
How To Become a Cybersecurity Analyst? An Informative Guide
Mar 10, 2026 5 Min Read 3831 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered who protects banks, startups, and even governments from hackers and digital threats? In a world where every swipe, click, and transaction leaves a digital footprint, cybersecurity analysts are the invisible shields keeping data breaches and cybercrime at bay.
From ransomware attacks on hospitals to phishing scams targeting everyday users, the demand for cyber defenders has never been higher, and India is right at the center of this digital battlefield.
Whether you’re a student, a self-learner, or a career switcher, this article will walk you through everything you need to know, from skills and certifications to salaries and job roles. So, without further ado, let us get started!
Table of contents
- Who is a Cybersecurity Analyst?
- Role of a Cybersecurity Analyst
- Why Cybersecurity Matters in India?
- Educational Pathways in India
- Recommended Certifications
- Essential Skills (Technical & Soft)
- Cybersecurity Quiz Challenge: Can You Crack This?
- Salary Expectations in India
- Career Growth and Advanced Roles
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What qualifications are required to become a cybersecurity analyst in India?
- Which certifications are essential for a cybersecurity analyst in India?
- What is the average salary of a cybersecurity analyst in India?
- What are the core skills required for a cybersecurity analyst?
- Can a fresher become a cybersecurity analyst in India?
Who is a Cybersecurity Analyst?
A cybersecurity analyst is essentially a digital detective and protector. As a cybersecurity analyst, you’ll be responsible for monitoring and defending an organization’s networks and systems against cyberattacks. Below are some of the roles and responsibilities that you will play if you become a cybersecurity analyst:
Role of a Cybersecurity Analyst
- Monitor Network Traffic: Continuously observe network activity to detect suspicious behavior, anomalies, or security breaches.
- Conduct Vulnerability Assessments: Identify and assess vulnerabilities in the system using tools like Nessus, OpenVAS, or Qualys.
- Respond to Security Incidents: Act swiftly during data breaches or cyberattacks to contain damage, recover systems, and document the incident.
- Implement Security Measures: Set up firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and endpoint protection tools to safeguard digital assets.
- Analyze Security Logs: Use SIEM tools (like Splunk or QRadar) to analyze logs from servers, firewalls, and other devices for threat patterns.
- Perform Penetration Testing: Simulate cyberattacks to test the effectiveness of existing defenses and identify potential vulnerabilities.
With these abilities, your role as a cybersecurity analyst is to proactively protect data and systems – everything from firewalls and networks to applications and cloud environments – and to respond quickly when incidents occur.
Why Cybersecurity Matters in India?
India’s digital economy is growing explosively, and with it, the need for cybersecurity. Nearly every industry – from finance and healthcare to e-commerce and government – relies on digital platforms and data.
This growth has unfortunately been matched by surging cyberthreats. Recent reports show Indian organizations suffering record numbers of security incidents: one industry study recorded over 369 million cyberattacks in India in a single year.
As a result, the need for cybersecurity has become a top priority for business leaders. For example, 93% of Indian executives now plan to increase their cybersecurity budgets in 2025, with many boosting funding by 15% or more.
In short, the landscape for cybersecurity professionals is extremely favorable: organizations are allocating more resources to security, and a significant talent shortage means that your skills will be highly valued.
Educational Pathways in India

Formal Degrees:
The most common route is a bachelor’s degree in a tech field. Traditionally, that means a B.Tech or BE in Computer Science, Information Technology, or Electronics degrees, which many employers expect.
However, newer specialized programs are also emerging. For example, some universities now offer BCA/BSc in Cybersecurity or B.Tech in Cybersecurity and Digital Forensics. These courses often cover network security, cryptography, ethical hacking, and related topics.
In any case, a degree helps clear initial HR screening and lays the groundwork for technical know-how.
Self-Learning & Online Courses:
Given the fast pace of cyber threats, many analysts also learn through online courses and certifications for Cybersecurity Beginners.
Government and industry bodies have launched resources: for example, Skill India’s Digital Hub offers free online cybersecurity courses, and initiatives like the National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology (NIELIT) have introductory programs.
While these don’t replace a degree, they can fill gaps in your knowledge and show initiative on your resume. Ultimately, the important thing is skills, whether you earned them in a classroom or through self-study: focus on building a portfolio of hands-on projects as evidence of your abilities.
Read More: The Ultimate Cybersecurity Roadmap for Beginners
Recommended Certifications
Cybersecurity Certifications can significantly boost your profile, especially if your formal education is general. In India, a few industry-recognized certs are highly valued by employers:
- CompTIA Security+ – This is a great starter cert covering core security principles (attacks, access control, risk management, etc.). Many bootcamps in India train students for Security+, and it’s known globally.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) – Offered by EC-Council, CEH teaches you to think like a hacker. It’s well-known in India and covers penetration testing tools/methods.
- Cisco Security (CCNA/CCNP Security) – Since many companies use Cisco networking gear, a Cisco security certification can be useful (it covers firewalls, VPNs, etc.).
Whichever you choose, remember that certifications are most valuable when combined with practical experience. The job market is currently rewarding certified pros – companies in India are actively searching for certified professionals, offering competitive salaries and growth opportunities.
Essential Skills (Technical & Soft)

