What is a Neural Network in AI? A Beginner’s Guide 2025
Sep 04, 2025 7 Min Read 1355 Views
(Last Updated)
Neural networks in AI essentially mimic the way the human brain works, creating structures of interconnected neurons that process information intelligently. You’ve likely interacted with neural networks already without realizing it—Google’s search algorithm is one of the most widely used examples of this technology.
When you begin to explore neural networks, you’ll discover powerful models that can make intelligent decisions with minimal human assistance. In fact, these systems can complete complex tasks like speech recognition or image classification in minutes compared to the hours it would take human experts.
This beginner-friendly guide will walk you through everything you need to know about neural networks in AI—from basic definitions to practical applications and deep learning concepts. You’ll learn how these remarkable systems learn from data, identify complex patterns, and solve intricate challenges in our increasingly AI-driven world. Let’s begin!
Table of contents
- What is a Neural Network in AI?
- Why neural networks matter in AI today
- Core Components of a Neural Network Model
- 1) Input layer, hidden layers, and output layer
- 2) Weights, biases, and activation functions
- 3) Feedforward and backpropagation explained simply
- How Neural Networks Work Step-by-Step
- Data input and preprocessing
- Forward propagation and activation
- Loss calculation and error measurement
- Backpropagation and weight updates
- Iterative learning and convergence
- Types of Neural Networks You Should Know
- 1) Feedforward Neural Networks (FNN)
- 2) Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
- 3) Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)
- 4) Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
- 5) Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
- Real-World Applications of Neural Networks
- 1) Speech and image recognition
- 2) Natural language processing (NLP)
- 3) Recommendation systems
- 4) Medical diagnosis and healthcare
- 5) Autonomous vehicles and robotics
- Concluding Thoughts…
- FAQs
- Q1. What is the basic structure of a neural network?
- Q2. How do neural networks learn?
- Q3. What are some common types of neural networks?
- Q4. What are real-world applications of neural networks?
- Q5. How do neural networks relate to the human brain?
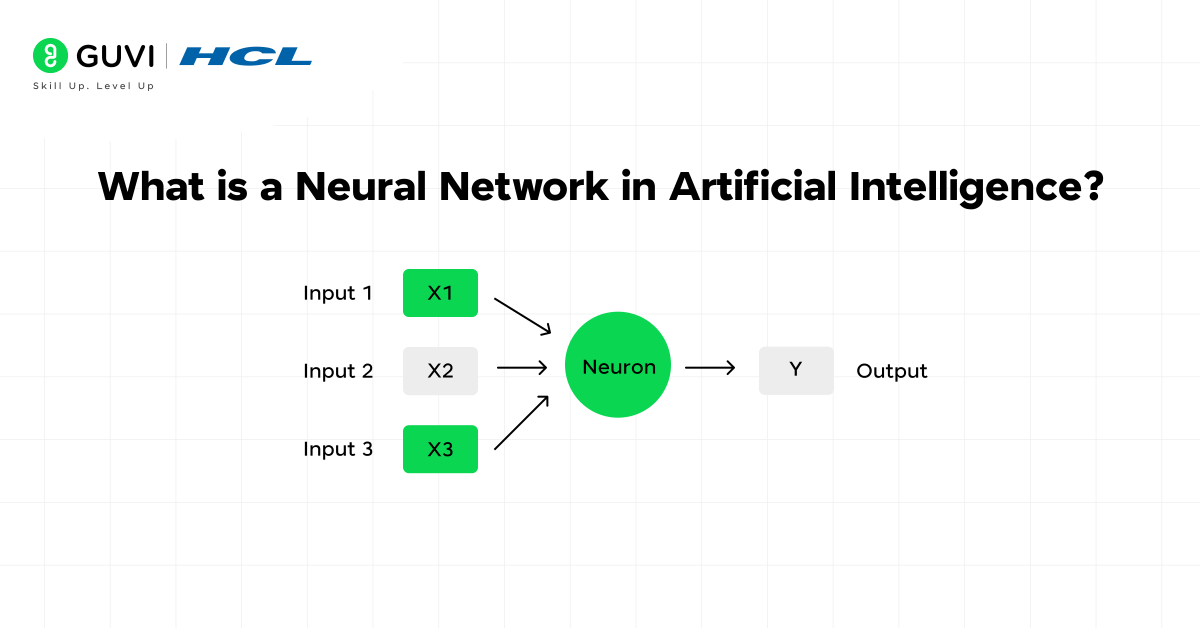
What is a Neural Network in AI?
