What Is Ethernet in Computer Network?
Feb 11, 2026 5 Min Read 1021 Views
(Last Updated)
Every time you plug a LAN cable into your laptop or PC and the internet starts working instantly, there is a powerful technology making it happen. That technology is Ethernet, and it is one of the most trusted ways to build a wired network. It offers fast speed, stable connections, and secure data transfer, which is why it is used everywhere from homes and offices to schools, labs, and large data centers.
For beginners, understanding Ethernet in computer network systems is important because it is the backbone of most wired communication. It allows multiple devices to share data smoothly using simple cables and well-defined rules. Whether you are learning networking, setting up a small network, or planning to work in IT, knowing how Ethernet works gives you a strong foundation.
In this blog, we will explore what Ethernet really is, how it works, the different types of Ethernet, where it is used, and the advantages it offers. By the end of this blog, you will clearly understand the role of Ethernet in computer network communication and how it helps create fast and reliable connections in the real world.
Table of contents
- What Is Ethernet?
- Importance Of Ethernet In Networking
- How Ethernet Works
- Types Of Ethernet
- Fast Ethernet
- Gigabit Ethernet
- 10 Gigabit Ethernet
- Fiber Ethernet
- Ethernet Cables And Connectors
- Advantages Of Ethernet
- Disadvantages Of Ethernet
- Real-World Applications Of Ethernet
- Ethernet vs Wi-Fi
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the main purpose of Ethernet in a computer network?
- Is Ethernet always faster than Wi-Fi?
- What cable is best for home Ethernet?
- Can Ethernet work without a router or switch?
- Do all laptops support Ethernet?
What Is Ethernet?
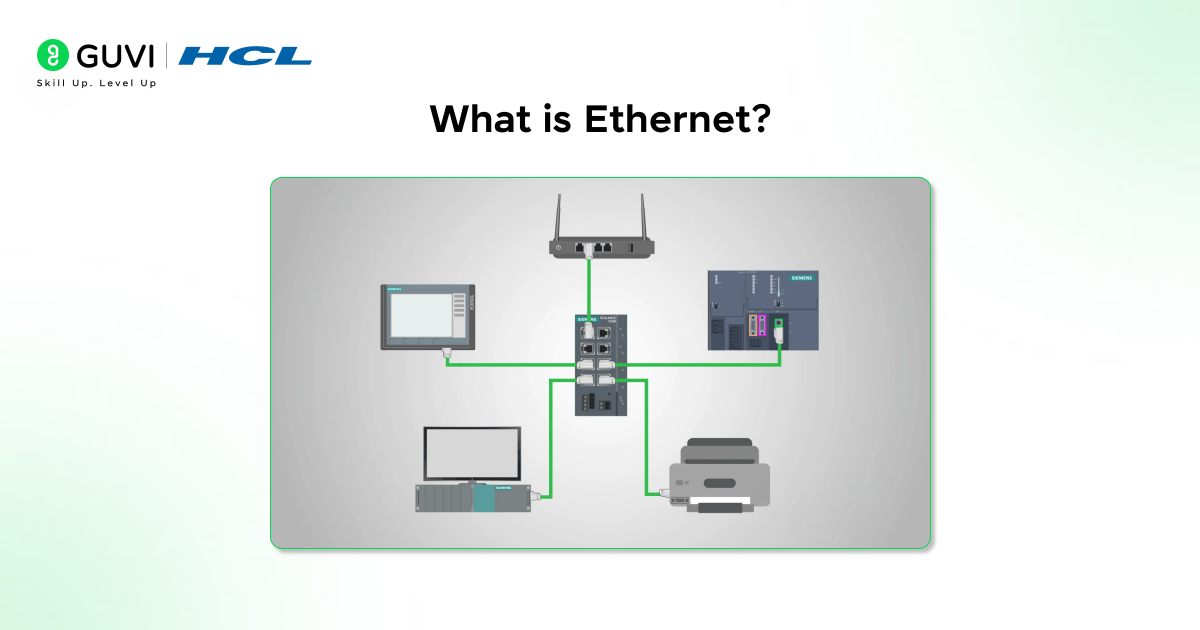
Ethernet in computer network systems works through a set of important features that control how data is sent, received, and identified across devices. These features make Ethernet fast, reliable, and widely used in homes, offices, and data centers. Below are the key features that explain how Ethernet functions most simply:
- Wired Communication:
Ethernet connects devices using physical cables, which keeps the connection stable and free from sudden signal drops. - Ethernet Frames:
Information is sent in small, structured packets called frames, helping data move safely and efficiently across the network. - Unique MAC Address:
Every device has its own MAC address, acting like a digital identity, so data always reaches the correct destination. - Switch-Based Forwarding:
Switches read MAC addresses and send data only to the intended device, improving speed and reducing unwanted traffic. - Low Interference:
Because signals travel through cables, Ethernet faces very little interference, which keeps communication smooth and predictable. - High-Speed Performance:
Ethernet supports fast and consistent speeds, making it ideal for gaming, streaming, video calls, and large file transfers.
