
Calculus for data science often works quietly in the background, but it plays a critical role in how data models understand and respond to change. It helps quantify how values shift, how trends evolve, and how variables influence one another. Without calculus, data science would lack the mathematical foundation needed to explain why models behave the way they do.
In practical machine learning workflows, calculus shows up when a model learns from data. Derivatives are used to adjust parameters during training, gradients help minimize errors, and integrals appear when dealing with probability distributions and continuous data. These concepts directly impact how accurate and efficient a model becomes.
In this blog, we’ll explore calculus for data science, starting from beginner-friendly fundamentals and gradually moving into advanced concepts. The goal is to show not just what to learn, but how each concept connects to real modeling and decision-making in the field.
Table of contents
- Importance of Calculus in Data Science
- Beginner Topics in Calculus for Data Science
- Derivatives – Understanding Change
- Integrals – Accumulating Data
- Multivariable Calculus – Working with Complex Data
- Optimization Using Calculus
- Advanced Topics in Calculus for Data Science
- Partial Derivatives
- Chain Rule & Higher-Order Derivatives
- Vector Calculus
- Jacobian and Hessian Matrices
- Differential Equations (Intro Level)
- Real-World Applications
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Why is calculus important in data science?
- Which calculus concepts are most used in machine learning?
- How does calculus help in neural networks?
- Can beginners learn data science without calculus?
- How is calculus applied in real-world data science projects?
Importance of Calculus in Data Science
Calculus for data science plays a foundational role in how machine learning models learn, adjust, and make accurate predictions. It helps quantify how values change, how outcomes can be optimized, and how continuous data can be interpreted. Without calculus, many core algorithms used in data science would not function effectively. In this section, we’ll explore the core and most important features of calculus for data science and how they are applied in real-world scenarios.
- Derivatives in Calculus for Data Science – Measure how one variable changes with respect to another, helping detect trends and understand rates of change in data.
- Gradient Calculation – In machine learning, derivatives guide gradient descent, updating model weights to minimize prediction error.
- Integrals for Accumulation – Integrals calculate total accumulation in data, such as total revenue, continuous probability, or area under curves.
- Optimization with Calculus – Finds minimum or maximum values in models, improving prediction accuracy and performance.
