
Top 40 Operating System Interview Questions and Answers for 2025 (Basic to Advanced)
Nov 26, 2025 7 Min Read 1933 Views
(Last Updated)
One of the significant topics every candidate must prepare for is Operating System Interview Questions for technical interviews. In general, whether you apply for a software engineering, data analyst, or system administrator role, having an understanding of operating systems is critical. These questions will not only assess the depth of your theoretical knowledge but, additionally, also help you understand how computer systems operate from the inside-out.
This blog will take you through 40 thoughtfully selected Operating System Interview Questions in three categories: basic, intermediate, and advanced so you can feel fully prepared for the next interview.
Table of contents
- Basic Operating System Interview Questions
- Intermediate Operating System Interview Questions
- Advanced Operating System Interview Questions
- Wrapping It Up:
- What are frequently asked questions in an Operating System Interview?
- How do I get ready for Operating System Interview Questions?
- Do Operating Systems Interview Questions come up for freshers?
- What is the best way to answer Operating System Interview Questions?
Basic Operating System Interview Questions
The section below will cover some operating system interview questions in basic concepts that all interviewees should be familiar with, regardless of experience level.

1. What is an Operating System, and what does it do?
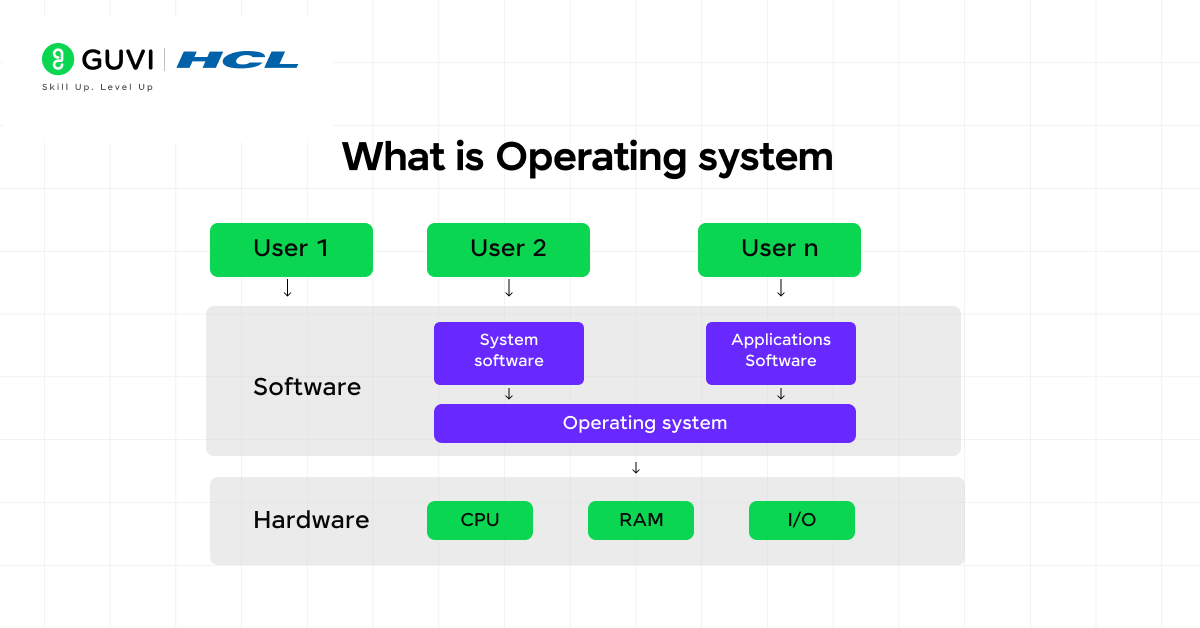
Operating systems are pieces of system software that provide an interface between the end user and the hardware. An Operating System is responsible for managing a device’s resources (memory, CPU, storage) as well as allowing applications to be used in an intuitive way. Otherwise, a computer is useless to the end user as it would not be able to execute programs.
Also read: Introduction to Operating Systems
2. What are the basic functions of an Operating System?
An operating system will carry out several different tasks, including going between processes (process management), memory management, file system management, input and output services, and device management. All of these components must function together and can be managed within the operating system. These functions of an operating system are what truly bring an operating system to life and make it the heart of any computing system.
