Divide & Conquer Algorithm Explained: A Beginner’s Guide 2026
Feb 12, 2026 4 Min Read 2786 Views
(Last Updated)
The Divide & Conquer Algorithm is a basic method of programming for solving difficult problems. The idea is simple yet powerful: break a large problem down into a smaller, more manageable pieces, solve the subproblems, and then combine the results to solve the entire problem.
This is a fundamental principle for many common DSA algorithms as well, such as Merge Sort, Quick Sort, and Binary Search, because the Divide & Conquer Algorithm takes a big problem and breaks it down into smaller chunks before it solves it as a whole. A “chunked” approach to problems allows them to be manageable, understandable, and ultimately solved in the most efficient manner.
For many who are just learning Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA), mastering the Divide & Conquer Algorithm is essential for problem-solving techniques and this blog will help you understand the basics of divide and conquer algorithms.
Table of contents
- What is Divide & Conquer Algorithm?
- The Three Steps of Divide & Conquer Algorithm
- Why Use Divide & Conquer Algorithms?
- Common Examples of Divide & Conquer Algorithms
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Binary Search
- Strassen's Matrix Multiplication
- Karatsuba's Algorithm
- Real-World Applications of the Divide & Conquer Algorithm
- Advantages of the Divide & Conquer Algorithm
- Disadvantages of the Divide & Conquer Algorithm:
- Wrapping it up:
- FAQs
- What is the main idea of the Divide & Conquer Algorithm?
- Can you provide examples of Divide and Conquer Algorithms?
- What is the time complexity of Divide and Conquer Algorithms?
- Is Divide and Conquer better than Dynamic Programming?
What is Divide & Conquer Algorithm?
The Divide and Conquer Algorithm is a basic strategy for solving all sorts of problems in computer science. It breaks a large problem into smaller, more manageable subproblems, solves each subproblem independently, and integrates their solutions to determine a solution to the original, larger problem.
This strategy helps tackle challenging problems by incrementally shrinking the problem size.
In short,
1. Divide the problem
2. Conquer (solve) the smaller problems
3. Combine the solutions.
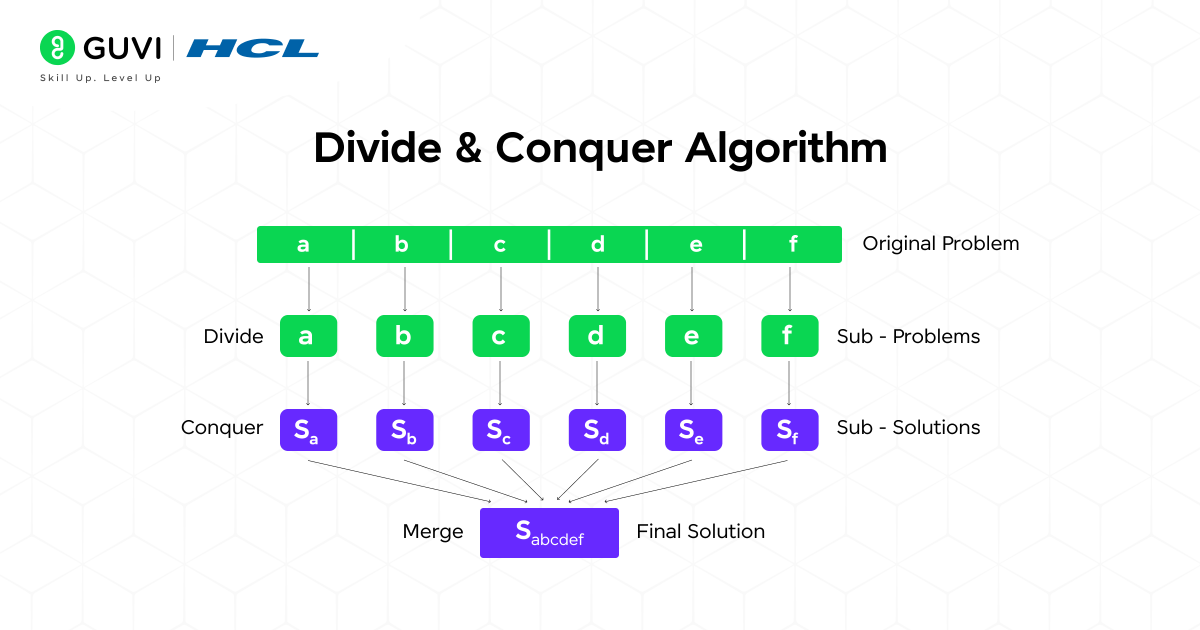
This strategy is especially powerful in cases when you can break a problem down into smaller instances of the same type of problem (called subproblems).
