
Generative AI vs Discriminative AI: Complete Guide
Oct 31, 2025 6 Min Read 1223 Views
(Last Updated)
What if the secret behind today’s most advanced AI systems came down to two very different ways of learning: one that creates and one that classifies? This contrast defines generative AI vs. discriminative AI, two core approaches that shape how machines understand and interact with data. Generative models capture underlying patterns to produce new text, images, or sounds, while discriminative models focus on drawing precise boundaries between categories.
Grasping the difference between the two is key to understanding why some AI systems generate original outputs while others excel at accurate predictions. Let’s learn more:
- The global generative AI market is estimated at USD 37.89 billion in 2025, and is estimated to reach about USD 1,005.07 billion by 2034.
- Generative AI is deeply embedded in business, as 71% of organizations now regularly use it in at least one operation.
- Over 50% of executives report that their organizations use generative AI in day-to-day operations, with text generation being the most common form of usage.
Table of contents
- What is Generative AI?
- Types of Generative AI
- Features of Generative AI
- Tools for Generative AI
- Benefits of Generative AI
- Faster Prototyping in Product Development
- Augmentation of Human Creativity
- Restoration and Enhancement of Data
- Scenario Simulation and Forecasting
- Accessibility Through Personalization
- Best Applications of Generative AI
- Personalized Education Platforms
- Creative Marketing Campaigns
- Synthetic Biology and Material Design
- Virtual Assistants with Multimodal Capabilities
- Limitations of Generative AI
- What is Discriminative AI?
- Types of Discriminative AI
- Features of Discriminative AI
- Tools for Discriminative AI
- Benefits of Discriminative AI
- Strong Generalization from Training Data
- Scalability Across Large Datasets
- Reduced Error in Real-Time Tasks
- Interpretability in Applied Contexts
- Resource Efficiency in Deployment
- Best Applications of Discriminative AI
- Legal Document Analysis
- Cybersecurity Threat Detection
- Healthcare Imaging Diagnostics
- Customer Behavior Segmentation
- Limitations of Discriminative AI
- Generative AI vs Discriminative AI: Key Differences
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Why do businesses use both generative AI and discriminative AI?
- How does discriminative AI improve decision-making speed?
- Can generative AI help in areas beyond content creation?
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence models designed to create new data that resembles existing information. These systems learn patterns within training datasets and then produce outputs such as text, images, audio, or video that align with those patterns. Generative AI is valuable because it does more than replicate data; it produces novel outputs that can support content creation, design exploration, drug discovery, and synthetic data generation for research.
Types of Generative AI
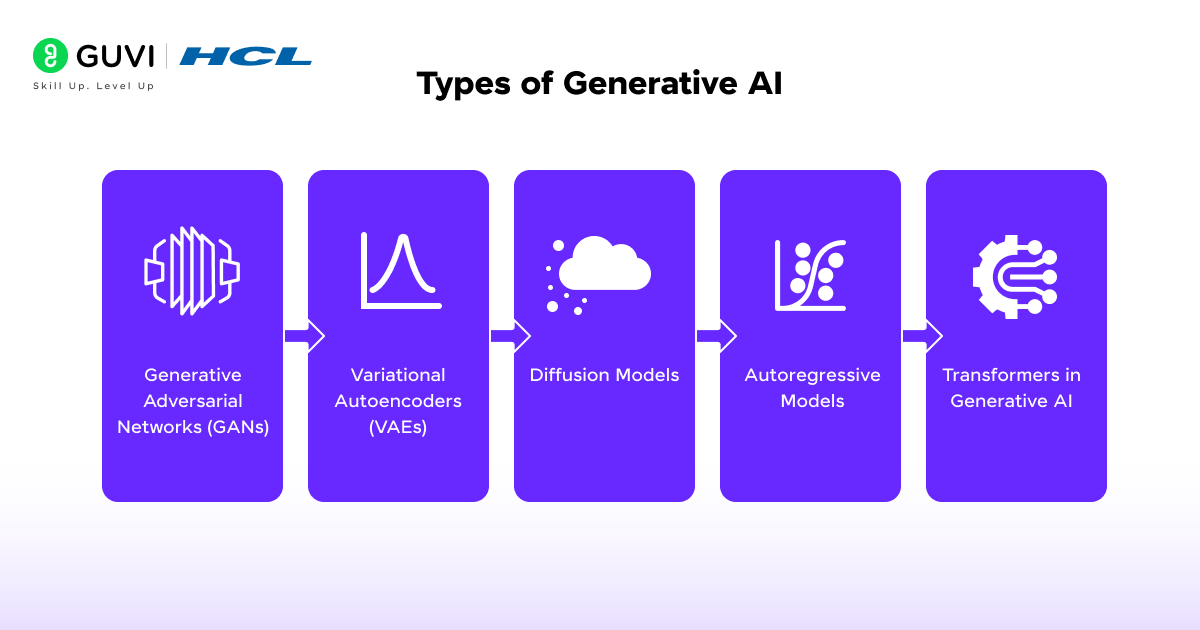
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs consist of two neural networks, a generator and a discriminator, working against each other. The generator creates new data samples, while the discriminator evaluates authenticity. This process continues until the generator produces highly realistic outputs.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): VAEs learn how to encode data into a compressed form and then decode it back into new samples. They are especially effective for creating synthetic images, anomaly detection, and tasks that require smooth variation between generated outputs.
