A Practical Guide to Epoch in Machine Learning Models
Oct 22, 2025 7 Min Read 2341 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered how a machine learning model actually learns after seeing the same data multiple times? The answer lies in understanding the epoch meaning in machine learning. It is a concept that shapes the way algorithms improve with each pass through data. An epoch represents one complete cycle where every training sample is used to adjust the model’s parameters, which makes it one of the most important hyperparameters in building accurate machine learning models.
Keep reading this blog to explore what an epoch in machine learning is and how it impacts the success of both simple models and advanced deep learning systems.
Table of contents
- What is Epoch in Machine Learning?
- What is Epoch in Deep Learning?
- Importance of Choosing the Right Number of Epochs
- Techniques to Handle Epoch Selection
- Batch Size in Machine Learning
- Definition
- Top Features
- Top Uses
- Iteration in Machine Learning
- Definition
- Top Features:
- Top Uses:
- Batch vs Iteration in Machine Learning: Key Differences
- How Epochs, Batches and Iterations Work Together?
- Applications or Use Cases of Epoch
- • Epoch in Supervised Learning
- • Handwritten Digit Recognition
- • Sentiment Analysis
- • Image Classification with Large Datasets
- Top Benefits of Epochs in Machine Learning
- Improved Learning Accuracy
- Better Weight Adjustment
- Detection of Underfitting and Overfitting
- Support for Large Datasets
- Foundation for Optimization Techniques
- Top Challenges of Epochs in Machine Learning
- Tools for Managing Epochs in Machine Learning
- TensorFlow and Keras
- PyTorch
- Scikit-learn
- Experiment Tracking Platforms
- Epoch in AI: Broader Context
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Q1. Why do machine learning models need more than one epoch?
- Q2. How are epochs different from training steps?
- Q3. Do all models require the same number of epochs?
- Q4. Can the ideal number of epochs change over time?
- Q5. What role do epochs play in model evaluation?
What is Epoch in Machine Learning?
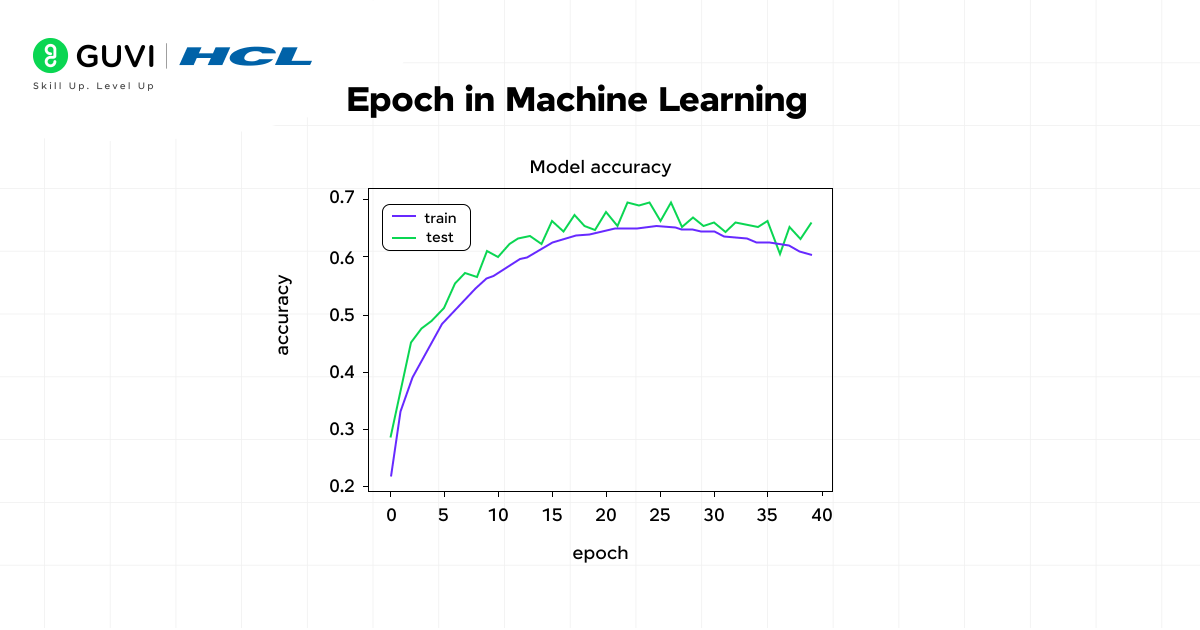
An epoch in machine learning is a fundamental concept that represents one full cycle through the entire training dataset. Here, every data point has been used once to update the model’s parameters. You can consider it as a complete learning round: the model “sees” all the training examples and makes predictions. It further compares them against the actual labels and adjusts its internal weights accordingly.