- Neural Networks & Backpropagation – Calculus enables the computation of gradients layer by layer, making deep learning models learn efficiently.
- Probability and Statistics – Integrals and continuous functions rely on calculus for probability modeling and statistical inference.
In short, calculus for data science is the mathematical backbone that allows models to learn, optimize, and make precise, data-driven decisions. If you prefer learning through short, daily lessons, you should check out this 5-Day Data Science Email Series. Each email introduces one key concept at a time — from data preprocessing to simple model building — making it easy to stay consistent. It’s perfect for learners who want progress without pressure.
Beginner Topics in Calculus for Data Science
1. Derivatives – Understanding Change
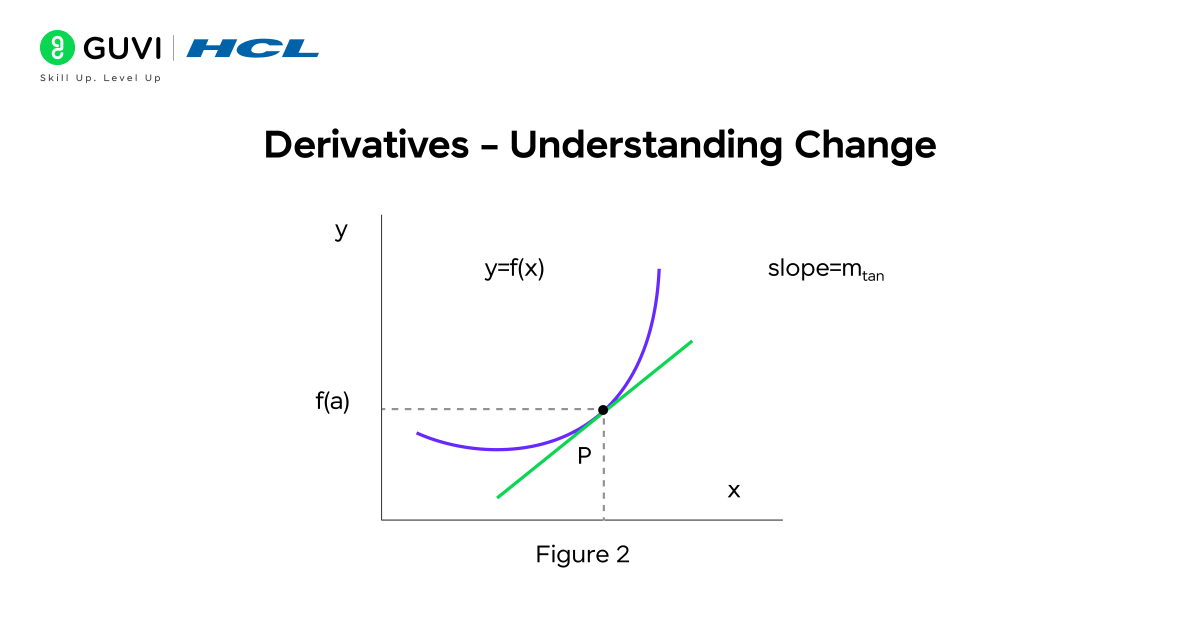
Derivatives are one of the most important concepts in calculus for data science. A derivative measures how one quantity changes with respect to another. In simple terms, it’s like checking the speed of change at a particular moment. For example, if you track a company’s revenue over time, the derivative tells you how fast the revenue is increasing or decreasing at any given point. This helps data scientists identify trends, understand patterns, and make accurate predictions.
- Example: If you have a stock price graph, the derivative shows how fast the price is moving up or down at a specific time. A positive derivative indicates a rapid increase, while a negative derivative shows a decrease.
- Advanced Application: In machine learning, derivatives are used in gradient descent to train models. The derivative of the error with respect to model parameters is calculated, and parameters are updated step by step to minimize the error. This is how models learn from data and improve predictions.
Derivatives are a core part of calculus for data science because they allow precise measurement of change, enable optimization of models, and provide insights into real-world data patterns. Mastering derivatives helps data scientists interpret complex datasets and make informed, data-driven decisions.
2. Integrals – Accumulating Data
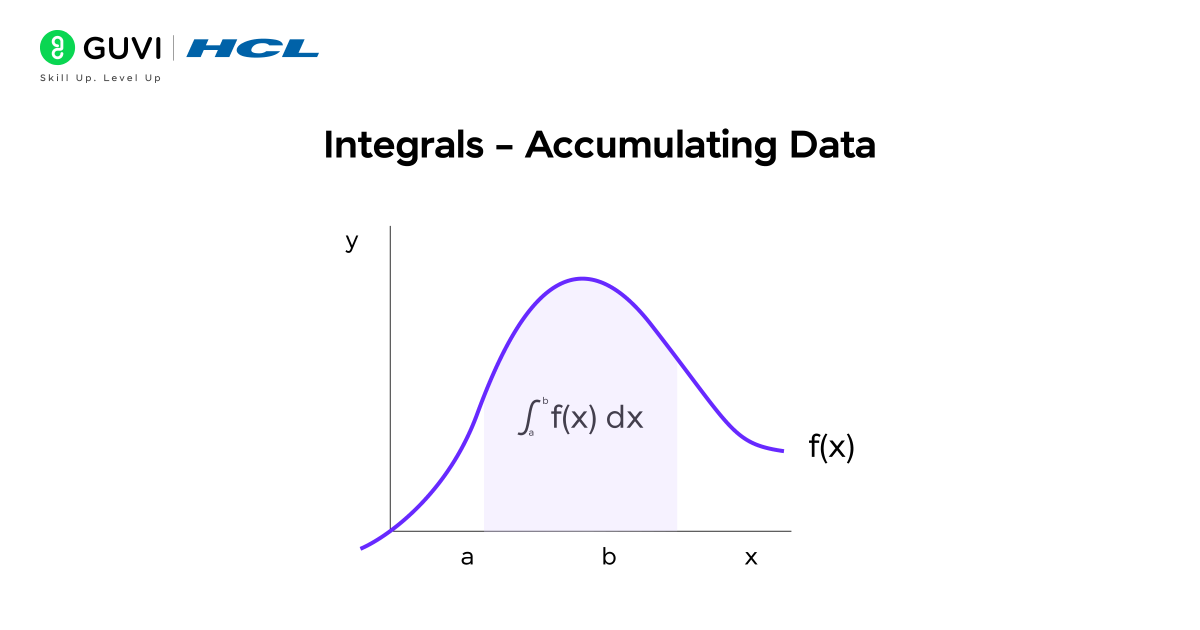
Integrals are a key concept in calculus for data science. They help calculate the total accumulation of a quantity over time or across a range of values. In simple terms, if derivatives measure the rate of change, integrals measure the total amount accumulated. This is especially useful when analyzing cumulative metrics, such as total revenue, total clicks, or continuous probabilities. Understanding integrals allows data scientists to work with continuous data and evaluate totals over a period or range.
