
Machine Learning Pipeline Explained: Beginner to Pro Guide
Sep 22, 2025 6 Min Read 1769 Views
(Last Updated)
When it comes to machine learning, a lot of people immediately think of algorithms. However, the story really starts much earlier, with the data. Data isn’t always neat and ready ot use. It is often very messy, has missing values, and is scattered across different places. In order to make sense of it all and use the data, we need a clear process. A systematic process, a structured workflow that converts raw data into useful insights. And this structured workflow is known as the machine learning pipeline.
If you are someone who are just starting out, understanding the pipeline is crucial. It lets you know how ML projects go from raw data to real-world application. In this blog we’ll cover each step of the machine learning pipeline in simple terms. By the end of this blog, you will not only understand about the ML pipeline but you can build one on your own.
Table of contents
- What is the Machine Learning Pipeline?
- Understanding the Machine Learning Workflow
- Stages of a Machine Learning Pipeline
- Data Collection
- Data Validation
- Data Preprocessing
- Feature Engineering Pipeline
- Model Training
- Model Evaluation
- Model Deployment
- Monitoring and Maintenance
- Essential ML Pipeline Tools
- Data Processing Tools
- Pipeline Orchestration Tools
- Model Development Tools
- Deployment Tools
- Monitoring Tools
- Building Your First Pipeline: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Project Setup
- Data Pipeline Implementation
- Preprocessing Pipeline Creation
- Model Training Integration
- Evaluation Framework
- Simple Deployment
- Benefits of Machine Learning Pipelines
- Efficient Automation
- Consistency & Reliability
- Scale with Confidence
- Reproducibility
- Deployment Speed
- Challenges in Machine Learning Pipelines
- Data inconsistency
- Scaling
- Monitoring
- Tooling Complexity
- Data Security and Privacy
- The Future of ML Pipeline Development
- No-Code/Low-Code Platforms
- Edge Computing Integration
- Federated Learning Pipelines
- MLOps Integration
- Final Thoughts..
- FAQs
- What is a machine learning pipeline in simple terms?
- Why are machine learning pipelines important?
- Do I need to know programming to build ML pipelines?