- Diffusion Models: Diffusion models gradually transform random noise into structured data through a sequence of refinement steps. They have become central to image generation because they produce high-quality visuals with fine details.
- Autoregressive Models: Autoregressive architectures generate outputs step by step. They predict the next element in a sequence based on previous ones. Large language models that generate text are prime examples of this approach.
- Transformers in Generative AI: Transformer-based models leverage attention mechanisms to deal with long-range dependencies in data. This architecture has advanced generative AI in both text and multimodal tasks by improving coherence and contextual relevance.
Features of Generative AI
- Probabilistic Modeling: Generative AI depends on probability distributions to predict sequences and produce outputs that resemble patterns within training data. This allows the system to generate results that feel natural and contextually aligned with real information.
- Domain Adaptability: These models can be fine-tuned for specific fields such as medical imaging or scientific research. Adaptability ensures that outputs remain relevant across specialized AI use cases.
- Feedback-Driven Refinement: Generative AI improves through iterative feedback. Reinforcement learning, adversarial training, and human-in-the-loop adjustments help refine model behavior and reduce errors in generated outputs.
- Multimodal Generation: A key feature is the ability to generate across multiple formats such as text, images, and audio. Once trained on diverse datasets, generative AI can link different modalities and create content that spans formats.
Tools for Generative AI
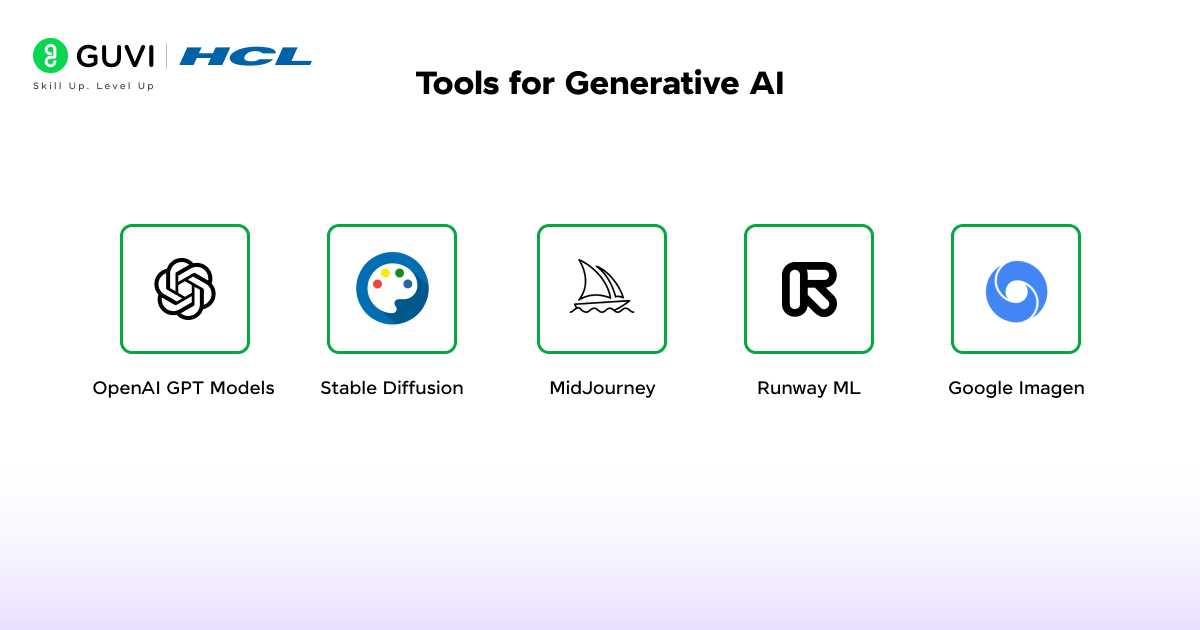
- OpenAI GPT Models: Large language models like GPT power applications that generate human-like text. They are widely used for content creation, chat assistants, and knowledge expansion.
