
Software Design Documentation (SDD): The Blueprint for Software Development
Oct 19, 2025 6 Min Read 1710 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever been stuck in a maze? If not, let’s imagine for a moment that you are traveling from one point to another and get confused along the way due to the complex paths. Instead of having a clear vision, you are now making unnecessary efforts to reach your destination.
In this case, before starting your journey, you would have a comprehensive and detailed roadmap that outlines how easy it will be to navigate through these complex paths. Similarly, in this context, Software design documentation (SDD) serves as a roadmap or guidebook for developers, testers, and engineering managers. Without this, the entire development cycle becomes non-productive and inefficient, leading to a degradation of build quality and a failure to meet users’ expectations.
In this blog, we will guide you through all the essential information you need to understand the Software design document and explain why it is crucial to create a robust software project. So, let’s begin our discussion.
Table of contents
- Software Design Documentation (SDD) and Its Role in Software Engineering
- Types of Software Design Documentation (SDD)
- High-Level Design (HLD)
- Low-Level Design (LLD)
- Why Software Design Documentation (SDD) Matters
- Importance of SDD
- Purpose of SDD
- Benefits/Advantages of SDD
- Significance of Software Design Documentation (SDD) in Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Process
- Software Design Documentation (SDD) Guidelines and Best Practices
- How To Write Software Design Documentation (SDD)
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is a Software Design Document (SDD)?
- Why is a Software Design Document important in software development?
- Who is responsible for creating a Software Design Document?
- What key elements should a Software Design Document include?
Software Design Documentation (SDD) and Its Role in Software Engineering
(Definition)
SDD is a professional way of creating a formal and comprehensive description of the project development process. This stage is the next step in the succession of the requirement gathering and analysis phase. The primary purpose behind writing this documentation is to highlight how the final application or platform will align with the requirements mentioned in the Software Requirements Specifications (SRS).
All key elements, including system components, modules, algorithm complexity, navigational flow, design architecture, and technology stacks, are included in the SDD. To ensure the consistency, scalability, and usability of the product, developers, testers, and designers meticulously follow this blueprint. In simple words, SDD is an entity that transforms project ideas into fully functional and interactive software solutions.
(It’s Role)
From a core development perspective, the significance of SDD is very high, as it helps the development team transform abstract project requirements and objectives into a concrete plan. It empowers the engineers to excel at problem-solving and analytical thinking. It also ensures clarity and accuracy during code execution and integration of features and functionalities.
As it also provides a practical reference point for all key aspects of development, such as quality assurance, risk mitigation, and project scope, the ease of identifying and preventing possible bottlenecks and security vulnerabilities increases significantly.
However, SDD goes beyond just development; it also fosters team collaboration, while establishing an environment that suits the future developers who will be deployed in those specific projects without getting muddled.