- How long does it take to build a complete ML pipeline?
What is the Machine Learning Pipeline?
A machine learning pipeline (ML pipeline) is a step-by-step workflow that automates the process of converting raw data into deployed models. This includes several steps, from data collection to the deployment of the model.
Rather than managing every step individually, pipelines simplifies and standardizes the process and makes machine learning development much quicker, more efficient, and easier to scale. It also makes for better data management as it facilitates the extraction, transformation, and loading from different data sources.
Understanding the Machine Learning Workflow
Before we go into the specific details of pipelines, let’s take a step back and think about the general machine learning workflow. All ML projects have the same basic workflow, no matter if you are predicting stock prices, diagnosing diseases, or recommending movies.
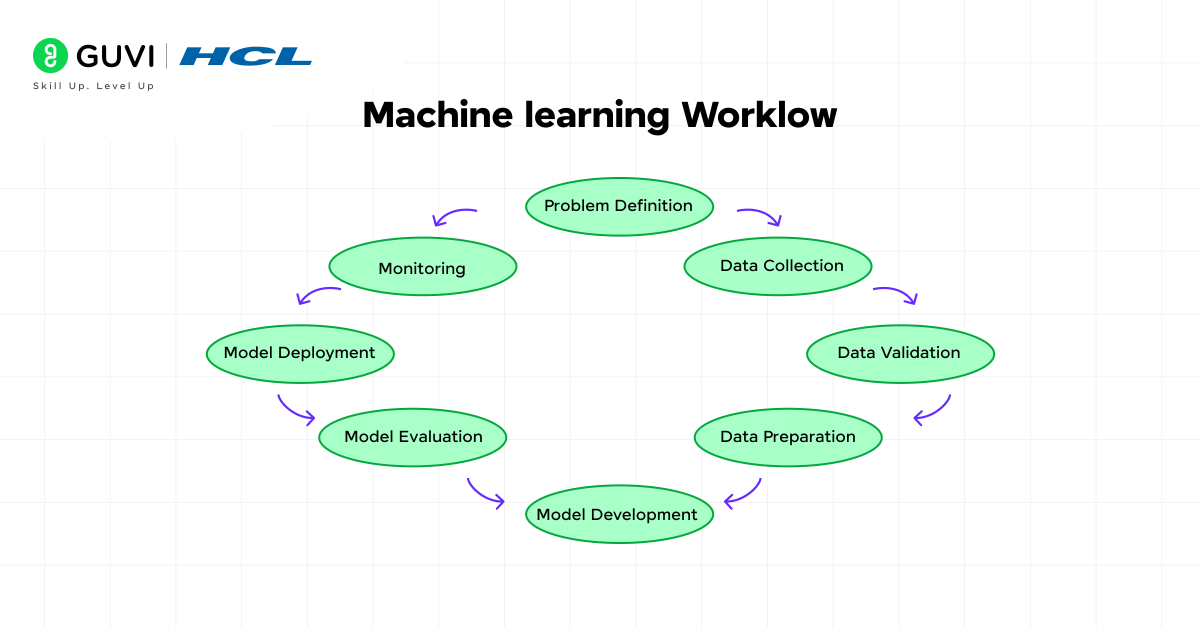
The ML lifecycle typically involves these steps:
- Problem Definition – what are we predicting or classifying?
- Data Collection – obtaining relevant data from various sources
- Data Validation – figuring out what our data tells us, and checking if the data is accurate and complete
- Data Preparation – cleaning up our data and transforming it into a usable format
- Model Development – creating and training algorithms to learn patterns
- Model Evaluation – testing how good our model is
- Model Deployment – making the model available for use in the real-world context
- Monitoring – ensuring the model remains viable over time
Each process includes several steps, and this is where pipelines are very useful. They allow us to organize, automate, and efficiently repeat complex processes.
Stages of a Machine Learning Pipeline
Let’s break down the steps in the machine learning pipeline:
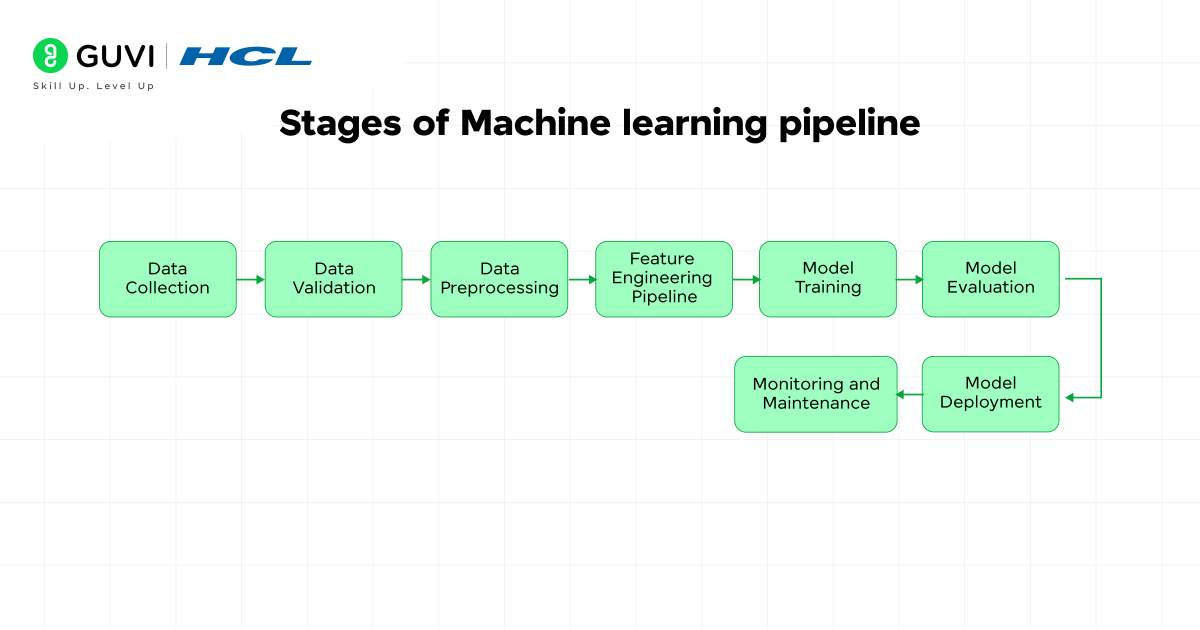
1. Data Collection
Data collection is the first step in the ML pipeline. Data rarely comes in perfect and ready-to-use condition. You might be getting the information from APIs, databases, CSV files, or even images. Your pipeline should be able to handle these different types of data without breaking, it should clean, standardize, and get them ready for the next step.
