
A Detailed Guide to MLOps Roadmap
Sep 25, 2025 7 Min Read 3843 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered why so many machine learning projects struggle to move from promising prototypes into real business impact? The MLOps roadmap delivers a structured path for building and maintaining models with reliability. It explains how each stage connects technical practices with business needs. The roadmap seamlessly helps teams reduce risks and achieve lasting results. A clear roadmap turns machine learning efforts into sustainable success.
Read this blog to comprehend how a clear roadmap can turn machine learning efforts into sustainable success.
- Companies that apply MLOps practices often see profit margins rise. Gains typically range from 3% to 15%.
- The MLOps market was valued at about USD 2.2 billion in 2024. Forecasts suggest it could grow to USD 16.6 billion by 2030.
- Organizations with mature MLOps practices are twice as likely to scale AI pilots into production compared with teams lacking formal pipelines.
Table of contents
- What Are LangChain Prompt Templates?
- What Does a Good LangChain Prompt Template Actually Look Like?
- How to Install LangChain
- Types of LangChain Prompt Templates
- PromptTemplate — The Beginner Level
- ChatPromptTemplate — The Intermediate Level
- MessagesPlaceholder — The Advanced Level
- Building Your First LangChain Prompt Template Step by Step
- 5 Copy-Paste LangChain Prompt Templates You Can Use Right Now
- Blog Post Introduction Generator
- Code Explainer for Beginners
- Customer Support Reply Generator
- Study Notes Summariser
- Job Interview Question Generator
- LangChain Prompt Templates vs Writing Prompts Manually
- Common Mistakes Beginners Make with LangChain Prompt Templates
- Tips for Writing Better LangChain Prompt Templates
- 💡 Did You Know?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What are LangChain prompt templates?
- What is the difference between PromptTemplate and ChatPromptTemplate?
- Do I need Python to use LangChain prompt templates?
- What does from_template() do in LangChain?
- Can I use the same LangChain prompt template with different AI models?
What is MLOps Roadmap?
The Machine Learning Operations roadmap is a structured guide that shows how to bring machine learning projects from experimentation into reliable production systems. It explains the sequence of steps, starting with data preparation and moving through model development, deployment, and monitoring. Each stage highlights practices and tools that help teams build scalable solutions and reduce risks during implementation. The roadmap also outlines how collaboration between data scientists and business teams supports consistent outcomes and long-term value.
The role of an MLOps engineer is different from that of an ML engineer. An ML engineer focuses on building and optimizing models, while an MLOps engineer designs the pipelines, infrastructure, and processes that move those models into production. Here is a roadmap that explains the skills and practices needed to grow in MLOps:
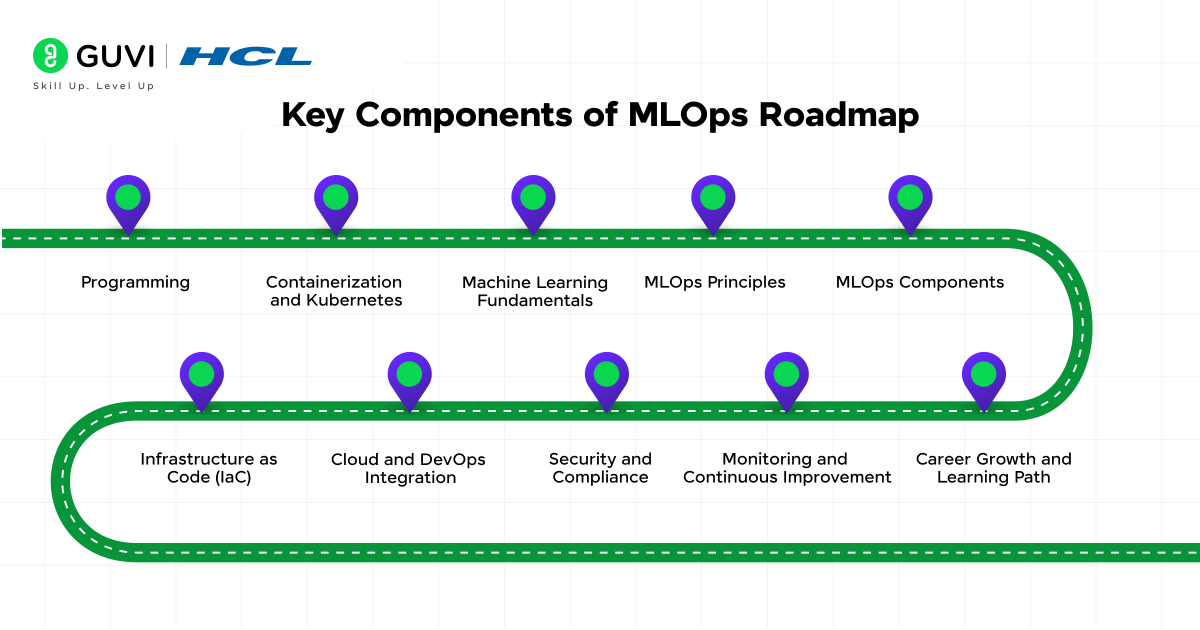
1. Programming
1.1 Why Programming Matters in MLOps?
