
Anomaly Detection With Machine Learning: Techniques and Uses
Jan 19, 2026 6 Min Read 1180 Views
(Last Updated)
Every digital system we use, such as banking apps, online stores, healthcare tools, and security platforms, generates a huge amount of data every second. Hidden in this data are unusual patterns that can indicate fraud, system errors, cyberattacks, or unexpected user behaviour. Finding these unusual patterns is known as anomaly detection, and machine learning has made this process faster, smarter, and more accurate than traditional methods.
In this blog, you will learn what anomaly detection means in simple words, why it is important in today’s data-driven world, the main machine learning techniques used to detect anomalies, real examples of how it is used and the challenges it involves. By the end, beginners will have a clear understanding of how anomaly detection works and why it is a valuable skill for anyone interested in data and technology.
Quick Answer
Anomaly detection is a way of spotting unusual data or behaviour that does not match the normal pattern. Machine learning helps make this faster and more accurate, which is useful for detecting fraud, system errors, cyberattacks, or any unexpected risks early. It can be done using methods like statistics, clustering algorithms, classification models, and neural networks.
Table of contents
- What Is Anomaly Detection?
- Importance Of Anomaly Detection
- Key Techniques For Anomaly Detection Using Machine Learning
- Statistical Modelling
- Clustering-Based Detection
- Classification Models
- Neural Networks
- Time-Series Analysis
- Real-World Uses Of Anomaly Detection
- Banking Fraud
- Healthcare Monitoring
- Cybersecurity
- Manufacturing
- E-commerce
- Challenges In Anomaly Detection
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is anomaly detection in simple terms?
- What causes anomalies in data?
- Do I need machine learning for anomaly detection?
- Which machine learning techniques work best for anomaly detection?
- Where is anomaly detection used the most?
What Is Anomaly Detection?
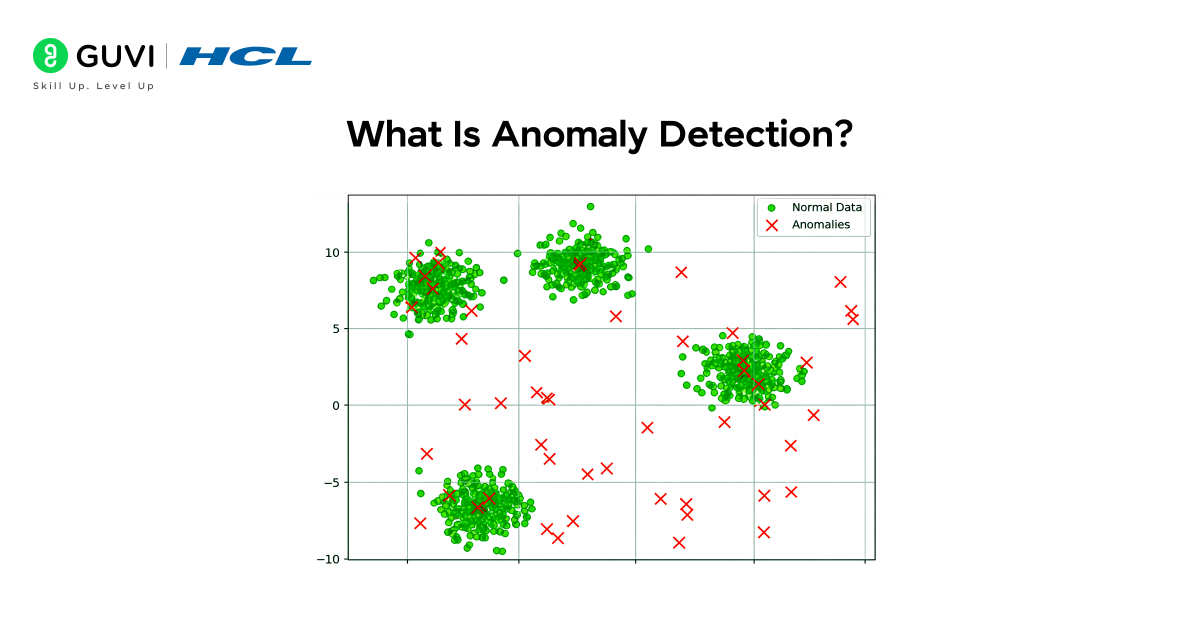
Anomaly detection is a method used to find unusual patterns in data that do not match normal behaviour. It helps identify when something unexpected happens, such as a sudden spike in transactions, a strange login attempt, or a sensor reading that looks abnormal. Machine learning makes this process more accurate by learning what “normal” looks like and quickly spotting anything that stands out.
