
Have you ever wondered how your computer manages multiple programs at once — like playing music, downloading files, and running a browser all together without crashing? That’s the magic of an Operating System (OS). It’s the heart of your computer, handling tasks like process management, file handling, memory control, and system security.
Understanding how an OS works is essential for anyone stepping into the world of tech — whether you want to become a software developer, system engineer, or cybersecurity analyst. But the best way to grasp these concepts isn’t just by reading about them — it’s by building real-world projects that simulate how an operating system functions behind the scenes.
In this blog, we’ll dive into simple yet powerful Operating System projects ideas built using Python. These projects will help you understand key OS concepts like process management, resource allocation, and file organization — all through practical coding exercises. By the end, you’ll not only improve your coding and debugging skills but also gain a strong foundation in system-level programming that can boost your career in software and tech.
Table of contents
- Importance of Learning OS Through Projects
- Prerequisites for These Projects
- Operating System Project Ideas Using Python
- Task Manager Clone
- File Organizer App
- Alarm and Reminder System
- Simple Command-Line Shell
- Memory Allocation Visualizer
- File Encryption and Decryption Tool
- Disk Scheduling Algorithm Simulator
- Deadlock Detection System
- CPU Scheduling Visualizer
- Mini Operating System Simulation
- Summary of Operating System Projects
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What are the best beginner-friendly projects to start learning Operating Systems?
- Which programming language is best for Operating System projects?
- Can I build these projects on any operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux)?
- How can these projects help in my career?
- What should I learn next after completing these Operating System projects?
Importance of Learning OS Through Projects
Building projects that mimic OS operations helps you develop logical thinking and problem-solving skills. Instead of just memorizing how an OS works, you’ll actually see it in action through your code. Here’s why it’s valuable:
- Enhances system-level understanding: Learn how software interacts with hardware through code.
- Improves debugging and logical thinking: Understand how processes are managed, paused, and terminated.
- Prepares you for real-world applications: The skills gained from these projects are directly applicable to app development and automation.
- Boosts your portfolio: These projects demonstrate hands-on knowledge — a big plus for tech interviews.
If you’re starting, this approach will make OS concepts like process scheduling, memory allocation, and file systems easier and more fun to learn.
Prerequisites for These Projects
Before jumping into the projects, make sure you have:
- Basic knowledge of Python (loops, conditionals, and file handling).
- A code editor like VS Code, PyCharm, or even a simple terminal setup.
- The os, psutil, and time modules are installed in Python (you can install any missing ones using pip install module-name).
With these basics ready, you can start building your own OS-inspired utilities step by step — from monitoring processes to automating system tasks.
Operating System Project Ideas Using Python

If you’re curious about how operating systems function and want to learn by building real projects, Python is one of the best languages to begin with. It’s simple, powerful, and ideal for experimenting with system-level concepts easily and interactively.
In this section, we’ll explore 10 practical Operating System project ideas — starting from beginner-friendly tools to more advanced visual simulators that mirror real OS operations.
Here’s what you’ll find below:
- Task Manager Clone
- File Organizer App
- Alarm and Reminder System
- Simple Command Line Shell
- Memory Allocation Visualizer
- File Encryption and Decryption Tool
- Disk Scheduling Algorithm Simulator
- Deadlock Detection System
- CPU Scheduling Visualizer
- Mini Operating System Visualizer
Each project includes its purpose, key features, Python implementation, how to run it, and bonus tips to make it more engaging and practical.
