
Full-Stack Development Evolution: From LAMP to MERN
Dec 16, 2025 6 Min Read 1863 Views
(Last Updated)
Isn’t it amazing when we use mobile and web applications to perform everyday tasks such as writing documents, transferring funds, or shopping for our desired products online? If you are aware of the current technological landscape, you will notice how these interactive virtual platforms and tools have transformed the way we live and make our decisions.
However, this transformation is not a result of recent events; rather, it is a gradual evolution of the software industry. In this context, we will now examine how the field of Full-Stack Development has evolved from the LAMP technology stack to the MERN stack.
In this blog, our primary focus will be on answering this question and exploring the pragmatic reasons associated with it. But before that, let’s have a quick glance at what Full-Stack Development is:
Full-stack Development: It is the process of building software applications or projects by integrating both frontend (client-side) and backend (server-side) systems. Full-stack developers are professionals responsible for designing and developing end-to-end digital products. This means they are capable of creating visually appealing user interfaces (UIs) as well as handling internal app operations and complex business logic.
Table of contents
- The Rise of LAMP Stack
- Why LAMP Dominated Early Full-Stack Development
- Cost-Effective
- Easy to learn
- Fast Adoption by Hosting Providers
- Reliability and Stability
- Extensive Resources and Strong Community Support
- Challenges and Limitations of LAMP
- Emergence of MERN Stack
- How MERN Solves Modern Full-Stack Challenges
- LAMP vs MERN: A Brief Comparative View
- LAMP
- MERN
- What is The Future of Full-Stack Development?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Why was the LAMP stack so popular in the early days of web development?
- What challenges did developers face with LAMP that led to the rise of MERN?
- How does MERN meet the needs of modern full-stack development?
The Rise of LAMP Stack
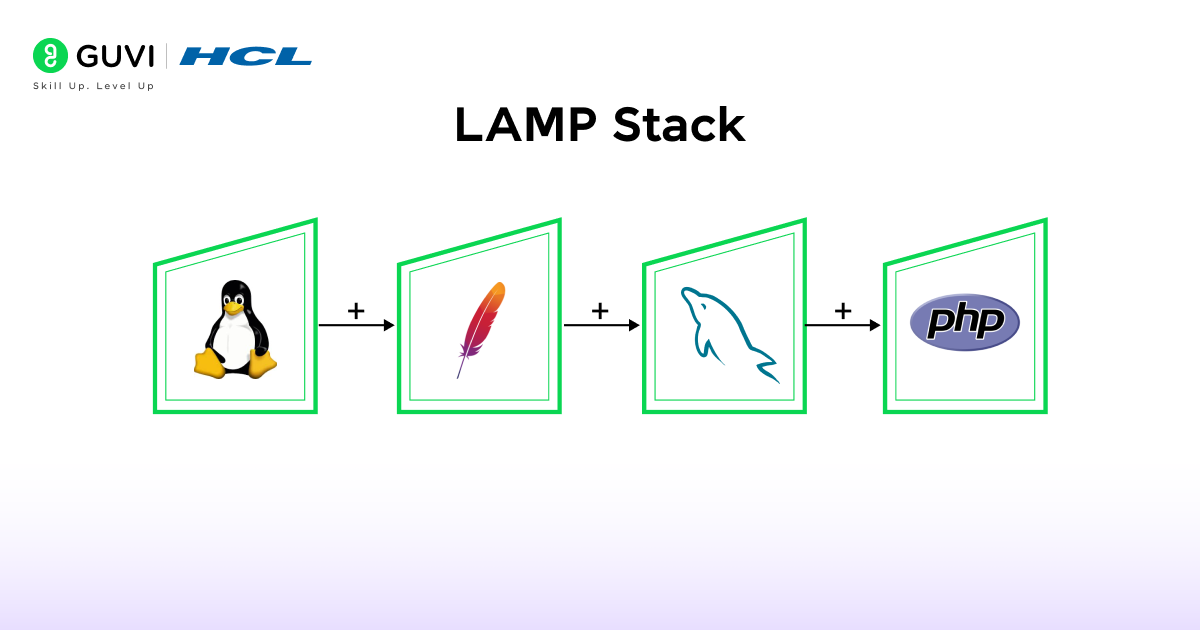
In the mid-1990s and early 2000s, the internet was slowly gaining popularity among the general public, and commercial businesses began offering their services online. It was nothing short of a revolution, and as a result, numerous types of software and digital tools were developed to further boost this revolution. Similarly, the LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) stack was created during that period.