Key Characteristics:
- Identifies Unusual Behaviour: Spots data points that differ from the regular pattern.
- Learns From Normal Data: Understands what typical behaviour looks like.
- Works Across Data Types: Can be used for numbers, text, images, or time-based data.
- Finds Rare Events: Detects anomalies even when they occur very rarely.
- Adapts Over Time: Updates itself as patterns change or evolve.
- Supports Real-Time Monitoring: Helps catch issues instantly in banking, security, and systems.
Example:
If your electricity bill is usually around 800 rupees and suddenly jumps to 3500 rupees without any major change at home, that unusual increase is an anomaly.
Types Of Anomalies:
Anomalies can appear in different forms depending on how data deviates from normal behaviour. Understanding these types helps choose the right detection method.
- Point Anomalies: A single data point that is significantly different from the rest of the dataset, such as an unusually high bank transaction compared to your regular spending.
- Contextual Anomalies: Values that are only unusual in a specific context, like a high temperature at midnight, which would be normal during the day but abnormal at night.
- Collective Anomalies: A set of data points that individually may seem normal but together indicate an unusual pattern, such as multiple failed login attempts within a short period.
Importance Of Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection is a critical process in data analysis because unusual patterns can lead to security risks, financial losses, or system breakdowns. With machine learning, anomaly detection becomes faster, smarter, and more accurate, helping businesses maintain reliable and safe operations. Here are the key features and characteristics that highlight its importance:
- Early Risk Identification – A key characteristic of anomaly detection is its ability to catch unusual behaviour early, helping prevent major issues before they escalate.
- Improved System Security – A core feature that helps detect fraud, unauthorised access, and cyberattacks in real time, protecting sensitive data and systems.
- Better Operational Efficiency – A major benefit where anomaly detection identifies system faults early, reducing downtime and improving workflow efficiency.
- Stronger Decision-Making Support – A useful characteristic that provides accurate insights, helping businesses make data-driven and risk-free decisions.
