
Visual Design Loop with AI: From LLMs and Image Generators
Feb 10, 2026 6 Min Read 1011 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever looked at an AI-generated visual and thought, This is close, but not quite what I had in mind? That tiny gap between what you imagine and what the model produces is exactly where a visual design loop shines.
Instead of treating LLMs and image generators as isolated tools, the loop brings them together in a way that feels surprisingly collaborative. You guide the idea, the LLM sharpens it, the image model visualizes it, and each round gets you closer to the design you actually want.
When you understand how to shape this cycle, you turn AI from a one-off generator into a creative partner that keeps improving with every iteration. To teach you how to build a visual design loop with AI, we created this article. So, without further ado, let us get started!
Quick Answer
A visual design loop pairs an LLM with an image generator so your ideas are translated into structured prompts, turned into images, and refined through fast feedback cycles—giving you clearer, more consistent visuals with every iteration.
Table of contents
- Why a Visual Design Loop Matters
- How LLMs and Image Generators Work Together
- LLMs Interpret Your Ideas
- LLMs Structure Image-Friendly Prompts
- Image Generators: Visualize the Strategy
- You Give Feedback, and the LLM Translates It
- The Loop Tightens
- The Core Components of a Visual Design Loop
- Prompt Planning
- LLM Prompt Structuring
- Image Generation
- Feedback Integration
- Iterative Refinement
- Building Your Own Loop: A Practical Blueprint
- Step 1: Start With a Clear Vision
- Step 2: Ask the LLM to Turn That Into Multiple Prompt Options
- Step 3: Generate a Batch of Images
- Step 4: Look Closely and Give Honest, Specific Feedback
- Step 5: Let the LLM Rewrite the Prompt Based on Your Notes
- Step 6: Generate the Next Round
- Step 7: Capture and Save What You Learned
- What a Good Visual Design Loop Looks Like in Practice
- Step 1: You Set the Idea
- Step 2: LLM Creates Prompt Variants
- Step 3: Image Model Generates Samples
- Step 4: You Provide Targeted Feedback
- Step 5: LLM Rewrites the Prompt
- Step 6: Image Model Generates the Updated Batch
- Step 7: Short Final Adjustments
- Step 8: Final Image
- Avoiding Common Visual Design Loop Failures
- The Future of Visual Design Loops
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is a visual design loop in AI?
- How do LLMs and image generators actually work together?
- Why do my AI-generated images look inconsistent?
- How can I improve the quality of my AI-generated visuals?
- Can I use LLM + image generator loops for educational content?
Why a Visual Design Loop Matters
You already know that AI can generate text or images on command. But a visual design loop with AI is something different. It’s an iterative process where:
- You set the creative direction
- The AI proposes visual outputs
- You evaluate and refine
- The LLM absorbs the feedback and adjusts prompts
- The image model re-renders
- The loop continues until your design hits the mark
This process mirrors how creative teams already work, but with far fewer handoffs and delays. What this really means is that you’re no longer just asking AI to generate content. You’re using it as a collaborative design partner.
A functional loop solves three big problems designers run into:
- Losing intent when translating ideas to prompts
- Inconsistent visuals across iterations
- Slow experimentation due to repetitive manual adjustments
When done well, a design loop turns AI into a tool that reflects your vision, not one you constantly fight against.
Learn More: A Beginner’s Guide to Artificial Intelligence, LLMs, and Prompting
How LLMs and Image Generators Work Together

A lot of people think of LLMs and image generators as two separate tools that happen to sit next to each other. The real magic shows up when they work as one system. Each one balances out what the other can’t do alone.
Here’s how that partnership actually plays out.
1. LLMs Interpret Your Ideas
Most projects start with rough thoughts:
- a loose description
- a creative direction
- a product concept
- a teaching idea
- a general theme
An LLM takes that early, unpolished thinking and turns it into something an image generator can actually understand: a structured, usable prompt.
It sharpens things like:
- Clarity
- Tone
- Emotional cues
- Visual keywords
- Constraints
- What matters most vs. what to avoid
In this stage, the LLM acts like your design strategist, turning abstract ideas into real creative direction.