1. Task Manager Clone
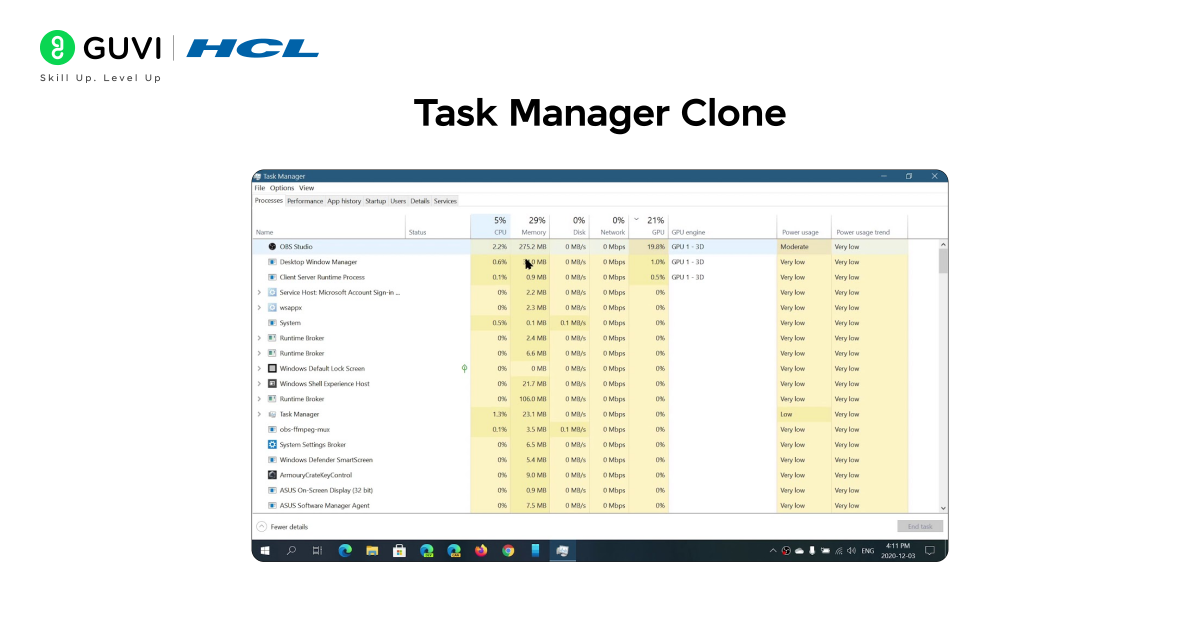
Have you ever checked your computer’s Task Manager to see which app is using too much memory or CPU? You can build your own simple version of that in Python! This project helps you understand how operating systems track and manage running processes.
This Task Manager Clone displays details like the process name, process ID, CPU usage, and memory percentage for each running application on your computer.
Key Features:
- Displays all currently running processes
- Shows CPU and memory usage for each process
- Refreshes data in real time
- Can be extended to terminate processes
Language/Tools Used:
Python, psutil library
Project Code:
import psutil
import time
import os
while True:
os.system('cls' if os.name == 'nt' else 'clear')
print("{:<30} {:<10} {:<10} {:<10}".format("Process Name", "PID", "CPU %", "Memory %"))
print("-" * 70)
for proc in psutil.process_iter(['pid', 'name', 'cpu_percent', 'memory_percent']):
print("{:<30} {:<10} {:<10} {:<10}".format(
proc.info['name'][:25],
proc.info['pid'],
proc.info['cpu_percent'],
round(proc.info['memory_percent'], 2)
))
time.sleep(2)
How to Run the Code:
- Install the required library using pip install psutil.
- Save the file as task_manager.py.
- Run it in your terminal using python task_manager.py.
Bonus Tips:
- Add an option to end a process by entering its PID.
- Include thread count or execution time.
- Build a GUI version using tkinter.
