Network Architecture in Computer Network: A Complete Guide
Jan 27, 2026 6 Min Read 1192 Views
(Last Updated)
If you were to look beneath the surface of your laptop or smartphone, you would find a structure that tells every message, video, and file where to go. There are paths, ways to communicate, and a way to coordinate everything in a controlled manner (think of it as a well-mannered organisation!). Nothing is happening randomly.
This organised framework is called network architecture in computer networking. It decides how devices interact, how efficiently data is delivered, and what you will do when something goes wrong in the network.
In this blog, you will find this underlying architectural blueprint presented in a clear, practical way, so you can understand how network architecture affects the digital phenomena we use every day.
Table of contents
- What is Network Architecture in a Computer Network?
- Key Elements of Network Architecture
- Network Devices
- Transmission Media
- Network Protocols
- Software Components
- Topology Structure
- Types of Network Architecture
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Architecture
- Client-Server Architecture
- Cloud-Based Architecture
- Hybrid Network Architecture
- Network Architecture Models
- OSI Model (7 Layer Model)
- TCP/IP Model (4 Layer Model)
- Wrapping It Up:
- FAQs
- How does network architecture affect internet speed?
- Can different architectures be used in the same network?
- Who designs network architecture for companies?
- Does network architecture impact security?
What is Network Architecture in a Computer Network?
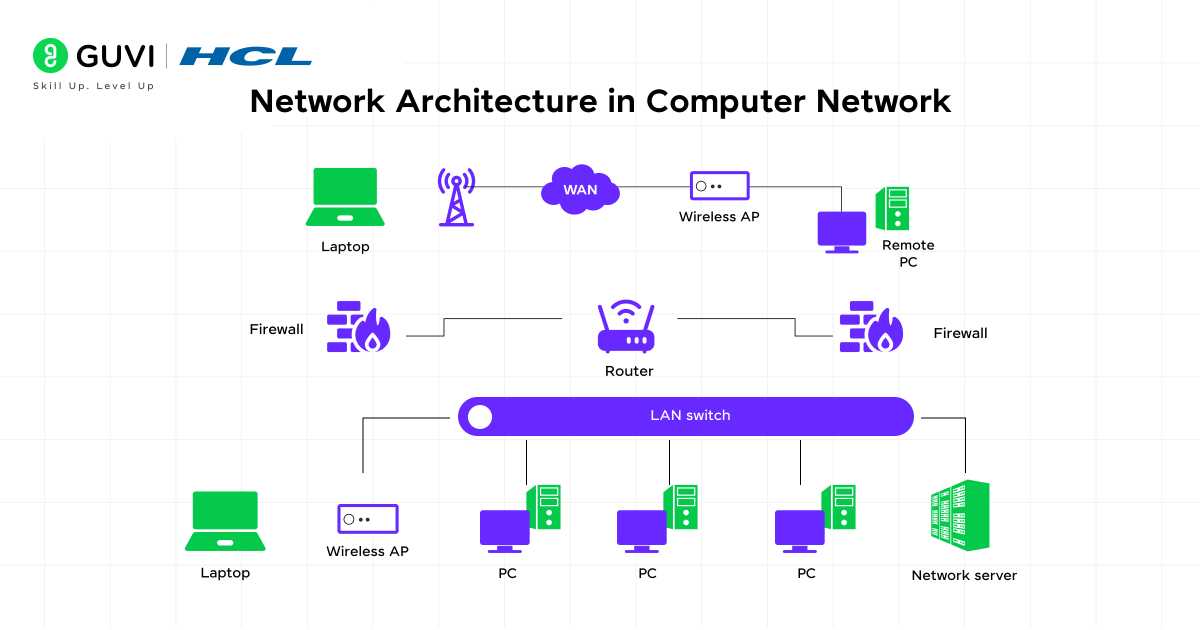
The term Network Architecture in Computer Network refers to the overall framework that defines how devices connect, how communication is facilitated, and how data is organised and managed. Network Architecture includes:
- Network Design
- The Layers of Communication
- Protocols
- Hardware Components
- Software Components
- Topology
- Security Measures
A good Network Architecture ensures:
- Rapid Communication
- Minimal Downtime
- Security of data transfer
- Easy to scale
- Efficient at solving problems
Key Elements of Network Architecture
A network architecture is built using several elements. Each element has a role in ensuring smooth communication.