- Example: If a company tracks daily sales, the integral of sales over a month shows the total revenue generated during that period. Similarly, in statistics, integrals are used to calculate the probability of continuous events, like the chance of a sensor reading falling within a certain range.
- Advanced Application: In machine learning, integrals are used in probability theory, continuous loss functions, and evaluating areas under curves, such as in ROC-AUC analysis for model performance. They also help in determining total error over a dataset, which is critical for optimizing models.
Integrals are a foundational part of calculus for data science because they allow the accumulation of data, the calculation of totals, and the evaluation of probabilities in continuous systems, making them essential for both analysis and modeling.
3. Multivariable Calculus – Working with Complex Data
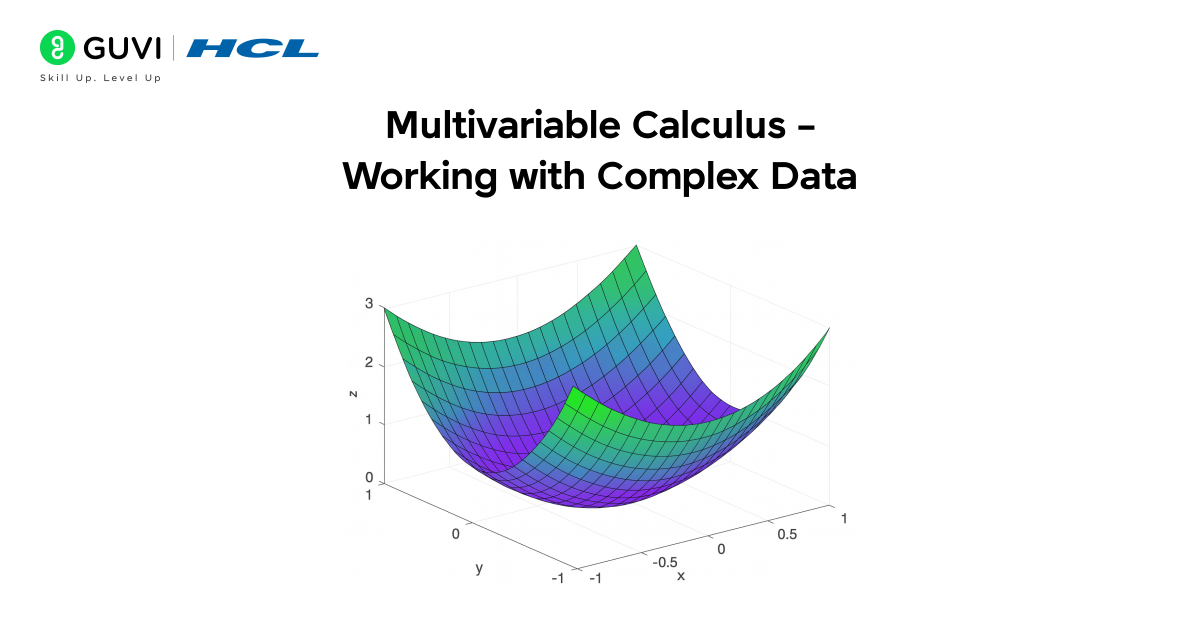
Multivariable calculus is an extension of basic calculus used when more than one variable affects an outcome. In data science, most real-world datasets have multiple features interacting together, such as size, location, and number of rooms, affecting housing prices. Multivariable calculus helps measure how changes in one variable affect the outcome while keeping other variables constant, allowing data scientists to understand complex relationships in data.
