DSA Syllabus 2026: Learn Algorithms and Data Structures Efficiently
Mar 04, 2026 3 Min Read 2558 Views
(Last Updated)
Having a clear DSA Syllabus helps you learn in a structured, stress-free, and smart way. Instead of jumping randomly on the topics, you can have a neat and organized syllabus that helps to understand each topic quickly and easily.
Here, in this blog, you can find a comprehensive syllabus that covers all the basic and advanced topics you need to know about Data Structures and Algorithms.
Table of contents
- Part 1: Data Structures
- Arrays
- 2. Strings
- 3. Linked List
- 4. Stack
- 5. Queue
- 6. Trees
- 7. Graphs
- 8. Hashing
- 9. Heap
- 10. Trie (Prefix Tree)
- 11. Disjoint Set (Union-Find)
- 12. Matrix
- Part 2: Algorithms
- Recursion
- 2. Searching Algorithms
- 3. Sorting Algorithms
- 4. Divide and Conquer
- 5. Dynamic Programming (DP)
- 6. Greedy Algorithms
- 7. Backtracking
- 8. Bit Manipulation
- Wrapping It Up
- FAQs
- Why learn according to DSA syllabus?
- How much time does it require to learn DSA?
- Which programming language is best for learning DSA?
- Can a beginner learn DSA?
Part 1: Data Structures
1. Arrays
The major step into DSA is the array. They save the elements of data in continuous memory positions.
- Key Concepts:
- Static vs Dynamic arrays
- Index-based access
- Traversing, Insertion, Deletion.
- Searching and Sorting of arrays.
- Example:
- Think of 100 students you are storing marks for, you can access any student’s mark within an array of 100 students.
- Common Algorithms
- The Algorithm of Max Subarray Sum by Kadane.
- Two Pointer Technique
- Sliding Window Problems
2. Strings
Characters arranged into strings – sequences of characters aid in the processing of text and pattern recognition.
- Key Concepts:
- Comparison of strings, concatenation and manipulation.
- Subsequences and sub-strings.
- Palindrome checks
- Pattern matching
- Applications:
- Applied in search engines, file systems and spell checkers.
- Common Algorithms:
- KMP Algorithm
- Rabin-Karp Algorithm
Also Explore: 5 Best Reasons to Learn Data Structures and Algorithms [DSA]
3. Linked List
In a linked list, the information is stored in nodes by means of pointers. They are dynamic, unlike arrays, and can either expand or reduce as required.
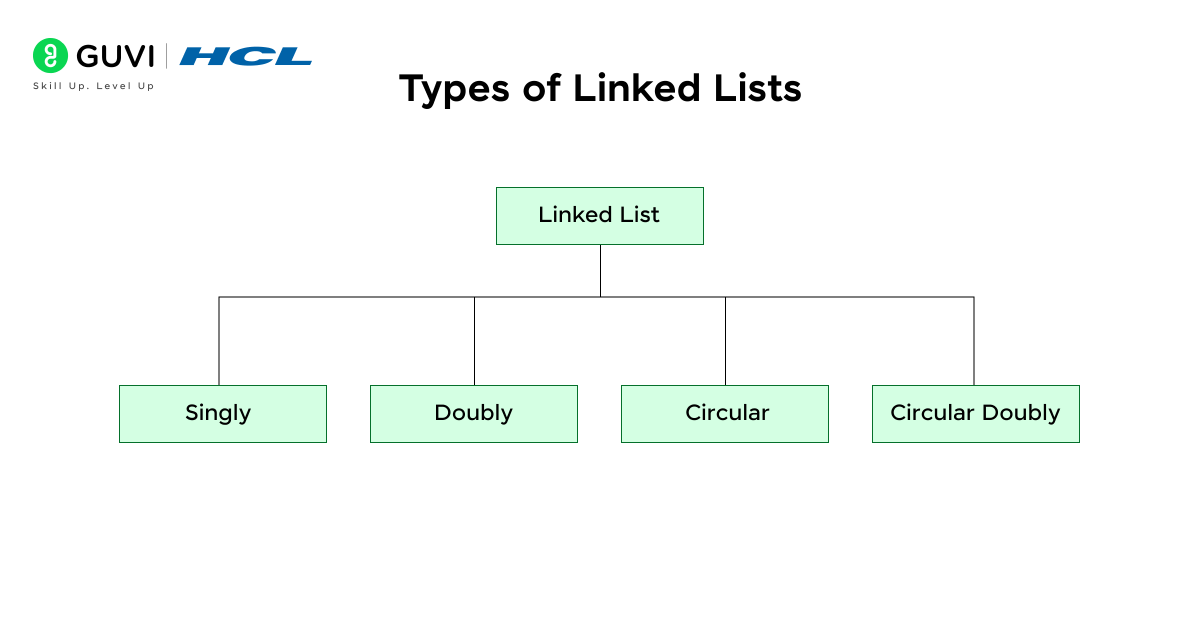
- Types of Linked Lists:
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
- Key Operations:
- Insertion, Deletion, Traversal, and Reversal.