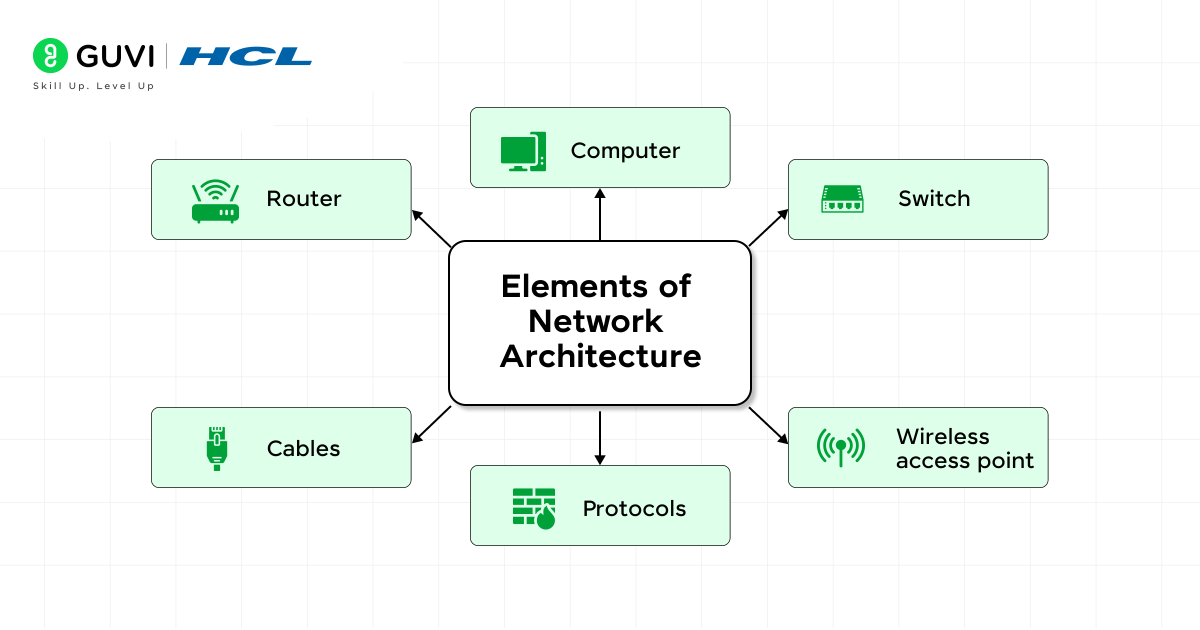
1. Network Devices
These are the hardware components that help in computer communication. Each device has a unique job in moving data smoothly from one place to another.
- Router – Routes sends connections between various networks and ensures that information is sent to the right destination, just as a traffic controller.
- Switch – The switch is used to provide a connection between two or more devices in the same network and only transmits data where required to avoid unnecessary traffic.
- Hub – Broadcasts information to all interconnected devices, and it is easy but less effective than switches.
- Modem– This is a device that turns digital information into signals that are transmitted over cables and enables your network to access the internet.
- Access Point – Creates a wireless zone where laptops, mobile phones, and IoT devices can be connected wirelessly.
Also read: Routing and Switching
2. Transmission Media
This is what is referred to as data paths. Without transmission media means that communication will not happen.
- Copper Cables – They are used most commonly in Local networks, such as cables, and are usually stable and less expensive.
- Fiber Optic Cables – Use light signals to transmit data at very high speeds, hence it is suitable in high-speed networks such as the internet and company networks.