- Stable Diffusion: Stable Diffusion is an open-source tool for generating high-quality images from text prompts. It is used by designers, marketers, and researchers for visual ideation.
- MidJourney: MidJourney specializes in artistic image generation. It supports creators in producing unique visual styles for design, storytelling, and branding projects.
- Runway ML: Runway ML provides generative AI tools for video, image, and design workflows. Its user-friendly interface allows creatives to apply AI models without deep technical expertise.
- Google Imagen: Google Imagen is a text-to-image model that generates photorealistic visuals. It demonstrates the potential of generative AI in areas like advertising and product mockups.
Benefits of Generative AI
1. Faster Prototyping in Product Development
GenAI accelerates design cycles by producing multiple prototypes quickly. Engineers and designers use it to test variations of a product concept, which reduces development time and lowers costs in industries such as automotive and consumer electronics.
2. Augmentation of Human Creativity
Artists and writers use generative AI as a collaborative tool that introduces unexpected ideas. It expands the space of possibilities instead of replacing creativity. It assists humans in exploring directions they might not consider on their own.
3. Restoration and Enhancement of Data
Generative AI can reconstruct missing details in images or videos. This is especially useful in historical preservation and surveillance, where incomplete or noisy data must be turned into clear and usable outputs.
4. Scenario Simulation and Forecasting
Organizations employ generative AI to simulate environments and run what-if scenarios. They also integrate GenAI to project outcomes under different conditions. This benefit is valuable in climate modeling and financial risk analysis, where testing every scenario manually is impossible.
5. Accessibility Through Personalization
Generative AI creates adaptive tools that improve accessibility for users with diverse needs. Examples include AI systems that generate real-time captions or personalize educational content to match different learning styles.
Best Applications of Generative AI

1. Personalized Education Platforms
Generative AI produces adaptive content such as quizzes and explanations. It also adjusts practice materials to match the pace of each student, which supports individualized learning. It creates pathways for inclusive education that can serve learners with diverse needs.
2. Creative Marketing Campaigns
Generative AI helps brands generate draft visuals and initial slogans. Marketing teams refine these outputs into full campaigns that resonate with specific audiences. It reduces production cycles and allows marketers to test multiple creative directions quickly.
3. Synthetic Biology and Material Design
Scientists use generative AI to simulate new protein structures. It also suggests material compositions that accelerate progress in biotechnology and renewable energy. It expands innovation into areas where traditional experimentation is slow and resource-intensive.
4. Virtual Assistants with Multimodal Capabilities
GenAI powers assistants that respond through text and voice. They can also integrate visual elements, which makes interactions more natural for users. GenAI also creates conversational systems that function closer to human interaction.
Limitations of Generative AI
- High Computational Cost: Training and running generative models is a stubborn challenge of generative AI. The GenAI models require massive hardware resources and energy, which makes them expensive to deploy at scale.
- Bias in Outputs: If the training data contains bias, the generated content often reflects those same patterns. It can further lead to skewed or harmful results.
- Data Dependency: Generative AI needs vast datasets to perform effectively. This raises challenges in domains where data is limited, sensitive, or difficult to obtain.
- Risk of Misuse: The proficiency to generate convincing text or video can be exploited for misinformation, deepfakes, or fraudulent activities.
- Lack of Interpretability: Decisions and outputs produced by generative AI are often difficult to trace back to specific reasoning steps, which limits transparency and trust.
What is Discriminative AI?
Discriminative AI refers to models designed to distinguish between different categories of data rather than generating new content. These systems focus on learning the conditional probability P(Y|X) or the probability of a label (Y) given a set of input features (X). They draw precise boundaries between classes and assign probabilities to predictions by directly mapping inputs to outputs.
Types of Discriminative AI
- Logistic Regression: A widely used statistical model that estimates the probability of an input belonging to a particular class. It is effective for binary classification tasks such as spam detection or disease risk prediction.
- Support Vector Machines (SVMs): SVMs create decision boundaries that separate data points into categories. They are valuable for applications that require high accuracy in text classification and image recognition.
- Decision Trees: Decision trees split data into branches based on feature values until a final classification is reached. They are easy to interpret and useful in fields like finance and healthcare.
- Random Forests: Random forests combine multiple decision trees to reduce error and improve stability. They are applied in fraud detection, credit scoring, and predictive analytics where reliability is critical.
- Neural Networks for Classification: Neural networks trained on labeled data can capture complex patterns and classify inputs with high precision. They are especially effective in large-scale tasks such as image recognition and sentiment analysis.