To succeed as a cybersecurity analyst, you’ll need a mix of technical and soft skills. Here are the key ones:
- Networking and Systems: A Deep understanding of TCP/IP, subnets, routers/switches, and common protocols (HTTP, DNS, etc.) is crucial.
- Security Tools & Concepts: Be proficient with firewalls, IDS/IPS systems, and endpoint protection. Learn to use a SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) platform like Splunk or QRadar to aggregate logs and spot anomalies.
- Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing: Knowing how to find weaknesses is a core skill. Learn common pentesting tools (Metasploit, Burp Suite, nmap) and practice on lab environments.
- Incident Response & Forensics: When a breach happens, analysts must respond quickly. Learn the basics of incident handling – for example, following a documented incident response plan.
- Programming/Scripting: You don’t need to be a software engineer, but some coding helps. Python and Bash scripting are widely used for automating tasks.
- Soft Skills: Analysts must communicate effectively. You’ll write security reports and advise non-technical managers on risks, so clear writing and speaking skills are essential. Cybersecurity is a high-pressure field, so staying calm under pressure and maintaining a learning mindset are critical.
Cybersecurity Quiz Challenge: Can You Crack This?

Let’s take a break and test your cybersecurity instincts. Ready?
Q1. You receive an alert about multiple failed login attempts from the same IP address within a short timeframe. What’s the most likely explanation?
A. Legitimate user forgot password
B. Server maintenance issue
C. Brute-force attack
D. Network latency
Q2. Which of these tools is most commonly used for network scanning?
A. Wireshark
B. Burp Suite
C. Nmap
D. Nessus
Q3. What does “Defense in Depth” mean in cybersecurity?
A. Defending against malware only
B. Using multiple layers of security controls
C. Avoiding the cloud
D. Building firewalls alone
Q4. Which Indian government organization handles cybersecurity incidents?
A. TRAI
B. CERT-In
C. NIELIT
D. NCERT
Q5. You’re conducting a vulnerability scan and find that a web app is vulnerable to SQL injection. What’s the FIRST thing you should do?
A. Publicly report it on Twitter
B. Run more attacks to explore
C. Alert the development team
D. Reboot the server
ANSWERS:
- Answer: C. Brute-force attack
This is a classic sign of a brute-force attempt where attackers try many combinations to guess passwords. - Answer: C. Nmap
Nmap is widely used for scanning networks and identifying open ports and services. - Answer: B. Using multiple layers of security controls
It’s a key strategy that ensures that if one defense fails, others still protect the system. - Answer: B. CERT-In
The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) is the national nodal agency for cyber incident response. - Answer: C. Alert the development team
Always follow responsible disclosure policies. Never exploit further without permission.
Bonus Challenge:
Build your own mini SOC (Security Operations Center) at home using free tools.
Install:
- Kali Linux for pen-testing
- Splunk (Free) for log monitoring
- Snort or Suricata for intrusion detection
- Practice by monitoring your system for suspicious activity!
Salary Expectations in India
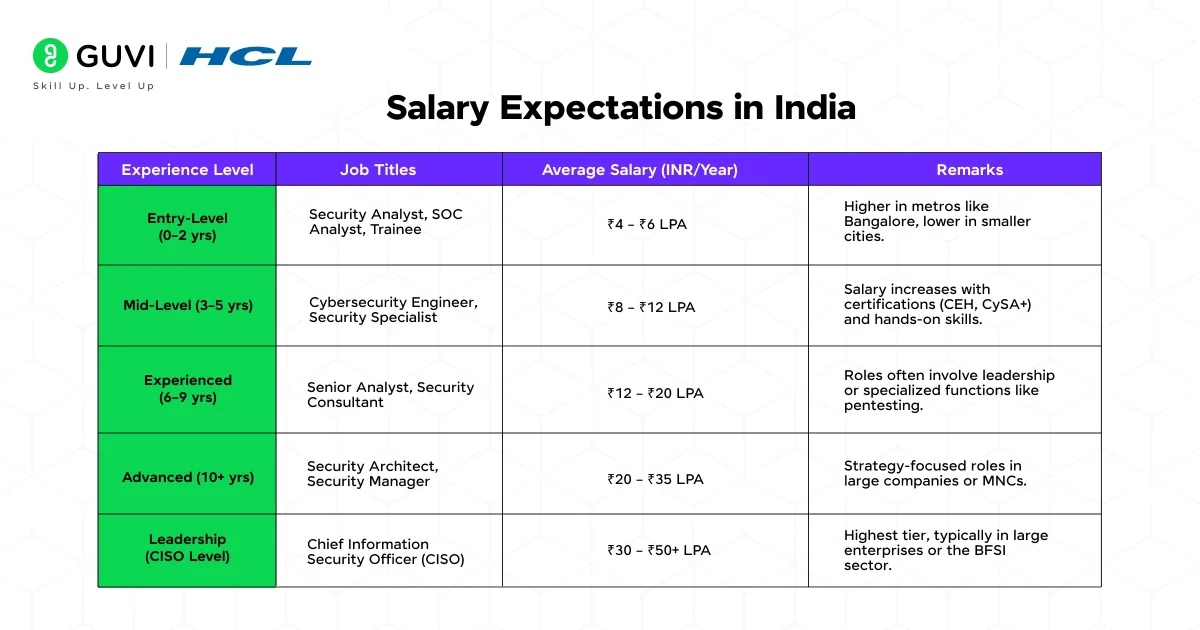
Salaries for cybersecurity roles in India are generally higher than in many other IT domains, reflecting the demand. Here’s a brief on the salary of a cybersecurity analyst in India:
| Experience Level | Job Titles | Average Salary (INR/Year) | Remarks |
| Entry-Level (0–2 yrs) | Security Analyst, SOC Analyst, Trainee | ₹4 – ₹6 LPA | Higher in metros like Bangalore, lower in smaller cities. |
| Mid-Level (3–5 yrs) | Cybersecurity Engineer, Security Specialist | ₹8 – ₹12 LPA | Salary increases with certifications (CEH, CySA+) and hands-on skills. |
| Experienced (6–9 yrs) | Senior Analyst, Security Consultant | ₹12 – ₹20 LPA | Roles often involve leadership or specialized functions like pentesting. |
| Advanced (10+ yrs) | Security Architect, Security Manager | ₹20 – ₹35 LPA | Strategy-focused roles in large companies or MNCs. |
| Leadership (CISO Level) | Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) | ₹30 – ₹50+ LPA | Highest tier, typically in large enterprises or the BFSI sector. |
Career Growth and Advanced Roles