3. What is the difference between a process and a program?
A program is a set of instructions, which is stored either wholly or in part on disk, while a process is an instance of a program that is executing (running) in memory. Each process has defined memory space associated with it, and each process contains a state. This difference is important to Operating System Interview Questions because it provides the basis for several ideas (multitasking and concurrency, for example).
4. What is a thread and how is it different from a process?
A thread is a lightweight sub-unit of a process that allows multiple threads to run at the same time and it runs in the same memory address space as the process. Threads exist in shared memory while processes are independent of each other. Threads can be more efficient with communication because they can directly access shared memory, but generally are more dangerous if not managed correctly. It is crucial to fully understand the difference between threads and processes in order to make the system run more efficiently.
Also read: Understanding Program, Process, and Thread in Operating Systems
5. What is multitasking in an operating system?
Multitasking allows multiple processes or threads to run at the same time to give the illusion of being parallel. This is performed by time-sharing or allowing the CPU to switch from one process to another very fast. Multitasking is one of the fundamentals that allow a modern system to provide a responsive system as well as an efficient system.
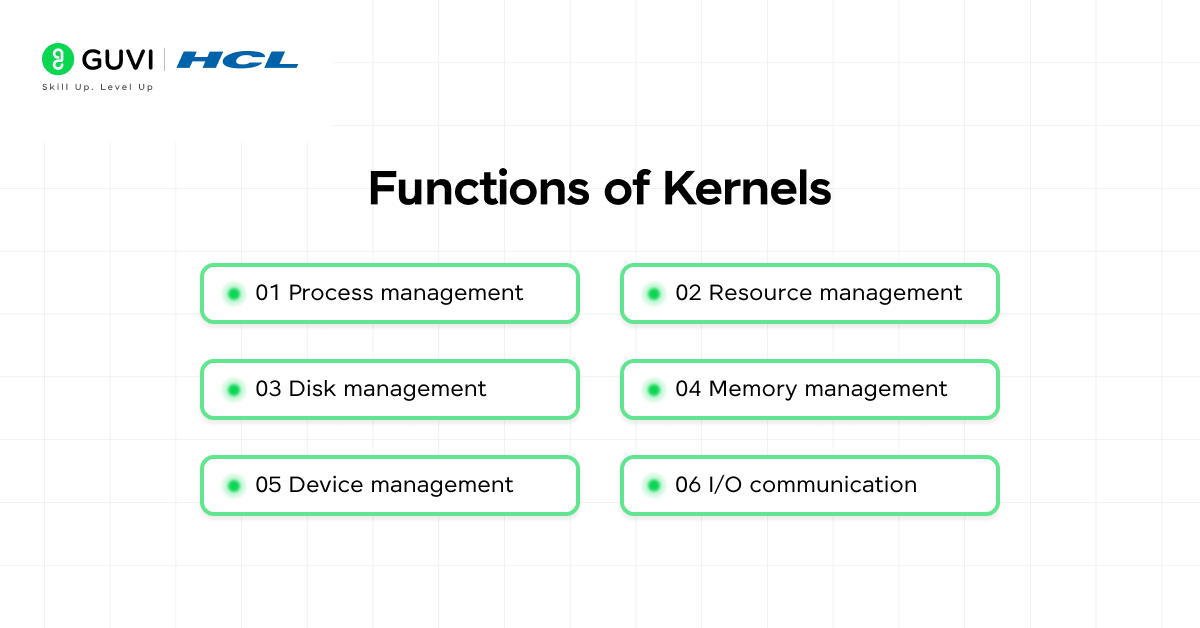
6. What is a kernel and what types of kernels are there?
The kernel is the central program in the operating system that manages basic hardware and system calls. There are two main types of kernels, monolithic and microkernels. Monolithic kernels have all operating system services in one location, while microkernels split services to user space to provide better security and stability.
9. What is an interrupt, and how does the OS respond to it?
An interrupt causes the CPU to stop what it’s currently doing and handle some sort of event, like input from a keyboard, the completion of an I/O operation, or some other event. The OS first saves the state of the process that was running, then executes the related interrupt service routine, before returning the CPU to its normal operations. Interrupts are an essential mechanism of responsive computing.
10. What is a system call?
System calls provide a controlled interface between the user programs and the OS kernel. For example, when a file is read or written, it happens through system calls. System calls ensure all hardware is accessed safely and efficiently.