Programming forms the backbone of every machine learning system. Without solid coding skills, it becomes difficult to build reliable pipelines, debug issues, or collaborate across teams. Python stands out because of its simplicity and the broad ecosystem of tools it offers for data handling, modeling, and deployment. A good grasp of programming also helps when adapting to automation, infrastructure, and production environments.
1.2 Core Areas to Master
Strong programming skills in MLOps are not limited to syntax. They include environment management, testing, and the ability to work efficiently from the command line. Each of these areas supports productivity and reproducibility in projects.
- Python fundamentals: syntax, control flow, functions, object-oriented concepts
- Libraries: NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib for data analysis and visualization
- Environment setup: venv, conda, Poetry for dependency management
- IDEs: VS Code or PyCharm tailored for MLOps workflows
- Testing tools: Pytest, pre-commit hooks, flake8, black for quality checks
- Command-line skills: Bash basics, shell scripting, file permissions, Vim
Read More: How Long Does it Take to Learn Machine Learning? A Know-it-All Guide
1.3 Building Confidence Through Practice
Skills grow when they are applied. Practicing through coding challenges, small ML projects, and automation scripts helps connect theory with practical execution. Start with small exercises and gradually move toward complete workflows.
- Use platforms like LeetCode or HackerRank for coding challenges
- Work on a data cleaning project using Pandas
- Automate a simple daily task with a Bash script
- Write unit tests for an existing Python project
2. Containerization and Kubernetes
2.1 Docker Fundamentals
Docker makes it possible to bundle code, dependencies, and configurations into portable containers that run consistently across environments. A strong foundation in Docker involves attention to several important aspects:
- Learn the concepts of images, containers, and layers
- Write efficient Dockerfiles with minimal base images
- Use volumes to handle persistent storage
- Manage networks for communication between containers
- Practice building and running containers locally
Also, read: How to Install Docker on an AWS EC2 Instance – Step-by-Step Guide
2.2 Kubernetes Essentials
When projects involve many containers, manual management is no longer practical. Kubernetes brings order by automating deployment, scaling, and fault recovery. The most useful skills in Kubernetes include:
- Understanding Kubernetes objects: Pods, Deployments, Services, and ConfigMaps
- Writing YAML manifests for resource configuration
- Organizing workloads with namespaces for separation
- Using rolling updates and rollbacks for safer changes
- Setting resource requests and limits for balanced usage
2.3 Tools and Best Practices
Containerization becomes far more effective when combined with supportive tools and disciplined workflows. A few practices can make your setup faster, safer, and easier to manage:
- Use kubectl for cluster management
- Explore K9s for interactive Kubernetes operations
- Adopt CI/CD pipelines to automate container builds and deployments
- Scan images for vulnerabilities with tools like Trivy
- Keep images lightweight to reduce deployment time and security risks
3. Machine Learning Fundamentals
3.1 Core Concepts