Importance Of Ethernet In Networking
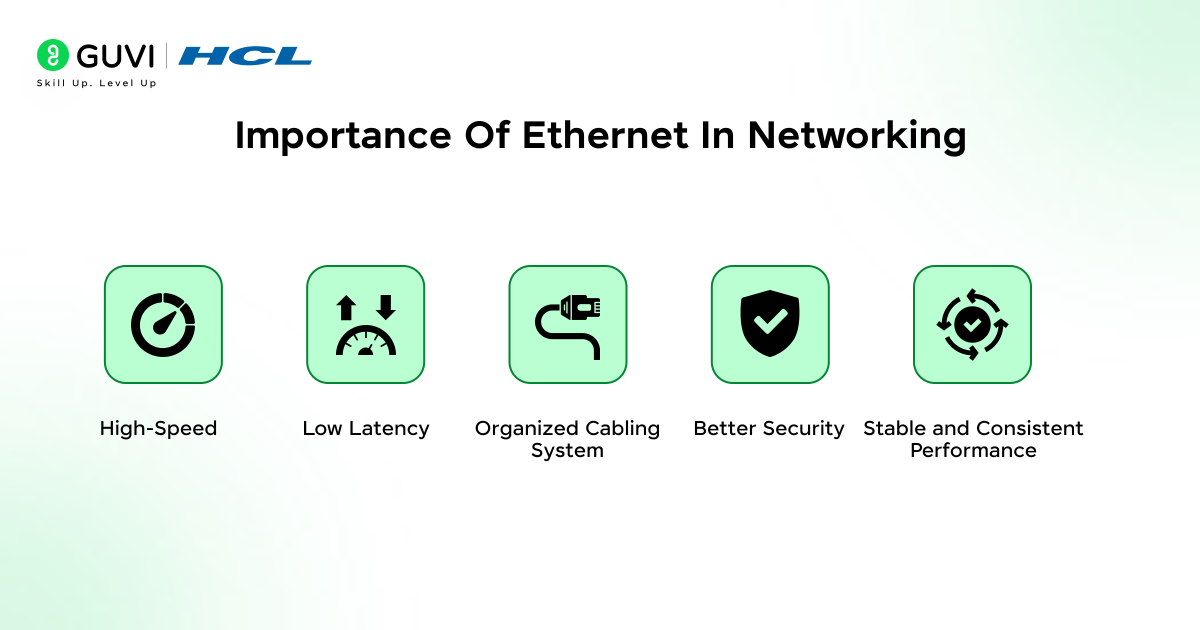
Ethernet plays a crucial role in modern networking because it offers a reliable and high-performance way for devices to communicate. In most setups, Ethernet in computer network environments is trusted for stability, security, and predictable speed. The following features explain why Ethernet remains important today:
- High-Speed Data Transfer:
Ethernet supports fast data movement, making it suitable for everyday tasks as well as heavy activities like cloud access and large file transfers. - Low Latency:
It reduces delays in data transmission, which is essential for real-time tasks such as gaming, video calls, and live streaming. - Organized Cabling System:
Ethernet uses structured cabling that keeps networks neat, scalable, and easy to maintain. - Better Security:
Wired connections are harder to interfere with, giving Ethernet stronger security compared to wireless networks. - Stable and Consistent Performance:
Since signals travel through cables, Ethernet delivers fewer interruptions and more predictable performance.
Because of these strengths, Ethernet continues to be the backbone of corporate networks, educational campuses, data centers, and high-performance computing environments.