Also read: Sorting in Data Structure: Categories & Types [With Examples]
The Three Steps of Divide & Conquer Algorithm
The whole process proceeds as three ordered steps:
1. Divide
The first step is to divide the problem into smaller, similar subproblems.
For example, in Merge Sort, you divide an array into two halves. For Binary Search, you divide the array into two pieces depending on the position of the middle element.
2. Conquer
Then, you will recursively solve each smaller subproblem. If the subproblem is too large, you will continue to divide them until they are small enough to solve directly.
3. Combine
At the end, you will combine the results from the solved subproblems to create the final solution. For example, in Merge Sort, once the halves are sorted, you would combine them to create a sorted array.
Also Explore: 5 Best Reasons to Learn Data Structures and Algorithms [DSA]
Why Use Divide & Conquer Algorithms?
When an algorithm is slow or complicated for big inputs, divide and conquer takes the problem and separates it into smaller and easier subproblems.
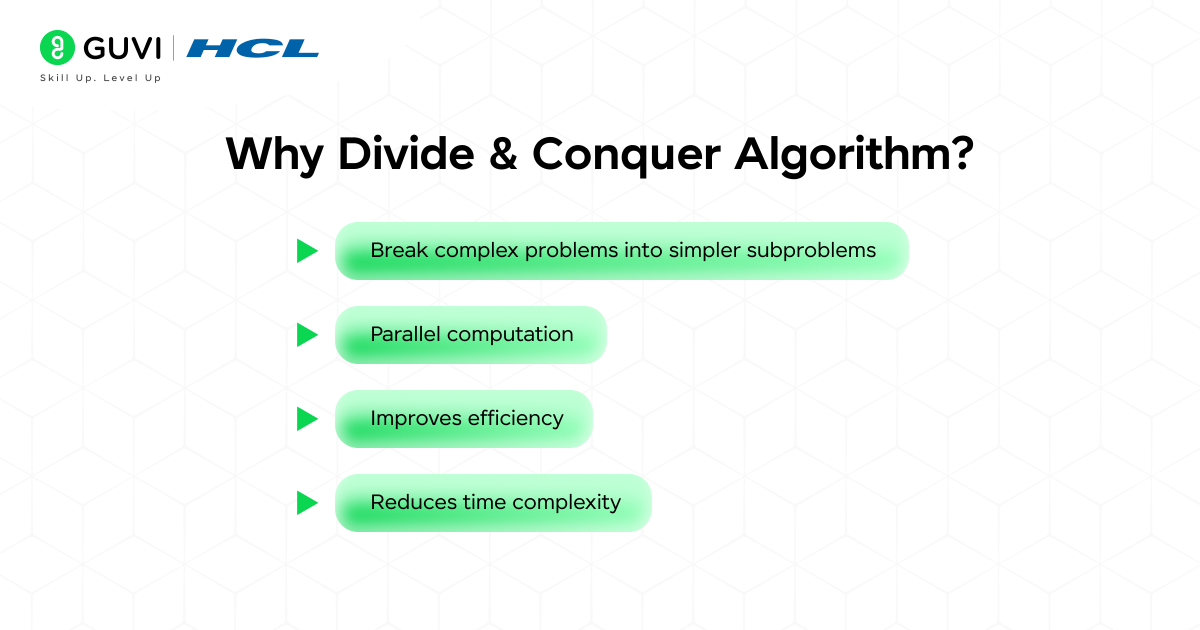
Advantages:
- You can break a complex problem into simpler subproblems.
- It can allow for parallel computation (can solve part of the problem at once).
- It improves efficiency and reduces the time complexity.
- It is what many advanced algorithms rely on.