Understanding the basics of machine learning helps MLOps professionals communicate with data scientists and design pipelines that fit real needs. A strong grasp of the following ideas builds the right foundation:
- Supervised and unsupervised learning
- Regression, classification, and clustering methods
- Training, validation, and testing workflows
- Overfitting, underfitting, and regularization techniques
- Common evaluation metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score
3.2 Essential Tools and Libraries
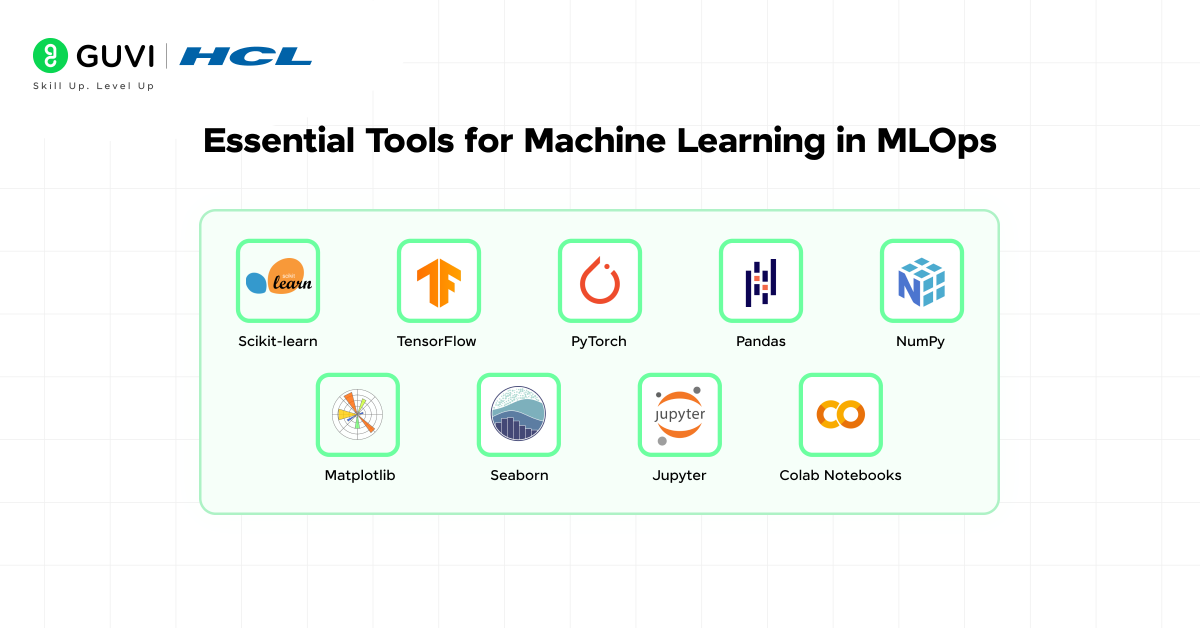
Practical skills depend on working with the frameworks and libraries most widely used in machine learning. Building fluency in these tools prepares you for experimentation and deployment:
- scikit-learn for standard algorithms and preprocessing
- TensorFlow and PyTorch for deep learning models
- Pandas and NumPy for handling data
- Matplotlib and Seaborn for visualization and analysis
- Experiment notebooks such as Jupyter or Colab for testing ideas quickly
3.3 Applied Practice
Knowledge of theory matters, but real confidence comes from applying concepts in projects. Working through small but complete workflows helps connect each stage of ML to the broader MLOps pipeline:
- Clean and prepare datasets for training
- Train a baseline model and compare it with a rule-based approach
- Track experiments with different hyperparameters
- Save trained models for later use with libraries like joblib or pickle
- Share notebooks and results with team members for feedback
4. MLOps Principles
4.1 Understanding the Role of MLOps
MLOps provides a framework that links machine learning development with operational stability. It ensures that models move from research into production while staying reliable, reproducible, and scalable. The following ideas capture the essence of MLOps principles:
- Collaboration between data scientists, engineers, and business stakeholders
- Continuous integration and delivery of ML pipelines
- Automation for testing, deployment, and monitoring
- Governance around security, compliance, and privacy
- Focus on reliability and maintainability in production systems
4.2 Maturity Models and Stages
Organizations often progress through levels of MLOps adoption. Early stages may involve manual workflows, while advanced stages emphasize automation and monitoring across the lifecycle. Recognizing these levels helps teams measure progress and set realistic goals. Key stages often include:
- Level 0: Manual processes with no automation
- Level 1: Partial automation for training and deployment
- Level 2: Automated pipelines covering data, training, and serving
- Level 3: Full-scale adoption with continuous monitoring and feedback loops
4.3 Best Practices for Applying Principles
Principles remain abstract until they guide real work. Applying them in daily practice makes machine learning systems more sustainable and business-ready. Effective approaches include:
- Define clear ownership for data, models, and pipelines
- Use version control for both code and datasets
- Build automated testing for data quality and model performance
- Track experiments consistently with metadata and logs
- Establish monitoring dashboards for production models
- Document workflows so new team members can onboard quickly
5. MLOps Components
5.1 Version Control and CI/CD