2. File Organizer App
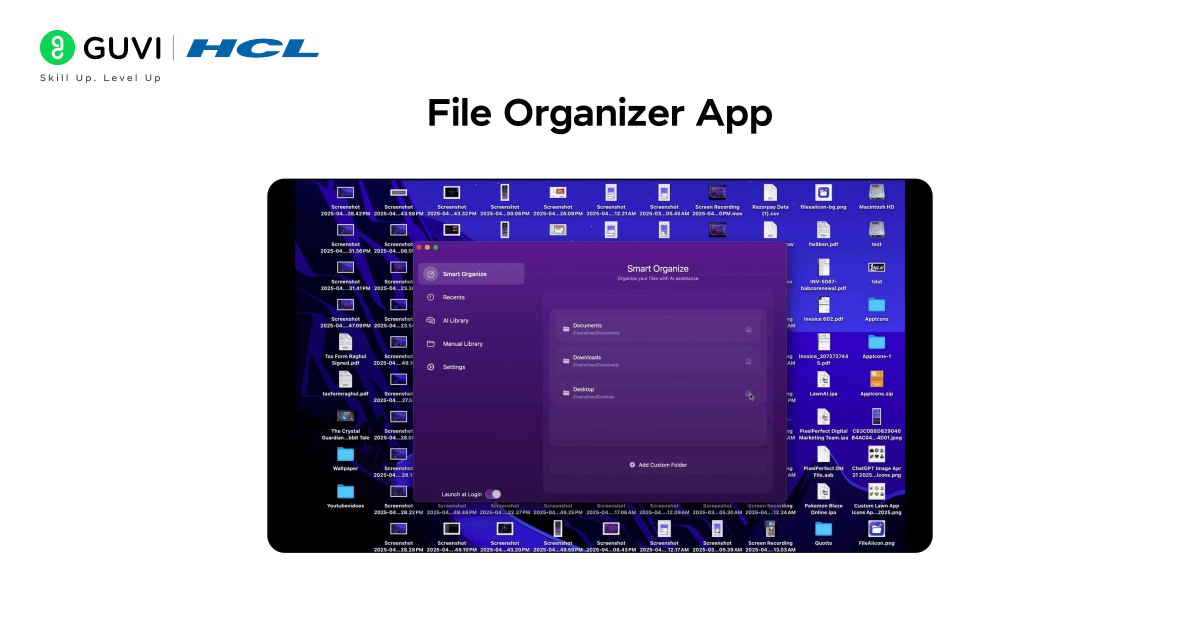
Tired of a cluttered downloads folder? Build a File Organizer that automatically sorts files into folders based on their type. This mimics how an operating system organizes files efficiently.
Key Features:
- Automatically categorizes files (images, documents, videos, etc.)
- Supports multiple file types
- Works in any directory
Language/Tools Used:
Python, os, shutil
Project Code:
import os
import shutil
def organize_files(folder_path):
for file in os.listdir(folder_path):
name, ext = os.path.splitext(file)
ext = ext[1:]
if ext == '':
continue
if not os.path.exists(folder_path + '/' + ext):
os.makedirs(folder_path + '/' + ext)
shutil.move(folder_path + '/' + file, folder_path + '/' + ext + '/' + file)
path = input("Enter folder path: ")
organize_files(path)
print("Files organized successfully!")
How to Run the Code:
- Save as file_organizer.py.
- Run it and enter the path to your folder.
Bonus Tips:
- Add logging to show how many files were moved.
- Support subfolders.
- Add a GUI for selecting folders.
Discover: 8 Different Types of Operating Systems You Should Know
3. Alarm and Reminder System

Sometimes we forget meetings or deadlines. This Alarm system runs in the background and alerts you at a specific time.
Key Features:
- Custom time input
- Audio notification
- Simple time comparison logic
Language/Tools Used:
Python, datetime, time, playsound
Project Code:
from datetime import datetime
import time
from playsound import playsound
alarm_time = input("Enter time in HH:MM:SS format: ")
while True:
current_time = datetime.now().strftime("%H:%M:%S")
if current_time == alarm_time:
print("Wake up! It’s time!")
playsound('alarm.mp3')
break
time.sleep(1)
How to Run the Code:
- Install playsound with pip install playsound.
- Save an alarm.mp3 file in the same directory.
- Run python alarm.py.
Bonus Tips:
- Add recurring alarms.
- Use tkinter for a user interface.