It was an open-source set of tools explicitly designed for designing and developing dynamic websites, such as blog pages, e-commerce stores, and content management systems like WordPress, PHP-Nuke, and Drupal.
It was an ideal choice for a time when users navigated through websites primarily to read information, fill out forms, and run basic commands and programs. In this particular tech stack, Linux served as the operating system (OS) to ensure smooth operation and provide stability. Apache was used for creating web servers, MySQL for managing and handling databases, and PHP for building interactive features in websites and writing server-side scripts. All of these four tech elements worked seamlessly together to establish a strong online presence.
Why LAMP Dominated Early Full-Stack Development

LAMP was the go-to choice due to the following reasons:
1. Cost-Effective
LAMP was completely free and open-source, due to which it gradually became the preferred option for developing fully functional dynamic websites (with both frontend interactivity options and backend operations). In the early days, most software was expensive and accessible only to large corporations. However, the LAMP stack enabled freelancers, students, startups, and even small business units to create their own digital presence on the web by building full-stack websites and applications without incurring licensing fees and the costs of costly software tools, which ultimately minimized the overall development cost.
2. Easy to learn
In LAMP, PHP and MySQL were relatively straightforward to comprehend, allowing individuals with minimal coding knowledge to easily grasp the concepts required to create dynamic websites. Software developers can quickly create interactive HTML forms, user accounts, and visual components without complications, and also write server-side logic to handle end-user requests.
3. Fast Adoption by Hosting Providers
One of the fundamental reasons for the adoption of LAMP was also its widespread adoption among hosting providers. The majority of them supported LAMP as the default technology stack. Linux servers, Apache, MySQL, and PHP were already installed and configured on many hosting platforms. It was a convenient and reliable option for developers and programmers to utilize LAMP in the product-building process, as it allowed them to deploy websites smoothly without stressing about the technical setup, which saved both unnecessary effort and time.
4. Reliability and Stability
LAMP was the most optimal choice for that time, as it provided stability and reliability for web applications to operate efficiently. Linux and Apache provided dependable servers, MySQL managed data efficiently, and PHP served dynamic content effectively. These stable LAMP-based products performed exceptionally well in cases of heavy traffic concentration, which led many companies to adopt this technology stack for building and managing their own websites.
5. Extensive Resources and Strong Community Support
There was a vast global developer community where various LAMP resources, including tutorials, optimization techniques, troubleshooting guides, and open-source projects, were shared. When building websites, individuals who encounter technical issues or get stuck at any development stage can resolve their doubts with the experts. This support network significantly contributed to guiding novice developers by reducing their theoretical learning time, improving their efficiency and productivity, and encouraging more people to adopt LAMP, further reinforcing its dominance in early full-stack development.
Challenges and Limitations of LAMP
Along with its advantages and capabilities, the LAMP technology stack had significant issues and limitations. The following are some of the most fundamental challenges:
- Scaling Issues
LAMP was the perfect choice for designing and developing medium-scale websites, but it proved inefficient when handling a large number of user requests.
- Language Complexity
It was tedious for software developers to build different layers of websites, as multiple programming languages (PHP for the backend, SQL for the database, and HTML/CSS/JS for the frontend) were required to create these layers, leading to a slow development process.
- Rigid Database
MySQL is a primary component of the LAMP stack. It is a relational database, which makes handling unstructured and dynamic data more challenging compared to NoSQL databases.