A neural network in AI is a computational model that processes information through interconnected units called artificial neurons. Unlike traditional computing systems, neural networks don’t follow explicit programming instructions but learn from data to perform tasks. These powerful systems form the foundation of modern artificial intelligence, enabling machines to recognize patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
Why neural networks matter in AI today
Neural networks have become crucial in modern AI because of their remarkable ability to learn from experience and identify complex patterns in data. They excel at tasks traditional algorithms struggle with, including image recognition, speech processing, and language translation.
Additionally, neural networks can:
- Learn and model non-linear relationships between inputs and outputs
- Make generalizations and inferences from limited data
- Reveal hidden patterns and make predictions
- Process massive amounts of structured and unstructured information
The importance of neural networks has grown with the rise of deep learning, which involves neural networks with many layers. These deep networks power innovations across industries, from medical diagnosis to autonomous vehicles and financial forecasting.
Core Components of a Neural Network Model
Every neural network model comprises essential building blocks that work together to process information and learn from data. Understanding these fundamental components is crucial as you begin exploring AI neural networks.
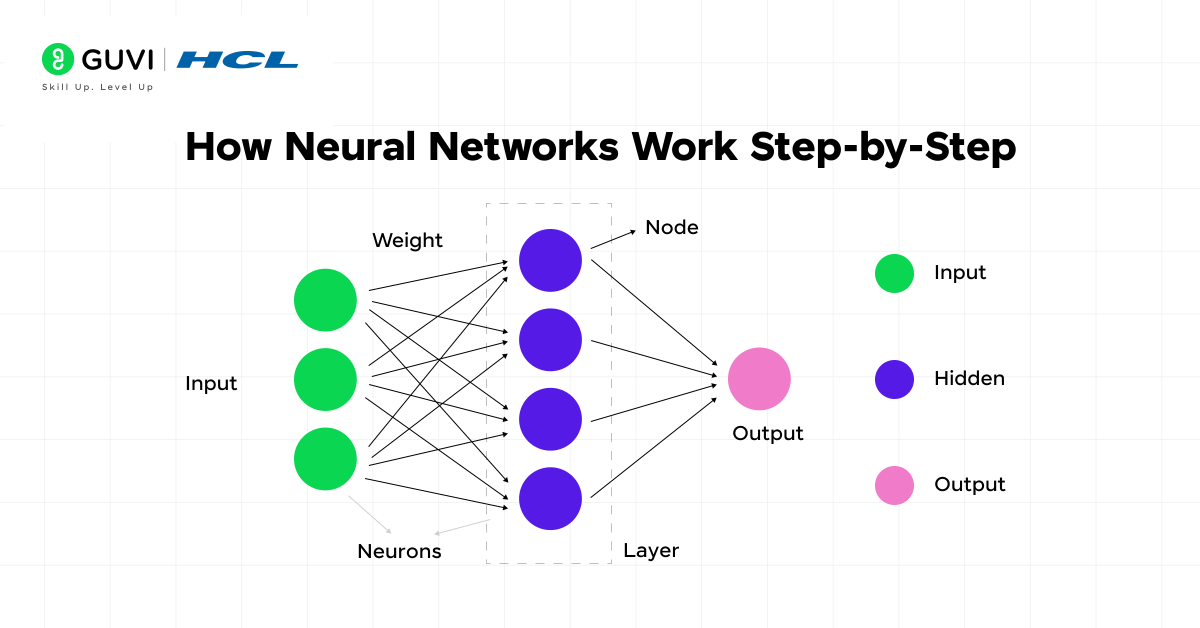
1) Input layer, hidden layers, and output layer
The architecture of a neural network consists of three primary types of layers that process information sequentially.
- First of all, the input layer serves as the gateway for raw data entering the network. This layer doesn’t perform any computations but passes information forward. For instance, in an image recognition system, each neuron in this layer might represent a pixel value.
- Next, hidden layers perform most of the complex computations. These intermediate layers between input and output are where the actual “thinking” happens. A neural network can have multiple hidden layers—networks with at least two hidden layers are typically called deep neural networks. Each hidden layer extracts increasingly abstract features from the data, enabling the network to recognize complex patterns.
- Finally, the output layer delivers the network’s prediction or decision. The number of neurons in this layer depends on the task—a single neuron for binary classification or multiple neurons for multi-class problems.
2) Weights, biases, and activation functions
- Weights represent the strength of connections between neurons. Think of weights as determining how important a particular input is to the next neuron. During training, these weights are constantly adjusted to improve the network’s accuracy.
- Biases are additional parameters that allow neurons to produce output even when all inputs are zero. They’re like extra neurons with a constant value of 1 that provide flexibility to the model. Biases help shift the activation function, enabling the network to fit data that doesn’t pass through the origin.
