
Have you ever wondered what happens to all our personal data that gets collected every time we shop online, browse social media, or use a mobile app? From purchase histories and browsing patterns to chat messages and digital forms, an enormous amount of data is being stored every second. But where does it all go once its immediate use is over? That’s where data retention comes in.
Data retention is the process of deciding how long data should be kept, where it should be stored, and when it should be safely deleted. It helps organizations manage their storage efficiently, meet legal obligations and use information for analysis or future improvements.
Think of it like keeping receipts which you don’t need forever, but holding onto them for a while helps track expenses or handle returns. Similarly, companies store data just long enough to serve its purpose before safely deleting it.
Table of contents
- Why Data Retention Is Important
- Types Of Data Retention
- Short-Term Data Retention
- Long-Term Data Retention
- Compliance-Based Retention
- Operational Retention
- Key Features Of an Effective Data Retention Policy
- Defined Retention Periods
- Automated Deletion
- Secure Storage
- Regular Audits
- Transparency
- How To Build A Data Retention Strategy
- Identify Data Sources
- Classify Data
- Define Retention Timelines
- Automate Deletion Or Archival
- Real-World Examples Of Data Retention
- Banking Sector
- Healthcare Industry
- E-Commerce Platforms
- Government Agencies
- Challenges In Data Retention
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Q1. What happens if a company doesn’t follow data retention laws?
- Q2. Is data retention the same as data backup?
- Q3. How often should a data retention policy be updated?
- Q4. Can individuals control how long their data is stored?
Why Data Retention Is Important
Data retention might sound like a complicated topic, but it’s actually something every business relies on. It helps companies keep the right information for the right amount of time so that useful data is available when needed, and old data is safely deleted when it’s no longer required.
Here’s why it’s important:
- Legal compliance: Many industries such as banking and healthcare have rules that require data to be stored for specific time periods.
- Data security: Keeping data for too long can lead to security risks. A proper retention plan helps reduce the chances of leaks or misuse.
- Cost efficiency: Storing unnecessary data takes up space and increases costs. Managing it properly keeps storage efficient and affordable.
- Improves Decisions: Old data can reveal patterns and insights that help businesses make better choices in the future.
- Builds Customer Trust: When companies handle data responsibly and transparently, customers feel safer sharing their information.
Example – A healthcare clinic keeps patient records for a few years, as required by medical laws. This ensures doctors can access past information when needed. But after that period, the clinic deletes the data to protect patient privacy. This approach keeps both the clinic and the patients safe.
Understanding why data retention matters goes beyond compliance – it’s about managing and interpreting data effectively. To strengthen your grasp on such concepts, explore HCL GUVI’s 5-day free Data Science Email Series – quick, beginner-friendly lessons that simplify Python, analytics, and AI concepts step-by-step.
Types Of Data Retention
Every organization collects and stores different types of data, and each serves a different purpose. Some data is needed only for a short time, like when analyzing customer activity or fixing small issues. Other data must be kept for years to meet legal or business requirements.
In simple terms, how long data is stored depends on why it’s collected in the first place. Let’s look at the main types of data retention and understand how each one works in real-world situations.
1. Short-Term Data Retention
Have you ever noticed that some apps forget your data after a few weeks or months? That’s short-term data retention.
Short-term retention means keeping data for a limited period, usually from a few days to a few months. Businesses use this data for quick analysis, fixing temporary issues, or improving short-term performance. Once the data has served its purpose, it’s deleted automatically to free up space and protect privacy.
Example – Platforms like Netflix or Hotstar keep your recently watched shows for about 30 days to recommend similar content. After that time, your history is cleared to keep your account secure and uncluttered.
Features:
- Supports short-term analytics and troubleshooting
- Saves storage space and costs
- Reduces the risk of unnecessary data exposure
2. Long-Term Data Retention
Some data is too important to delete quickly and it needs to be preserved for years. Long-term data retention is all about storing information that may be needed in the future for legal, financial, or analytical purposes. This data helps organizations track history, analyze trends, and maintain compliance. Because it’s stored for a longer period, it must be protected with strong security and reliable backup systems.
Example – A bank can store customer transaction details for up to seven years. This helps them meet financial regulations and ensures transparency during audits.
Features:
- Helps maintain long-term legal compliance
- Useful for audit trails and historical analysis
- Requires secure storage and backup solutions
3. Compliance-Based Retention
Some types of data must be stored because the law says so and there are no exceptions and that’s Compliance based retention.
Compliance-based data retention happens when organizations are required by government or industry regulations to keep certain data for specific time periods. This ensures accountability and traceability, especially in sensitive industries like healthcare and finance. Failure to follow these rules can lead to heavy penalties and loss of public trust.
Example – Hospitals must keep patient records under laws like HIPAA for a set number of years. This makes it easier to ensure proper patient care and legal accountability.