- No Real-Time
It is not an ideal choice for building real-time features and functionalities, such as live chat bots, notification systems, voice assistants in the search bar, or streaming options. Due to these limitations, crafting a modern and advanced-grade application with LAMP becomes extremely difficult.
- Performance Limits
High online traffic and users’ requests often strain PHP and Apache, resulting in slower performance unless optimization methods are applied meticulously.
- Frontend Challenges
The integration of next-generation front-end frameworks, such as React or Angular, is not a smooth process, which makes the entire development process more complex and time-consuming.
- Slower Development
The act of switching or altering between multiple languages and tools associated with them makes the full-stack development process slower compared to other single-language stacks, such as MERN.
To address these issues with LAMP, developers and top tech companies have begun adopting the MERN stack to build high-quality websites and applications that meet the expectations of end customers and business stakeholders, without compromising on build quality, speed, performance, reliability, usability, security, and ongoing maintainability.
Emergence of MERN Stack
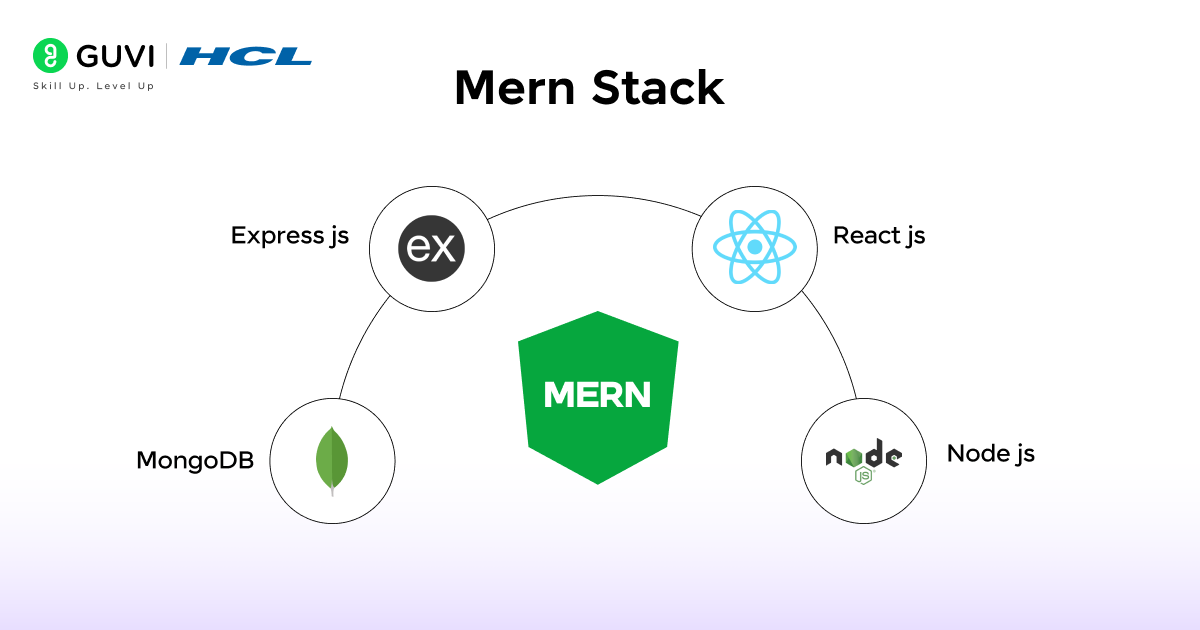
As the requirements and needs of users evolved, web applications and websites also changed in response to them. Due to this evolving nature of the market, developers felt the need for a faster and more flexible solution than LAMP. This very objective led to the rise of the MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js) stack, where developers create real-world full-stack applications entirely based on JavaScript (JS). Implementing a single programming language for both front-end and back-end systems enables the development team to develop software products more quickly and simply, while also reducing the likelihood of errors in the development process.