- Enhanced Data Quality – A key feature that identifies corrupted, missing, or inconsistent data, improving the accuracy of analytics and machine learning models.
Key Techniques For Anomaly Detection Using Machine Learning
Machine learning offers several powerful ways to detect unusual patterns in data. Each technique works differently and helps identify anomalies like fraud, system failures, suspicious behaviour, or sudden changes. The main techniques used in anomaly detection include:
- Statistical Modeling
- Clustering-Based Detection
- Classification Models
- Neural Networks
- Time-Series Analysis
Below is a detailed explanation of each technique with its key aspects and an easy-to-understand example.
1. Statistical Modelling
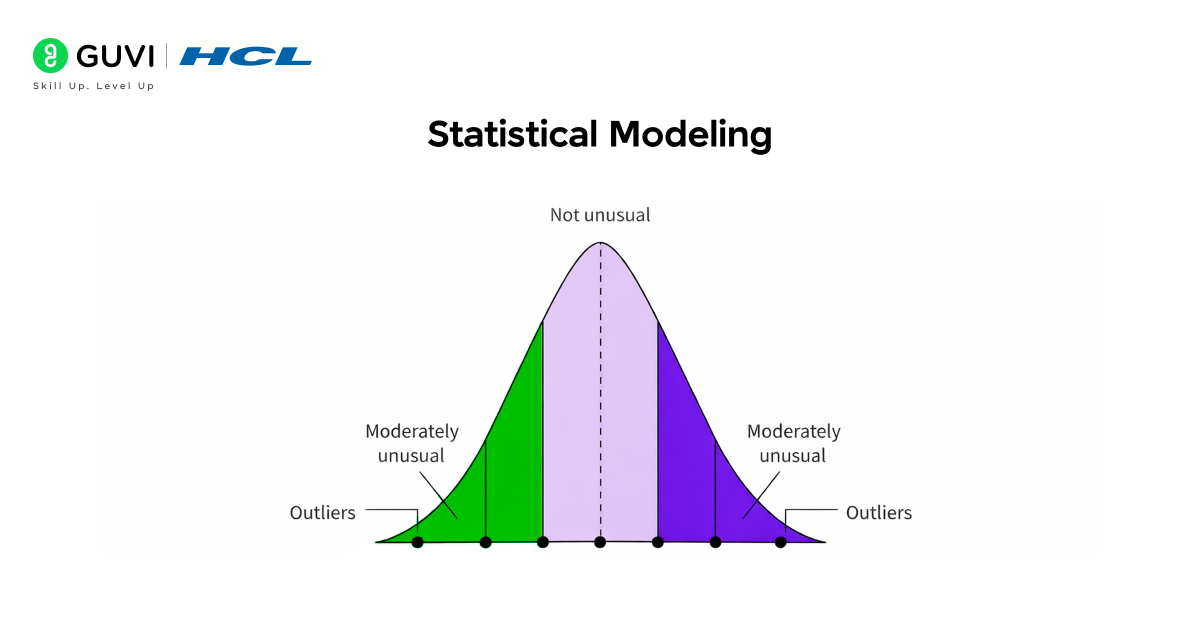
Statistical modelling detects anomalies by studying how data normally behaves. It assumes that most data points fall within a predictable numerical range, and anything too far from that range signals unusual behaviour. This technique is especially useful when the system follows stable patterns, like monthly expenses, server response times, or sensor readings. By analysing values such as the mean, median, variance, and standard deviation, machine learning systems can automatically set thresholds. When a data point crosses these thresholds, it is marked as an anomaly. This method works best for clean, structured numeric data where relationships between values remain consistent over time.
Key Features:
- Uses numerical measures such as mean, median, variance, and standard deviation
- Detects outliers based on statistical thresholds
- Works best in stable, predictable datasets with low variation
Example:
A bank monitors average daily withdrawal amounts and flags a sudden, unusually large transaction compared to a customer’s normal pattern.
2. Clustering-Based Detection
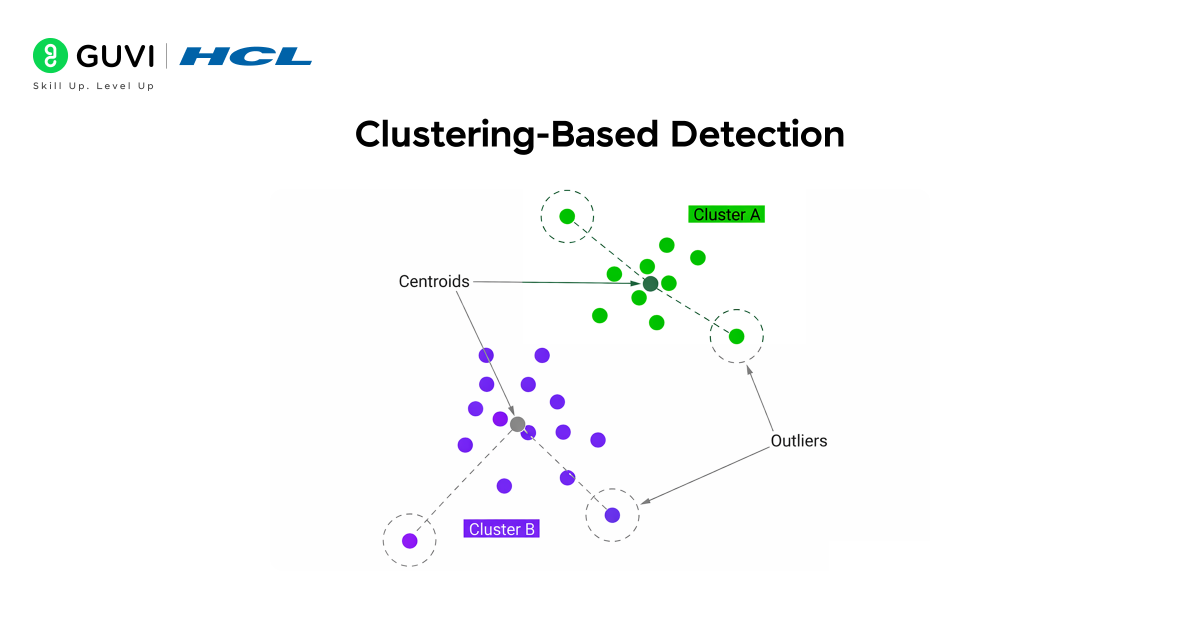
Clustering-based detection groups similar data points together based on shared characteristics. Machine learning models like K-means or DBSCAN automatically analyse the data and create clusters. Any point that does not belong to these clusters or appears too far from the central group is treated as an anomaly. This approach is powerful when the dataset does not have labels, which is common in real-world scenarios like customer behaviour, website traffic, and IoT sensor monitoring. Since it identifies natural structure in data, clustering is effective for uncovering unexpected behaviour patterns and hidden irregularities that simple statistical techniques may miss.