4. Simple Command-Line Shell
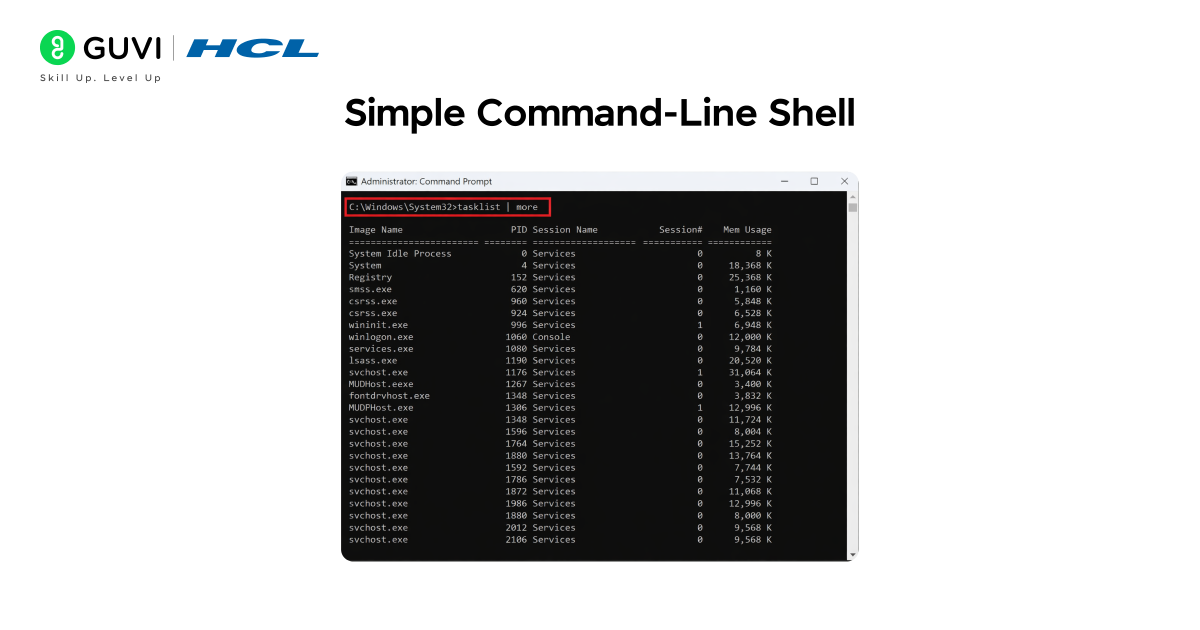
Want to know how your terminal executes commands? Build your own mini shell!
Key Features:
- Accepts and executes system commands
- Handles errors gracefully
Language/Tools Used:
Python, os
Project Code:
import os
while True:
command = input(">> ")
if command.lower() == "exit":
break
os.system(command)
How to Run the Code:
Run it in the terminal and try commands like dir, ls, or cd.
Bonus Tips:
- Add command history.
- Support multiple commands in one line.
5. Memory Allocation Visualizer
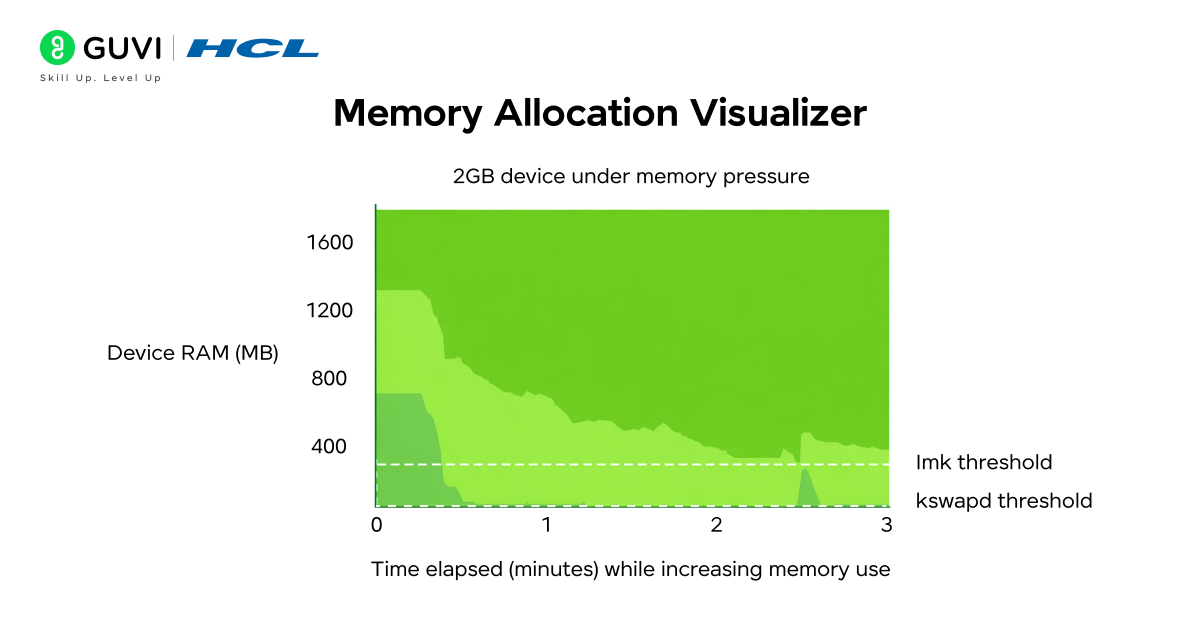
This project visually demonstrates how an OS divides memory among processes.