How Ethernet Works
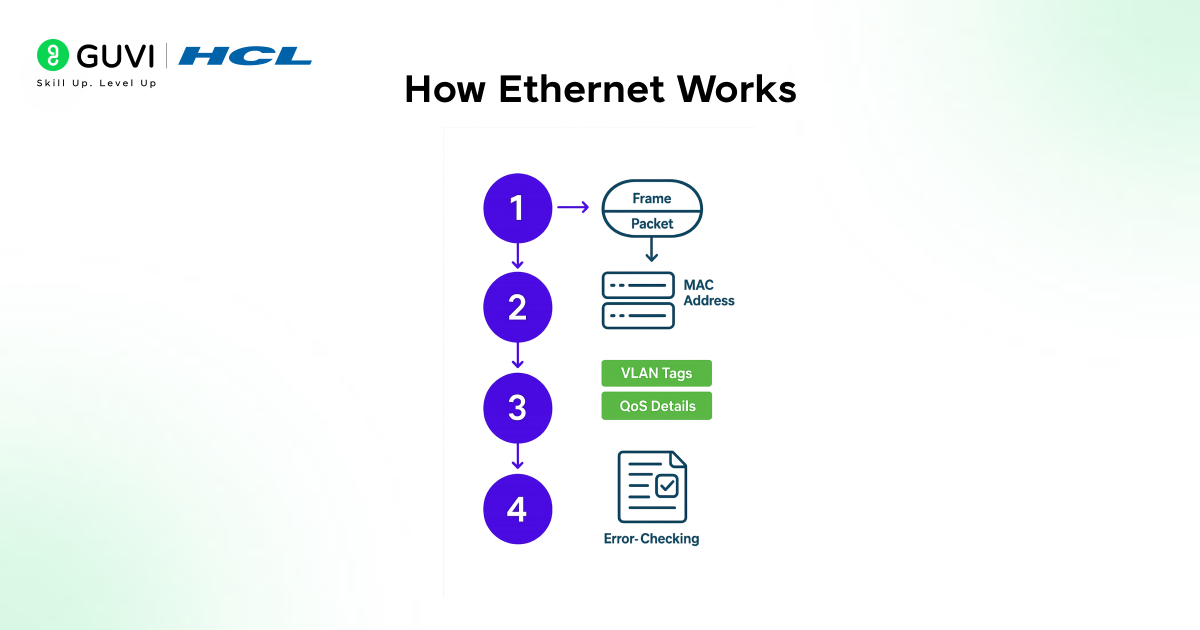
Ethernet in computer network systems works through a clear and organized communication process that allows devices to exchange data smoothly. Instead of sending information randomly, Ethernet follows a structured method that prepares data, labels it correctly, sends it through cables, and delivers it to the right device. Understanding how Ethernet works step by step makes it easier to see why it is one of the most reliable and widely used networking technologies today.
- Step 1: Data Is Prepared
When a device wants to send information, the data is first organized and prepared for transmission. - Step 2: Data Is Put Into Frames
The information is divided into small units called Ethernet frames. These frames make the communication structured and reliable. - Step 3: MAC Addresses Are Added
Each frame gets two MAC addresses:
one for the sender and one for the receiver.
This ensures the data reaches the right device. - Step 4: The Frame Is Sent Through a Cable
The frame travels through an Ethernet cable such as Cat5e, Cat6, or fiber. Cables keep the signal strong and stable. - Step 5: Switch Receives the Frame
The switch reads the destination MAC address and decides which device should receive the data. - Step 6: Frame Is Forwarded Correctly
The switch sends the frame only to the correct device, avoiding unnecessary traffic. - Step 7: Device Receives and Reads the Data
The receiver takes the frame, checks it for errors, and then extracts the data for use. - Step 8: Collision Handling (Older Ethernet Only)
In older systems, CSMA/CD helped manage collisions when two devices tried sending data at the same time. - Step 9: Collision-Free Communication (Modern Ethernet)
Modern switched Ethernet avoids collisions entirely by giving each device its own communication path.
These simple steps explain how Ethernet creates smooth and reliable communication in both small LANs and large enterprise networks.
Types Of Ethernet
Ethernet in computer network systems comes in multiple versions, each designed to handle different speed levels and performance needs. The four major types of Ethernet you will commonly come across are:
- Fast Ethernet
- Gigabit Ethernet
- 10 Gigabit Ethernet
- Fiber Ethernet
These types evolved to support greater bandwidth, better efficiency, and higher reliability. Below, each type is explained in detail to help you understand where and how it is used.
1. Fast Ethernet
Fast Ethernet was introduced as an improvement over the older 10 Mbps Ethernet. It helped networks handle more users and heavier data usage without slowing down. This made it extremely popular in schools, offices, and early LAN setups.
Features:
- Speed: Supports up to 100 Mbps, which was a major upgrade from the 10 Mbps era.
- Cables Used: Works with Cat5 or Cat5e cables.