An Example of Epochs in Machine Learning:
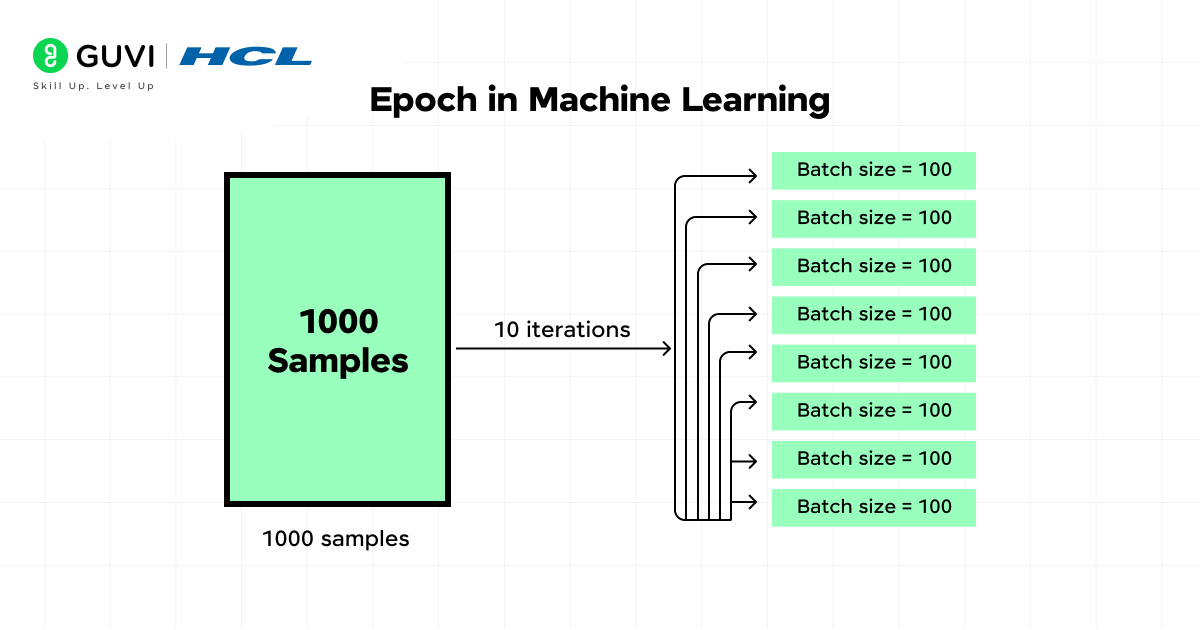
An epoch depends on the dataset size and updates. Suppose a dataset has 1000 samples. With no batching, one epoch means processing all 1000 samples once and then updating the model.
If the batch size is 100, the 1000 samples split into 10 batches. Each batch updates the model, so one epoch takes 10 iterations. An iteration is one update from a batch of 100 samples.
Key insights:
• 1000 samples with batch size 100 → 10 iterations per epoch.
• Smaller batches → more iterations, more updates, slower training.
• Larger batches → fewer iterations, faster training, sometimes weaker generalization.
• Batch size sets the number of iterations in an epoch.
What is Epoch in Deep Learning?