Common Examples of Divide & Conquer Algorithms
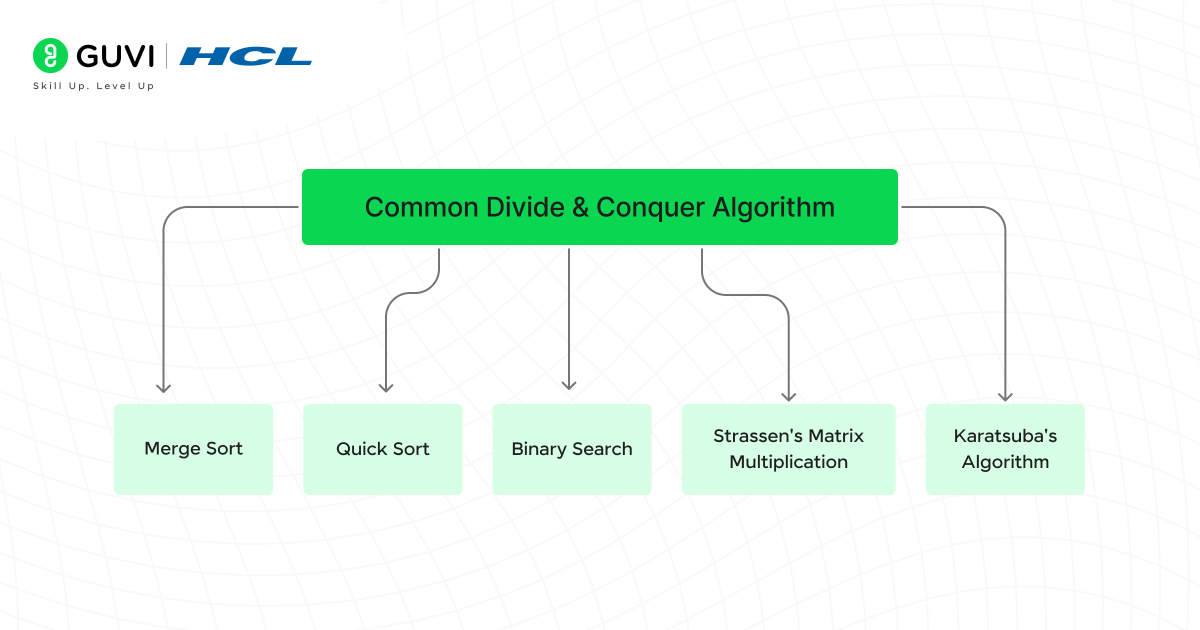
1. Merge Sort
Merge Sort is a well-known example of a Divide & Conquer Algorithm.
It divides the array into two halves, recursively sorts each half, and then merges the sorted halves back together.
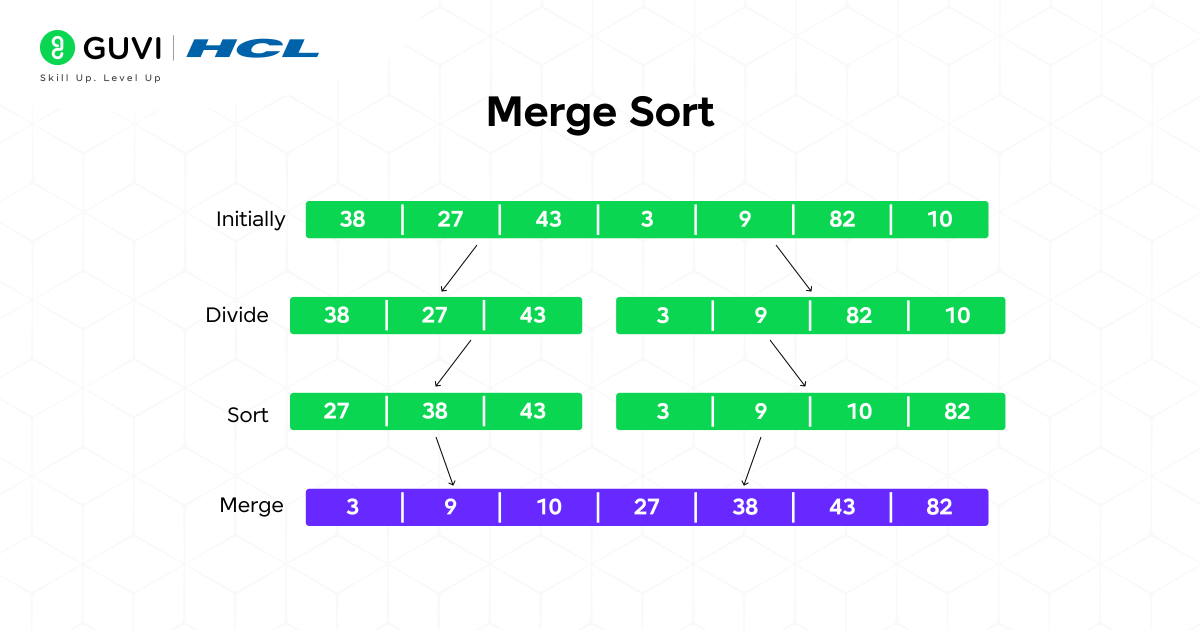
Steps:
- Divide the array into two halves.