2. Data Validation
As you know, raw data are really messy, your pipeline should have automated checks to find missing values, outliers, inconsistent formats, or any other quality issues. This step acts as a quality checker, where it ensures only good data moves forward to your pipeline.
People tend to underestimate this step, but experienced data scientists know that poor data quality is the quickest way to create bad models. Your pipeline should be able to put a flag on suspicious data automatically, and it should either fix it or create an alert for you to correct it.
3. Data Preprocessing
Perhaps data processing is the most critical and time-consuming stage in ML., This is where you clean, transform, and otherwise manipulate data for modeling. Some common preprocessing tasks include:
- Handling Missing Values: Here, you decide about the missing data (whether to remove or fill) the missing or incomplete information.
- Data Type Conversion: Ensuring data – numbers, dates, are stored as their corresponding types
- Outlier Detection: Finding and handling any unusual values that may affect your model.
- Data Normalization: Scaling numerical features so they’re on similar ranges
- Encoding Categorical Variables: Converting text categories into numerical formats that algorithms can understand
4. Feature Engineering Pipeline
Feature pipelining requires more than just selecting the best features from your data. Feature pipelining requires you to extract new features, select good features, and transform the existing features to represent patterns in your data better.
Your pipeline should automate feature creation, selection, and transformation processes. This ensures consistency between training and prediction phases
5. Model Training
The model training phase consists of some important steps:
- Algorithm Selection: Selecting appropriate machine learning algorithms for your problem
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Optimizing algorithm settings for best performance
- Cross-Validation: Testing model performance across different data subsets
- Training Process: Actually teaching the algorithm to recognize patterns
Modern ML pipelines often train multiple models simultaneously, comparing their performance to select the best performer. This automated comparison saves time and reduces human bias in model selection.
6. Model Evaluation
Model evaluation in ML goes beyond simply checking if your model is accurate. A robust evaluation pipeline tests:
- Performance Metrics: Accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and other relevant measures
- Generalization: How well the model performs on completely new, unseen data
- Fairness: Whether the model treats different groups equitably
- Robustness: How the model handles unusual or adversarial inputs
- Interpretability: Whether you can understand why the model makes specific predictions
Your evaluation pipeline should automatically generate comprehensive reports, making it easy to compare different models and understand their strengths and weaknesses.
7. Model Deployment
The machine learning deployment pipeline transforms your trained model from a research artifact into a production system that can handle real-world requests. This involves:
- Model Packaging: Wrapping your model in a format that can be easily deployed
- Infrastructure Setup: Configuring servers, databases, and networking
- API Development: Creating interfaces that applications can use to get predictions
- Load Balancing: Ensuring your system can handle many simultaneous requests
- Version Management: Tracking different model versions and enabling rollbacks
8. Monitoring and Maintenance
Once deployed, your model enters a continuous monitoring phase. The pipeline should track:
- Prediction Accuracy: Is the model still performing well?
- Data Drift: Has the incoming data changed compared to the training data?
- System Performance: Are predictions being served quickly enough?
- Business Metrics: Is the model actually helping achieve business goals?
The term “confusion matrix” comes from the fact that it literally shows where a model is confused between different classes.
Confusion matrices have been around since the 1960s in statistics, long before machine learning became mainstream.
A model can achieve 95% accuracy and still be useless if the dataset is imbalanced. The confusion matrix helps expose these hidden flaws.
In fields like healthcare, missing a disease case (False Negative) can be much more dangerous than a False Positive, which is why metrics like recall matter more than just accuracy.