- Activation functions introduce non-linearity, allowing neural networks to learn complex patterns that go beyond simple linear relationships. Without activation functions, neural networks would be limited to modeling only linear relationships.
3) Feedforward and backpropagation explained simply
- The feedforward process describes how information flows through a neural network. Starting at the input layer, data moves forward through each layer until reaching the output. At each step, the network calculates the weighted sum of inputs, adds the bias, and then applies an activation function to determine the neuron’s output.
- Whereas feedforward moves information forward, backpropagation works in reverse to help the network learn. After making a prediction, the network calculates the error—the difference between predicted and actual outputs. This error is then propagated backward through the network to adjust weights and biases, minimizing future errors.
- During backpropagation, the network computes gradients using the chain rule from calculus, showing how much each weight contributed to the error. Weights that contributed more to the error undergo larger adjustments. Through this iterative process, the neural network gradually improves its performance on the given task.
Understanding these core components provides the foundation for grasping how neural networks function and learn from data—key knowledge as you venture deeper into the world of artificial intelligence.
How Neural Networks Work Step-by-Step
The training of a neural network in AI follows a structured workflow, taking raw data and progressively refining its internal parameters to learn patterns. Let’s break down this fascinating process into manageable steps.
1. Data input and preprocessing
The journey begins with data preparation and preprocessing, a critical first step that directly influences model performance. Raw data often contains inconsistencies that can hinder learning:
- Handling missing values: Fill gaps with averages or remove incomplete records
- Converting categorical data: Transform text labels into numerical values through techniques like one-hot encoding
- Normalization: Scale features to similar ranges (typically 0-1 or -1 to 1)
Proper preprocessing prevents certain features from dominating others merely due to their scale. For example, when features have vastly different ranges, neural networks may struggle to learn effectively. Additionally, splitting data into training, validation, and test sets (commonly 70%-15%-15%) ensures the model can be evaluated on unseen examples.
2. Forward propagation and activation
Once data is prepared, forward propagation begins—the “thinking” phase of a neural network. Starting at the input layer, information flows through the network layer by layer:
- Each neuron calculates a weighted sum of inputs plus bias: z = W·x + b
- This result passes through an activation function (like ReLU or sigmoid)
- The output becomes input for the next layer’s neurons
This process transforms raw inputs into increasingly abstract representations as data moves deeper into the network. The mathematical operation can be expressed as: Output = f(weighted sum + bias), where f represents the activation function. Without these activation functions, neural networks would be limited to learning only linear relationships.
3. Loss calculation and error measurement
After generating predictions, the network measures its performance using a loss function. This crucial component quantifies the difference between predicted values and actual outcomes.
Different types of tasks require specific loss functions:
- Mean Squared Error (MSE): Ideal for regression problems predicting continuous values
- Cross-Entropy: Frequently used for classification problems involving probabilities
The loss function distills all aspects of model performance into a single number—smaller values indicate better predictions. For instance, in classification tasks using cross-entropy loss, a perfect prediction has a loss of 0.0, while poor predictions receive higher penalties.
4. Backpropagation and weight updates
Backpropagation represents the core learning mechanism of neural networks. After calculating the loss, this algorithm:
- Applies the chain rule to compute gradients backward through the network
- Determines how much each weight contributed to the error
- Calculates partial derivatives of the loss function
- Updates weights proportionally to reduce future errors
This process moves backward from the output layer to the input layer, avoiding redundant calculations. The size of each weight adjustment is controlled by a tunable hyperparameter called the learning rate. Too large a rate may cause overshooting the optimal solution, whereas too small a rate can lead to slow convergence.
5. Iterative learning and convergence
The entire process—forward propagation, loss calculation, and backpropagation—repeats numerous times with different training examples. This iterative approach gradually refines the network’s weights and biases.
A neural network is considered converged when its training error stops decreasing or reaches an acceptable minimum level. Convergence can be improved through techniques such as:
- Properly initializing weights (using methods like Xavier or He initialization)
- Implementing batch normalization to stabilize learning
- Applying regularization to prevent overfitting
- Using advanced optimizers like Adam instead of basic gradient descent
Throughout this cycle, the network progressively improves its ability to make accurate predictions on unseen data, ultimately producing a model that can effectively perform its intended task.
Types of Neural Networks You Should Know
As AI evolves, several specialized neural network architectures have emerged to tackle specific challenges. Each type excels at different tasks based on its unique structure and capabilities.