Also read: The Process of Application Execution in Computer Systems Explained
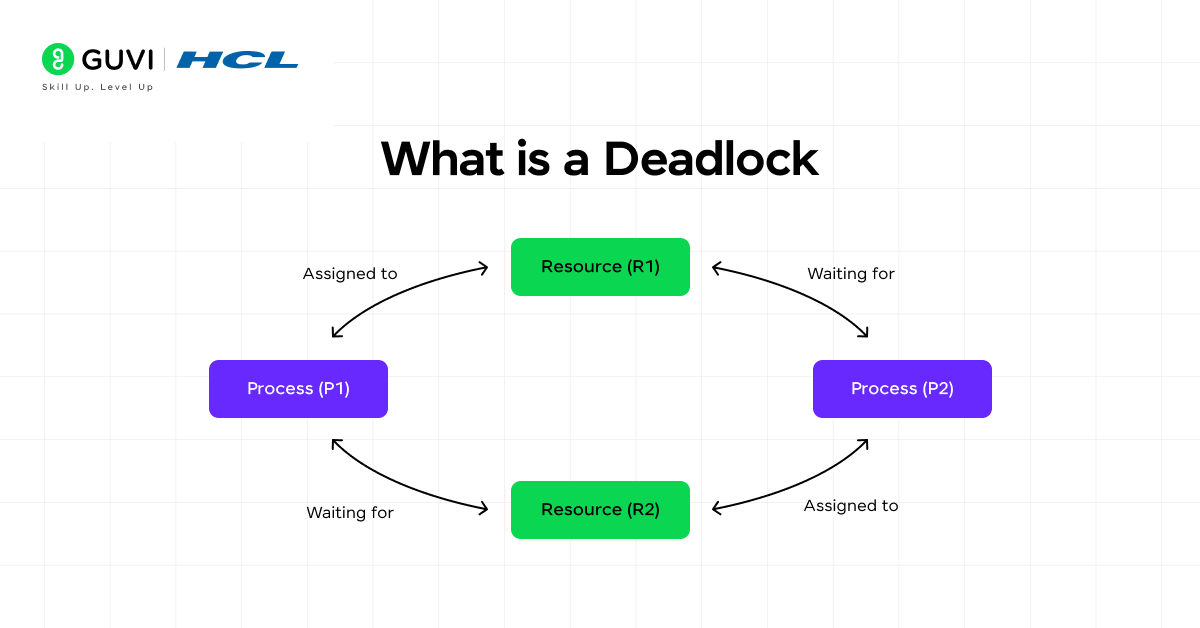
11. What is a deadlock in an OS?
A deadlock occurs when multiple processes are each waiting on other processes to release resources, none of the processes will ever run again. Deadlocks occur under four conditions: mutual exclusion, hold-and-wait, no preemption, and circular wait. Knowing how to detect and prevent deadlocks is important for OS-related interview questions.
12. What is process scheduling?
Process scheduling is the program used to decide which process will utilize the CPU in order to carry out its instructions at a specific time. Scheduler algorithms, such as FCFS, Round Robin, and Priority Scheduling, are used for this purpose. The goal of scheduling is to make sure that processes are treated with fairness while optimizing CPU utilization.