Essential ML Pipeline Tools
The right ML pipeline tools can make the difference between a successful project and a frustrating experience. Here are categories of tools every student should know:
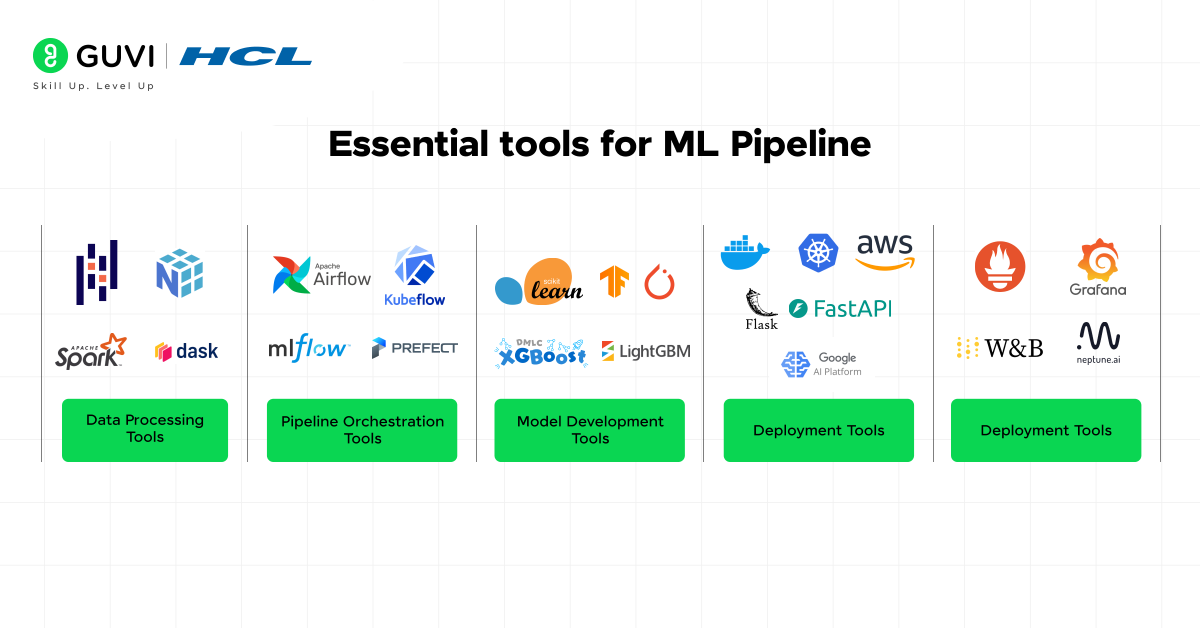
Data Processing Tools
- Pandas and NumPy: Python libraries for data manipulation and numerical computation
- Apache Spark: Distributed computing framework for large datasets
- Dask: Parallel computing library that scales Python workflows
Pipeline Orchestration Tools
- Apache Airflow: A Workflow management platform that helps schedule and monitor pipeline execution
- Kubeflow: Kubernetes-native platform for ML workflows
- MLflow: Platform for managing the complete ML lifecycle
- Prefect: Modern workflow orchestration tool with intuitive Python interface
Model Development Tools
- Scikit-learn: Comprehensive machine learning library with consistent APIs
- TensorFlow/PyTorch: Deep learning frameworks for complex neural networks
- XGBoost/LightGBM: Gradient boosting libraries for structured data problems
Deployment Tools
- Docker: Containerization platform for consistent deployment environments
- Kubernetes: Container orchestration for scalable deployments
- Flask/FastAPI: Web frameworks for creating model APIs
- AWS SageMaker/Google AI Platform: Cloud platforms with integrated ML pipeline tools
Monitoring Tools
- Prometheus + Grafana: Monitoring and visualization stack
- Weights & Biases: Experiment tracking and model monitoring
- Neptune: Platform for experiment management and model monitoring
Building Your First Pipeline: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s create a simple but complete pipeline for a classification problem. This example will help you understand how all components work together:
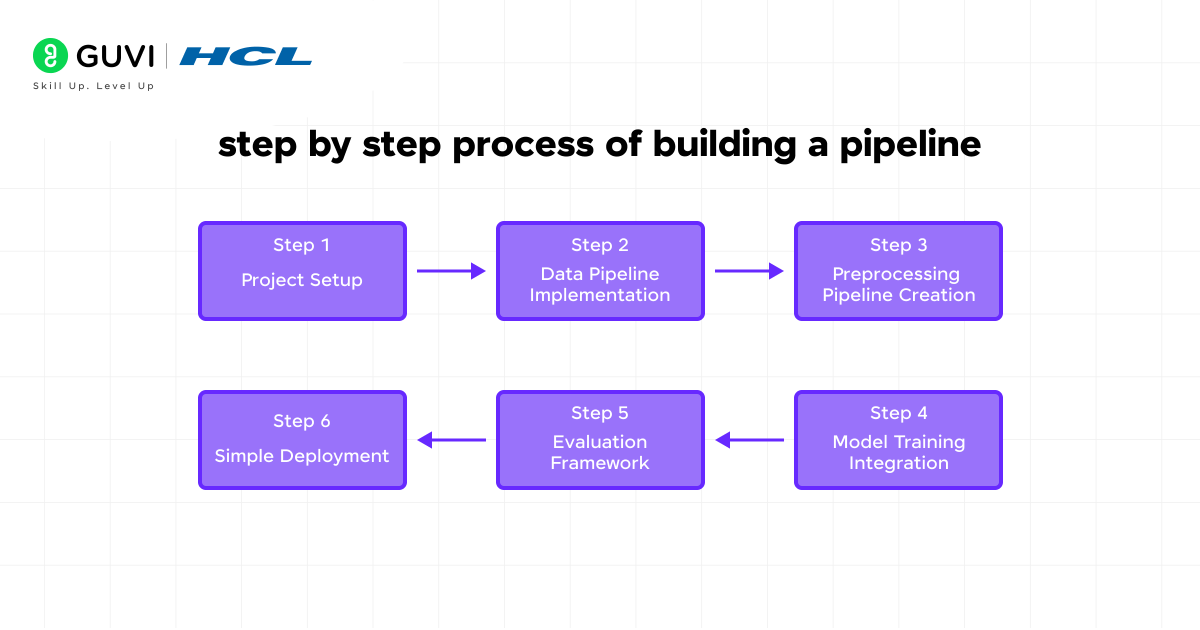
Project Setup
Choose an easy-to-use dataset such as the Titanic survival prediction or the iris flower classification. These datasets are well-documented and have clear objectives, making them perfect for learning pipeline development.