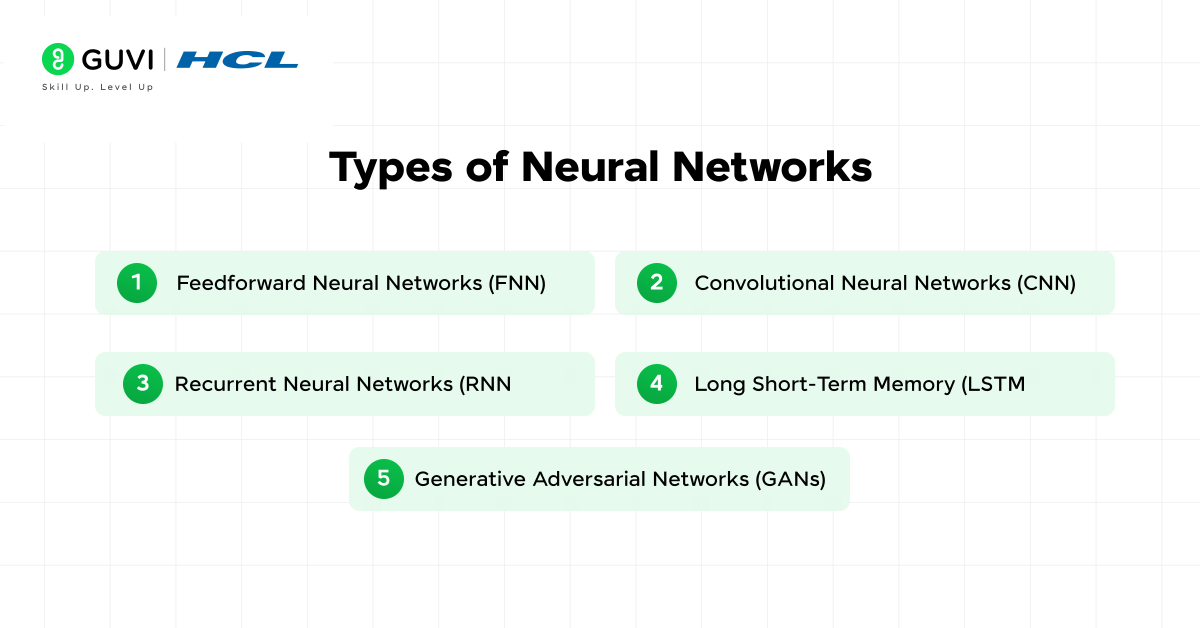
1) Feedforward Neural Networks (FNN)
- Feedforward neural networks represent the simplest architecture where information travels in one direction only—from input through hidden layers to output, without forming any cycles.
- These networks process each input independently, making them ideal for classification and regression tasks where data doesn’t require sequential processing. FNNs rely on a structured, layered design that progressively transforms raw data into meaningful predictions through weighted connections and activation functions.
2) Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
- CNNs specialize in processing grid-like data, particularly images and videos. Through specialized layers that apply convolution operations, these networks efficiently identify spatial hierarchies and patterns.
- The convolution process uses small filters that slide across input data, creating feature maps that highlight important patterns while significantly reducing the number of parameters needed. This makes CNNs particularly effective for tasks like image recognition, object detection, and medical imaging analysis.
3) Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)
- Unlike standard networks, RNNs maintain “memory” of previous inputs through feedback loops. This unique ability to track context by maintaining a hidden state at each time step makes them especially suited for sequential data.
- RNNs excel at language translation, speech recognition, and time-series prediction, where understanding context is crucial.
4) Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
- LSTMs are specialized RNNs designed to overcome the vanishing gradient problem that limits standard RNNs from remembering long-term dependencies. They feature memory cells controlled by three gates—input, output, and forget—that regulate information flow.
- This architecture allows LSTMs to selectively remember relevant information for thousands of timesteps, making them powerful for speech recognition, language modeling, and sequence learning tasks.
5) Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
- GANs consist of two competing neural networks: a generator that creates new data and a discriminator that evaluates its authenticity. Through this adversarial process, GANs learn to generate increasingly realistic outputs.
- Notable GAN varieties include Vanilla GAN (the basic model), Conditional GAN (allowing targeted generation), and Deep Convolutional GAN (integrating CNN architectures). These networks excel at creating photorealistic images, style transfer, and data augmentation.
Neural networks might feel like a modern invention, but their roots go back much further than you’d expect:
The First Neural Network Model (1943): Psychologist Warren McCulloch and mathematician Walter Pitts created the first mathematical model of a neural network, laying the foundation for today’s AI.
The Birth of the Perceptron (1958): Frank Rosenblatt developed the “perceptron,” an early neural network algorithm designed to mimic how the human brain processes visual data.
