Secure by Default: Deploying LLMs Safely in Enterprise Web Applications
Feb 22, 2026 4 Min Read 846 Views
(Last Updated)
LLMs (Large Language Models) are being used extensively across various software products nowadays, and among them, web applications are among the best examples. Companies across different business verticals with an online presence or those aspiring to establish a digital stronghold are gradually shifting their focus to deploying LLMs in their web applications.
However, when deploying these advanced AI models, safety is always the top priority, as they involve a massive amount of sensitive data and user inputs. If the security layers are weak or improperly protected, there is a high probability that these LLMs will be manipulated or distorted by malicious prompts, potentially giving answers or responses that can damage the internal architecture of web applications.
In this blog, we will be discussing how these LLMs can be deployed safely in enterprise-grade web applications.
Quick Answer:
To deploy LLMs safely in enterprise web applications, first integrate the model with proper access controls and data privacy measures. Next, add safety filters to prevent harmful or incorrect outputs. Finally, continuously monitor usage and secure APIs to protect against potential attacks.
Table of contents
- How Safety Can Be Hampered in Deploying LLMs
- Data Leaks
- Prompt Injection Attacks
- Incorrect or Harmful Outputs
- Unauthorized Access
- Improper Integration
- Safe Deployment of LLMs in Enterprise Web Applications
- Access Control
- Data Privacy
- API Security
- Prompt Filtering
- Monitoring and Logging
- Model Fine-Tuning
- User Authentication
- Encryption
- Regular Audits
- Compliance Checks
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Why should enterprises deploy LLMs in their web applications?
- What is the most considerable risk when deploying LLMs?
- How can companies ensure the safe deployment of LLMs?
How Safety Can Be Hampered in Deploying LLMs

Organisations integrate LLMs (Large Language Models) into their web apps to enhance overall build quality and user experience by resolving customer queries, summarizing information, guiding end users, and automating tasks. In simple terms, they eliminate all the manual effort required to perform operations.
Below are some of the primary methods for dismantling LLM integration in web apps:
1. Data Leaks
Data leaks are the result of large language models (LLMs) being provided with sensitive data without the necessary limitations. In case the model is not monitored, it might, in its answers, unintentionally disclose private company or users’ data.
The main reason for such a situation to arise is that the system fails to distinguish between confidential data and general prompts. The implementation of strict data-access regulations is a measure that can eliminate this threat.
2. Prompt Injection Attacks
In this digital assault, an ill-intentioned individual aims to deceive the LLM by employing ingenious or concealed instructions. The objective is to force the model to expose information or carry out tasks that it is not supposed to.
The problem is alleviated to a great extent by incorporating robust verification and filtering.
Also Read: A Beginner’s Guide to Artificial Intelligence, LLMs, and Prompting
3. Incorrect or Harmful Outputs
Large language models (LLMs) occasionally produce incorrect, biased, or even harmful output if they are not given clear instructions. In such cases, users may be misled, and the company’s image may be affected.
These problems arise from the fact that models make their decisions on patterns rather than having real comprehension.
4. Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access occurs when external people use LLM or its data without proper sanction. The main reason for such an occurrence is commonly a weak login system or a poorly secured API.
If the attackers manage to get in, they may misuse the data or put the system under excessive pressure. In order to avoid this, there should be tight authentication and role-based access control.
Also Read: Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity: The Future of Smarter, Safer Systems
5. Improper Integration
Wrong integration signifies that the LLM is linked to the web application in an insecure manner, i.e., by the use of unencrypted APIs or the absence of basic security checks.
Such loopholes in the system give hackers an easy way to exploit it. Proper coding, encryption, and constant checking of the system are methods by which the system can be kept safe.
Safe Deployment of LLMs in Enterprise Web Applications
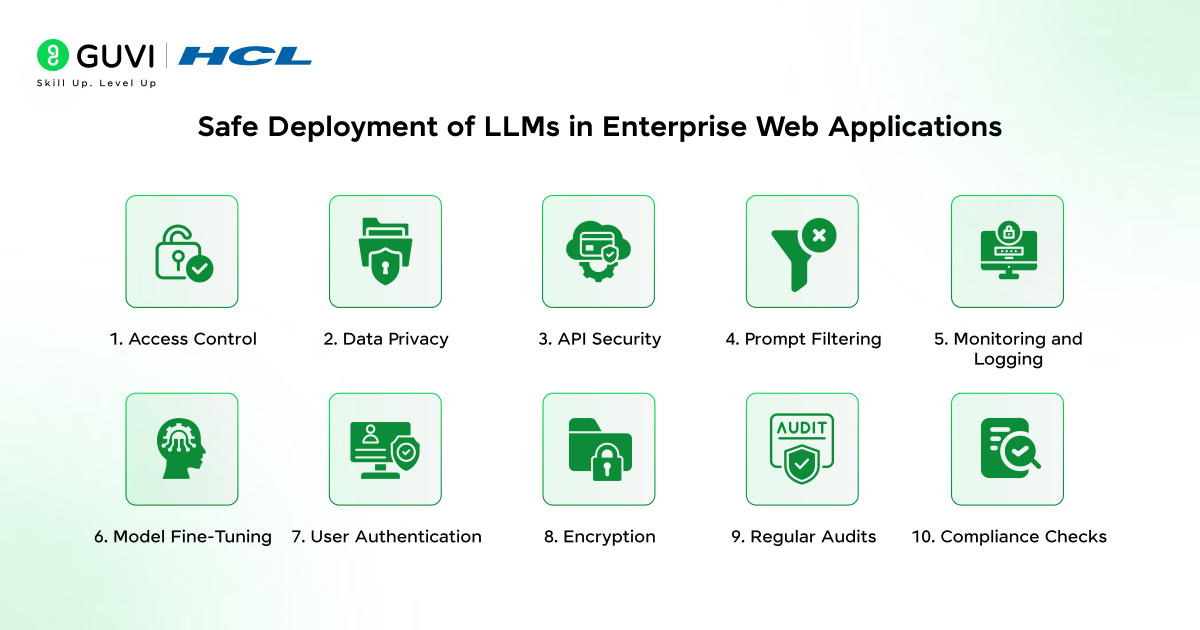
In this section, we outline best security practices to ensure the safe deployment of LLMs in their web applications.