- Recursively sort the two halves.
- Merge the two sorted halves back together to create one sorted array.
Example:
If you had an array [38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10],
Divide would be: [38, 27, 43] and [3, 9, 82, 10]
Conquer would be sorting each of the halves
Combine would be: [3, 9, 10, 27, 38, 43, 82]
Time Complexity: O(n log n)
Why it’s effective:
Despite dividing the array many times, the merging process is linear in complexity, making it useful to work with large datasets.
Also Read: Is DSA Important for Placement in 2026?
2. Quick Sort
Another well-known example of a Divide & Conquer Algorithm is Quick Sort.
It begins by picking a “pivot” element, and partitions the array such that all of the elements that are smaller than the pivot will go on one side, while all elements larger than the pivot will go on the other side.
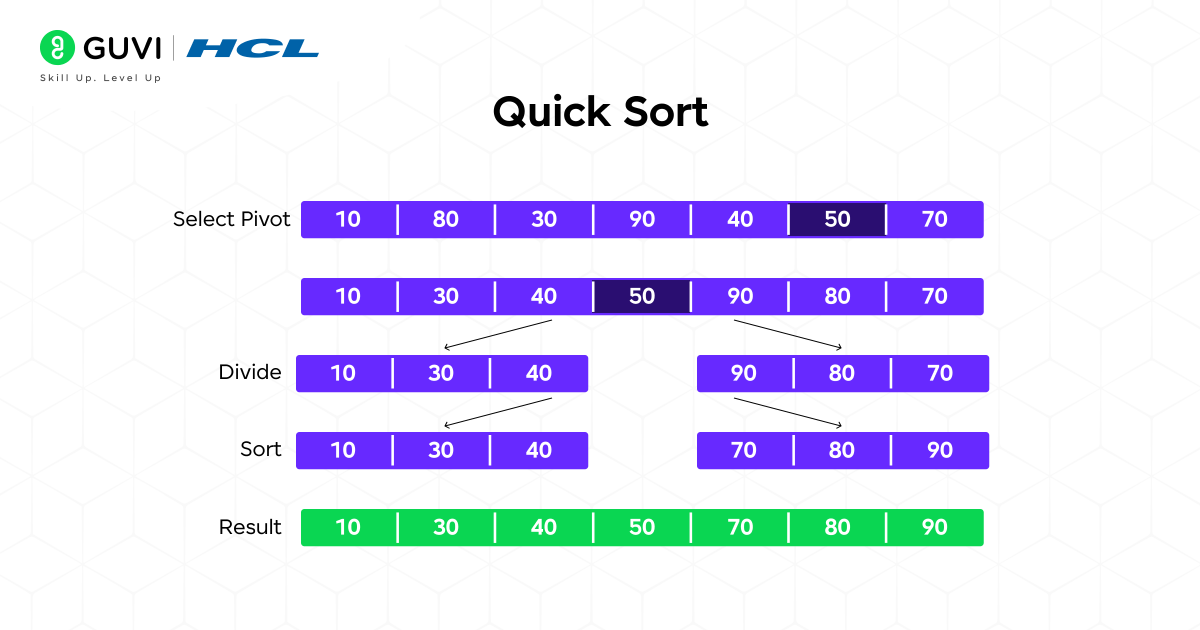
Steps:
- Pick a pivot element.