- Example: In a housing price prediction model, multivariable calculus helps determine how changing the number of rooms affects the price while keeping the area and location fixed.
- Advanced Application: Gradient computation in machine learning uses multivariable calculus to optimize models with multiple parameters, such as weights in neural networks, allowing the model to learn efficiently from data.
4. Optimization Using Calculus
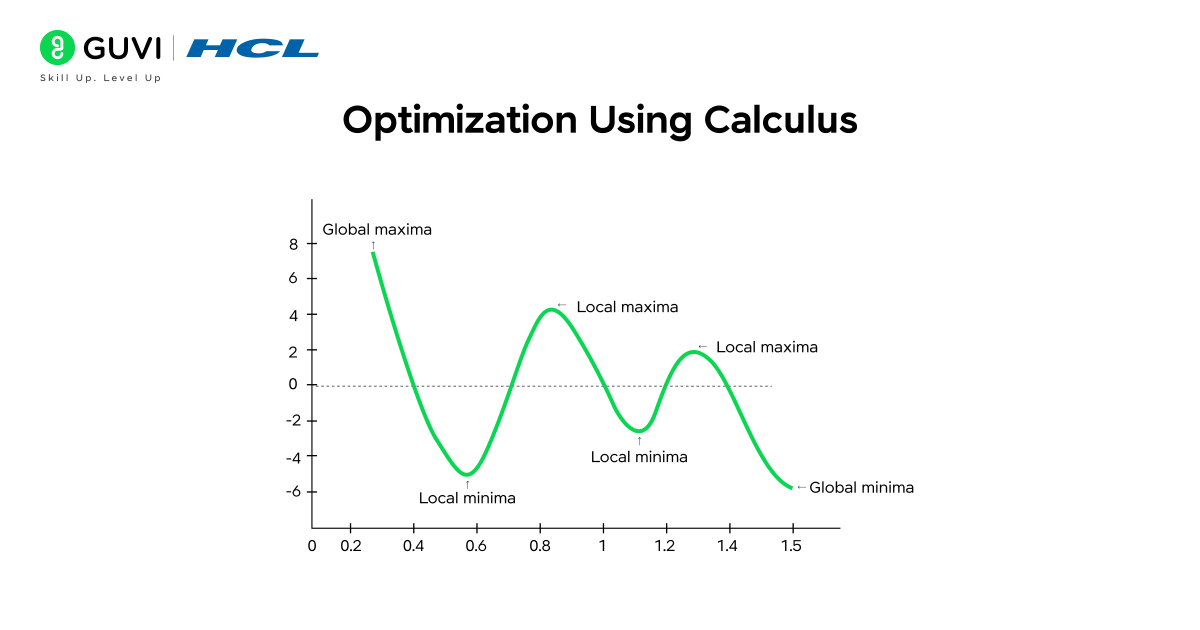
Optimization is a central concept in calculus for data science. It involves finding the best possible solution by maximizing or minimizing a function, such as profit, accuracy, or efficiency. Calculus provides tools to locate these maximum or minimum points by analyzing derivatives, making it easier to optimize models and processes.
- Example: A marketing team may want to maximize return on investment. By modeling ROI as a function of advertising spend and applying calculus, they can determine the optimal spend to achieve the highest returns.
- Advanced Application: In machine learning, optimization is used to minimize the error of a model. Techniques like gradient descent rely on derivatives to iteratively adjust parameters and find the minimum error, improving model performance.