Version control and continuous integration form the backbone of collaborative machine learning projects. Git allows teams to track changes and manage contributions. CI/CD pipelines then automate testing and deployment, which reduces errors and shortens release cycles.
Here are the practices to focus on:
- Use Git for tracking changes in code
- Organize branches for development and production
- Add pre-commit hooks to enforce quality checks
- Configure CI pipelines with GitHub Actions or GitLab CI
- Automate deployments after successful tests
5.2 Orchestration
Orchestration tools coordinate workflows across multiple stages of machine learning. They connect data ingestion, training, evaluation, and deployment into reproducible pipelines. This structure avoids manual handling and supports scaling.
Here are the skills that matter most:
- Learn Apache Airflow for scheduling and task management
- Explore Prefect or Mage as alternatives
- Write DAGs that define dependencies clearly
- Monitor pipeline runs with dashboards
- Automate retraining when new data arrives
5.3 Experiment Tracking and Model Registry
Tracking experiments helps compare models and select the best candidate for deployment. A model registry then provides a central place to manage versions and stages of approval. Together, these tools improve collaboration and reliability.
The following steps help build strength in this area:
- Use MLflow to log parameters and metrics
- Store artifacts such as trained models and plots
- Register models with clear version numbers
- Promote models from staging to production with approvals
- Document results for reproducibility and audits
6. Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
6.1 Why IaC Matters
Infrastructure as Code allows teams to define infrastructure using configuration files instead of manual setup. This brings consistency across environments and makes scaling predictable. For MLOps, IaC reduces human error and simplifies collaboration between engineering and operations.
6.2 Core Tools
Several tools dominate the IaC landscape. Terraform is widely adopted because it works across cloud providers. Cloud-native options such as AWS CloudFormation and Google Deployment Manager also appear in many setups.
Skills worth building include:
- Writing Terraform scripts to provision resources
- Using variables and modules for reusable code
- Storing state securely in remote backends
- Applying linting and validation for configuration files
- Reviewing IaC code through pull requests
6.3 Best Practices
Good practices ensure IaC remains reliable and easy to maintain over time. They also reduce risks linked to misconfiguration. The most valuable practices are:
- Keep IaC scripts under version control
- Apply changes through CI/CD pipelines
- Separate environments such as dev and prod with workspaces
- Document resource definitions for team reference
- Regularly update modules to patch vulnerabilities
7. Cloud and DevOps Integration
7.1 Role of Cloud in MLOps
Cloud platforms provide the flexibility and scalability that machine learning systems require. They offer managed services for storage, compute, and orchestration, which reduces the operational load on teams. For MLOps, cloud adoption means faster experimentation and smoother production workflows.