Types of Software Design Documentation (SDD)
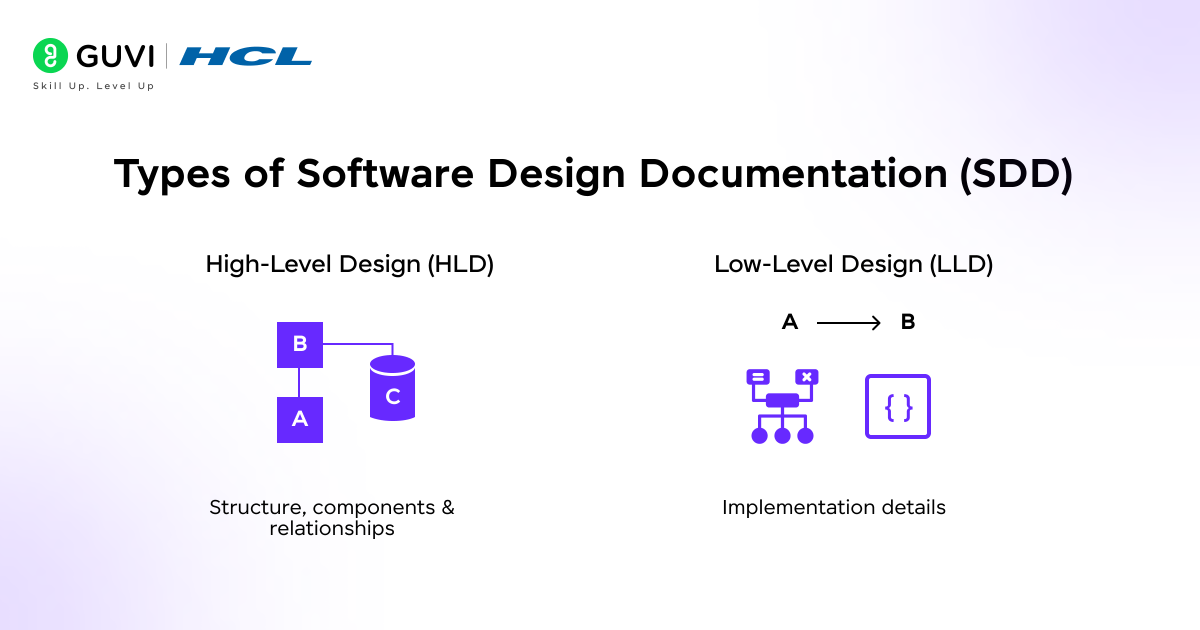
Cumulatively, we can categorize the Software Design Documentation (SDD) into two main types:
1. High-Level Design (HLD)
High-Level Design is an approach that focuses on the overall architecture of the software system, rather than concentrating time and effort on studying each component of the system. HLD is designed to demonstrate how the entire software will function and how data will flow through this interconnected system.
This design helps developers, solution architects, and business stakeholders gain clarity on the system’s scope before actual development begins. Through HLD, we can get specific about data storage mechanisms, fault tolerance, and how the complete system is planned for scalability and maintainability.
What it includes: Component services, Module interactions, Data flow navigation, external resource integration, and tech stack implementation.
Examples
- The HLD of an interactive and user-friendly e-commerce platform encompasses modules such as User Interaction Management, Product Catalog, Payment System, Notification System, Order Processing, and Real-time Tracking System.
- HLD for a highly complex and advanced banking system should encompass: User Credentials Management, KYC (Know Your Customer) System, Fund Transfer and Loan Processing Modules, and Customer Support.
2. Low-Level Design (LLD)
Low-level design is conducted to examine the working mechanism of each system component thoroughly. It involves learning all the essential implementation details, such as logic, data structures & algorithms, the internal workflow of each process, and the reaction of each component when it encounters any user event.
This design is created to eliminate all possible ambiguity, ensuring the feasibility of the development process in terms of technicality and cost-effectiveness. A Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram is one of the best examples of LLD; software developers create this intricate diagram to get a thorough visualization of code architecture and the operation of complex software functions.
What it includes: Module logic, Data structures and algorithms, Database Schemas, Class diagrams, Internal workflow, Error and exceptions handling.
Examples
- For an Appointment Scheduling Application, the LLD must include components such as slot selection, booking confirmation, regular reminder support, and query resolution through ticketing.
- The LLD for a Payment Gateway System should highlight the following vital elements: online transaction validation, logging, error handling, and database tables (including those for payment and user records).