- Wireless Radio Waves – Enable Wi-Fi and mobile networks that assist devices to communicate without wires.
- Satellite Links – Link remote or far locations when cables cannot be used, but where they might experience a little more latency.
3. Network Protocols
Protocols act like communication rules. They ensure that all the devices are using the same language such that messages do not get mixed.
- TCP/IP – This is the internet that determines the path followed by the data packets sent by the sender to the receiver.
- HTTP/HTTPS – Enable websites to be loaded on your browser. Safe browsing has been provided with HTTPS.
- FTP – Assists in exchanging big files among devices, particularly in servers and in hosting solutions.
- IPv4/IPv6 – Reserve special addresses to devices as a way of locating them in a network.
- DNS – Converts names of websites to IP addresses (i.e., converting guvi.in to a computer-readable number).
- DHCP – IP addresses are assigned automatically to the appliances, eliminating the manual system.
Also read: What is IoT? A Comprehensive Guide
4. Software Components
These are components that are not physical but are necessary in the administration and protection of the network.
- Network Operating Systems – Manage file sharing and control network functions, as well as user management.
- Firewalls – Indicate outgoing and incoming traffic in order to block unauthorized access.
- Monitoring Tools – Gather performance data of the network and assist in identifying problems before they occur.
- Authentication Systems – verify user identities in order to have only authorized individuals accessing valuable resources.
5. Topology Structure
Topology describes how devices are arranged. The structure impacts the speed, cost, and reliability of the network.
- Star Topology – All the devices are connected to a central hub or switch; simple to administer but it relies on the central device.
- Bus Topology – Equipment is connected to one common cable; inexpensive but can easily suffer collisions.
- Ring Topology – This involves a structure in which all the devices are in the form of a circle, and all have equal access to communication, yet are vulnerable to failure at one point.
- Mesh Topology – All devices are interconnected with several devices, which is highly reliable, but expensive to set up.
- Hybrid Topology– This is a topology that combines two or more topologies so that they can be more flexible and perform very well.
Also read: How to Become a Network Engineer? 6 Easy Steps To Get Started
Types of Network Architecture
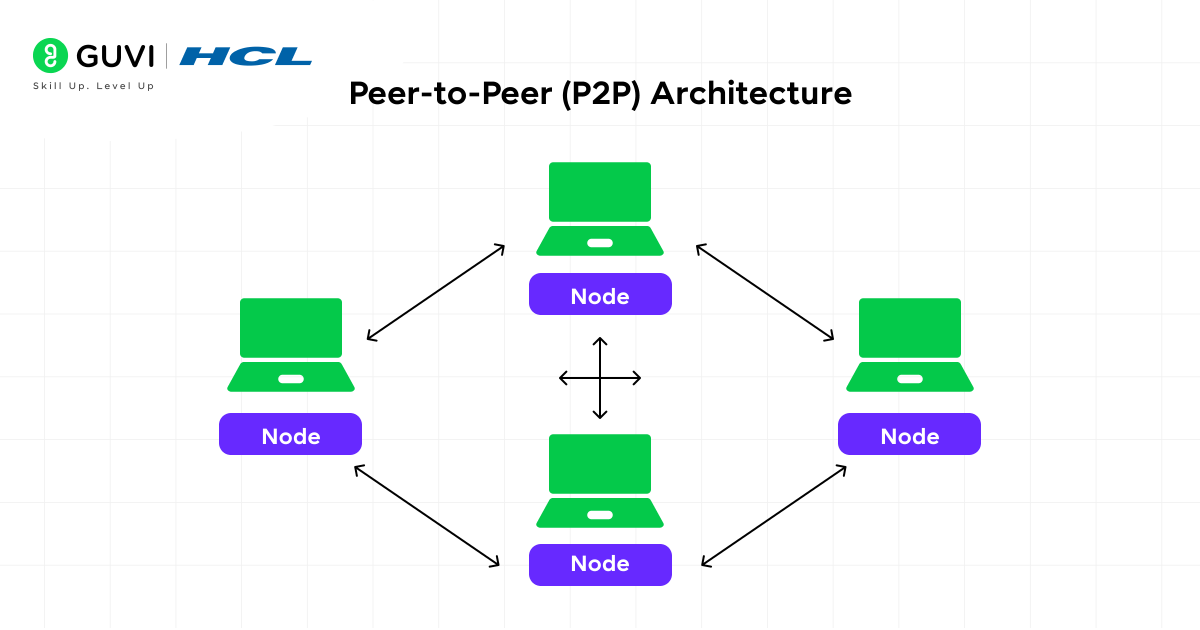
1. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Architecture
The easiest form of networking is the peer-to-peer architecture. Every device (so-called peers) is equal in this arrangement. No one manages the communication with a central server. Each device is able to directly share files, printers, and other resources with another device within the network.