- Standards: Includes versions like 100BASE-TX (copper) and 100BASE-FX (fiber).
- Usage: Suitable for basic networking needs such as internet browsing, printing, and file sharing.
2. Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet became the standard choice for most home and office networks because it offers much faster performance. As internet usage grew, streaming, cloud usage, and large file transfers became common, and Gigabit Ethernet handled all of these smoothly.
Features:
- Speed: Provides up to 1 Gbps (1,000 Mbps), giving a noticeable speed boost.
- Cables Used: Uses Cat5e, Cat6, or fiber optics.
- Common Devices: Found in Wi-Fi routers, switches, computers, and servers.
- Usage: Ideal for high-speed browsing, HD/4K video streaming, backups, and cloud applications.
3. 10 Gigabit Ethernet
10 Gigabit Ethernet is designed for environments that require extremely fast and uninterrupted communication. Businesses dealing with huge amounts of data rely on it for its high capacity and reliability.
Features:
- Speed: Offers 10 Gbps, ten times faster than standard Gigabit Ethernet.
- Cables Used: Works with high-performance cables like Cat6a, Cat7, or fiber optics.
- Usage: Common in data centers, enterprise servers, and high-performance computing setups.
- Best For: Virtual machines, databases, big data processing, and cloud infrastructure.
4. Fiber Ethernet
Fiber Ethernet uses light instead of electrical signals, making it the fastest and most advanced form of Ethernet. It is used where speed, long distance, and noise-free communication are essential.
Features:
- Speed: Can deliver speeds from 1 Gbps up to 100+ Gbps.
- Interference-Free: Completely immune to electromagnetic noise, providing clean and stable communication.
- Long Distance: Supports connections across buildings, campuses, cities, and even international networks.
- Usage: Used by internet service providers, cloud companies, universities, and large enterprises.
Ethernet Cables And Connectors
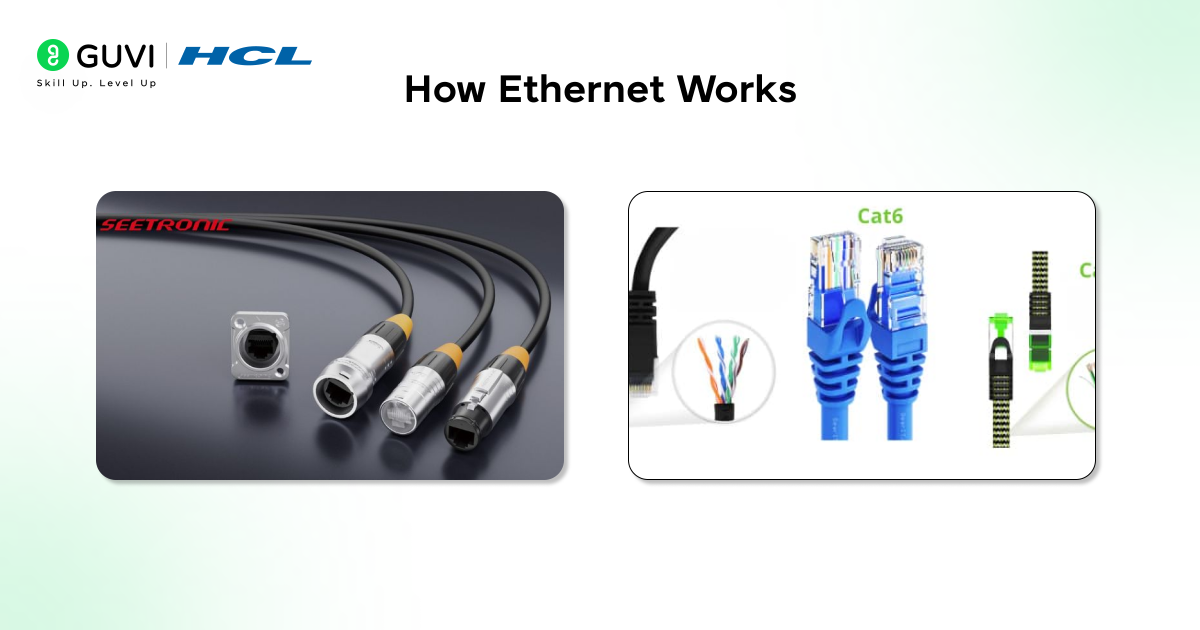
Ethernet communication relies heavily on the type and quality of cables used, because each cable category supports different speeds, bandwidths, and use cases. Choosing the right cable ensures reliable connectivity and consistent network performance. Below are the commonly used Ethernet cables and connectors:
- Cat5e – Ideal for standard home networks and supports up to 1 Gbps speeds.