The following points significantly contribute to adding layers of protection to prevent technical misuse and ensure that the LLM operates safely, avoids data leaks, and remains reliable in enterprise environments.
1. Access Control
Access control is the gatekeeper that allows only the right people or systems to use the LLM. If there are no proper limitations, then it is possible for anyone to cause the most sensitive operations to be executed or to use the model improperly.
Through the setting up of roles and permissions, enterprises are in a position to stop the occurrence of unauthorized actions and thus lower the internal threats that may result from unintentional leaking of data or employees who use the internal system in the wrong way.
2. Data Privacy
Data privacy measures are put in place to prevent the release of sensitive information through the LLMs. In case the model handles private data without any protective measures, it might disclose it in the generated text.
Companies should ensure that the data fed to the model is anonymized, masked, or limited in such a way that the information about users, trade secrets, or confidential files remains secure.
Also Read: Database Security: 8 Best Practices That You Should Follow
3. API Security
API security makes the communication between the web app and the LLM safe. If the APIs are weak, they can be used to send malicious requests or to fetch private business data, leading to both technical and financial losses.
By implementing secure tokens, rate limits, and proper cross-validation, the attackers are blocked from abusing the LLM endpoint, and at the same time, unauthorized users are prevented from gaining access.
4. Prompt Filtering
Before the model gets the user inputs, prompt filtering performs a check on them. An attacker might send a prompt that is meant to confuse LLM in such a way that it reveals information or behaves incorrectly.
Enterprises by filtering out the prompts that are either harmful or suspicious keep the dialogues and requests safe, and also put an end to prompt injection attacks at the very beginning.
5. Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring provides an overview of how the LLM is performing in real-time. Therefore, if there is an abnormal situation—for example, continuous attempts to access the system—it can be detected immediately.
Logging generates a ledger of interactions, thereby providing a means for teams to locate the root cause of the problem, evaluate the risks, and gradually elevate the security level of the model.
6. Model Fine-Tuning
Fine-tuning is essential to help the model reflect the desired behavior required by the business. If the model is not appropriately fine-tuned, the Large Language Model (LLM) might produce generic, unsafe, or even wrong outputs.
Organizations can definitely achieve more precise, reliable, and regulation-compliant answers by utilizing their familiar internal data to train the model.
7. User Authentication
User authentication is the process of verifying the users who are allowed to access and utilize the LLM functionalities and features in the web app. In a weak authentication system, hackers can exploit the workflow of the application.
In order to avoid unauthorized users from taking advantage of the system and to safeguard confidential business data, secure logins, MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication), and identity verification are necessary measures.
8. Encryption
Encryption acts as the protector of the data that is moving between the user, web app, and LLM. If it were not for encryption, attackers could easily intercept or even misuse the valuable information.
Encrypted communication ensures the privacy of both model inputs and outputs, particularly when the data involved is confidential enterprise or customer data.
9. Regular Audits
Regular audits provide a means to look through the whole LLM system for any security gaps. Basically, models and apps change with time, and there is always the emergence of new risks.
Through audits, it is guaranteed that the policies, access, and configurations are kept in the latest condition, thus lowering the possibility of the existence of vulnerabilities that are unnoticed.
10. Compliance Checks
Compliance checks ensure that the LLM configuration adheres to industry laws and regulations. Enterprises are obligated to safeguard user rights and must responsibly use the data.
By meeting standards like GDPR or HIPAA, companies avoid legal issues and maintain trust with clients and users.
According to a recent industry report, 98% of organizations have adopted or are adopting LLMs, and 75% are already integrating them into customer-facing applications.
Unlock your potential in the world of AI and ML with HCL GUVI’s Intel & IITM Pravartak Certified Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) Course. Gain hands-on experience from seasoned professionals and earn a certification that can make your resume shine for high-profile tech roles. Start your journey today and set yourself apart in the competitive tech landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when enterprises deploy LLMs in their web applications, they gain smarter, more efficient systems—but safety must always remain at the core. By deploying these models with strong guardrails, monitoring, and security practices, companies can enjoy the full benefits of AI without risking data or user trust. With careful deployment and protection, LLMs can become powerful and safe tools for modern business.
FAQs
Why should enterprises deploy LLMs in their web applications?
To improve user experience, automate workflows, and enhance application intelligence for better efficiency.
What is the most considerable risk when deploying LLMs?
The main risk is the leakage of sensitive data due to unsafe outputs, poor controls, or targeted attacks.
How can companies ensure the safe deployment of LLMs?
Add guardrails, secure APIs, control data access, and continuously monitor model activity for safety.





























Did you enjoy this article?