Advantages:
- Easy to set up: No professional set-up required. You can share information between two or more computers using a simple cable or Wi-Fi, and begin to communicate.
- Low cost: It does not require a server machine or costly hardware. Everything can be done using ordinary computers.
- No dedicated server: The files are stored and handled in each device separately. No single machine is used to address requests.
Common Uses:
- Home networks: Excellent to connect a small number of laptops, smart TVs, printers or even mobile phones at home.
- File-sharing apps: P2P practices, such as the use of torrent clients, are an application that enables users to exchange files directly without the help of a central server.
- Small office setups: Good with small teams and only essential sharing, e.g. documents or printers.
P2P works best in case the network is small and the security needs are less. It is easy and not applicable in big or sensitive settings.
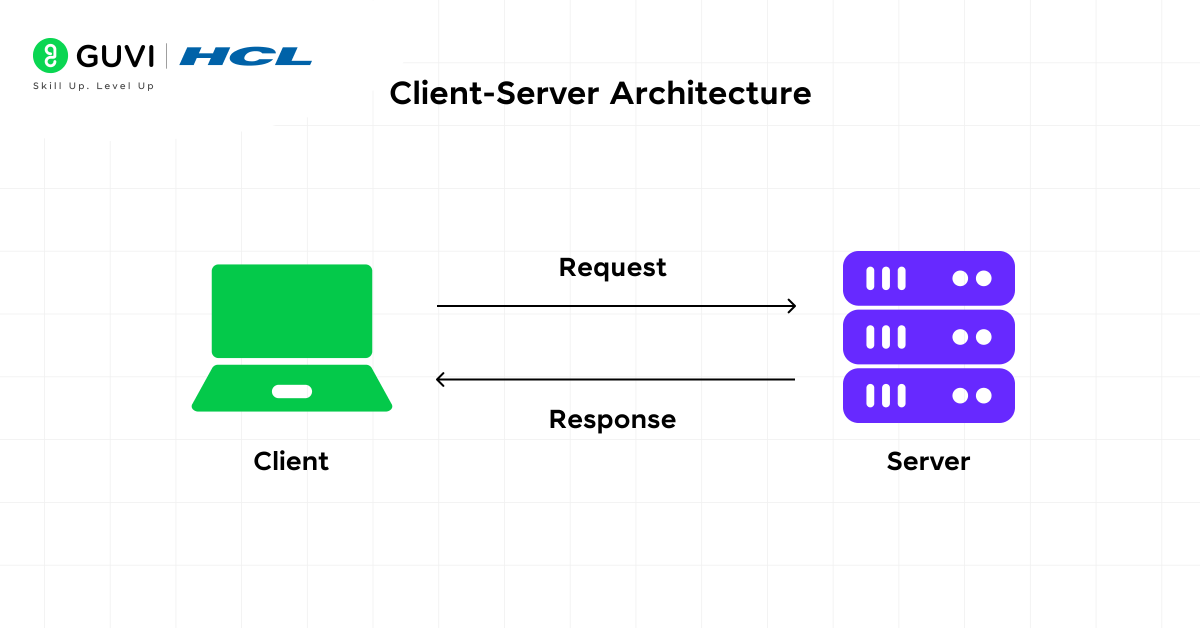
2. Client-Server Architecture
This is the professional and most commonly used network architecture. In this case, the system is separated into two:
- Client: devices such as laptops, mobiles, and desktops, which make demands.