The concept of an epoch in deep learning takes on even greater significance because of the complexity and scale of modern neural networks. Each epoch represents a full pass over the training dataset and broken down into smaller batches that gradually update millions (or even billions) of parameters.
Importance of Choosing the Right Number of Epochs
Epoch count acts as a hyperparameter in machine learning. A hyperparameter is a setting chosen before training begins, and the number of epochs is one of the most influential choices.
Also, are you aware that a small number of epochs often leaves the model undertrained and unable to capture meaningful patterns? On the other hand, a very large number of epochs can cause overfitting, where the model memorizes training data and fails to perform well on unseen data. Striking a balance is necessary, and this balance depends on the dataset size and the type of problem being solved.
Techniques to Handle Epoch Selection
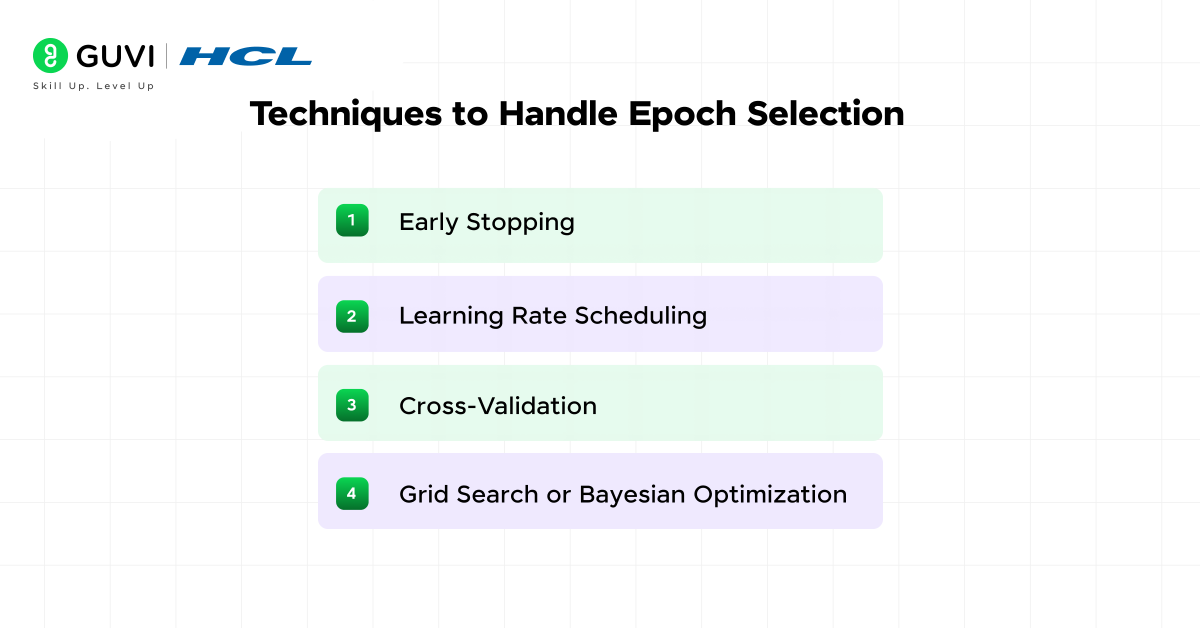
Practitioners use several approaches to manage the choice of epochs and reach optimal epochs in ML:
- Early stopping halts training once the model’s performance stops improving on validation data.
- Learning rate scheduling adjusts how quickly weights are updated across epochs, which makes the training process more efficient.
- Cross-validation divides the dataset into folds and measures performance on each fold, which gives a stronger estimate of the ideal number of epochs.
- Employ grid search or Bayesian optimization. They help combine epochs with other hyperparameters in structured searches to find the best configuration.
Batch Size in Machine Learning
Definition
Batch size in machine learning refers to the number of training samples processed together before the model’s weights are updated. The data is divided into batches instead of sending the entire dataset into the model at once. And then the chosen batch size determines how many samples go through the model in a single forward and backward pass. Batch size directly affects computational efficiency and the quality of learning.