- Partition the array into two sides based on the pivot.
- Recursively apply the process to both sides of the partitioned array.
Example:
If the array is [10, 80, 30, 90, 40, 50, 70], and the pivot is chosen to be the value 50.
After the partition is complete, the array would look like: [10, 30, 40] 50 [80, 90, 70].
Then, you would recursively sort the left side, and recursively sort the right side.
Time Complexity:
- Best & Average Case: O(n log n)
- Worst Case (if pivot is poorly chosen): O(n²)
Why it’s efficient:
Quick Sort is often faster in practice than other sorting algorithms due to low overhead and good cache performance.
3. Binary Search
Binary Search is one of the simplest and efficient divide-and-conquer algorithms.
It works on sorted arrays only. The algorithm divides the search space in half repeatedly until the target element is located (or the entire search space is empty).
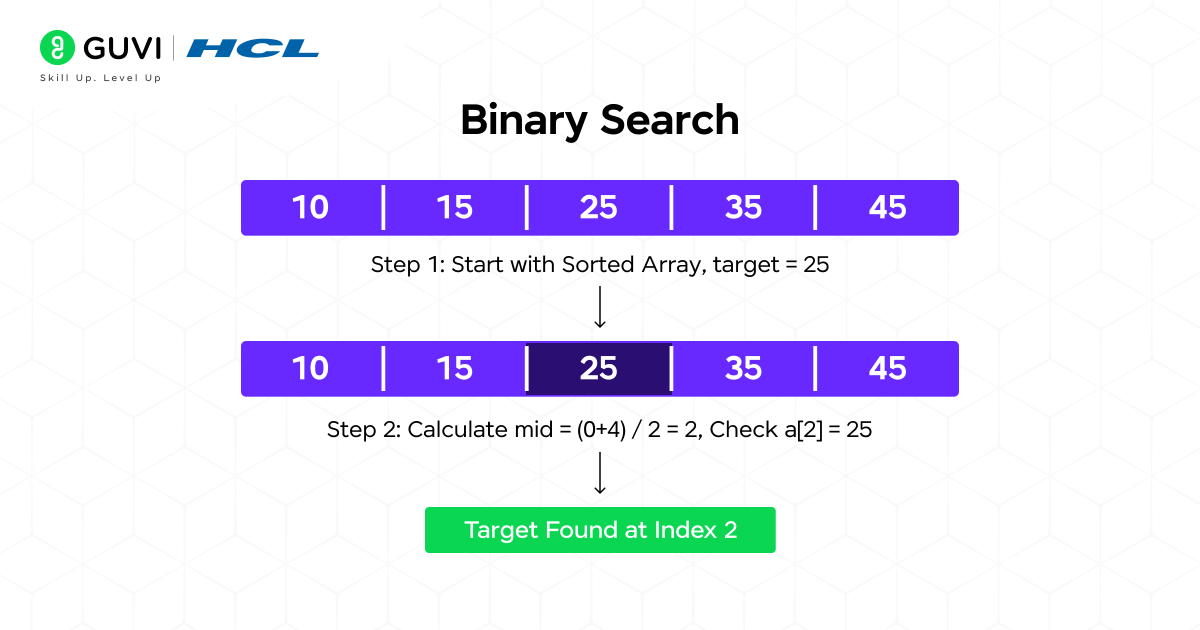
Steps:
- Locate the middle element of the array.
- If equal to target → return index.
- If less → search the left half.
- If larger → search the right half.
Example: search 25 in [10, 15, 25, 35, 45]
- Middle element = 25 → found!
Time Complexity: O(log n)
Why is it efficient:
Instead of checking each element individually, it removes half of the search space each time.
Download HCL GUVI’s free Data Structures & Algorithms eBook and start mastering problem-solving skills that every top developer needs!
4. Strassen’s Matrix Multiplication
Multiplying matrices can be computationally expensive and slow, but Strassen’s Algorithm (a divide and conquer method) is more efficient than the traditional O(n³) method.
It divides the matrices into sub-matrices, recursively multiplies them, and efficiently combines them.