The cybersecurity field has a clear ladder of advancement. After a few years as an analyst, you might move up to senior or lead roles. For example:
- Security Specialist/Engineer: More ownership of systems; you might design security solutions or lead major audits.
- Incident Response Team Lead or Forensics Expert: You might head the response team, coordinating threat investigations, or become a digital forensic specialist.
- Security Architect/Manager: Focusing on the big picture – designing the organization’s overall security framework or leading the security department.
- Consultant or Auditor: Some analysts branch into consulting (working for firms that advise clients) or into compliance/auditing careers (with CISOs or regulators).
Ultimately, the top role is CISO, where you’re responsible for the entire security posture of a company. CISOs in India can earn as much as ₹50 lakh per year in large firms.
Other senior roles like Chief Security Officer or Security Consultant can also be very lucrative. Along the way, you may choose to specialize (for instance, as a Cloud Security Expert, DevSecOps Engineer, or Threat Intelligence Analyst), which often comes with its growth and salaries.
Looking Ahead: With cyber threats evolving rapidly, the demand for skilled analysts will only grow. Government initiatives and corporate investments ensure the field stays dynamic. By building a solid foundation now, you’ll be well-positioned for a rewarding, high-impact career as a cybersecurity analyst – one of the most critical roles in today’s digital world.
If you want to learn more about Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking that too in an advanced level, consider enrolling in HCL GUVI’s Advanced Cyber Security and Ethical Hacking Course, where you’ll learn how to monitor systems and alleviate threats when they happen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the exact path for the Cybersecurity Analyst role depends on your interests, but the trajectory is steep, with continuous learning and experience, you can progress from entry-level to leadership over a decade.
Given the talent shortage, even early in your career, you may be entrusted with significant responsibilities, so seize every learning opportunity (such as leading a small security project or mentoring juniors).
In short, starting as a cybersecurity analyst opens doors to many advanced roles and leadership positions in India’s tech industry.
FAQs
1. What qualifications are required to become a cybersecurity analyst in India?
To pursue a career as a cybersecurity analyst in India, a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field is typically required. However, with the increasing demand for cybersecurity professionals, many organizations also value practical skills and certifications.
2. Which certifications are essential for a cybersecurity analyst in India?
Key certifications that are highly regarded in the Indian cybersecurity job market include:
– CompTIA Security+: A foundational certification covering essential security concepts.
– Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): Focuses on identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities.
– Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): An advanced certification for experienced professionals.
3. What is the average salary of a cybersecurity analyst in India?
The average salary for a cybersecurity analyst in India varies based on experience and location. Entry-level positions typically offer salaries ranging from ₹4 to ₹6 lakhs per annum. With experience, professionals can expect to earn between ₹8 to ₹12 lakhs per annum. Highly experienced analysts or those in specialized roles may earn upwards of ₹15 lakhs annually.
4. What are the core skills required for a cybersecurity analyst?
A cybersecurity analyst should possess a blend of technical and soft skills, including:
– Technical Skills: Proficiency in networking, understanding of operating systems, knowledge of security tools like firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and familiarity with scripting languages such as Python.
– Soft Skills: Strong communication abilities, analytical thinking, problem-solving skills, and adaptability to rapidly changing security landscapes.
5. Can a fresher become a cybersecurity analyst in India?
Yes, freshers can start a career as cybersecurity analysts in India. While a relevant degree provides a solid foundation, acquiring certifications like CompTIA Security+ or CEH and gaining hands-on experience through internships, labs, or personal projects can significantly enhance employability.




































Did you enjoy this article?