7.2 Popular Cloud Platforms

Each major provider offers tools tailored to ML and DevOps needs. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud lead the space with their specialized services. Building familiarity with at least one provider creates a strong foundation for production-grade deployments.
Areas worth learning are:
- AWS SageMaker for model training and deployment
- Google Vertex AI for pipelines and monitoring
- Azure ML for enterprise-focused ML solutions
- Managed Kubernetes clusters such as EKS, GKE, and AKS
- Cloud storage options for data pipelines and artifacts
7.3 DevOps Practices for MLOps
DevOps practices extend naturally into MLOps. Continuous delivery, automated testing, and monitoring ensure that ML systems stay stable after deployment. Integration of these practices helps align data teams with engineering standards.
Practical steps include:
- Implement CI/CD pipelines that handle ML code and data
- Automate environment setup with Infrastructure as Code
- Use container registries hosted in the cloud for deployments
- Integrate monitoring dashboards into DevOps workflows
- Apply security checks as part of the pipeline
8. Security and Compliance
8.1 Why Security Matters in MLOps
Machine learning systems often handle sensitive data and business-critical models. Weak security creates risks of data leaks and model misuse. Strong protections safeguard both users and organizations.
8.2 Compliance in Practice
Regulations shape how data is collected and processed. Teams must align with laws such as GDPR or HIPAA when working in regulated industries. Compliance also builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
Important actions include:
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit
- Limit access with role-based permissions
- Anonymize personal data before training
- Keep audit logs for all model operations
- Apply retention policies to stored datasets
8.3 Best Practices for Security
Security is more effective when it is integrated into daily workflows rather than treated as an afterthought. Applying structured practices keeps systems resilient against threats.
Key practices are:
- Scan containers and dependencies for vulnerabilities
- Use secret managers instead of storing credentials in code
- Run penetration tests against ML APIs
- Automate security checks within CI/CD pipelines
- Review security policies on a regular schedule
9. Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
9.1 Why Monitoring Matters
Models often lose accuracy after deployment due to changing data or user behavior. Without monitoring, these shifts go unnoticed and harm decision-making. Tracking performance in real time helps maintain reliability.
9.2 Continuous Feedback Loops
Improvement depends on feedback. Gathering signals from production allows teams to refine data, retrain models, and fix weak points. This cycle keeps systems aligned with business goals.
Key activities include:
- Compare live predictions against ground truth when available
- Watch for input data drift against training data
- Alert teams when accuracy falls below a set threshold
- Collect user feedback to guide retraining
- Store monitoring reports for audits
9.3 Tools and Practices
Dedicated tools make monitoring systematic instead of manual. Combining observability with automated workflows creates a foundation for steady improvement.
Important practices are:
- Use Prometheus and Grafana for metrics and dashboards
- Apply MLflow or Weights & Biases for experiment tracking
- Log prediction requests and responses for analysis
- Automate retraining pipelines with orchestration tools
- Schedule regular reviews of monitoring results
10. Career Growth and Learning Path
10.1 Building Depth in MLOps
MLOps is a broad field that combines machine learning with software engineering and operations. Growing in this career means developing depth in both theory and practice. Professionals who invest in hands-on projects build stronger skills and stand out in the job market.
10.2 Expanding Skill Sets
Learning never ends in MLOps. New tools and methods appear often, so continuous study is essential. Expanding beyond one stack helps adapt to different environments.
Focus areas include:
- Gain experience with multiple orchestration tools
- Explore cloud services from more than one provider
- Study advanced topics such as model explainability
- Practice debugging production pipelines
- Learn about emerging trends in data-centric AI
10.3 Career Development Practices
Career growth requires deliberate action, not just technical learning. Networking and sharing knowledge play a central role in long-term success.