Features of Discriminative AI
- Focus on Classification: Discriminative AI models learn the decision boundaries that separate one class from another. Their core purpose is to predict the correct label for a given input.
- Direct Probability Estimation: These models calculate the probability of an input belonging to a specific category. The output is a clear mapping between input features and class labels.
- Efficiency in Supervised Learning: Discriminative models are widely used in supervised tasks because they can handle labeled datasets effectively and deliver accurate predictions.
- Flexibility Across Algorithms: Logistic regression, decision trees in machine learning, and neural networks can all operate as discriminative models. This flexibility makes them suitable for a broad range of AI use cases.
Tools for Discriminative AI

- Scikit-learn: Scikit-learn offers a robust set of libraries for classification, regression, and clustering. It supports algorithms like logistic regression and SVMs.
- TensorFlow: TensorFlow provides frameworks to build discriminative neural networks. It is widely used in applications such as image recognition and speech classification.
- PyTorch: PyTorch enables researchers and developers to design flexible discriminative models. It is preferred for experimentation and deployment in computer vision and NLP tasks.
- XGBoost: XGBoost is optimized for gradient boosting in classification tasks. It delivers strong performance in structured data analysis such as fraud detection and risk modeling.
- LightGBM: LightGBM is a high-speed library for decision tree-based classification. It is applied in recommendation systems and large-scale prediction tasks.
Benefits of Discriminative AI
1. Strong Generalization from Training Data
Discriminative AI models can adapt well to new inputs once trained on quality datasets. They learn boundaries that extend beyond the training examples. It authorizes them to handle unseen cases with accuracy.
2. Scalability Across Large Datasets
These models can be scaled to handle high-dimensional and extensive datasets without losing predictive strength. This scalability is critical in fields such as genomics and large-scale fraud detection.
3. Reduced Error in Real-Time Tasks
Discriminative AI supports low-latency decision-making. It minimizes errors in fast-response applications like transaction approvals or medical screening, where speed and accuracy must work together.
4. Interpretability in Applied Contexts
Models such as logistic regression and decision trees provide results that can be explained and audited. This interpretability helps organizations comply with regulatory standards and maintain trust in AI-driven systems.
5. Resource Efficiency in Deployment
Compared to generative approaches, discriminative models often require less computational power during deployment. Their leaner architecture makes them more practical for production environments where cost and efficiency matter.
Best Applications of Discriminative AI
1. Legal Document Analysis
Discriminative AI classifies clauses in contracts with precision. It also highlights compliance risks, which reduces the manual burden on legal teams. Legal professionals gain more confidence in reviews, especially in cases involving complex regulatory frameworks.
2. Cybersecurity Threat Detection
Discriminative AI identifies malicious patterns in network traffic. It also distinguishes safe connections from harmful ones, which strengthens enterprise security systems. Adaptive threat detection provides organizations with a critical safeguard against emerging attacks.
3. Healthcare Imaging Diagnostics
Discriminative AI evaluates scans and classifies anomalies. It also assists doctors in differentiating between normal and abnormal findings, which improves diagnostic confidence. Faster and more reliable assessments help clinicians deliver timely treatments.
4. Customer Behavior Segmentation
Discriminative AI groups customers by purchase history. It also classifies behavior patterns, which allows businesses to design strategies tailored to each segment. Companies gain sharper insights into consumer needs, which leads to more powerful retention efforts.
Limitations of Discriminative AI
- Dependence on Labeled Data: Discriminative models require large volumes of accurately labeled datasets. Collecting and curating such data can be expensive and time-intensive.
- Difficulty with Complex Distributions: These models stress on drawing boundaries between classes but struggle when data has overlapping or ambiguous patterns, which limits accuracy in noisy environments.
- Limited Generative Capability: Unlike generative models, discriminative AI cannot create new data or simulate variations. This restricts its usefulness in applications where synthesis or simulation is required.
- Risk of Overfitting: Discriminative models can adapt too closely to training data. This overfitting reduces their ability to generalize to unseen inputs, especially in smaller datasets.
- Challenges in Multimodal Integration: Dealing with diverse inputs such as text and images together is more complex for discriminative models, since they are optimized mainly for classification.
Knowing the difference between Generative AI and Discriminative AI is powerful, but building expertise with both is career-changing. HCL GUVI’s AI & ML Course with Intel Certification equips you with Python, deep learning, transformers, GANs, and real-world ML projects under expert mentorship. With global recognition, lifetime access, and placement support, you’ll gain the skills to stand out in the AI revolution. Enroll today and earn your Intel-backed certification!