Top Features
- Handles large amounts without exhausting memory resources
- Provides stable gradient updates by averaging across samples
- Allows flexibility to balance training speed and accuracy through batch size selection
Top Uses
- Managing large datasets during training
- Improving training efficiency with parallel processing on GPUs
- Controlling convergence behavior by adjusting batch size
Iteration in Machine Learning
Definition
An iteration in machine learning refers to one parameter update that occurs after processing a single batch of data. Since a dataset is usually divided into many batches, completing one epoch requires multiple iterations.
Top Features:
- Represents the smallest measurable step in the training process
- Directly linked to the dataset size and the chosen batch size
- Updates model weights batch by batch until the epoch ends
Top Uses:
- Tracking how many updates happen within each epoch
- Monitoring convergence speed during training
- Identifying issues such as slow or unstable learning
Batch vs Iteration in Machine Learning: Key Differences
| Concept | Definition | Relation to Epochs | Key Control Factor | Impact on Training Efficiency | Practical Example |
| Batch Size | Number of samples processed before updating weights | Determines how many iterations make up one epoch | Batch size | Larger batch sizes speed up training but may lower accuracy, smaller batch sizes improve stability | In image classification, a batch size of 64 means 64 images are processed before weights are updated |
| Iteration | One parameter update after processing a batch | Several iterations are required to complete one epoch | Number of batches | More iterations provide frequent updates, which improve the granularity of learning | In sentiment analysis, one iteration updates weights after |
How Epochs, Batches and Iterations Work Together?
Here is how these three elements interact during the training process:
- Epoch: One full cycle where the model processes the entire training dataset.
- Batch Size: The chosen number of samples processed before the model updates its weights.
- Iteration: A single update of model parameters after one batch is processed.
Together, they create the structure of training. A dataset is divided into batches, each batch produces an iteration, and a collection of iterations completes one epoch. This relationship shows how model learning moves step by step, from individual batches to complete training cycles.
Applications or Use Cases of Epoch
• Epoch in Supervised Learning
An epoch plays a central role in supervised learning because models rely on labeled data to learn the mapping between inputs and outputs. Each epoch represents a full pass through the labeled dataset. It permits the model to adjust its parameters step by step based on the difference between predicted and actual labels.
Tasks such as classification of emails into spam and non-spam, or regression problems like predicting house prices, require multiple epochs to reduce error and improve accuracy. The repeated passes help the model generalize better, and this makes epochs a practical measure of progress in supervised learning use cases.
• Handwritten Digit Recognition
Training a neural network to recognize handwritten digits provides one clear case. The dataset contains thousands of labeled images, and during a single epoch the model processes each of these images once. The network improves its accuracy in predicting the correct digits because it has adjusted its weights through repeated exposure to the data. This takes place after several epochs.
• Sentiment Analysis
Another case can be seen in natural language processing tasks such as sentiment analysis. A model trained on customer reviews requires many epochs to learn the patterns of positive and negative expressions. Each pass through the dataset helps the model refine its predictions. It gradually increases its reliability on unseen reviews.
Also, read: Basics of NLP: A Beginner’s Guide to Natural Language Processing
• Image Classification with Large Datasets
Image classification with complex datasets such as ImageNet provides a third case. Training requires dozens of epochs since the model must learn from millions of images spread across thousands of categories. Performance often rises sharply during the first few epochs and then levels out. It basically shows why selecting the right number of epochs is critical for balanced learning.
Top Benefits of Epochs in Machine Learning
Here are the key benefits explained with context:
1. Improved Learning Accuracy
Each epoch allows the model to pass through the full dataset. It further reinforces its proficiency to seize patterns and reduce prediction errors. The model learns subtle relationships between input features and output labels over repeated passes. It eventually helps it perform better on unseen data.
2. Better Weight Adjustment
Weights in a model cannot settle into reliable values after a single exposure to data. Multiple epochs provide repeated opportunities for adjustment. This step-by-step refinement makes the learning process smoother and supports the model to reach a more stable performance level.