Why Software Design Documentation (SDD) Matters
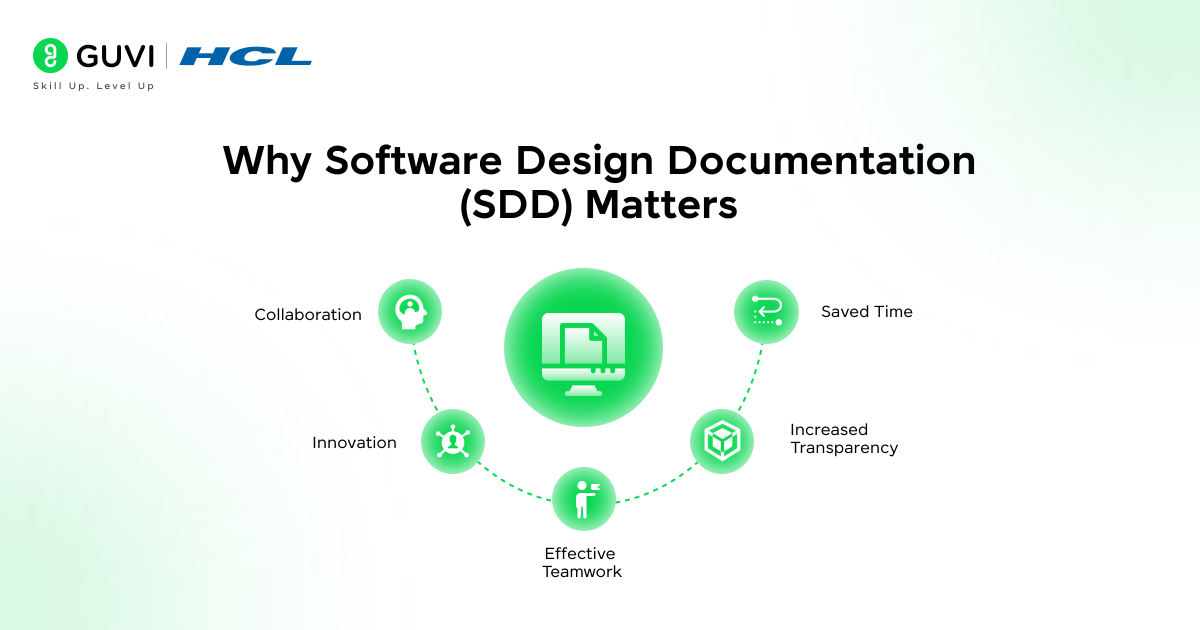
1. Importance of SDD
- Provides a clear and comprehensive roadmap that helps developers and testers follow best coding practices for building top-notch software products without confusion.
- It helps reduce the overall development budget by smartly identifying potential risks and security issues and resolving them with optimal resource allocations.
- It fosters team collaboration by allowing professionals with their core competencies to work closely together, while maintaining transparent communication.
- SDD significantly improves client relationships as it becomes easier to demonstrate to stakeholders how the development flow aligns with their business requirements and goals. Through the SDD, clients can be assured of their desired results.
- The SDD is created with respect to the evolving technological landscape. Purpose of this method is to make software applications and platforms future-proof, allowing them to undergo any transformations that require significant modifications.
2. Purpose of SDD
- It defines an effective system architecture that explains the working mechanism of different modular components of an application or platform and also describes the interconnectivity of multiple services.
- Incorporating SDD into the development life cycle helps bridge the gap between clients and the technical team, as it translates project ideation into a workable software solution.
- SDD clearly outlines the project scope, resulting in the avoidance of unnecessary tasks and additional development efforts, which leads to cost-effectiveness and meeting deadlines without delay.
- After the completion of High-Level Design (HLD), a strong foundation for Low-Level Design (LLD) is established, facilitating a seamless transition from conception to actual implementation.
- SDD supports traceability, which means design details of each modular component in the interconnected system can be traced back to their respective requirements to validate their existence.
3. Benefits/Advantages of SDD
- The overall productivity and efficiency level of developers, testers, and managers increases drastically, as SDD helps them detect flaws, areas for improvement, and saves them from making incorrect assumptions, which prevents expensive changes later.
- The system architecture is designed to consider all intricacies and aspects; as a consequence, the design serves as a reference for program execution, and the codebases become cleaner, modular, and easier to maintain.
- New members who join the technical team to work on specific projects don’t feel anxious and jumbled, as the SDD acts as a friendly companion and guidebook for them.
- SDD minimizes the cognitive load of developers by keeping track of every design decision and the rationale behind its inclusion, allowing developers to focus on solving complex problems and building features and functionalities that have a real-world impact.