Key Features:
- Uses unsupervised learning algorithms like K-means, DBSCAN, and Hierarchical Clustering
- Ideal for datasets where labels are not available
- Detects data points that deviate from naturally formed clusters
Example:
An e-commerce platform discovers a user whose browsing pattern does not match any existing customer group, signalling possible bot activity or unusual interest.
3. Classification Models
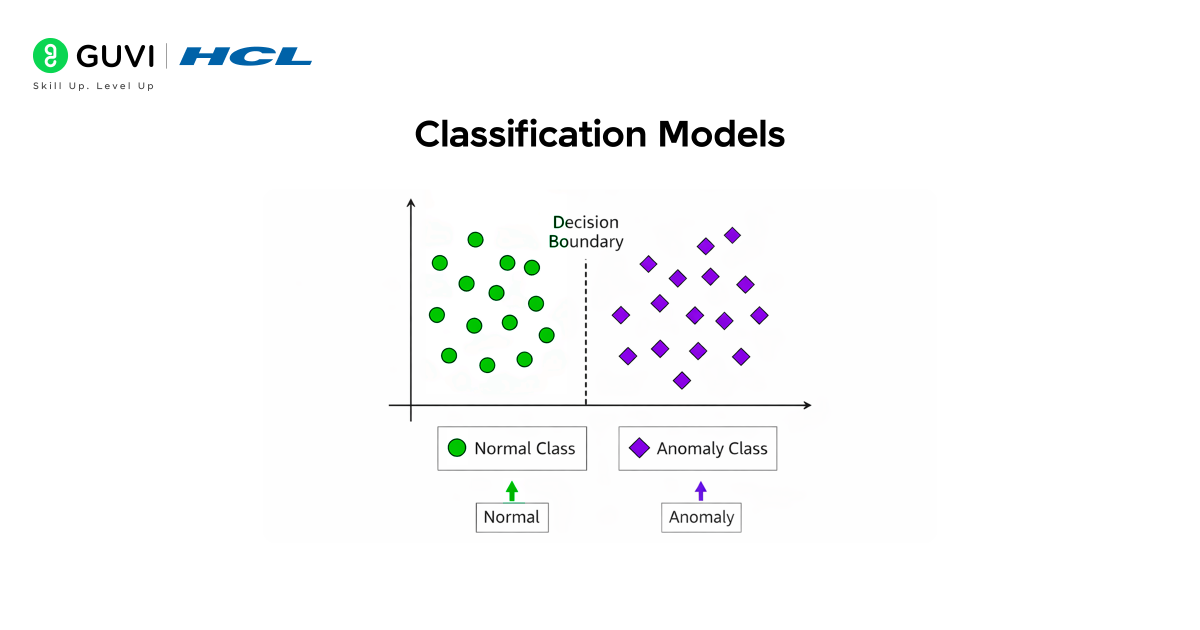
Classification models learn the difference between normal and abnormal behaviour through labelled examples. Machine learning algorithms such as logistic regression, decision trees, support vector machines, and random forests examine past data and identify patterns linked to anomalies. Once trained, the model predicts whether new data points are normal or suspicious. This method is highly accurate when plenty of labelled history exists, such as past fraud cases, rejected transactions, or flagged login attempts. Classification is widely used in industries like finance, insurance, cybersecurity, and healthcare, where differentiating normal behaviour from risk is crucial.
Key Features:
- Uses supervised learning with labelled datasets
- Algorithms include logistic regression, decision trees, and random forests
- Offers high accuracy when sufficient labelled data is available
Example:
A fraud detection system analyses past credit card transactions and learns to classify new transactions as genuine or suspicious.