Advanced Topics in Calculus for Data Science
1. Partial Derivatives
Partial derivatives are used when a function depends on multiple variables. They measure how the function changes with respect to one variable while keeping the other variables constant. In data science, this is essential for understanding the individual impact of each feature on a prediction.
- Example: In a housing price model, the partial derivative shows how the price changes if only the number of rooms changes while keeping the area and location fixed.
- Advanced Application: Partial derivatives are fundamental in gradient descent for multi-variable models, helping optimize parameters in neural networks and other machine learning algorithms.
2. Chain Rule & Higher-Order Derivatives
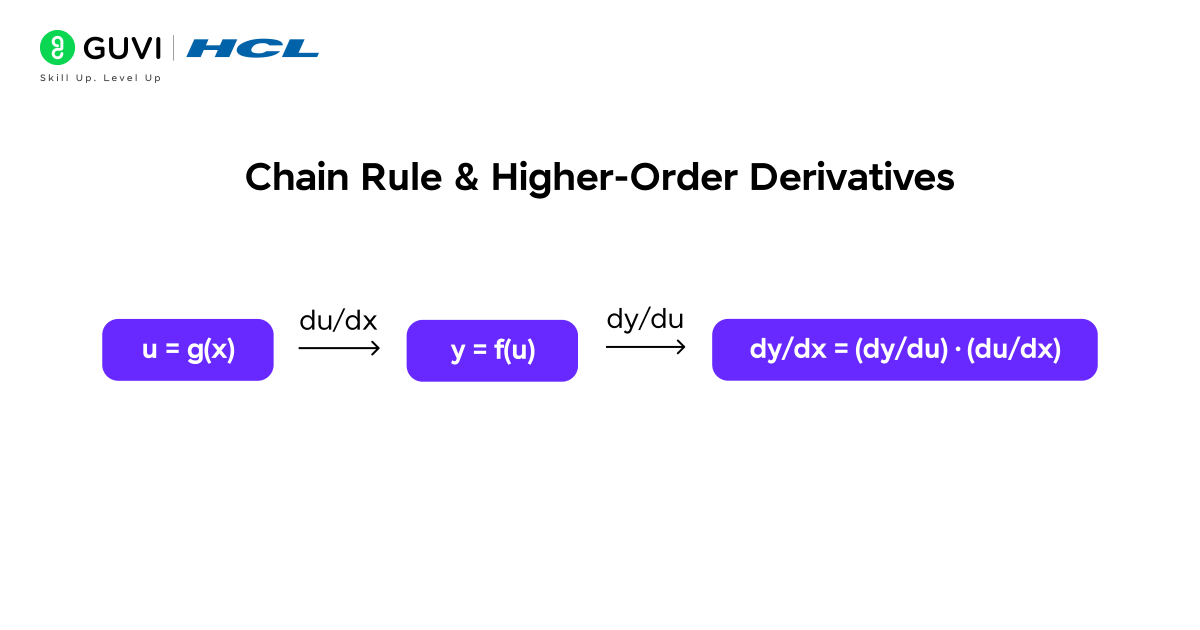
The chain rule allows differentiation of composite functions, which is common when one variable depends on another variable that, in turn, depends on a third variable. Higher-order derivatives provide information about curvature and how the rate of change itself changes, which is useful for more precise optimization and understanding complex relationships.
- Example: In neural networks, the chain rule is used during backpropagation to calculate how changes in weights affect the final output. Without it, models couldn’t learn from errors efficiently.
- Advanced Application: Second-order derivatives, including the Hessian matrix, help in optimization by showing how steep or flat the error surface is. This helps algorithms converge faster and avoid local minima, improving the accuracy and efficiency of machine learning models.
3. Vector Calculus
Vector calculus deals with functions that have vector inputs or outputs, which is common in high-dimensional datasets. It is crucial for understanding interactions between multiple variables at once. In data science, vector calculus is used to compute gradients across many features simultaneously, enabling more effective optimization.
- Example: When training a deep learning model, the gradient of a loss function with respect to all features is calculated as a vector. This tells the model how to adjust all parameters at once to minimize error.