3. Detection of Underfitting and Overfitting
Training across several epochs reveals how performance changes over time. Monitoring validation accuracy and loss across epochs highlights whether the model is learning too little or memorizing the dataset. This feedback helps practitioners decide whether to increase epochs and stop training earlier. It also helps adjust related hyperparameters.
4. Support for Large Datasets
Large datasets create practical challenges for training. Dividing them into batches and completing them through epochs keeps resource usage balanced. This approach makes it possible to train on complex data collections while avoiding computational bottlenecks.
5. Foundation for Optimization Techniques
Epochs formulate the structure on which advanced methods operate. Early stopping depends on monitoring results across epochs to halt training at the right moment. Learning rate schedules rely on epoch counts to control how quickly weights change. These techniques improve both efficiency and final accuracy.
Top Challenges of Epochs in Machine Learning
Here are the common challenges explained clearly:
- Risk of Underfitting: Too few epochs prevent the model from learning enough patterns. This reduces its ability to make reliable predictions on both training and test data.
- Risk of Overfitting: Excessive epochs push the model to memorize training data. As a result, the model struggles to generalize when exposed to new data.
- High Computational Cost: Training across many epochs demands considerable time and processing power. The challenge becomes greater with very large datasets that require repeated passes.
- Difficulty in Selecting the Right Number: Finding a balance between too few and too many epochs often requires careful experimentation. Practitioners must monitor accuracy and loss across epochs to determine the best stopping point.
- Dependence on Batch Size: The impact of epochs is closely tied to batch size. Smaller batches lead to more iterations per epoch. It increases training time and may affect efficiency if not planned well.
Tools for Managing Epochs in Machine Learning
Choosing and adjusting epochs is rarely done manually alone. A variety of tools and frameworks support practitioners in managing epochs efficiently and aligning them with other hyperparameters.
1. TensorFlow and Keras
TensorFlow, along with its high-level API Keras, provides built-in support for setting epochs during model training. Practitioners can specify the number of epochs directly in the model.fit() function. Keras also supports callbacks such as EarlyStopping that monitor validation loss or accuracy to automatically halt training once improvement stalls. This prevents overfitting and reduces wasted computation.
2. PyTorch
PyTorch offers flexible control over epochs through its training loop. Developers can define exactly how many epochs to run and monitor performance after each cycle. PyTorch also supports Learning Rate Schedulers that adjust weight updates across epochs, making the training process more efficient. Its ability to track metrics at the end of each epoch helps with fine-grained analysis.
3. Scikit-learn
Scikit-learn, commonly used for traditional machine learning models, includes parameters such as max_iter or n_estimators that often serve the role of epochs. Though it is more abstract compared to deep learning libraries, it gives straightforward control over repeated passes through the data during optimization.
4. Experiment Tracking Platforms
Tools like MLflow, Weights & Biases (W&B), and Neptune.ai record training metrics across epochs. They provide visual dashboards to analyze accuracy and loss curves epoch by epoch. This makes it easier to identify underfitting, overfitting, or stable convergence. These platforms also allow comparison across experiments, which helps in deciding the right epoch configuration.
Take the guesswork out of training models and master the art of tuning epochs, batch size, and iterations with HCL GUVI’s Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Course powered by Intel Certification. This comprehensive course gives you hands-on experience with real-world datasets, from clustering methods to deep learning optimization, ensuring you understand not only what epochs are but also how to apply them effectively in modern AI workflows. Enroll now and get Intel-certified in AI and Machine Learning to accelerate your career.
Epoch in AI: Broader Context
Here is how the role of epochs broadens when viewed from the perspective of artificial intelligence as a whole:
- Training Large-Scale AI Systems
Epochs are not merely about refining models on small datasets but also about sustaining learning in massive architectures in artificial intelligence. Foundation models that support applications like chatbots or autonomous driving undergo thousands of epochs during pre-training. These cycles allow them to absorb information from diverse data sources and build representations that power downstream tasks.