- Server: A powerful computer that is used to store data, secure it, and offer services.
All this is managed at the server. This implies that updates, file storage, access permissions, and backups can all be done under the same location.
Advantages:
- High security: It is up to the server to determine access control. This ensures that unauthorized access does not occur and confidential data is not compromised.
- Centralized management: Admins are able to control users, software, and update systems at one location.
- Easy backup: All valuable information is stored in the server, thus making it easy and uniform to make backups.
- Reliable performance: The server is efficient and will not slow down even in cases where the number of users is high.
Common Uses:
- Banking systems: Servers are used by banks to store customer information, transactions, and manage accounts securely.
- E-commerce websites: When you buy anything over the Internet, you handle the server with product information, orders, and payments.
- Social media platforms: Applications such as Instagram or Facebook are processing millions of user requests with powerful servers.
- Corporate networks: In offices, server-based networks are used to offer email systems, storage, authentication, and the internet.
The modern Network Architecture of Computer Networks is based on Client-Server architecture, particularly in business and enterprise settings.
3. Cloud-Based Architecture
In this architecture, the server will not be located physically in your house or office. Rather, your data and applications are stored on remote cloud servers offered by companies such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. These servers are accessed by the users via the internet.
Also read: AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud: Comparing the Top Cloud Service Providers
Cloud architecture has become highly trendy nowadays as it does not require physical maintenance, and it is easier to scale.
Advantages:
- Access from anywhere: You can access your files and applications no matter where you are, as long as you have a stable internet connection.
- Flexible storage: Need more space? Just upgrade the cloud without purchasing hardware.
- High uptime: There are backup facilities and data centers to guarantee the service, which is available at all times.
- No physical maintenance: You do not have to worry about server breakdowns, updates, and repairs. Everything is taken care of by the cloud provider.
Common Uses:
- Google Drive: Store files through online storage and can be accessed using phones or laptops.
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): Offers cloud servers, databases, and solutions to companies to execute applications.
- Microsoft Azure: Enterprise-level app development, hosting, and management in the cloud.
- Cloud apps and databases: Most of the applications that are used today, such as Zoom, Canva, Dropbox accounts, and Netflix, are all cloud-based.
In Computer networks, cloud-based architecture has been a major component of Network Architecture, particularly in businesses that require flexibility and large-scale functionality of the architecture.
- Over 80% of large enterprises now use Hybrid Network Architecture because it blends the scalability of cloud systems with the control of on-premise infrastructure.
- Modern data centers can process terabits of data every second — made possible by intelligent network design and high-speed connectivity layers.
- A single enterprise-grade switch can route and manage millions of data packets per second without compromising performance.
- Cloud-based networks automatically maintain redundant backups, ensuring exceptional reliability with up to 99.99% uptime.
4. Hybrid Network Architecture
Hybrid architecture combines two or more integrated types, such as On-Premise + Cloud, or Client-Server + P2P to provide a hybrid network that is considered more optimal and efficient. A hybrid architecture allows organizations to take advantage of multiple architectural outcomes while reducing their limitations.
Advantages:
- Flexible: Organizations can keep their sensitive information stored on local servers while simultaneously using one or more cloud services for expanded storage or global access.
- Cost-effective: You are not obligated to make an entire expensive server investment, nor are you obligated to make an entire cloud expense commitment.
- Efficient performance: You can offload your workloads. An example is running real-time loads locally, but stripping large storage in the cloud.
- More reliable: It’s unlikely both could fail together, so if one goes down, the other should be able to continue the network’s function.
Common Uses:
- Larger enterprises: They manage both cloud capacity and hybrid physical servers, resulting in increased control and scalability.