2. LLMs Structure Image-Friendly Prompts
Image models need prompts in a certain shape. They rely on clear building blocks:
- Foreground and background
- Subject and style
- Lighting and color palette
- Composition and detail level
- Negative prompts
Most people miss one or two of these pieces or mix them unevenly. The LLM cleans that up and turns your thoughts into precise prompts that image models understand consistently.
3. Image Generators: Visualize the Strategy
Once the LLM hands off a polished prompt, the image generator takes over and turns the plan into visuals.
That usually means:
- Generating multiple variations
- Exploring different styles
- Keeping elements consistent
- Introducing creative twists that still fit the idea
If the LLM is the director, the image model is the art department, bringing the vision to life.
4. You Give Feedback, and the LLM Translates It
Your feedback usually comes out naturally:
- This looks too childish
- The colors feel too harsh
- The background is distracting
- The characters look too young
The LLM turns comments like these into clear, structured directions that an image model can respond to.
5. The Loop Tightens
The LLM updates the prompt. The generator produces new visuals. You react. The LLM adjusts again. Each pass gets closer to what you imagined. The visuals sharpen, the style settles, and the loop gradually aligns the output with your mental picture.
The Core Components of a Visual Design Loop
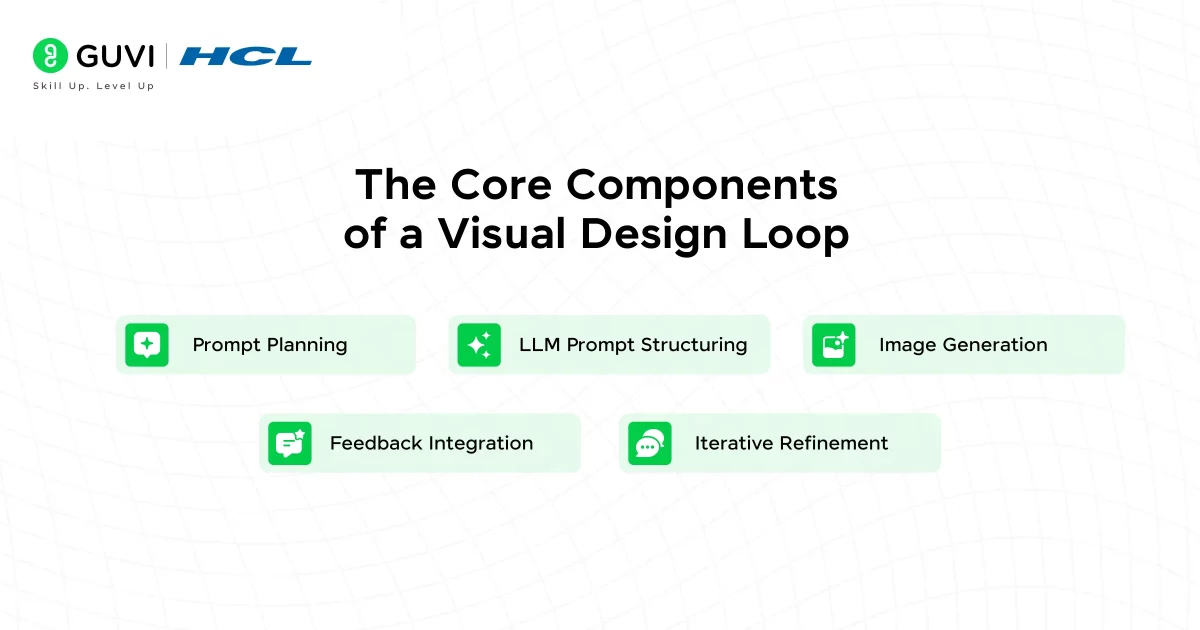
For this workflow to feel stable and predictable, you need a solid structure behind it. These are the essential parts of a healthy loop and what each one actually does.
1. Prompt Planning
This is the stage where you set the creative boundaries. It keeps the loop focused and prevents the process from drifting.
Your plan may cover:
- The learning goal (for example, a middle school physics lesson)
- The tone (friendly, neutral, serious)
- The visual style (flat, illustrative, semi-realistic)
- Who the visuals are for (age, culture, context)
- Technical needs (orientation, resolution, thumbnails, etc.)
Good planning keeps every later iteration aligned with the original vision.
2. LLM Prompt Structuring
Here, the LLM turns your direction into a prompt that image models can follow.