- Identification and elimination of loops.
- Example:
- Linked lists are used internally in a music app in the form of a playlist in which you swipe to the next or previous song.
Also Read: Is DSA Important for Placement in 2026?
4. Stack
A Stack operates using the principle of Last In, First Out (LIFO) – the last one in is the first one out.
- Applications:
- Undo/Redo functionality
- Syntax parsing in compilers
- Backtracking problems
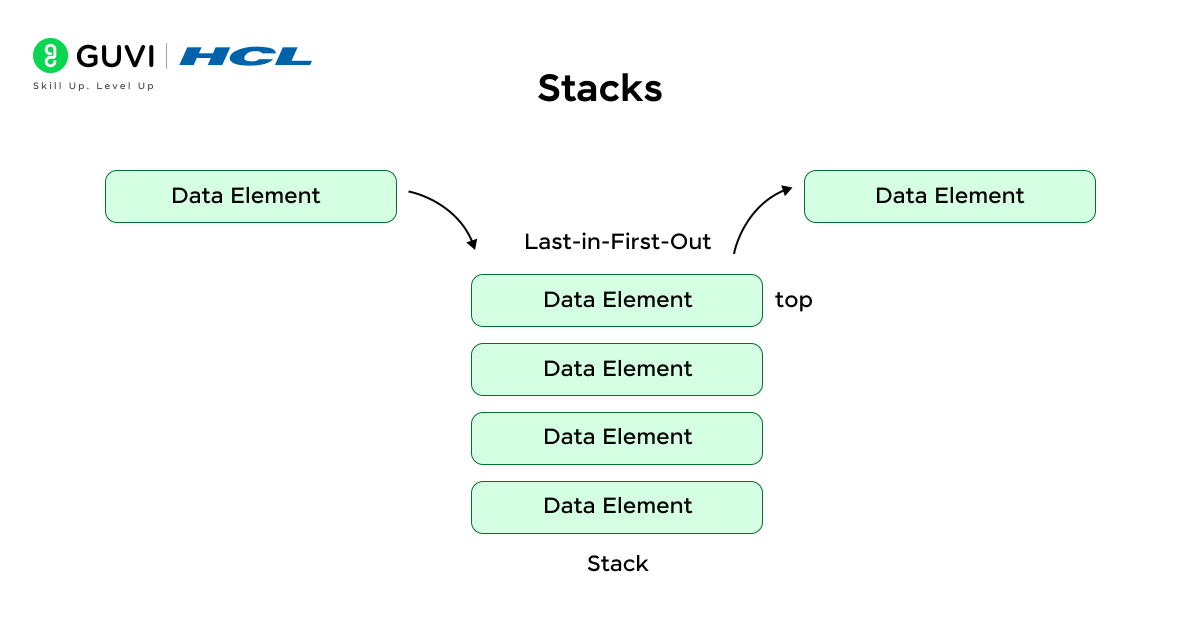
- Key Operations:
- Push (insert)
- Pop (remove)
- Peek (view top element)
Download HCL GUVI’s Free DSA eBook: A perfect beginner-friendly resource with visuals, examples, and hands-on coding.