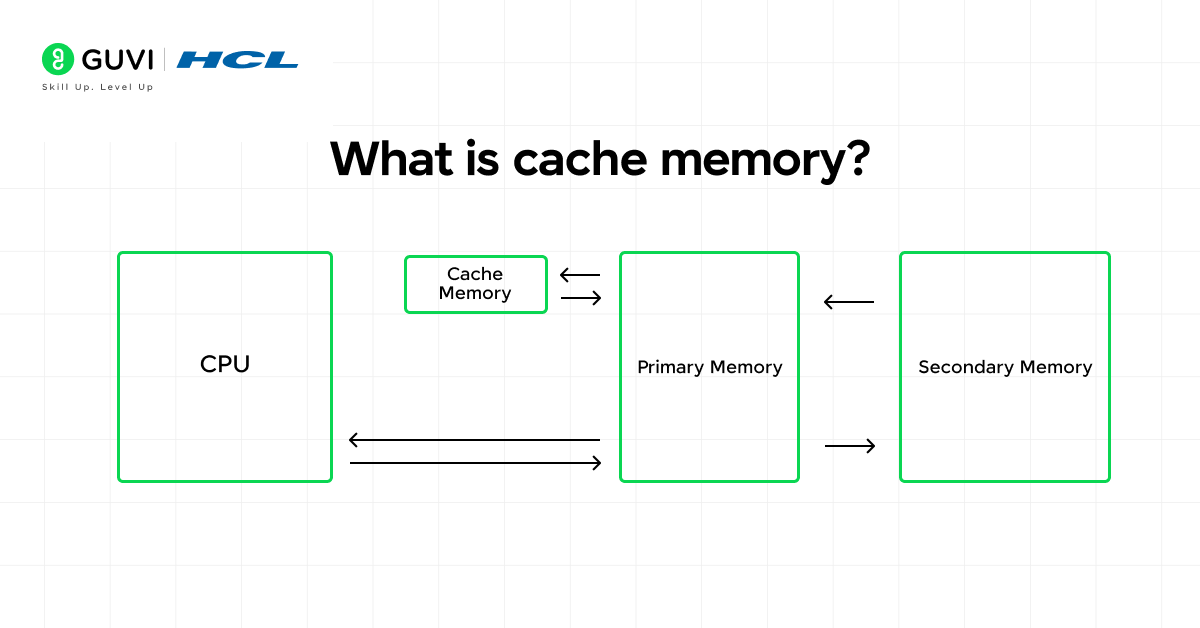
13. What is the difference between primary and secondary memory?
Primary memory (also called Main Memory), such as RAM, is volatile and directly interactable by the CPU, meaning the data in primary memory disappears when power is lost. Secondary memory, such as hard drives, is non-volatile and resorted to when files and data need to be stored. Learning the difference between primary and secondary is helpful for understanding questions regarding system architecture.
14. What is a file system?
A file system organizes the actual data inside the disk drives and is responsible for creating, deleting and regulating access to all files for the user. Without a file system in place, all data would just be an unorganized maze of information, which would make it very inconvenient to retrieve information upon request.
Also read: Full Stack Developer Roadmap: A Complete Guide [updated]
15. What is cache memory?
Cache memory is a small, high speed memory close to the CPU that caches the data the CPU needs regularly so the CPU can run its instructions faster. Most Operating System Interview Questions discuss cache memory in the context of performance optimization.
Intermediate Operating System Interview Questions
Intermediate-level questions check your understanding of processes, memory, and system management.
16. What is the difference between user-level and kernel-level threads?
User-level threads are managed by user-level libraries without kernel knowledge, while kernel-level threads are managed by the kernel. Kernel threads give better response time from turning around and executing, but there is a higher cost because of the overhead of getting back to executing the thread over context switches.
17. What is context switching?
Context switching occurs when the CPU changes from one process or thread to another, which means the current process state is saved and a new process state is loaded. Context switching enables multitasking; however, overhead comes with it, affecting performance. If the operating system has to do it often, a slowdown is likely.