- Educational institutions: Local labs might run client-server systems, while the extensive online learning ecosystem runs exclusively in the cloud, or in a hybrid.
- Healthcare: They only run their hospital systems locally, dermatology, and bucket storage in the cloud, with analytics completely run in the cloud.
- IT companies: The IT department does the development locally, but runs the entire deployment process from the cloud and uses the cloud for testing.
Network Architecture Models
1. OSI Model (7 Layer Model)
The OSI model explains how data travels through seven structured layers. Each layer has a specific responsibility, making it easier to design and troubleshoot networks.
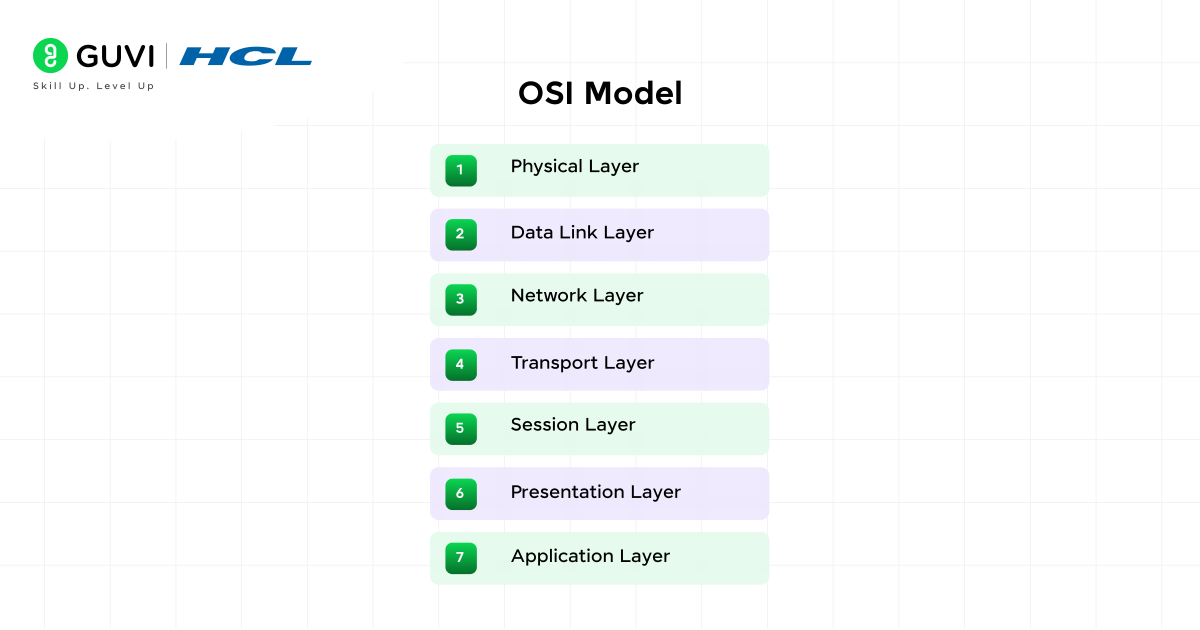
The 7 layers are:
- Physical Layer: Cables, signals, and hardware.
- Data Link Layer: Handles the detection of errors and frames of data.
- Network Layer: Selects the best path of the data with the use of IP.
- Transport Layer: It offers dependable transport with TCP or rapid transport with UDP.
- Session Layer: It is the layer that deals with communication between devices.
- Presentation Layer: Transforms data formats (text, images, videos).
- Application Layer: This is where the users get to deal with applications such as browsers or email.
2. TCP/IP Model (4 Layer Model)
A simplified version of the OSI model, used widely on the Internet and real-world networks.