Data Pipeline Implementation
Develop functions to load data, handle missing data, and perform basic exploratory data analysis. Your data pipeline should follow a modular design, and each function should have one responsibility so that you can easily test each function without requiring other functions.
Preprocessing Pipeline Creation
Implement systematic preprocessing steps: handling missing values, encoding categorical variables, scaling numerical features, and splitting data into training and testing sets. Use scikit-learn’s Pipeline and ColumnTransformer for clean, reproducible preprocessing.
Model Training Integration
Implement training logic that can handle multiple algorithms. Start with simple algorithms like logistic regression and decision trees before moving to complex ensemble methods.
Evaluation Framework
Develop evaluation functions that compute multiple metrics and visualizations. A good evaluation will help you understand how your model behaves and how to effectively communicate your result.
Simple Deployment
Create a basic web interface or command-line tool that can load your trained model and make predictions on new data. This completes your end-to-end pipeline experience.
Benefits of Machine Learning Pipelines
Machine learning pipelines aren’t just for code; they also make things faster, cleaner, and more consistent.
1. Efficient Automation
The pipeline takes care of repetitive, tedious tasks such as cleaning the data and retraining the model for you, so you can concentrate on solving the problem instead of performing manual tasks.
2. Consistency & Reliability
Every stage follows a set process that minimizes possible errors and ensures reliable, consistent results.
3. Scale with Confidence
Whether you are dealing with small datasets or millions of rows, the pipeline can scale with your data.