Generative AI vs Discriminative AI: Key Differences
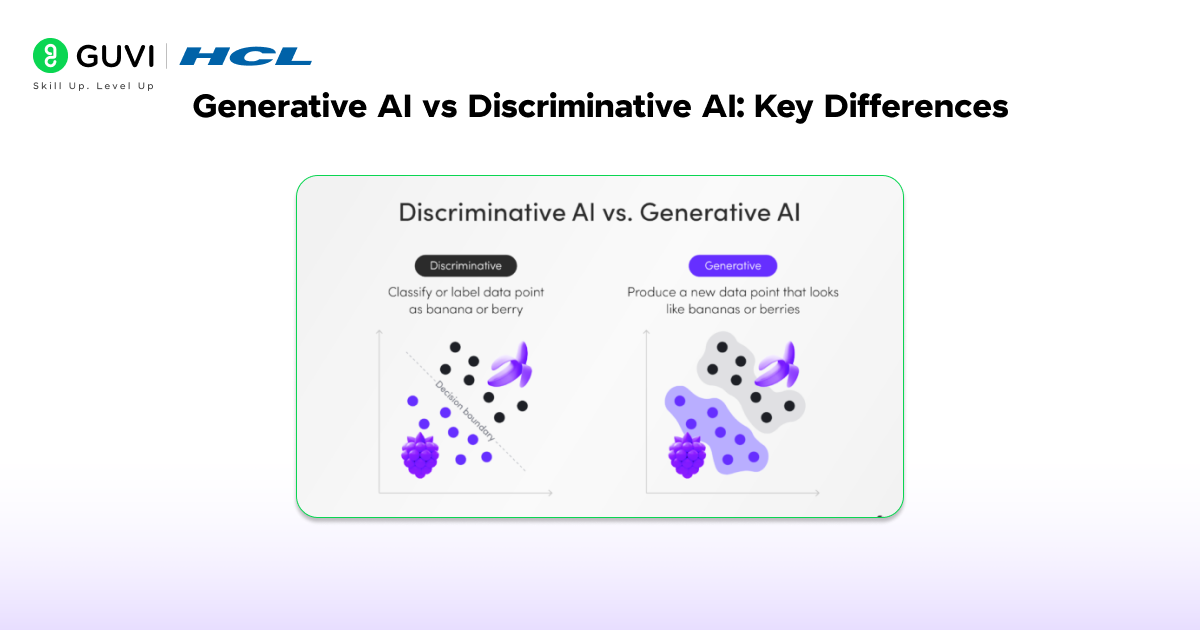
| Feature | Generative AI | Discriminative AI |
| Core Purpose | Learns data distribution to generate new samples | Learns decision boundaries to classify existing data |
| Output | Produces new text, images, audio, or video | Assigns labels or probabilities to input data |
| Data Requirement | Requires large datasets for training distribution patterns | Requires labeled datasets for mapping inputs to outputs |
| Examples of Models | GANs, VAEs, Diffusion Models, Transformers | Logistic Regression, SVMs, Decision Trees, Random Forests, Neural Networks |
| Use Cases | Content creation, drug discovery, synthetic data generation, design automation | Fraud detection, medical diagnosis, spam filtering, sentiment analysis |
| Strength | Generates novel and contextually aligned outputs | Provides accurate and efficient classification |
| Limitation | High computational cost and risk of bias in generated outputs | Limited to classification and lacks data generation ability |
Conclusion
Comprehending the difference between generative AI and discriminative AI reveals how both approaches complement each other in advancing machine intelligence. Generative models expand possibilities by creating new data and simulating variations. On the other side, discriminative models bring clarity through precise predictions and classifications. Together, they shape practical AI use cases that range from content creation to fraud detection. As industries continue to integrate both methods, the future of AI will be defined by systems that combine creativity with accuracy to solve complex real-world challenges.
FAQs
1. Why do businesses use both generative AI and discriminative AI?
Generative AI creates new possibilities such as synthetic data and personalized content, while discriminative AI strengthens accuracy in prediction and classification. Together, they give organizations a balance of creativity and reliability in their AI use cases.
2. How does discriminative AI improve decision-making speed?
Discriminative models calculate probabilities directly between inputs and labels, which reduces processing overhead. This allows industries like finance and healthcare to make fast predictions without sacrificing accuracy.
3. Can generative AI help in areas beyond content creation?
Generative AI supports applications such as drug discovery, scenario simulations, and restoration of incomplete data. These use cases show its value in science and industry, far beyond producing text or images.





























Did you enjoy this article?