In this stack MongoDB is used to provide a flexible path to handle the unstructured and dynamic data with efficiency, Node.js which is a JavaScript runtime environment and Express.js which is framework for Node.Js these two tools are used for creating and handling the server-side algorithm and operations, and React which is open-source JS library is implemented for building interactive and engaging user interfaces based on class and functional components.
Websites developed with the MERN stack are fast, user-friendly, and provide a smooth navigational flow to the users, which enhances the overall user experience. Real-time features and functionalities, such as dynamic dropdowns, advanced search bars, live chat bots, and frequent reminder pop-ups, can be easily developed using the MERN stack. Due to its exceptional advantages, MERN has become the top choice for modern web applications, product-based companies, and scalable and complex projects that typically follow an agile development methodology.
How MERN Solves Modern Full-Stack Challenges
We can understand the reason behind this question with the help of the following points:
- Single Language
JavaScript is the primary language used in the MERN stack. For both frontend and backend tasks, a single language is being implemented, which eliminates the language complexity issue.
- Flexible Database
MongoDB is a cross-platform, NoSQL document-oriented database model suitable for storing and managing data in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format, making it easier to handle unstructured and frequently changing data.
- Real-Time Functionality
MERN also includes Node.js, a JavaScript runtime environment that supports asynchronous operations, which means it doesn’t block the parsing performed by the JavaScript engine. This exclusive feature enables real-time features, including live chat, notifications, and delivery tracking.
- Fast Development
Through the use of reusable classes and functional React components, along with Node.js modules and Express middleware, the entire development process becomes significantly faster, eliminating unnecessary and tedious development tasks.
- Dynamic UI
React’s virtual DOM and modular component architecture enable developers to design dynamic user interfaces that are rendered only when user events are triggered or data is modified.
- Scalability
Node.js, an event-driven system, and MongoDB’s distributed database model are both responsible for handling high traffic concentration and large datasets effectively without any hindrances. As a result, the applications can scale easily as the number of users and volume of data increase.
- API Integration
Express.js offers a robust routing system and comprehensive middleware support, streamlining backend logic and facilitating seamless integration with external APIs and services. This makes building feature-rich applications easier.
- Community Support
MERN has a large, open-source community that contributes libraries, modules, and updates. Developers can access best practices, ready-made solutions, and security patches, which reduces development effort and risk.
LAMP vs MERN: A Brief Comparative View
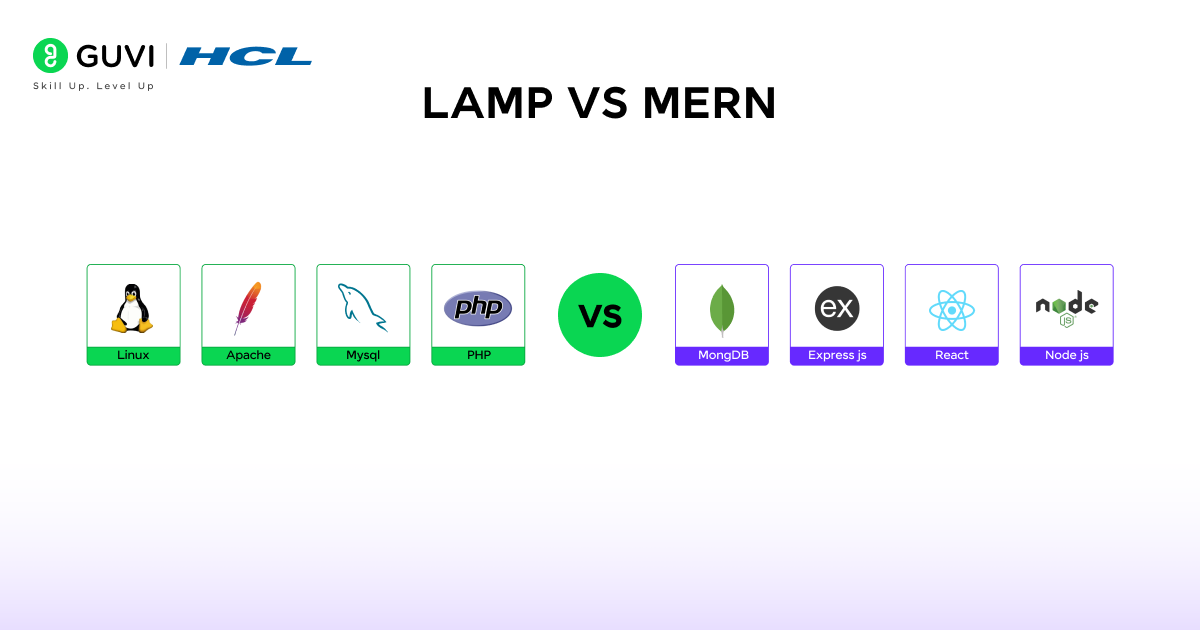
LAMP
- Cost-Effective – Free and open-source.