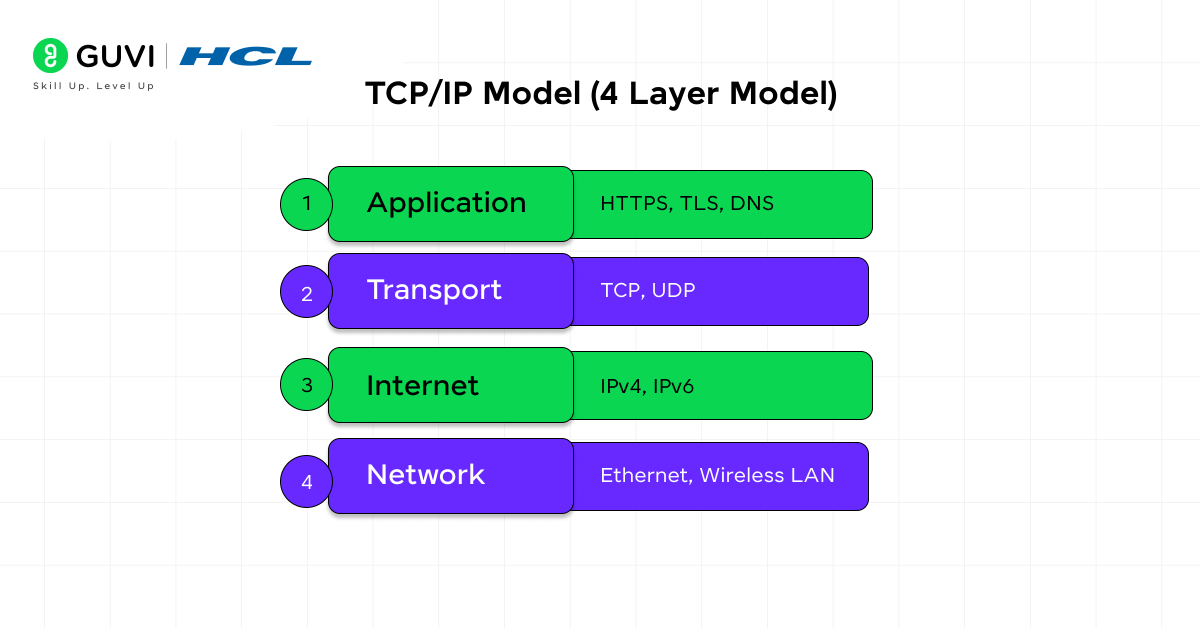
The 4 layers are:
- Network Access Layer: Physical connection and transmission of frames.
- Internet Layer: Addressing and routing using IP.
- Transport Layer: Provides a seamless communication with the help of TCP/UDP.
- Application Layer: Provides web browsing, mail, file transfer, and so on.
If you’re excited to master the art of Network Architecture in computer networks, then take the next step and Join the AI Software Development Course by HCL GUVI, IITM Pravartak, MongoDB, a 9-month industry-ready program covering Java, System Design, Generative AI, 15+ hands-on projects, and 4 globally recognized certifications.
Wrapping It Up:
Network architecture in computer networks provides the basis for everything we do digitally today, whether it is sending an email, accessing a business application, or utilizing cloud-based services. A well-planned architecture defines how devices connect, how data flows, and how secure and reliable the system remains as it grows.
From peer-to-peer configurations to massive client–server systems, and from cloud structures to hybrid environments, each architecture brings its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the size of the network and the goal. Understanding these architectures provides a basis for evaluating the performance requirements, choices in technology, and designing secure and agile networks that are ready for the future.
FAQs
1. How does network architecture affect internet speed?
An effective architecture will reduce congestion and data travel on the shortest possible path speed it up overall.
2. Can different architectures be used in the same network?
Yes. Many organizations use what is known as a Hybrid architecture, which combines aspects of cloud-based assets, on premise resources, and client–server-based systems.
3. Who designs network architecture for companies?
Network architects, system engineers, and IT administrators will usually design and implement the architecture.
4. Does network architecture impact security?
Definitely, the architecture will determine how inter-device firewall, encryption, authentication, and access control work and are organised in the network.































Did you enjoy this article?