- Advanced Application: Vector calculus is widely used in deep learning and advanced machine learning algorithms, allowing models to handle complex, high-dimensional data efficiently and optimize multiple parameters simultaneously.
4. Jacobian and Hessian Matrices
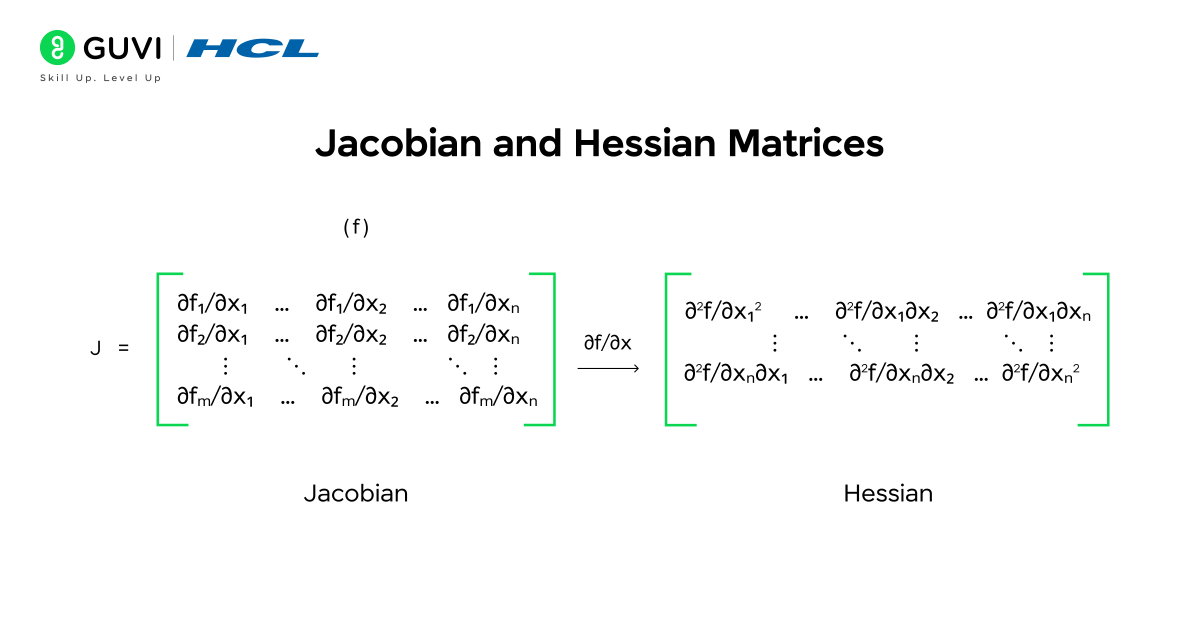
Jacobian and Hessian matrices are advanced tools in multivariable calculus that summarize derivatives in a structured way:
- Jacobian: Shows how each output variable changes with respect to each input variable. It is crucial in understanding relationships in multi-output systems.
- Hessian: Captures the curvature of multivariable functions, providing insight into maxima, minima, and saddle points. This is useful in optimization problems
- Example: In a neural network with multiple layers, the Jacobian helps understand how changes in input affect each output, while the Hessian shows how the loss function curves, guiding optimization.
- Advanced Application: Jacobian and Hessian matrices are used in second-order optimization methods, improving training efficiency and convergence in complex machine learning models.
5. Differential Equations (Intro Level)
Differential equations describe how quantities change continuously over time and are used to model dynamic systems. In data science, they are particularly useful for understanding trends in time-series data, such as stock prices, sensor readings, or population growth. By modeling the rate of change and how it evolves, differential equations allow more accurate forecasting and analysis.
- Example: Predicting population growth over years can be modeled with a differential equation, showing not just total numbers but how quickly the population is increasing or decreasing at each moment.
- Advanced Application: Differential equations are used in time-series forecasting, physics-informed machine learning, and dynamic simulations. They enable models to capture continuous patterns and provide more precise predictions for evolving datasets.