Practical steps are:
- Contribute to open-source MLOps projects
- Share insights through blogs or conference talks
- Join professional groups or meetups focused on ML systems
- Seek mentorship from experienced engineers
- Build a portfolio that highlights projects across stages of the roadmap
Turn your understanding of the MLOps roadmap into real-world expertise with our Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Course. This industry-driven program offers live mentor-led sessions, hands-on projects, and a globally recognized certification, equipping you to master ML pipelines, deployment, and monitoring, skills at the core of MLOps. With 1:1 mentorship, placement support, and an industry-aligned curriculum, you’ll not only learn machine learning but also gain the confidence to take models from experimentation to production, just as MLOps best practices demand. Begin your MLOps-aligned AI & ML journey with HCL GUVI today!
Best Practices in MLOps
Implementing best practices in MLOps helps teams move from experimentation to production with confidence. These practices improve collaboration and strengthen the reliability of machine learning workflows. They also make systems easier to scale and maintain over time.
The most effective best practices in MLOps lifecycle are:
- Version control for code and data: Git and DVC keep changes traceable and reproducible. Models should also be versioned for reliable rollbacks.
- Automated pipelines with CI/CD: Testing and validation become faster with automation. Deployment also becomes less error-prone.
- Continuous monitoring and observability: Prometheus tracks metrics and Grafana builds dashboards. Alerts notify teams when performance drops.
- Strong security practices: Encryption protects data and role-based access limits exposure. Secret managers prevent leaks of sensitive credentials.
- Cross-team collaboration: Communication between data scientists and engineers keeps workflows aligned. Business stakeholders should also be included for clarity on goals.
- Reproducible environments: Docker ensures consistency in packaging, and Kubernetes manages scaling. Together, they remove issues caused by mismatched setups.
- Comprehensive documentation: Workflows must be described clearly to reduce onboarding time. Documentation also shortens recovery after failures.
- Feedback-driven improvement: Retraining with updated data prevents drift. User feedback can further guide model updates.
Well-applied MLOps best practices turn fragile experiments into stable pipelines that continue to deliver business value.
Quick Quiz on MLOps Roadmap
1. Why is programming considered the foundation of MLOps?
a) It helps with container orchestration
b) It enables reliable pipelines and debugging
c) It is only required for data visualization
2. Which tool is most often used for containerization in MLOps?
a) Docker
b) Terraform
c) Prometheus
3. What is the main role of a model registry?
a) To build data pipelines
b) To manage versions of trained models
c) To monitor system health
4. Why is Infrastructure as Code important for MLOps teams?
a) It reduces manual configuration
b) It improves reproducibility across environments
c) Both a and b
5. What do monitoring and observability help detect after deployment?
a) Changes in data and performance issues
b) Security compliance
c) Package dependencies
Answers
- b) It enables reliable pipelines and debugging
- a) Docker
- b) To manage versions of trained models
- c) Both a and b
- a) Changes in data and performance issues
Conclusion
The MLOps roadmap provides a structured journey that connects early programming skills with long-term career development. Each stage builds gradually, starting from coding foundations and progressing through data handling, orchestration, and deployment. Later steps address monitoring, compliance, and security, which help sustain models in production. The roadmap closes with a focus on personal growth and continuous learning. Taken together, these steps turn machine learning projects into reliable systems that deliver real value.
FAQs
1. How does MLOps differ from traditional DevOps?
DevOps focuses on software applications. MLOps extends these ideas to machine learning workflows, where models and data pipelines need additional tracking and monitoring.
2. What are the biggest challenges in adopting MLOps?
Teams often face difficulties with data quality and experiment reproducibility. Scaling deployments also creates challenges when infrastructure is unprepared.
3. Can small businesses benefit from MLOps?
Yes. Even small teams gain from automated pipelines and monitoring. These practices reduce manual work and improve consistency across projects.
4. How long does it take to implement MLOps in an organization?
Timelines depend on team size and existing infrastructure. Some see results in a few months, while others require more time to reach full adoption.
5. Is MLOps only relevant for deep learning projects?
No. MLOps supports all forms of machine learning, including regression, classification, and clustering. Any project that needs deployment and monitoring can benefit.





























Did you enjoy this article?