It clarifies things like:
- Subject
- Setting
- Composition
- Style
- Color themes
- Lighting
- Negative prompts
- Technical details
This removes ambiguity so the generator can produce consistent results.
3. Image Generation
This is the exploration phase. You use the prompt to generate the first batch of visuals.
The goals here are to:
- See your ideas take shape
- Explore multiple design directions
- Find interesting possibilities
- Notice what needs fixing
This round isn’t about perfection; it’s about seeing the range of what’s possible.
4. Feedback Integration
You look at the images and point out what works and what doesn’t.
You may notice things like:
- The emotional tone
- Clarity
- Character style
- Color balance
- Composition
- Too much or too little detail
- Whether it fits the educational purpose
The more specific your feedback, the more accurately the LLM refines the next prompt.
5. Iterative Refinement
Here’s where everything comes together.
The LLM refines the prompt. The generator updates the visuals. You evaluate. The loop continues.
With each round:
- The style becomes more consistent
- The prompt becomes more precise
- Randomness fades
- Your intent becomes clearer in the visuals
By the end, you’re co-creating with the AI, guiding it the way you’d guide a creative partner.
Building Your Own Loop: A Practical Blueprint

If you want a solid, repeatable AI design loop, here’s a simple structure you can follow.
Step 1: Start With a Clear Vision
Forget prompt engineering for a moment. Just explain your idea in plain language.
Stuff like:
- What the image is for
- Who it’s for
- How it should feel
- What you want to avoid
This gives the LLM the raw material it needs.
Step 2: Ask the LLM to Turn That Into Multiple Prompt Options
Instead of jumping straight into image generation, let the LLM create several interpretations.
Ask it for:
- A few distinct prompt versions
- Different styles
- Different compositions
- Negative prompts
- Different levels of detail
This opens up your creative space right from the start.
Step 3: Generate a Batch of Images
Take the prompts and run them through the image model. Don’t judge too fast. Early batches are about scope, not perfection.
The goal is to see:
- What’s promising
- What’s weird
- What you didn’t expect
- What matches your taste
You’ll probably like pieces of different images, and that’s fine.
Step 4: Look Closely and Give Honest, Specific Feedback
Now tell the LLM exactly what you liked and what didn’t land.
Maybe:
- The colors are great
- The characters feel too young
- The background is too detailed
- The lighting is flat
- The composition feels cramped
Name what’s working and what isn’t. You want the LLM to understand your taste.
Step 5: Let the LLM Rewrite the Prompt Based on Your Notes
This is where the loop tightens. The LLM:
- Merges the good stuff
- Fixes the problem areas
- Adjusts style rules
- Clarifies details
- Improves negative prompts
Each iteration becomes more intentional.
Step 6: Generate the Next Round
Now the images should start converging. They’ll feel more “you” and less “random AI output.”
You’ll notice:
- More consistent characters
- Cleaner layouts
- Colors that make sense
- Better emotional tone
It’s like the AI finally understands your creative language.
Step 7: Capture and Save What You Learned
Before you move on, ask the LLM to summarize everything:
- The best prompt formula
- The ideal vocabulary
- Your preferred styles
- Your color logic
- Your don’ts
- The whole process in a compact format
This is how you turn one good session into a reusable system.
If you want to read more about these design loops, then read HCL GUVI’s Free UI/UX Ebook: A Beginner’s Guide to Design Excellence which covers everything from the key concepts of UI/UX to the core principles to the design process.
What a Good Visual Design Loop Looks Like in Practice

Let’s walk through a realistic example so you can see how everything works end to end.
Step 1: You Set the Idea
You: “I need an illustration style for a lesson on digital citizenship. Make it friendly, inclusive, and modern.”
This isn’t a prompt, it’s a direction.
Step 2: LLM Creates Prompt Variants
The LLM produces 3–5 refined image-ready prompts. For example:
- Flat illustration
- Light gradients
- Characters of diverse backgrounds
- Soft geometric shapes
- Clean educational theme
- Neutral pastel palette
- Negative prompts to avoid distortion
You get clear, neatly structured options.
Step 3: Image Model Generates Samples
The image generator creates multiple scenes.
- Some may be too playful.
- Some may be too serious.
- Some may hit the right vibe but miss small details.
This is normal, early rounds are for exploration.