4. Neural Networks
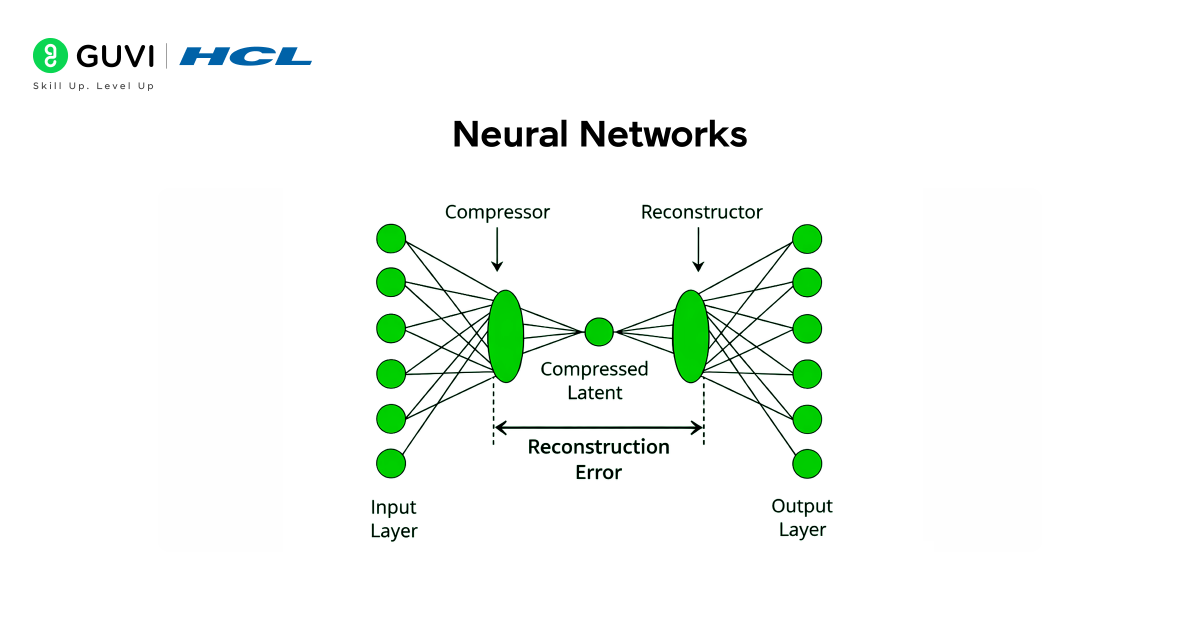
Neural networks are powerful for capturing complex, non-linear patterns in large datasets. They can detect even the smallest irregularities that simple models cannot notice. Autoencoders are commonly used for anomaly detection: they learn how to reconstruct normal data, and when they fail to accurately reconstruct a new data point, it signals an anomaly. Deep learning models also work exceptionally well with high-dimensional data, such as images, logs, or network traffic. Because they continuously learn from massive datasets, neural networks are ideal for real-time environments where anomalies need to be detected instantly.
Key Features:
- Uses deep learning techniques such as autoencoders and neural-based models
- Ideal for high-dimensional, complex, or unstructured data
- Detects subtle and rare anomalies missed by traditional models
Example:
A cybersecurity system uses an autoencoder to learn normal network traffic behaviour and immediately flags any traffic that differs from the learned pattern.
5. Time-Series Analysis
Time-series analysis focuses on data that changes over time, such as stock prices, web traffic, sensor readings, or server performance. Machine learning models identify normal time-based patterns like seasonality, daily cycles, or trends. When the system detects sudden spikes, dips, or irregular sequences, it marks them as anomalies. Techniques such as ARIMA and LSTM networks are commonly used because they understand temporal patterns and can forecast what values should look like in the near future. Any unexpected deviation from this forecast helps catch issues like outages, system overloads, or unusual market activity early.
Key Features:
- Uses models like LSTM networks, ARIMA, and Prophet
- Works best for data with time-based trends or seasonal patterns
- Detects sudden changes in sequences like spikes, drops, or irregular intervals
Example:
An LSTM model monitors real-time website traffic and flags an unexpected drop in visitors during peak hours, indicating a possible server issue.
Real-World Uses Of Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection is widely applied in industries that continuously monitor large amounts of data. By identifying unusual patterns early, organisations can prevent losses, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions. Machine learning automates this process by learning normal behaviour and flagging deviations automatically. Below are key real-world use cases and how anomaly detection is applied in each.