4. Reproducibility
You can run the pipeline again with the same results at any time, which is crucial, especially in terms of research and collaborative projects.
5. Deployment Speed
Pipelines will help to speed up the process of going from raw data to production by eliminating barriers for organizations to implement models quickly.
Challenges in Machine Learning Pipelines
1. Data inconsistency
If the data is incomplete, has duplicate entries, or has data entry mistakes, the pipeline is likely to give false results. Cleaning and validating data before it feeds to the pipeline is one of the most common challenges faced by data scientists even today.
2. Scaling
As businesses expand, the data volume expands proportionately with the business from gigabytes to terabytes. Scaling a pipeline from gigabytes and terabytes of data requires sufficient infrastructure capability, distributed computing infrastructure, and optimized ML tools. Without sufficient scaling hardware or software capability, the pipeline may take too long or even crash.
3. Monitoring
A model that is good enough today could fail tomorrow due to data trend shifting, commonly known as “model drift.” Hence, monitoring the pipeline ensures that the model adjusts itself and performs well even when the data evolves.
4. Tooling Complexity
When it comes to data preprocessing tools (e.g., Pandas, Spark) to training frameworks (e.g. TensorFlow, PyTorch) and deployment platforms (e.g. Docker, Kubernetes, MLflow), the number of tools used to implement machine learning are overwhelming. The challenge of selecting, integrating and maintaining a machine learning stack without making the pipeline over-complicated is difficult.
5. Data Security and Privacy
Often times machine learning deals with sensitive information, such as patient health records, financial transactions, and personal information. So managing data and ensuring that it is encrypted, controlled access, and compliant with laws (like GDPR or HIPAA) is a huge challenge. Inappropriately handling data can lead to legal issues and loss of trust.
The Future of ML Pipeline Development
Machine learning pipeline technology continues evolving rapidly. Current trends shaping the future include:
No-Code/Low-Code Platforms
AutoML platforms and other tools are making machine learning easier for people who don’t know how to code. But it’s still very important to know the basics of pipelines to customize and fix problems.
Edge Computing Integration
More ML applications are moving to edge devices (phones, IoT sensors, autonomous vehicles). This requires new pipeline architectures optimized for resource-constrained environments.
Federated Learning Pipelines
New privacy-preserving techniques allow training models across distributed data sources without centralizing data. This requires rethinking traditional pipeline architectures.
MLOps Integration
MLOps, or Machine Learning Operations, is a field that is standardizing how businesses handle large-scale ML pipelines.
Do you want to take your AI capabilities to the next level? Check out HCL GUVI’s Advanced AI & Machine Learning Course, co-designed with Intel and IITM Pravartak. You’ll master hands-on skills in Python, Deep Learning, NLP, Generative AI, and MLOps and a globally recognized Intel certification to turn your learning into a career advantage.
Final Thoughts..
Building a machine learning pipeline might seem overwhelming at first, but once you break it down step by step, it becomes much clearer. From collecting and cleaning messy data to deploying and monitoring models in the real world, every stage plays a vital role.
The beauty of ML pipelines is that they bring structure, automation, and consistency to projects that would otherwise be chaotic. Whether you’re a student just getting started or someone exploring real-world applications, understanding this workflow gives you a powerful foundation to grow in the AI/ML field.
I hope this blog helped you not just understand the machine learning pipeline but also feel inspired to start building one yourself.
FAQs
1. What is a machine learning pipeline in simple terms?
A machine learning pipeline is a step-by-step process of turning raw data into meaningful predictions using machine learning models.
2. Why are machine learning pipelines important?
They save time, reduce manual mistakes, and allow teams to scale and reuse processes for different projects, making ML workflows more reliable and efficient.
3. Do I need to know programming to build ML pipelines?
While there are no code and low-code platforms, you still need to have basic knowledge of programming, such as Python, to get started with a machine learning pipeline.
4. How long does it take to build a complete ML pipeline?
A basic pipeline can take 2 to 4 weeks to develop. And a professional pipeline can typically take 2 to 6 months.





























Did you enjoy this article?