- It also facilitates parallel work, allowing multiple team members to work on various services in a synchronized manner without diverting from the core objective. This methodology significantly contributes to accelerating the entire development process and eliminating stagnation.
Significance of Software Design Documentation (SDD) in Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Process
SDD is a crucial aspect of the SDLC process, created to serve both the technical team and business representatives by providing a clear and detailed plan of the system architecture and the execution process.
To reinforce our comprehension, let’s take a real-world example:
In a top product-based company (such as Amazon, Adobe, or ZOHO), the development team is tasked with designing and building a futuristic recommendation engine that incorporates all essential features.
Before beginning the code execution and tech implementation process, a Software Design Documentation (SDD) is prepared. In this insightful roadmap, various constituents, including system architecture (such as monolithic and microservices), different training models, data collection techniques, API (Application Programming Interface) integration, and the navigational flow of sensitive user and business data, are covered in detail. After inserting all the essential facets, the flowchart is prepared.
For instance, in this case, user events such as clicks, purchases, and browsing history are all captured in real-time and sent to the databases (or data warehouses) with all security parameters. In the databases, all this information is processed by algorithms, and the most optimal recommendations are served through a REST or GraphQL API to the frontend system. And through the frontend, the data is reflected on the screens. This ensures consistency and reliability in advance, even for designing and creating massive software systems that cater to millions of users.
Software Design Documentation (SDD) Guidelines and Best Practices
(Guidelines)
- Write clearly for both technical and non-technical readers.
- Include all key sections: architecture, modules, data flow, database, APIs, algorithms, security, performance, and error handling.
- Maintain consistent formatting, naming conventions, and diagrams.
- Link design elements to specific SRS requirements.
- Use diagrams (such as UML, flowcharts, and data flow diagrams) to simplify complex ideas.
- Follow standard templates to ensure structure and completeness.
(Best Documentation Practices)
- Start the SDD early after finalizing requirements.
- Review and validate with peers and stakeholders before coding.
- Keep it maintainable and updated by documenting decisions, trade-offs, and changes.
- Design modular, reusable components for scalability and future development.
- Specify security measures, performance targets, and error-handling strategies.
- Track versions to maintain document history.
How To Write Software Design Documentation (SDD)
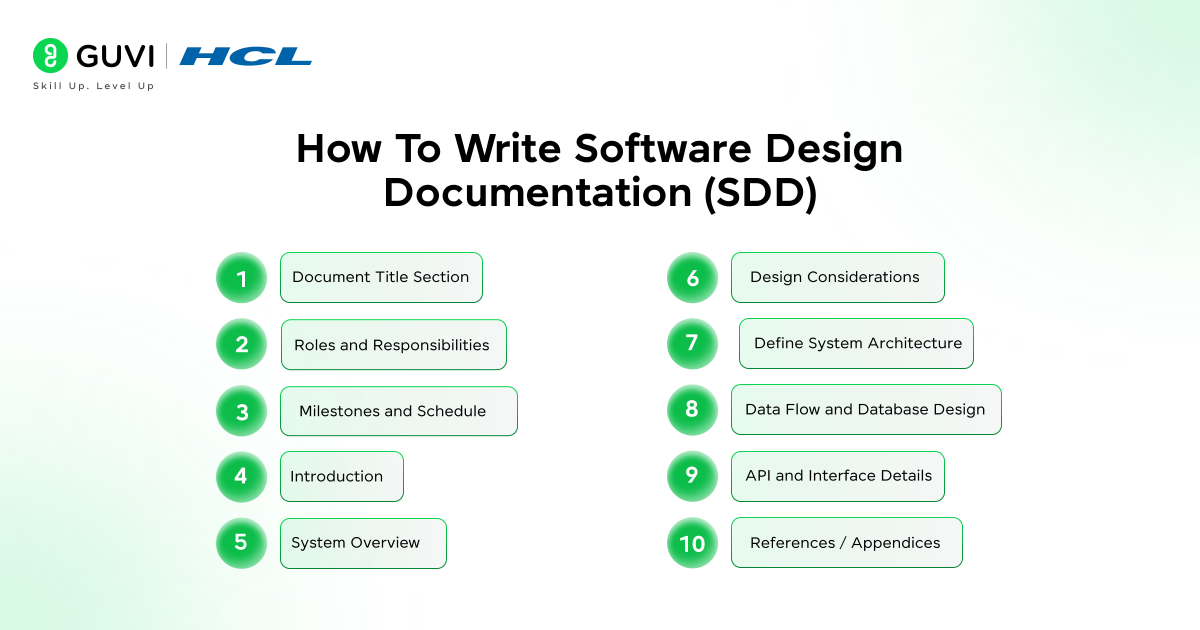
Here’s the standard composition of a software design document:
- Document Title Section
- Mention the name and title of the project.