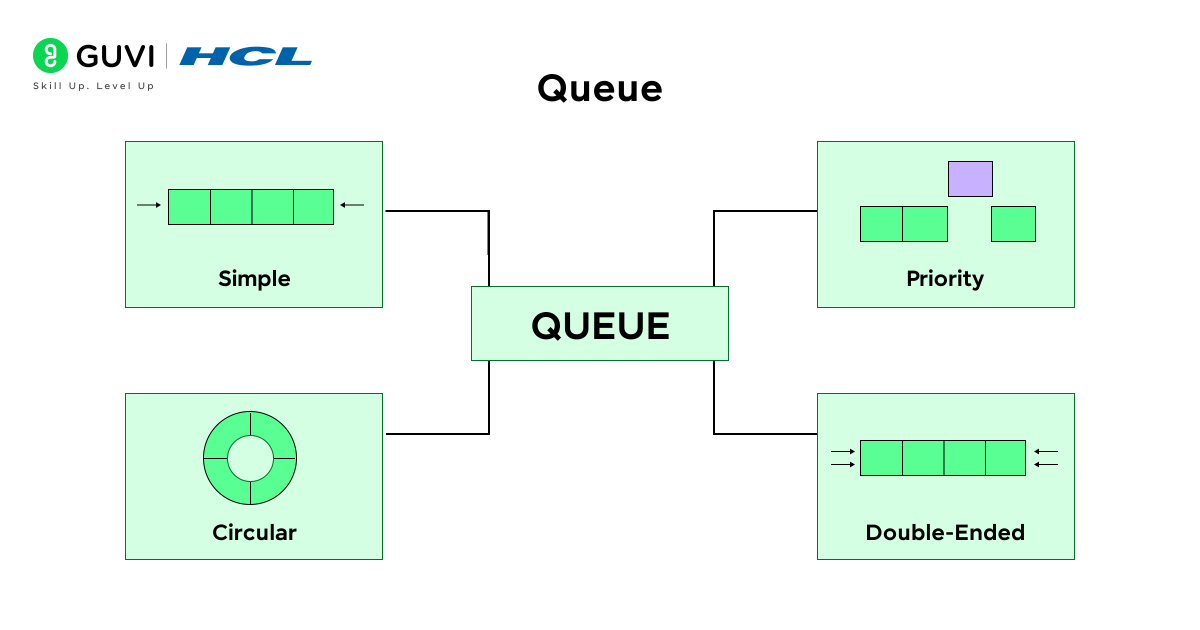
5. Queue
An ordered queue is founded on First in First out (FIFO) – first thing in is first thing out.
- Types of Queues:
- Simple Queue
- Circular Queue
- Priority Queue
- Deque (Double-ended Queue)
- Applications:
- In CPU scheduling, printers, and data buffers.
6. Trees
A Tree is a non-linear data structure that depicts the hierarchical relationship.
- Key Concepts:
- Nodes and Edges
- Binary Trees
- Binary Search Trees (BST)
- AVL Trees and Heaps
- Common Algorithms:
- Traversing of Trees: Inorder, Preorder, Postorder.
- Lowest Common Ancestor (LCA)
- Calculations of Depth and Height.
- Example:
- Your computer has a folder structure that is a tree.
Also Read: Is DSA Important for Placement in 2026?
7. Graphs
Graphs are networks – sets of nodes (vertices) which are linked by edges.
- Key Concepts:
- Directed and Undirected Graphs.
- Weighted and Unweighted Graphs.
- Adjacency List and Adjacency Matrix Representations.
- Popular Algorithms:
- BFS (Breadth-First Search)
- DFS (Depth-First Search)
- Shortest Path (Dijkstra) Algorithm.
- The Minimum Spanning Tree (Kruskal and Prim).
- Applications:
- Graph algorithms are used in Google Maps, Social Media Networks and Recommendation Systems all.
8. Hashing
Hashing to key-value mapping is a method of getting data on a constant time basis.