Real-World Applications
Calculus for data science is applied across many industries to optimize processes, make accurate predictions, and gain insights from complex data. Here’s how different sectors use it:
1. Finance and Banking
Concepts Used: Derivatives, integrals, optimization
Applications:
- Modeling stock prices and financial risk
- Calculating cumulative investment returns using integrals
- Using optimization to maximize portfolio returns or minimize losses
2. Healthcare and Life Sciences
Concepts Used: Differential equations, derivatives, integrals
Applications:
- Modeling disease spread and patient vital sign changes
- Calculating total drug dosage over time
- Understanding rates of change in patient conditions with derivatives
3. Technology and AI
Concepts Used: Derivatives, multivariable calculus, gradient descent, Jacobians
Applications:
- Training machine learning models using gradient descent
- Optimizing multiple parameters simultaneously with multivariable calculus
- Understanding input-output relationships in neural networks using Jacobians
4. Marketing and E-commerce
Concepts Used: Derivatives, integrals, optimization
Applications:
- Analyzing customer engagement trends using derivatives
- Calculating total sales or website interactions with integrals
- Optimizing pricing, campaigns, and ROI
5. Engineering and Robotics
Concepts Used: Vector calculus, differential equations, partial derivatives
Applications:
- Computing motion and trajectories in robotics with vector calculus
- Predicting system behavior over time using differential equations
- Optimizing control parameters using partial derivatives
6. Energy and Environment
Concepts Used: Integrals, derivatives, differential equations
Applications:
- Modeling energy consumption and efficiency
- Forecasting climate and environmental changes
- Calculating total energy output and monitoring rates of change
These examples highlight how calculus for data science is essential across industries, enabling accurate modeling, predictions, and optimization in real-world scenarios.
If you’d like to dive deeper into the core foundations of data science, do check out this Data Science eBook. It breaks down essential concepts like statistics, machine learning basics, and analytical thinking in a clear, step-by-step manner. The explanations are beginner-friendly and structured to help you learn without confusion.
Conclusion
Calculus for data science is the backbone of modern analytics and machine learning. From derivatives and integrals to multivariable calculus, partial derivatives, Jacobians, Hessians, and differential equations, these concepts allow data scientists to measure change, accumulate data, optimize models, and make accurate predictions. By understanding these principles, you can interpret complex datasets, fine-tune algorithms, and gain actionable insights across industries.
In practice, mastering calculus for data science helps you optimize machine learning models, forecast trends, analyze probabilities, and make data-driven decisions in sectors like finance, healthcare, AI, marketing, engineering, and energy. It is not just a theoretical tool — it is a practical skill that directly impacts how models perform and how insights are derived from data.
To put this knowledge into practice, HCL GUVI’s Data Science Course offers hands-on projects, mentorship, and applied exercises where you can implement calculus concepts in real-world data science problems. This structured approach ensures that you gain both technical expertise and practical experience.
FAQs
1. Why is calculus important in data science?
Calculus is crucial because it allows data scientists to measure change, optimize models, and analyze continuous data. Derivatives help track trends, integrals compute totals, and multivariable calculus enables optimization in complex models.
2. Which calculus concepts are most used in machine learning?
Derivatives, partial derivatives, gradient descent, integrals, and vector calculus are the most frequently used. They help in training models, minimizing error, and optimizing multiple parameters simultaneously.
3. How does calculus help in neural networks?
Calculus is used to compute gradients during backpropagation, allowing models to adjust weights efficiently. Partial derivatives and the chain rule are fundamental for understanding how each input affects the output.
4. Can beginners learn data science without calculus?
Yes, beginners can start with basic data analysis and machine learning, but to fully understand model optimization, gradient descent, and advanced algorithms, calculus knowledge becomes essential.
5. How is calculus applied in real-world data science projects?
Calculus is applied in finance (stock price modeling, risk analysis), healthcare (disease modeling, drug dosage), AI (model training and optimization), marketing (ROI optimization), and engineering (robotics motion, system control).



























Did you enjoy this article?