- Cat6 – Offers better performance, reduced interference, and stable Gigabit speeds.
- Cat6a / Cat7 – Designed for high-speed environments, supporting higher bandwidth and longer-distance performance.
- Fiber Cables – Used for ultra-fast communication across long distances with minimal signal loss.
- RJ45 Connectors – The standard connector used to terminate most Ethernet copper cables.
Advantages Of Ethernet
Ethernet remains one of the most preferred networking options because it delivers consistent, predictable, and secure performance. Its wired nature helps it avoid common issues seen in wireless networks, making it suitable for both home and enterprise setups. Key advantages include:
- High Reliability – Offers stable connectivity with very few interruptions.
- Faster Performance – Delivers greater speed than most Wi-Fi connections.
- Low Interference – Wired signals are unaffected by walls, distance, or radio noise.
- Stronger Security – Only devices physically connected can access the network.
- Easy Scalability – Networks can grow effortlessly by adding more switches and cables.
Disadvantages Of Ethernet
While Ethernet provides strong performance and stability, it also comes with certain limitations that may affect flexibility and setup convenience. These drawbacks mainly arise from its wired nature and installation requirements. Key disadvantages include:
- Requires Physical Cabling – Every connected device needs its own cable.
- Limited Mobility – Devices cannot move freely like they can on Wi-Fi.
- Challenging Installation – Running cables across large buildings can be difficult.
- Higher Upgrade Costs – Improving speed may require new cables or ports.
Real-World Applications Of Ethernet
Ethernet plays a vital role in powering modern connectivity across a wide range of environments. Because of its speed, stability, and security, it has become the default choice for both everyday and professional networking needs. Some of the most common real-world applications include:
- Home Networks – Used for PCs, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and streaming devices.
- Office LANs – Enable secure, fast, and reliable communication between employees and systems.
- Data Centers – Connects servers, storage systems, and high-performance computing setups.
- Industrial Automation – Powers smart factories, robotics, and machine-to-machine communication.
- Educational Institutions – Supports computer labs, e-learning systems, and campus-wide networks.
Ethernet vs Wi-Fi
| Aspect | Ethernet (Wired) | Wi-Fi (Wireless) |
| Speed | Faster and more consistent | Can vary depending on distance and interference |
| Stability | Very stable, no signal drops | Less stable due to obstacles and signal noise |
| Security | More secure (physical access needed) | Vulnerable to wireless attacks if not protected |
| Mobility | Limited — device must stay connected by cable | High mobility — move around freely |
| Best For | Desktops, servers, smart TVs, gaming, office LANs | Smartphones, tablets, laptops, portable devices |
| Interference | No interference (wired) | Can be affected by walls, devices, and other signals |
| Installation | Requires cables and sometimes setup effort | Quick and cable-free |
Conclusion
Ethernet in computer network systems continues to be one of the strongest foundations of modern connectivity. In this blog, we explored what Ethernet is, why it is important, how it works, its different types, cables, connectors, advantages, disadvantages, real-world uses, and how it compares with Wi-Fi. These insights help you clearly understand how Ethernet supports reliable communication in homes, offices, schools, and large data centers.
With this knowledge, you can now make better choices when setting up or upgrading a wired network. If you want to take your learning further and build deeper skills in switching, routing, and advanced networking, you can explore HCL GUVI’s Mastering Advanced Networking Concepts Course. This will help you grow confidently into more advanced areas of computer networking and strengthen your career in the tech domain.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of Ethernet in a computer network?
The main purpose of Ethernet is to help devices within a LAN communicate efficiently using a stable and structured wired connection.
2. Is Ethernet always faster than Wi-Fi?
In most cases, yes. Ethernet provides higher speed and better reliability because it uses cables and avoids wireless interference.
3. What cable is best for home Ethernet?
For regular home use, Cat5e works well, while Cat6 is recommended if you want faster speeds or plan for future upgrades
4. Can Ethernet work without a router or switch?
Two devices can be connected directly using an Ethernet cable, but a switch is required when you want multiple devices to communicate.
5. Do all laptops support Ethernet?
Many modern slim laptops don’t include an Ethernet port, but you can still connect using a USB-to-Ethernet adapter.































Did you enjoy this article?