- Importance in General AI Performance
The concept of epochs extends into AI performance at scale. Repeated training cycles help AI systems adapt to varied forms of input such as images, text, speech, and sensor readings. The quality of these passes affects how well an AI system can perform tasks in real-world conditions where data distribution may shift.
- AI-Specific Challenges with Epochs
Epochs in AI bring unique challenges beyond simple training efficiency. Resource demand grows sharply as models expand in size. It forces teams to balance training depth with hardware limitations. Distributed training across multiple GPUs or TPUs is often required. It further makes the number of epochs a factor in all-around system design rather than just a training choice.
- Broader Applications Across AI Domains
Different AI and generative AI domains leverage epochs in ways suited to their goals. In computer vision, epochs help refine feature extraction for object recognition or medical imaging analysis. In natural language applications, epochs drive better contextual understanding for machine translation and conversational systems. In robotics, epochs guide reinforcement cycles where agents learn from repeated interactions with environments.
- Strategic Role in AI Development
Beyond technical training, epochs play a role in how AI projects are planned and executed. Each epoch is tied to cost, time, and expected performance gains. This connection makes epoch planning a part of resource allocation and model deployment strategies. Teams working on large-scale AI projects evaluate epochs in relation to business goals and ethical considerations, which shows their broader impact in shaping AI outcomes.
Quick Quiz: Epoch in Machine Learning
Test your understanding with these short questions. Answers follow right after the quiz.
- What does one epoch represent in training?
A) One batch processed
B) One full pass over the training dataset
C) One parameter initialization
D) One validation step
- Which choice best describes iteration?
A) One complete pass over data
B) One update after processing a batch
C) One shuffle of the dataset
D) One hyperparameter search
- A dataset has 1,000 samples. Batch size is 100. How many iterations are in one epoch?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 50
D) 100
- Which statement about batch size is correct?
A) Larger batch sizes often reduce the number of iterations per epoch
B) Larger batch sizes increase iterations per epoch
C) Batch size does not affect iterations
D) Batch size only affects validation
- Which outcome signals possible underfitting with respect to epochs?
A) Training accuracy high and validation accuracy low
B) Training accuracy low and validation accuracy low
C) Training loss low and validation loss low
D) Training loss low and validation loss high
- Which tool helps choose a suitable number of epochs?
A) Random weight resets
B) Early stopping
C) Feature hashing
D) One hot encoding
Answers
- B
- B
- B
- A
- B
- B
Conclusion
Epochs represent more than a technical step in training; they define the rhythm through which models in machine learning and artificial intelligence evolve toward better performance. Right from shaping weight updates in small supervised tasks to guiding large-scale training of advanced AI systems, epochs serve as checkpoints of progress, efficiency, and balance. Their careful selection influences accuracy and even the strategic direction of AI projects. Comprehension of epochs equips practitioners with a clearer view of how models learn and ultimately deliver reliable outcomes across domains.
FAQs
Q1. Why do machine learning models need more than one epoch?
A single epoch often leaves the model undertrained because it sees each data point only once. Multiple epochs give the model repeated exposure, which helps it refine parameters and capture deeper patterns in the data.
Q2. How are epochs different from training steps?
An epoch covers the full dataset once, while a training step or iteration refers to updating model parameters after processing a single batch. Many steps combine to complete one epoch.
Q3. Do all models require the same number of epochs?
No, the number of epochs varies based on the model complexity and task type. Simpler models on small datasets may reach optimal performance in fe
Q4. Can the ideal number of epochs change over time?
Yes. As datasets grow or model architectures evolve, the optimal epoch count may change. This is why practitioners rely on validation metrics and monitoring to determine when training should stop for each new project.
Q5. What role do epochs play in model evaluation?
Epochs act as checkpoints for measuring performance. At the end of each epoch, metrics such as accuracy and loss are evaluated. This consistent tracking helps compare models and choose the best version for deployment.





























Did you enjoy this article?