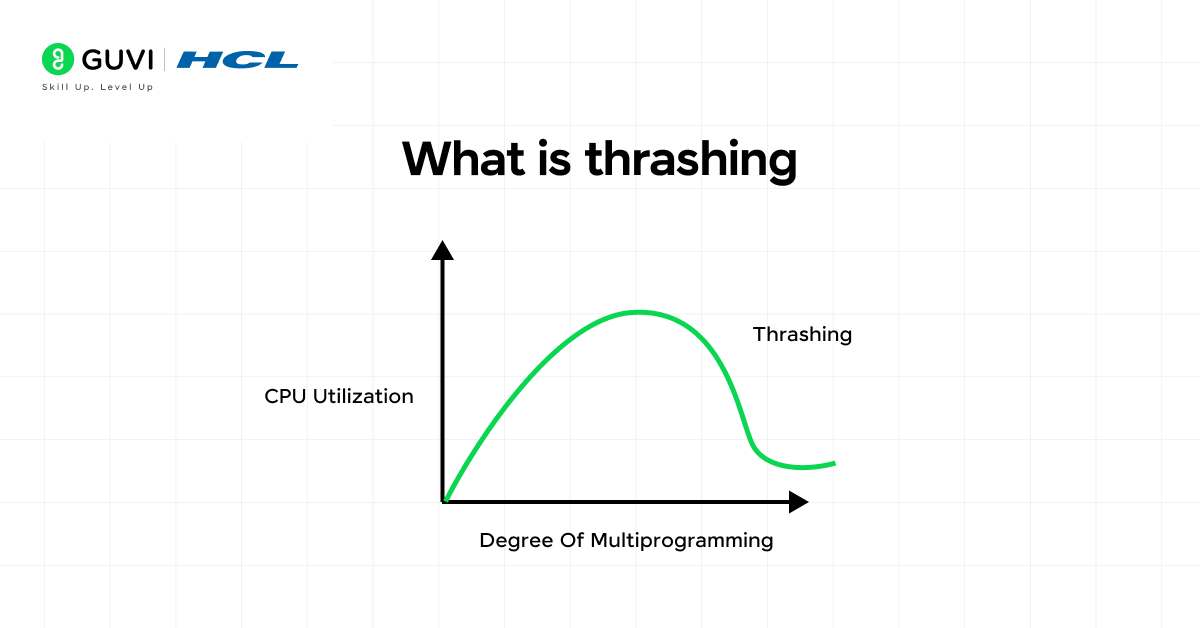
18. What is thrashing in an operating system?
Thrashing occurs when the system executes swapping a page in and a page out of memory more than doing any processing. This happens when the system runs out of memory because the processes want more than the memory can support. The simplest way to get the system out of thrashing is to combine processes or balance workloads.
Also read: Critical Section Problem in OS (Operating System)
19. Explain CPU scheduling algorithms.
The operating system has several scheduling algorithms to manage CPU time like FCFS, SJF, Round Robin, etc. Each of these serves a different use case (i.e., FCFS is the simplest, SJF is often the best in terms of wait time on average, Round Robin, for fairness, and so on). Which CPU scheduling algorithm a developer chooses impacts the responsiveness of the operating system.
20. What distinguishes paging from segmentation?
Paging is a way of organizing memory space into fixed-size chunks while segmentation separates it logically based on functionality. Paging helps eliminate fragmentation and segmentation allows us to represent the structure of a program better.
21. How does the operating system allocate memory?
The OS keeps track of free or used memory using techniques such as bitmap or linked lists. Then, it will allocate to processes that need memory and reclaim the memory afterward. It is important to manage memory efficiently to not run out of memory and crash the system.
Also read: 9 Compelling Project Ideas for Frontend Development [With Source Code]
22. What are inter-process communication methods?
Processes communicate using any of the mechanisms such as pipes, message queues, shared memory, and sockets. With IPC methods, data can be shared and processes can synchronize with each other regardless of running on the same or different machines.
23. What is a semaphore, and how is it used?
A semaphore is a synchronization that is used to control access to resources. Semaphores prevent race conditions by allowing only oone process at a time to access a critical section
24. What is a page replacement algorithm?
When the physical memory is full, the operating system will replace an old page with a mechanism, such as FIFO, LRU, or Optimal Replacement. The goal being to minimize page faults and improve the operation of the system.
25. Distinguish between virtual and physical address space.
Virtual address space is designated for application use, while the physical address space refers to actual memory. The operating system uses page tables to convert virtual addresses into physical addresses while providing process isolation and security.
26. What is the procedure of booting?
Booting is the process of loading the operating system into memory after turning on the computer. The BIOS/UEFI loads the bootloader, which loads the kernel, thus enabling the loading of system processes. The booting process initiates all components of the system before user interaction.
27. How are the Device Drivers managed by OS?
Device driver is a translator between the hardware and software. An OS will load a device driver when a hardware component is called into the OS for functionality. It is efficient for the OS layer and provides a secure communication channel to the device itself.
Also read: Important CSS Interview Questions and Answers
28. Distinguish between monolithic kernels and microkernels?
A monolithic kernel is a single piece of software that is often referred to as non-microkernel; it has all of its services in a single layer. A monolithic kernel can offer high performance, but, it is less stable and has a greater risk of failure. A microkernel is one in which services are separated into user space. A microkernel can produce a higher degree of reliability subject to reduced performance of the OS.
29. What is the difference between internal and external commands in OS?
Internal commands are those commands that are hard-coded in the command interpreter, while external commands exist as separate executable files. Understanding this can help you understand how the shell and OS commands interact.