Key Features:
- Simulates memory allocation using lists
- Shows which block each process occupies
Language/Tools Used:
Python
Project Code:
memory = [0]*10
processes = {"A":3, "B":2, "C":4}
start = 0
for p, size in processes.items():
for i in range(start, start+size):
memory[i] = p
start += size
print("Memory Allocation:", memory)
How to Run the Code:
Run in any Python IDE or terminal.
Bonus Tips:
- Add a graphical display.
- Implement Best Fit or First Fit logic.
6. File Encryption and Decryption Tool
Protect your files using encryption, just like an OS secures data.
Key Features:
- Encrypts and decrypts files
- Uses a simple shift cipher
Language/Tools Used:
Python
Project Code:
def encrypt(text, key):
return ''.join(chr((ord(char) + key) % 256) for char in text)
def decrypt(text, key):
return ''.join(chr((ord(char) - key) % 256) for char in text)
choice = input("Encrypt or Decrypt (e/d): ")
key = int(input("Enter key: "))
filename = input("Enter file name: ")
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
data = file.read()
if choice == 'e':
result = encrypt(data, key)
else:
result = decrypt(data, key)
with open('output.txt', 'w') as file:
file.write(result)
print("Operation successful! Saved in output.txt")
How to Run the Code:
Save as encrypt_tool.py, run it, and follow prompts.
Bonus Tips:
- Add password-based encryption.
- Use AES for stronger security.
7. Disk Scheduling Algorithm Simulator
Understand how your OS decides disk read/write order.
Key Features:
- Implements FCFS scheduling
- Shows total head movement
Language/Tools Used:
Python
Project Code:
def fcfs(requests, head):
total = 0
for r in requests:
total += abs(r - head)
head = r
print("Total head movement:", total)
requests = [82, 170, 43, 140, 24, 16, 190]
head = 50
fcfs(requests, head)
How to Run the Code:
Run in the terminal. It prints the total disk head movement.
Bonus Tips:
- Add SCAN or SSTF algorithm options.
- Plot movement path with Matplotlib.
Explore: Operating System Commands
8. Deadlock Detection System
Simulate how the OS detects and prevents resource deadlocks.
Key Features:
- Uses simple wait graph logic
- Detects circular dependency
Language/Tools Used:
Python
Project Code:
processes = ["P1","P2","P3"]
resources = {"R1":"P1","R2":"P2","R3":"P3"}
wait = {"P1":"R2","P2":"R3","P3":"R1"}
def detect_deadlock():
for p in processes:
if wait[p] in resources and resources[wait[p]] == p:
print("Deadlock detected between", p, "and", resources[wait[p]])
return
print("No Deadlock")
detect_deadlock()
How to Run the Code:
Run it directly.
Bonus Tips:
- Let users input their own resources.
- Show graphical dependency diagrams.
9. CPU Scheduling Visualizer
Simulate how your OS switches between processes.
Key Features:
- Implements Round Robin scheduling
- Displays process execution order
Language/Tools Used:
Python
Project Code:
def round_robin(processes, burst_time, quantum):
rem = burst_time[:]
t = 0
while True:
done = True
for i in range(len(processes)):
if rem[i] > 0:
done = False
if rem[i] > quantum:
t += quantum
rem[i] -= quantum
print(processes[i], "executed for", quantum)
else:
t += rem[i]
print(processes[i], "finished at time", t)
rem[i] = 0
if done:
break
processes = ["P1","P2","P3"]
burst_time = [10,5,8]
quantum = 2
round_robin(processes, burst_time, quantum)
How to Run the Code:
Save and run directly.
Bonus Tips:
- Add Gantt chart visualization.
- Let users input processes interactively.
10. Mini Operating System Simulation

Combine everything you’ve learned into a simple shell-based OS simulation.