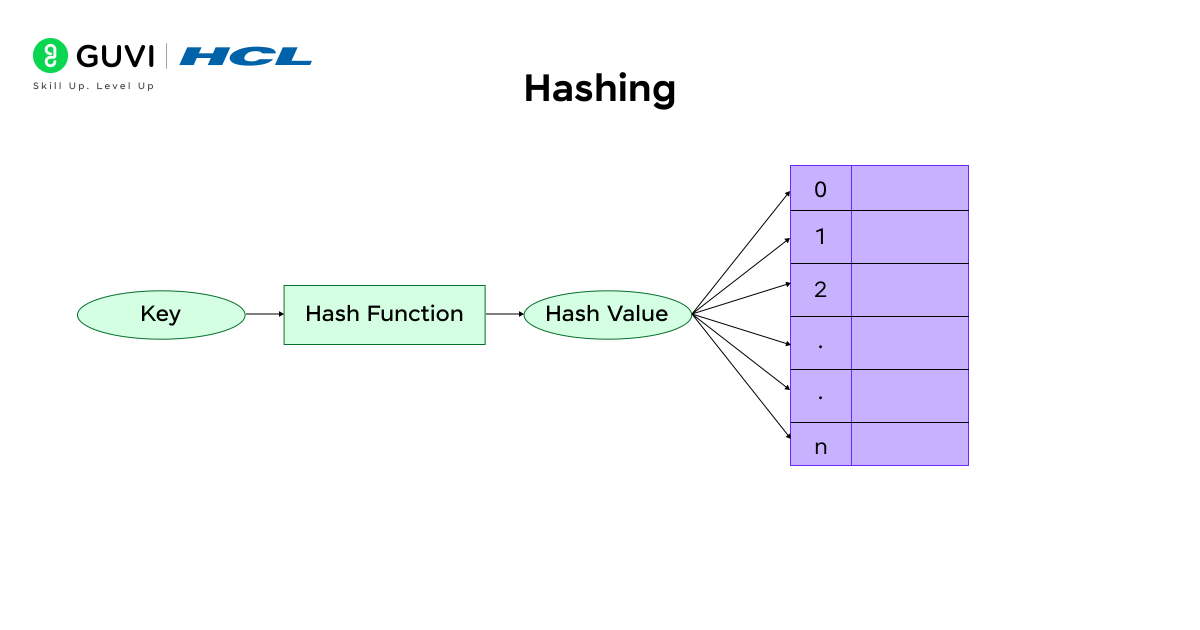
- Key Concepts:
- Hash Functions
- Collisions and collision control (Chaining, Open Addressing)
- Hash Tables and Hash Maps
- Applications:
- Database, password authentication, and caching.
9. Heap
A Heap refers to a complete binary tree that is applied in problems of priorities.
- Types of Heap:
- The smallest element on top is the Min-Heap.
- Max-Heap (biggest on the top)
- Applications:
- Heap Sort
- Priority Queues
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm
10. Trie (Prefix Tree)
A trie is a tree type that is used to store strings.
- Applications:
Search engine, spell checker, and IP routing autocomplete functionality.
11. Disjoint Set (Union-Find)
A structure that is utilized to deal with non-overlapping sets.
- Key Concepts:
- Union and Find operations
- Path Compression
- Applied in Kruskal’s Algorithm of MST.
12. Matrix
A Matrix is a two-dimensional array that is applied in numerous computational cases.
- Applications:
- Image processing
- Game development
- Dynamic programming grids
Part 2: Algorithms
Once the data structures are learned, the following section of the DSA syllabus is the algorithms, i.e. the logic and methods of solving problems in an efficient way.
1. Recursion
Recursion is a situation in which a function recurs to itself till a base condition is reached.
- Examples:
- Factorial, Fibonacci series, and Tower of Hanoi.
- It forms the basis of the divide and conquer and dynamic programming.
2. Searching Algorithms
Search algorithms are used in locating an item in a data set.
- Common Techniques:
- Linear Search
- Binary Search
- Jump Search
- Interpolation Search
3. Sorting Algorithms
Sorting algorithms can be said to organize the data into a given order, thus easier to search and process.
- Basic Algorithms:
- Bubble Sort
- Insertion Sort
- Selection Sort
- Advanced Algorithms:
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Heap Sort
- Counting Sort
4. Divide and Conquer
Divide and Conquer is a method in which a problem is broken down into smaller components and each component is solved, and the results are added together.