These breakthroughs decades ago sparked the revolution that eventually evolved into today’s deep learning, powering everything from facial recognition to self-driving cars!
Real-World Applications of Neural Networks
Neural networks have revolutionized multiple industries by solving complex problems that traditional computing approaches struggle with. These powerful AI systems are currently deployed across diverse sectors, creating tangible benefits in our everyday lives.
1) Speech and image recognition
- Neural networks excel at processing visual and audio data. In computer vision, they enable machines to identify objects, recognize faces, and interpret visual scenes with remarkable accuracy. For instance, CNNs power facial recognition systems that can identify faces and detect attributes like open eyes, glasses, and facial hair.
- In speech recognition, neural networks analyze human speech despite varying patterns, pitch, tone, language, and accent. This technology powers virtual assistants like Amazon Alexa and enables automatic transcription software that converts clinical conversations into documentation in real time.
2) Natural language processing (NLP)
- NLP enables computers to process and understand human language. Neural networks, particularly recurrent models, have achieved state-of-the-art results in sentiment analysis, language modeling, and discourse parsing.
- These systems power chatbots, automated document organization, business intelligence analysis, and article generation. Moreover, neural machine translation systems have made remarkable progress, facilitating real-time translation of spoken languages.
3) Recommendation systems
- Neural networks analyze user behavior to create personalized recommendations. They track activities and discover new products that might interest specific users. Companies like Curalate use intelligent product tagging powered by neural networks to automate the collection and curation of user-generated content from social media.
- Additionally, major organizations, including Airbnb, Facebook, and Pinterest, employ deep learning techniques for their recommendation engines.
4) Medical diagnosis and healthcare
- In healthcare, neural networks analyze medical images, including X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, to identify abnormalities with high precision. They effectively detect conditions like skin cancer with a specificity of 80% and a sensitivity of 94%, outperforming most dermatologists.
- Neural networks also predict interactions between chemical compounds and biological targets, accelerating drug development. Furthermore, they analyze genetic information to forecast treatment responses, enhancing effectiveness while minimizing adverse effects.
5) Autonomous vehicles and robotics
- Neural networks form the backbone of self-driving technology. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Volkswagen leverage neural networks for perception and autonomous decision-making. These networks process sensor data to make real-time driving decisions, ensuring safe navigation.
- Notably, neural networks help predict mechanical failures before they occur, facilitating timely repairs. Their ability to learn vehicle behavior on different road surfaces allows them to adapt to changing conditions without explicit friction estimation.
Ready to deepen your understanding beyond the basics of neural networks? Check out HCL GUVI’s IIT-M Pravartak & Intel-certified Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Course, where you’ll master hands-on skills in AI, from deep learning and NLP to model deployment, guided by industry mentors and enriched with live project experience.
Concluding Thoughts…
Neural networks have transformed artificial intelligence from science fiction into everyday reality. Throughout this guide, you’ve learned how these remarkable systems mimic the human brain, processing information through interconnected neurons to solve complex problems. Undoubtedly, their ability to learn from data, identify patterns, and make predictions has revolutionized countless industries.
Now that you understand the essential components and workings of neural networks, you can begin exploring this fascinating field further. The journey from basic concepts to practical applications might be challenging, but the potential to create intelligent systems that solve real-world problems makes it worthwhile. Good Luck!
FAQs
Q1. What is the basic structure of a neural network?
A neural network typically consists of an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. The input layer receives data, the hidden layers process it, and the output layer provides results. Neurons in these layers are connected by weights, which are adjusted during learning.
Q2. How do neural networks learn?
Neural networks learn through a process called backpropagation. After making predictions, the network calculates the error between predicted and actual outputs. This error is then propagated backward through the network to adjust weights and biases, minimizing future errors.
Q3. What are some common types of neural networks?
Common types include Feedforward Neural Networks (FNN) for basic classification, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for image processing, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) for sequential data, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) for long-term dependencies, and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for creating new data.
Q4. What are real-world applications of neural networks?
Neural networks are used in various fields including speech and image recognition, natural language processing, recommendation systems, medical diagnosis, and autonomous vehicles. They power technologies like facial recognition, language translation, personalized content recommendations, and self-driving cars.
Q5. How do neural networks relate to the human brain?
Neural networks are inspired by the structure and function of biological neural networks in our brains. Both systems feature interconnected nodes that process information collectively. However, artificial neural networks are much simpler, with far fewer “neurons” and connections compared to the human brain.





























Did you enjoy this article?