Features:
- Legally defined storage timelines
- Requires regular compliance checks and audits
- Must follow strict data security standards
4. Operational Retention
Some data is kept simply because it helps businesses run smoothly every day and that’s Operational retention. Operational data retention focuses on storing information that supports daily tasks such as managing customer accounts, tracking sales, or improving product performance. Once this data is no longer useful, it’s securely deleted to keep systems clean and efficient.
Example – An e-commerce company like Amazon or Flipkart may keep customer details, purchase histories, and product reviews to offer better recommendations and improve services. After the data becomes outdated, it’s safely removed from the system.
Features:
- Improves customer service and personalization
- Helps with everyday business operations
- Deleted once it’s no longer relevant or useful
Key Features Of an Effective Data Retention Policy
An effective data retention policy helps organizations find the right balance between using data effectively and protecting it responsibly. It ensures that information is stored safely, deleted on time, and managed according to clear rules.
Here are the key elements that make a data retention policy strong and reliable:
1. Defined Retention Periods
Every type of data – whether it’s employee information, financial records, or customer details should have a clear time limit for how long it’s stored. Setting defined retention periods helps avoid confusion and ensures old or unnecessary data is removed on time.
2. Automated Deletion
Relying on manual deletion can be risky and inconsistent. Automated systems help by regularly identifying and removing outdated data. This not only saves time but also reduces the chance of human error.
3. Secure Storage
It’s not enough to just store the data; it must be stored safely. Encryption, access controls, and secure servers protect sensitive information from misuse, theft, or unauthorized access.
4. Regular Audits
Even the best data policies need regular checkups. Frequent audits help organizations confirm that they’re following legal requirements and that no unnecessary data is being kept. It also ensures that data security practices are up to date.
5. Transparency
A good data retention policy should be easy to understand. Clear documentation helps employees know what to do, and it builds trust with customers when they understand how their data is handled and for how long it’s kept.
How To Build A Data Retention Strategy
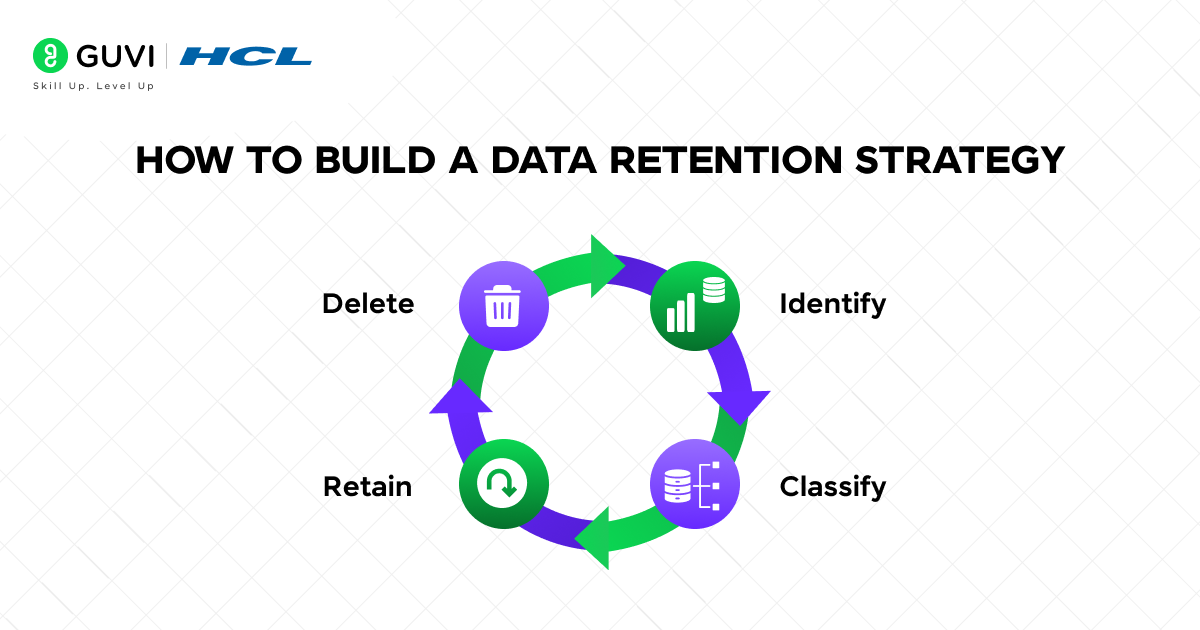
Every organization generates huge amounts of data every day starting with customer interactions to internal reports. To manage all this information safely and efficiently, companies need a well-planned data retention strategy. It defines what data should be stored, for how long, and when it should be deleted.