1. Banking Fraud
Banks use anomaly detection to monitor transactions in real time. Machine learning models analyse spending patterns, login locations, device usage, and transaction frequency. Any activity that deviates significantly from a customer’s usual behaviour, like an unusually large transfer or a login from a new country, is flagged as suspicious.
How It’s Done:
- Analyse historical transaction data to understand normal behaviour
- Apply statistical, clustering, or classification-based anomaly detection
- Trigger alerts when new transactions fall outside learned patterns
2. Healthcare Monitoring
Anomaly detection tracks vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. Machine learning models learn normal ranges for each patient and detect deviations that could indicate medical emergencies.
How It’s Done:
- Collect continuous time-series data from devices or sensors
- Use time-series analysis or neural networks to detect unusual patterns
- Notify healthcare providers when anomalies indicate risk
3. Cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, organisations use anomaly detection to detect hacking attempts, malware, or unauthorised access. Models monitor network traffic, user logins, and system behaviour to flag unusual patterns.
How It’s Done:
- Monitor network logs, login attempts, and system activity
- Use clustering or neural networks to identify deviations from normal traffic
- Automatically flag unusual behaviour for investigation
4. Manufacturing
In manufacturing, anomaly detection monitors machines and production lines to prevent failures. Sensors collect data on temperature, vibration, and pressure, and models learn normal operating ranges. Any deviation triggers maintenance alerts.
How It’s Done:
- Collect continuous sensor data from machinery
- Apply statistical or time-series anomaly detection
- Alert operators when values exceed safe thresholds
5. E-commerce
E-commerce platforms monitor unusual customer behaviour, fake reviews, or suspicious transactions. Machine learning models analyse purchasing trends, review patterns, and browsing behaviour to detect abnormalities.
How It’s Done:
- Track user interactions, transactions, and reviews
- Apply clustering and classification models to detect unusual patterns
- Highlight suspicious behaviour for review
Challenges In Anomaly Detection
Even though machine learning has made anomaly detection faster and more accurate, implementing it perfectly is not easy. Several practical challenges make it difficult for systems to catch every unusual pattern reliably. Understanding these obstacles helps teams plan better and improve detection outcomes.
- Scarce Anomaly Data: Rare anomalies make model training difficult.
- High False Alarms: Normal behaviour can be wrongly flagged as suspicious.
- Changing Patterns: System behaviour evolves, reducing model accuracy over time.
- High-Dimensional Complexity: Large, complex datasets require advanced models like deep learning.
- Unclear Anomaly Definitions: What counts as unusual varies across industries and datasets.
Conclusion
Anomaly detection using machine learning is changing the way companies spot risks, prevent fraud, and keep systems secure. Techniques like statistical modelling, clustering, classification, neural networks, and time-series analysis help detect unusual patterns in data quickly and accurately. This makes it easier for businesses to act fast and avoid problems before they become serious.
As more companies rely on data, the need for people who understand anomaly detection is growing. Learning how to find and handle unusual patterns is a valuable skill for anyone starting a career in data science, technology, or analytics. By mastering these techniques, you can solve real-world problems and make a real impact in keeping systems safe and efficient.
For beginners looking to gain hands-on skills in anomaly detection and machine learning, the HCL GUVI Zen class – IIT‑M Pravartak Certified Machine Learning Course is an excellent choice. This program teaches you how to build and deploy machine learning models, understand supervised and unsupervised techniques and work with real-world datasets. Enrolling in this course can help you strengthen your practical knowledge and confidently apply anomaly detection techniques in industries like finance, healthcare, cybersecurity, and more.
FAQs
1. What is anomaly detection in simple terms?
It is the process of spotting unusual data or behaviour that does not follow normal patterns.
2. What causes anomalies in data?
Anomalies can happen due to system errors, fraud attempts, sudden changes in behaviour, or mistakes in data collection.
3. Do I need machine learning for anomaly detection?
Not always, but machine learning makes it much faster and more accurate, especially for large or complex datasets.
4. Which machine learning techniques work best for anomaly detection?
There is no single method. Clustering, neural networks, and time-series models are popular choices depending on the type of data and patterns.
5. Where is anomaly detection used the most?
It is widely used in banking, cybersecurity, healthcare, manufacturing, e-commerce, and IoT systems.




























Did you enjoy this article?