- Include the names of authors and contributors.
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Define the responsibility for each module and task involved in the project.
- List all reviewers, approvers, and stakeholders who participated during the project planning process.
- Milestones and Schedule
- Mention the project deadlines and important dates when the different project implementation phases will be carried out.
- Introduction
- Clearly define the purpose behind creating the project.
- Explain the scope of the project.
- Briefly elaborate on key technical terms and acronyms from a reader’s point of view.
- System Overview
- Provide a meaningful description of the overall system.
- Mention all the key components included in the system.
- Design Considerations
- Clearly state the assumptions, dependencies, and all key constraints considered.
- Outline the risk mitigation techniques and methods.
- Define System Architecture
- Specify the type of internal architecture (layered, microservices, or monolithic).
- Diagrams showcasing module interactions and data flow.
- Data Flow and Database Design
- Explain how data moves between modules.
- Include database schema, tables, and relationships.
- API and Interface Details
- List API endpoints with request/response formats.
- Explain integration with other systems.
- References / Appendices
- Provide references to external resources, documentation, or standards.
- Add a glossary of terms if needed.
According to some research reports on open-source projects, software project development with clear design documentation and guidelines had 50% more active contributors than those projects that either didn’t have an SDD or had a vague one.
In today’s technological landscape, development is not just restricted to coding and developing software products. If we observe professionals who expand their technical knowledge, we will clearly find that they also give top priority to understanding the entire software architecture, which enables them to create SDDs without depending on others. So to transform yourself comprehensively into a proficient techie, join HCL GUVI ‘s IITM Pravartak & MongoDB certified AI Software Development course, where you also develop an in-depth understanding of High-level and Low-level Design (HLD & LLD) that are extensively used by top tech companies to build performant, maintainable, and scalable applications.
Conclusion
In this specific blog topic, we know what the actual earning of Software Design Documentation (SDD) is and why it is essential for the technical team (developers, testers, product managers) as well as business stakeholders in carrying out a successful development process. We also got an idea about Low-level design (LLD) and High-level design (HLD), along with understanding all the essential points that are required to create a high-quality SDD. I hope this blog has added value and provided you with a clear and comprehensive overview of SDD.
FAQs
What is a Software Design Document (SDD)?
A Software Design Document is a structured guide that explains the system’s architecture, components, data flow, and design decisions. It helps developers and stakeholders clearly understand how the software will be built.
Why is a Software Design Document important in software development?
It ensures alignment between teams, reduces development errors, and facilitates easier maintenance. Studies show that well-documented projects detect more defects early, resulting in both time and cost savings.
Who is responsible for creating a Software Design Document?
An SDD is usually prepared by software architects or senior developers. However, it’s a collaborative effort, with inputs from project managers, testers, and sometimes clients to ensure accuracy.
What key elements should a Software Design Document include?
An effective SDD contains system overview, architecture diagrams, module details, data structures, interfaces, non-functional requirements, and references to related documents.



































Did you enjoy this article?