVI’s Data Science Course to become a Data Scientist, learning Python, R, SQL, statistics, and machine learning. Work on real-world projects and get expert guidance to build a strong portfolio and land high-demand roles.
FAQs
1. Do I need a finance background to become a financial data scientist?
No, but understanding finance concepts is helpful. You can learn finance alongside data science skills.
2. Which programming language is most important?
Python is the most widely used, though R is also valuable for statistical modeling.
3. Can I work in finance without prior experience?
Yes, internships, projects, and certifications can help you enter the field.
4. How long does it take to become a financial data scientist?
Typically 6–12 months of consistent learning and hands-on practice.
5. Are financial data scientist roles high-paying?
Yes, due to their specialized skills, roles in banking, fintech, and investment firms are well-compensated.




























Did you enjoy this article?