30. How does an OS prevent deadlock?
Deadlocks can be prevented by eliminating one of the four necessary conditions. Techniques include resource ordering, preemption, or using algorithms like Banker’s Algorithm to maintain a safe state.
Advanced Operating System Interview Questions
31. What is Belady’s anomaly?
Belady’s anomaly refers to the situation in which increasing the number of page frames results in an increase in the number of page faults. Such a situation appears to stem from the use of FIFO algorithms, demonstrating that you can’t always improve performance by using more resources.
32. What is a zombie and orphan process?
A zombie process is one that has finished executing, but is still in the process table. An orphan process is one for which the parent has finished executing. Any orphan processes are “adopted” by init as a clean up mechanism.
Also read: Top 5 Full Stack Development Certification Courses in 2025
33. How does the Operating System protect memory?
The OS uses techniques such as base and limit registers, paging, and segmentation to isolate the memory of each of the processes. This protects one process from corrupting the data of another process, and keeps the system stable.
34. What is the difference between synchronous and asynchronous I/O?
Synchronous I/O waits for the request to complete before continuing execution, whereas asynchronous I/O will allow the CPU to execute additional requests while waiting for the request to be executed. Asynchronous operations can increase the overall efficiency of the system particularly in multitasking systems.
35. What is a Real-time Operating System (RTOS)?
An RTOS guarantees a specified response time, and is used in time-critical situations such as robotics, and embedded systems. An RTOS is use in time-critical applications, which is based more on determinism than to throughput as general-purpose OS was intended to.
36. What is demand paging?
Demand paging loads pages into memory only as they are demanded and decreases the page load time. On the other hand, demand paging may create a higher page fault rate if the pages are ever accessed in an irresponsible way.
Also read: Salary of a Full Stack Developer in India in 2025
37. How does the OS manage multicore scheduling?
Most OSes today manage scheduling to allow a task to be divided into threads which are assigned to the cores to run in parallel. The OS may manage load balancing between cores, cache locality and ensure that threats do not contend for resources.
38. What is virtualization?
Virtualizing technology allows multiple operating systems to run on the same hardware platform through the use of hypervisors. This type of technology ultimately improves resource utilization and scalability, becoming a common focus in operating system interview questions.
39. What is a memory-mapped file?
A memory-mapped file maps a file into the process’s memory address space. Memory mapping allows for efficient I/O by mapping files, for inter-process communication (IPC) or generally for large sets of data in files.
40. How does an OS manage security and protection?
The OS will implement user-allowed permissions, access-control lists, and transmission isolation between user space and kernel space. These act as safeguards against exploitation or malicious attack while managing system integrity.
Join HCL GUVI’s AI Software Development Course – IITM Pravartak & MongoDB and gain hands-on experience in building intelligent applications. Learn from industry experts, work on real projects, and fast-track your journey toward becoming a skilled AI developer.
Wrapping It Up:
For any technical position, preparing for Operating system Interview Questions is critical. In this blog, we’ve covered 40 operating system questions from a basic level (e.g. processes and memory management) to an advanced level (e.g. virtualization and real-time systems). The key to mastering operating systems is to understand the reasoning behind each mechanism rather than memorizing the definitions. With consistent practice and conceptual clarity, you’ll be well-prepared to handle any OS-related question in your next interview.
1. What are frequently asked questions in an Operating System Interview?
Questions that are often asked in an Operating System Interview includes areas like process management, memory management, CPU scheduling, virtual memory, and deadlocks.
2. How do I get ready for Operating System Interview Questions?
Start with understanding the context of the minimum requirements of your Operating Systems knowledge, and then some problem-solving, and even think about some real-life examples. There are always going to be some theory-based questions, and application-based questions.
3. Do Operating Systems Interview Questions come up for freshers?
Yes! Many interviewers will ask OS questions in their interviews for freshers to see if you have some understanding of system requirements, it also shows you have some understanding of computer architecture.
4. What is the best way to answer Operating System Interview Questions?
Keep your answers short, structured, and with some examples around your experiences. Interviewers would like you to be clear and show good understanding and reasoning rather than just memorization.



































Did you enjoy this article?