- Stable – Reliable for small to medium websites.
- Proven – Used in WordPress, Joomla, Drupal.
- Simple Backend – Easy to use for beginners.
- Hosting Support – Widely available on servers.
- Structured Data – Works best with relational databases.
MERN
- Single Language – JavaScript for frontend and backend.
- Flexible Database – MongoDB handles unstructured data.
- Real-Time Apps – Supports live updates and notifications.
- Fast Development – Easier for full-stack projects.
- Modern Frontend – React for dynamic, interactive UI.
- Scalable – Better performance for large applications.
What is The Future of Full-Stack Development?
The future of full-stack development is moving towards faster, more scalable, and highly interactive applications that can handle real-time updates, large amounts of data, and complex user experiences. Modern stacks, such as MERN, allow developers to work with a single language across the frontend and backend, integrate cloud services, and build applications that can scale easily as user demand increases. Tools like GraphQL, serverless architecture, and AI-powered features are also becoming part of the full-stack ecosystem, making development more efficient and intelligent.
While older stacks, such as LAMP, laid the foundation for web development with stability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, the focus today is on speed, flexibility, and a modern user experience. Full-stack developers of the future will need to stay updated with evolving frameworks, adopt best practices, and combine traditional knowledge with modern technologies to build the next generation of web applications.
One of the most significant milestones in full-stack development was in 2009, with the launch of Node.js.
This allowed JavaScript to run on servers, making full-stack JS apps and websites popular.
It also paved the way for tech stacks like MERN, changing how developers build web applications.
The current IT job market worldwide has become extremely competitive; landing a job at top product-based companies and highly recognized tech startups is akin to a golden ticket that only the most exceptional professionals receive. If you are someone who aspires to be a part of the best software companies, then wait no further, transform this dream in to reality by enrolling yourself in HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak Certified MERN Full Stack Development Course, which is not just limited to developing full-stack projects but also teaches you how to enhance the quality of your project by integrating the AI (Artificial Intelligence) tools and methods. Contact us today, and we will guide you forward in this enriching journey.
Conclusion
The journey from LAMP to MERN highlights how full-stack development has evolved to match the growing demands of modern web applications. While LAMP laid the foundation with its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and stability, MERN has taken the lead by offering speed, scalability, real-time capabilities, and a unified JavaScript environment. Together, they demonstrate how technology continually adapts to deliver improved performance, flexibility, and user experiences for the digital age.
FAQs
Why was the LAMP stack so popular in the early days of web development?
Because it was free, open-source, stable, and cost-effective, it made it the go-to choice for building dynamic websites.
What challenges did developers face with LAMP that led to the rise of MERN?
LAMP struggled with scalability, real-time features, and handling unstructured data, which modern apps required.
How does MERN meet the needs of modern full-stack development?
MERN utilizes JavaScript everywhere, supports flexible databases, real-time applications, and scalability, making it ideal for today’s needs.




































Did you enjoy this article?