Step 4: You Provide Targeted Feedback
You: “I like the color palette from sample 3, but prefer the character style in sample 5. Make the characters older, keep the background minimal, and avoid cartoonish proportions.”
The LLM converts your feedback into refined prompts, tightening the direction.
Step 5: LLM Rewrites the Prompt
It merges your preferences:
- Adult characters
- Minimalistic background
- The exact palette from sample 3
- Semi-realistic proportions
- Reduced exaggeration
- Consistent line thickness
This step is where precision grows.
Step 6: Image Model Generates the Updated Batch
Now the visuals look far closer to what you imagined. You’re narrowing toward the final look.
Step 7: Short Final Adjustments
You might adjust:
- Lighting
- Text placement
- Contrast
- Iconography
- Facial expressions
The LLM integrates these micro-adjustments and produces the last revision.
Step 8: Final Image
The final set feels intentional, consistent, and aligned with your educational purpose. And you didn’t have to manually rewrite prompts or start from scratch each time. That’s the power of a well-run visual design loop.
Little habits like these can make a big difference in reliability and speed.
Avoiding Common Visual Design Loop Failures
If you want smooth collaboration between models, steer clear of these pitfalls.
- Overloading Prompts: Too many ideas at once confuse the image model. Keep prompts layered and structured.
- Ignoring Negative Prompts: Negative prompts stop unwanted artifacts and tighten control. If you don’t use them, randomness creeps in.
- Switching Styles Mid-Loop: Consistency matters. If you jump from a 3D render to sketch style halfway through, both models lose alignment.
- Giving Vague Feedback: Models can’t fix what you don’t describe clearly.
- Letting the Loop Run Too Long: Know when you’ve hit your target. End the loop before it overfits to constraints and becomes stiff.
The Future of Visual Design Loops
Design loops are evolving fast. Here’s where things are heading:
- Real-time co-editing: LLMs and image models will interact in the same workspace, updating visuals as you type.
- Auto-learning visual identities: Models will remember your projects, brand rules, and style patterns by default.
- Modular visual systems: Instead of one-off prompts, you’ll build libraries of reusable components.
- Cross-media loops: Text, images, video, audio, and 3D will share a unified feedback cycle.
- Human-guided constraints: You’ll be able to set ethical, educational, or cultural constraints that guide all future outputs.
The loop becomes a creative ecosystem rather than a tool pipeline.
If you’re serious about learning visual design loops and how it impacts the design process, don’t miss the chance to enroll in HCL GUVI’s UI UX Design Course, which is a NASSCOM-approved program with Government-approved Certification that teaches everything about the subject from scratch!
Conclusion
In conclusion, a strong visual design loop isn’t about pushing a button and hoping AI nails your idea on the first try. It’s about shaping a conversation between you, the LLM, and the image generator, until the visuals match the story you’re trying to tell.
Once you get comfortable with this rhythm, the process becomes faster, clearer, and a lot more intuitive. You keep the creative control, the models handle the heavy lifting, and together you produce visuals that feel intentional instead of accidental.
Whether you’re building learning content, designing product visuals, or exploring new styles, a well-designed loop gives you a reliable, repeatable way to create work you’re genuinely proud of. If anything, this is where AI starts to feel less like a tool and more like a teammate.
FAQs
1. What is a visual design loop in AI?
It’s an iterative workflow where you guide the idea, the LLM structures the prompt, the image generator creates visuals, and you refine the result through repeated feedback. Each cycle gets closer to your intended design.
2. How do LLMs and image generators actually work together?
LLMs turn rough ideas into clear, structured prompts. Image models convert those prompts into images. Your feedback updates the prompt, and the loop keeps improving the output.
3. Why do my AI-generated images look inconsistent?
Inconsistency usually comes from unclear prompts or missing details like style, lighting, or negative prompts. A structured design loop creates stable rules that keep visuals aligned.
4. How can I improve the quality of my AI-generated visuals?
Start with layered prompts, give specific feedback, and refine in small steps. Let the LLM rewrite prompts based on what you liked or disliked in earlier images.
5. Can I use LLM + image generator loops for educational content?
Absolutely. The loop helps create consistent characters, styles, diagrams, thumbnails, and cultural variations: all while keeping visuals aligned with age-appropriate and learning goals.






















Did you enjoy this article?