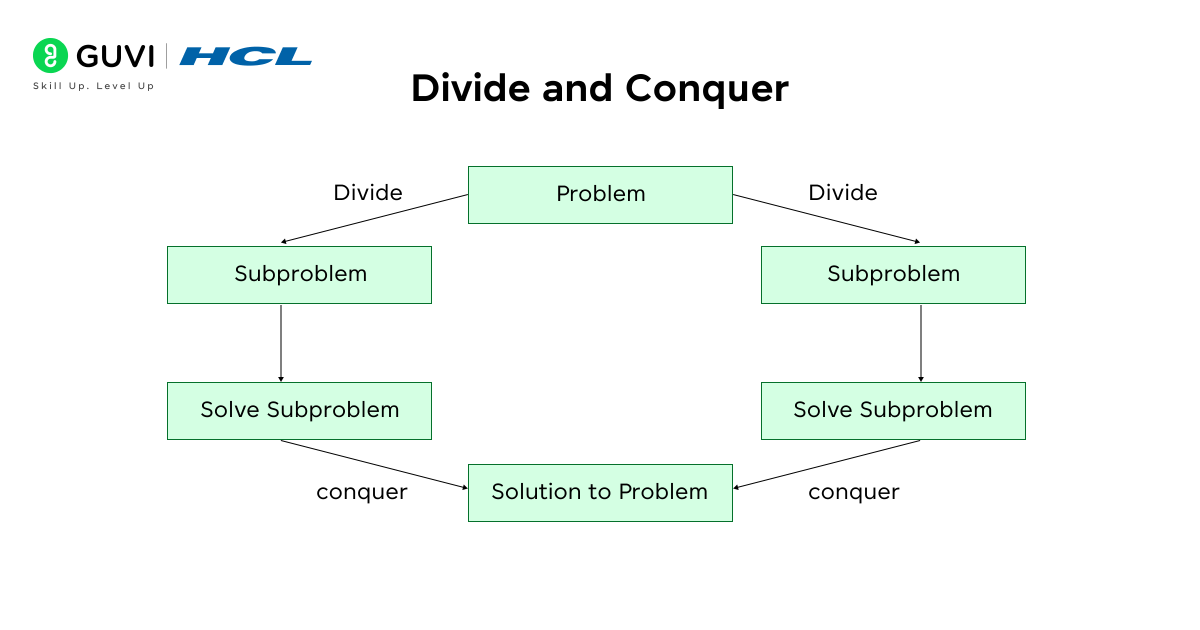
- Examples:
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Binary Search
5. Dynamic Programming (DP)
DP can solve problems by setting the output of sub-problems to save the result.
- Approaches:
- Top-down (Memoization)
- Bottom-up (Tabulation)
- Famous Problems:
- Longest Common Subsequence
- 0/1 Knapsack
- Coin Change
- Matrix Chain Multiplication.
Also read: How to Learn DSA in 2026: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide
6. Greedy Algorithms
Greedy algorithms take optimal decisions at any one time.
- Examples:
- Huffman Coding
- Activity Selection
- Algorithms of Kruskal and Prim.
7. Backtracking
Backtracking explores every possibility and revisits itself upon failure of a path.
- Common Problems:
- N-Queens Problem
- Sudoku Solver
- Rat in a Maze
Also, check out the roadmap.sh DSA Guide, a visual roadmap that helps you understand what to learn next and how every DSA topic fits into your learning path.
8. Bit Manipulation
Bit manipulation is a faster way of solving problems through bitwise operations.
- Concepts:
- AND, OR, XOR
- Counting set bits
- Checking odd/even
- Applications:
- Low-level programming, security algorithms, and data compression.
Now, take your next real step into mastering DSA with HCL GUVI’s hands-on Artificial Intelligence Software Development, co-created with IIT-M Pravartak. Learn by doing, get guided by mentors, and build the confidence to crack interviews like a pro.
Wrapping It Up
You can you this blog as a checklist and start learning DSA. Covering everything from simple data structures such as arrays and strings to complex algorithms like dynamic programming and graphs, following a syllabus will make the learning experience easier and more productive. Follow it, practice regularly, and return to concepts whenever you want to!
FAQs
1. Why learn according to DSA syllabus?
It helps you to learn in a structured manner and ensures you do not miss any important topics.
2. How much time does it require to learn DSA?
Typically, 3-6 months with regular practice. It totally depends on you and you learning speed.
3. Which programming language is best for learning DSA?
The common programming languages to start are Python, C++, or Java.
4. Can a beginner learn DSA?
Of course! Basic knowledge in programming is sufficient to get started.
























Did you enjoy this article?