Time Complexity: O(n^2.81)
Also Read: Best DSA Roadmap Beginners Should Know
5. Karatsuba’s Algorithm
It uses divide & conquer to multiply two large numbers efficiently. Instead of 4 multiplications, an additional step reduces that to 3 multiplications altogether.
Time Complexity: O(n^1.585)
- The Divide & Conquer Algorithm was first popularized by John von Neumann in 1945 through the Merge Sort algorithm.
- It’s the foundation of modern parallel computing, where tasks are split and processed simultaneously.
- Binary Search, a divide and conquer method, can find an element in a million entries in just 20 steps!
- Many AI models and data compression techniques secretly rely on divide and conquer to handle massive computations efficiently.
Real-World Applications of the Divide & Conquer Algorithm
- Processing large amounts of data: Algorithmic sorting techniques such as Merge Sort and Quick Sort utilize divide & conquer techniques to sort data efficiently and accurately.
- Searching applications: Binary Search uses the divide-and-conquer principle to facilitate quick searching of items within large data sets.
- Image processing and graphics: Image processing and graphics techniques, such as the Fast Fourier Transform, use the divide & conquer principle in both signal processing and compression techniques.
- Application in AI and machine learning: Divide and conquer applications facilitate the possible computation of complex matrix operations quickly in machine learning models.
- Cryptography algorithms: Divide and conquer will often support the fast multiplication of large numbers for computer cryptography algorithms, such as Karatsuba’s method.
- Applications in parallel computing and distributed systems: Divide & conquer can break problems into independent tasks, which allows for solutions that are quicker and scalable.
Advantages of the Divide & Conquer Algorithm
- Improved Efficiency: Divide & Conquer allows for complex tasks to be reduced to smaller subproblems to obtain answers more quickly.
- Simplicity in Design: It is easier to design recursive algorithms than iterative algorithms.
- Parallelism: The subproblems can be solved at the same time, leading to increased performance.
- Reduced Time Complexity: Many divide & conquer approaches will perform with O(n log n) efficiency.
- Better Memory Management: Because Divide & Conquer works with smaller amounts of data, it is more suited to the memory hierarchy of modern CPUs.
Also, Explore About 10 Best Data Structures and Algorithms Courses
Disadvantages of the Divide & Conquer Algorithm:
- Recursive Overhead: The overhead in recursion can lead to increases in stack memory use.
- Difficult to Implement for Certain Problems: Dividing problems into related subproblems will not work for all problem types.
- Merging Back Together May Have a High Cost: In some cases, it may be expensive to merge back together the engineered solutions.
- Difficult to Debug: When using recursion as a technique, it is difficult to debug and trace execution.
If you enjoyed learning about the Divide & Conquer Algorithm, take your skills to the next level with HCL GUVI’s AI Software Development Course, designed to help beginners master algorithms through real-world coding challenges.
Wrapping it up:
To become proficient in programming, it is important to master the Divide & Conquer strategy. It teaches you to solve complex problems by dividing them into smaller and more manageable pieces that you can validate independently, and the process of solving even the hardest problems becomes straightforward.
Once you have established an understanding of Divide & Conquer as a technique, you will not only create a solid foundation in Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA), but you will also be trained to solve problems in this mindset and style, which will help you in your coding interviews, in practical applications you become involved with and eventually have the potential to excel at recursive and algorithmic problems. Once you classify studying (or learning) Divide & Conquer as a technique, you’re essentially training yourself to write more effective, faster, and smarter code every time you program.
FAQs
1. What is the main idea of the Divide & Conquer Algorithm?
To address a large problem, Divide and Conquer Algorithm decomposes it into smaller subproblems; it recursively solves them and then merges their results to derive the solution.
2. Can you provide examples of Divide and Conquer Algorithms?
Some examples are Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Binary Search, Strassen’s Matrix Multiplication, and Karatsuba’s Algorithm.
3. What is the time complexity of Divide and Conquer Algorithms?
Time complexity differs depending on the algorithm, but many have O(n log n) hence are very efficient.
4. Is Divide and Conquer better than Dynamic Programming?
They are not the same. Divide and Conquer is used when the subproblems are independent, while Dynamic Programming is used when they have overlapping subproblems.

























Did you enjoy this article?