Key Features:
- Simple command execution
- File read/write operations
- Process listing
Language/Tools Used:
Python
Project Code:
import os
def list_files():
print(os.listdir())
def create_file():
name = input("Enter file name: ")
open(name, 'w').close()
print("File created!")
def read_file():
name = input("Enter file name: ")
with open(name, 'r') as f:
print(f.read())
while True:
cmd = input("Enter command (list/create/read/exit): ").lower()
if cmd == 'list':
list_files()
elif cmd == 'create':
create_file()
elif cmd == 'read':
read_file()
elif cmd == 'exit':
break
else:
print("Invalid command!")
How to Run the Code:
Run in the terminal, and try commands like list, create, or read.
Bonus Tips:
- Add delete and rename options.
- Introduce user login before access.
Also Read: Functions of Operating System: A Beginner’s Guide 2025
Summary of Operating System Projects
| Level | Project Name | Concept Covered | Key Learning Outcome |
| 1 | Task Manager Clone | Process Management | Learn how the OS monitors, lists, and terminates running processes. |
| 2 | File Organizer App | File System Management | Understand how operating systems handle file storage and categorization. |
| 3 | Alarm and Reminder System | Task Scheduling | Explore how the OS manages time-based events and process triggers. |
| 4 | Simple Command Line Shell | Command Execution | Discover how shells interpret and execute user commands. |
| 5 | Memory Allocation Visualizer | Memory Management | Visualize how memory is allocated and freed in real-time processes. |
| 6 | File Encryption and Decryption Tool | Data Security | Learn how the OS ensures secure data handling through encryption. |
| 7 | Disk Scheduling Algorithm Simulator | Disk Management | Simulate how disks prioritize read/write operations for efficiency. |
| 8 | Deadlock Detection System | Process Synchronization | Understand how systems identify and resolve deadlock conditions. |
| 9 | CPU Scheduling Visualizer | CPU Scheduling | See how different scheduling algorithms impact system performance. |
| 10 | Mini Operating System Visualizer | OS Integration | Combine all core OS functions into one interactive simulation. |
To build a stronger foundation for these projects, explore HCL GUVI’s Basics of Computer Course. It helps you understand how computers and operating systems work behind the scenes, offering an easy and interactive learning experience for beginners eager to grasp real-world system concepts.
Conclusion
Working on these Operating System projects helps you transform theoretical knowledge into real-world understanding. Each project takes you a step deeper into how systems control processes, allocate memory, and manage resources — the same functions that make every computer or smartphone run smoothly.
Starting from simple tools like a Task Manager clone and ending with a Mini OS Visualizer, you gradually learn how each OS component contributes to performance and stability. These projects not only build your coding skills in Python but also prepare you for advanced fields like system design, DevOps, and OS development.
The best way to learn about operating systems is by experimenting. Try extending these projects — add new scheduling algorithms, integrate GUIs, or simulate real-time data. The more you explore, the clearer the logic behind every operating system becomes.
FAQs
1. What are the best beginner-friendly projects to start learning Operating Systems?
If you’re just starting out, begin with simple Python-based projects like a Task Manager Clone or a File Organizer App. These help you understand core OS concepts such as process management and file handling without overwhelming complexity.
2. Which programming language is best for Operating System projects?
While C and C++ are commonly used for building actual OS kernels, Python is excellent for learning and simulation. It allows you to experiment with OS concepts like process control, memory allocation, and scheduling using minimal code.
3. Can I build these projects on any operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux)?
Yes. Most of these Python projects are cross-platform, meaning they work on any OS as long as you have Python installed. Just make sure to adjust file paths and permissions based on your system.
4. How can these projects help in my career?
Working on OS projects strengthens your understanding of system-level programming, which is valuable for roles in software development, DevOps, and cybersecurity. Employers appreciate candidates who understand how systems work behind the scenes.
5. What should I learn next after completing these Operating System projects?
After these projects, you can move on to more advanced topics like virtualization, networking, and Linux kernel scripting, or even explore mobile and embedded system development to see how OS concepts extend to other platforms.



































Did you enjoy this article?