Here’s a simple step-by-step process to build one:
1. Identify Data Sources
Start by finding out where your data comes from. It might be collected through mobile apps, websites, customer transactions, or connected devices like IOT sensors. Knowing your data sources helps you understand what you’re dealing with and what needs to be retained.
2. Classify Data
Not every piece of data has the same level of importance or sensitivity. Classify your data such as confidential, internal, or public. This makes it easier to apply the right protection measures and define how long each type should be kept.
3. Define Retention Timelines
Once data is categorized, decide how long to keep it. Some data, like financial records, may need to be stored for years due to legal requirements, while temporary logs can be deleted after a few weeks. Setting clear timelines prevents both unnecessary storage and legal issues.
4. Automate Deletion Or Archival
Manual deletion is time-consuming and is prone to error. Automating the process ensures that outdated data is regularly deleted or moved to secure archives. This keeps your systems organized and reduces the risk of keeping unnecessary information.
Real-World Examples Of Data Retention

Data retention isn’t just a policy on paper; it’s something that shapes how every industry manages and protects information. Let’s look at a few real-world examples that show how different sectors handle data retention in everyday operations.
1. Banking Sector
Banks deal with millions of transactions every day, so keeping accurate records is essential. Financial institutions retain customer transaction and account data for up to seven years. This helps them follow audit requirements, detect fraud, and resolve disputes whenever necessary.
Example:
If a customer questions a transaction made years ago, the bank can easily trace it back using retained data, ensuring transparency and accountability.
2. Healthcare Industry
In the healthcare sector, patient records are critical for providing proper treatment and ensuring legal compliance. Hospitals store medical data for a legally defined period, often several years, as required by medical regulations.
Example:
A doctor can refer to an older medical file to understand a patient’s history before prescribing new medication. This continuity of care is made possible through structured data retention policies.
3. E-Commerce Platforms
Online stores collect large amounts of customer data – from purchase history to feedback and preferences. This data is used to personalize recommendations, improve user experience, and plan marketing campaigns. However, it’s deleted or anonymized after a fixed time to protect privacy.
Example:
An e-commerce platform may use your last six months of browsing data to suggest products you might like, then delete that information once it’s no longer relevant.
4. Government Agencies
Government departments retain massive datasets for planning, policy-making, and research. Census data, tax information, and social welfare records are stored for long durations to study population growth and economic changes.
Example:
Census records collected every ten years help governments plan housing projects, educational programs, and healthcare systems more effectively.
Challenges In Data Retention
Managing data retention sounds simple, but it comes with several real-world challenges. Here are the main ones organizations face today:
1. Data volume and costs – Businesses create massive amounts of data daily. Storing it all for years increases costs.
2. Security and privacy risks – Old or unused data can become a security threat if not deleted on time. The longer it’s stored, the higher the risk of breaches.
3. Legal compliance – Different laws demand different data retention periods. Keeping up with these changing rules is complex and time consuming.
4. Data quality – Data that’s stored too long can become outdated or inaccurate, leading to poor insights and decisions.
5. Lack of awareness – Without proper training, employees might retain data longer than needed or delete it too early causing compliance issues.
You can also explore data-driven insights in HCL GUVI’s Data Science eBook — your compact guide to analytics, real-world tools, and beginner projects.Simple, structured, and perfect for anyone ready to dive deeper into data.
Conclusion
Data retention is more than just storing information; it’s about managing data wisely to balance accessibility, security, and compliance. With clear policies and the right tools, organizations can use data effectively while protecting user privacy and following legal standards.
If you’re interested in learning how to manage real-world data and build practical analytical solutions, explore HCL GUVI’s Zen Class Data Science Course — a hands-on course that turns beginners into job-ready data professionals. It covers Python, SQL, machine learning, Power BI, and Tableau, along with real-world projects, mentorship, live expert sessions, and placement support to help you launch a successful data career
FAQs
Q1. What happens if a company doesn’t follow data retention laws?
If a company fails to comply with data retention laws, it can face heavy fines, legal action, and reputational damage. Non-compliance may also lead to loss of customer trust and suspension of business operations until proper data practices are implemented.
Q2. Is data retention the same as data backup?
No, they serve different purposes. Data backup is about creating copies of data for recovery in case of loss or damage, while data retention focuses on how long information should be stored and when it should be deleted. In short, backups protect data, while retention manages its lifecycle.
Q3. How often should a data retention policy be updated?
A data retention policy should be reviewed and updated at least once a year, or whenever there are new laws, business changes, or technology updates. Regular reviews ensure compliance and prevent outdated data management practices.
Q4. Can individuals control how long their data is stored?
Yes, under data protection laws like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), individuals have the right to access, modify, or request deletion of their personal data. Organizations must honor these requests to stay compliant and maintain transparency.



























Did you enjoy this article?