
Difference Between Unix and Windows OS
Jan 06, 2026 5 Min Read 2101 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered what makes Unix and Windows operate so differently, even though both are among the most widely used operating systems in the world? From personal computers to massive data centers, these systems power billions of devices globally. Yet, the core difference between Unix and Windows OS lies in how they manage processes, handle files, ensure security, and support users.
Unix is known for its stability, multitasking capabilities, and open-source flexibility, making it a favorite among developers and system administrators. Windows, on the other hand, is celebrated for its user-friendly interface, compatibility, and widespread use in home and corporate environments. Understanding these contrasts helps learners grasp how operating systems are designed to meet different needs, from coding environments to business software ecosystems.
In this blog, we’ll explore the difference between Unix and Windows OS in depth, covering their architecture, interface, performance, security, and applications. You’ll also find a detailed comparison table, real-world use cases, and insights that help you identify which OS is best suited for learning, development, or professional use. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of how each operating system functions and where it fits in today’s tech landscape.
Table of contents
- Summary Table: Unix vs Windows OS
- Key Differences Between Unix And Windows OS
- System Type And Source Model
- User Interface
- File System And Directory Structure
- Command Line And Shell Usage
- Security And Permissions
- Performance And Stability
- Application And Software Support
- Networking Capabilities
- Cost And Licensing
- Real-World Applications
- Challenges Faced by Both Systems
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the main difference between Unix and Windows OS?
- Which operating system is more secure?
- Can Unix run Windows software?
- Why do developers prefer Unix?
- Which is better for beginners - Unix or Windows?
Summary Table: Unix vs Windows OS
| Aspect | Unix | Windows |
| Developer | AT&T Bell Labs (1969) | Microsoft (1985) |
| Type | Open-source (varies by version) | Proprietary (closed-source) |
| Architecture | Modular (kernel, shell, utilities) | Monolithic with integrated GUI |
| User Interface | Command-Line Interface (CLI) | Graphical User Interface (GUI) |
| File System | Hierarchical, root (“/”) structure | Drive-letter-based (C:, D:) |
| Security | Strong permission-based model | Frequent updates, more vulnerable |
| Portability | Runs on various hardware | Limited to Microsoft-compatible systems |
| Software Support | Ideal for developers and servers | Ideal for business and gaming |
| Performance | Stable, efficient multitasking | User-friendly, resource-heavy |
| Cost | Often free or open-source | Requires paid license |
| Use Cases | Servers, scientific research | Desktops, offices, education |
| Example | Linux, macOS, Solaris | Windows 10, 11, Server editions |
Key Differences Between Unix And Windows OS
The difference between Unix and Windows OS becomes clearer when we look at how both systems function across multiple aspects such as architecture, user interface, file management, and security. Earlier, we saw a summary table highlighting these major distinctions side by side. While that table provided a quick overview, this section takes a deeper look into each factor to help you truly understand how these two operating systems differ at their core.
Here, we’ll explore the detailed differences between Unix and Windows based on:
- System Type And Source Model
- User Interface
- File System And Directory Structure
- Command Line And Shell Usage
- Security And Permissions
- Performance And Stability
- Application And Software Support
- Networking Capabilities
- Cost And Licensing
Let’s dive into each of these aspects in detail to understand how Unix and Windows differ from each other.
1. System Type And Source Model
The foundation of the difference between Unix and Windows OS begins with how each system is developed and distributed.
Unix:
Unix is an open, multiuser, and multitasking operating system. Many versions of Unix, like Linux and FreeBSD, are open source, allowing developers to modify, customize, and distribute them freely. This openness makes Unix highly flexible for educational, research, and server-based applications.
Windows:
Windows is a proprietary operating system owned by Microsoft. Its source code is closed, and users cannot modify or redistribute it. This makes Windows more controlled but also ensures a consistent user experience across devices.
In short, Unix promotes open development and customization, while Windows offers a standardized, proprietary experience.
2. User Interface
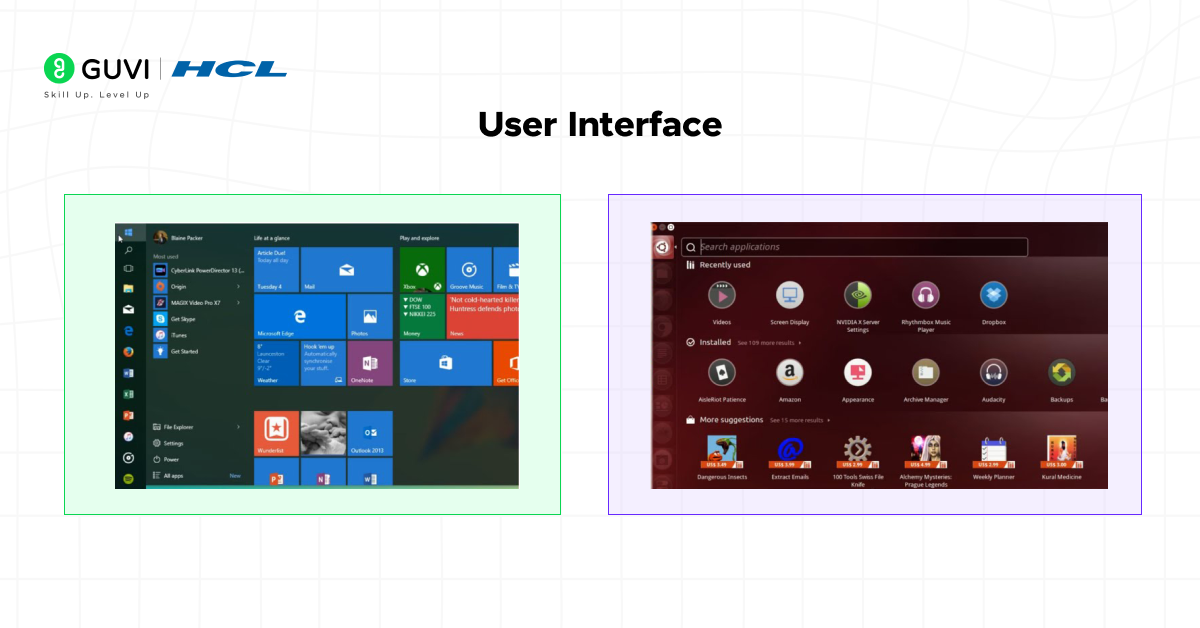
The difference between Unix and Windows OS is clearly visible in their approach to user interaction.
Unix:
Unix primarily relies on command-line interfaces (CLI), though modern distributions like Ubuntu offer graphical interfaces as well. The CLI-based control gives developers deep access to system functions, making it powerful but less beginner-friendly.
Windows:
Windows is famous for its graphical user interface (GUI), designed for easy navigation using icons, menus, and windows. It prioritizes visual interaction, making it ideal for general users and office environments.
In short, Unix focuses on command-line precision, while Windows delivers a user-friendly graphical experience.
3. File System And Directory Structure
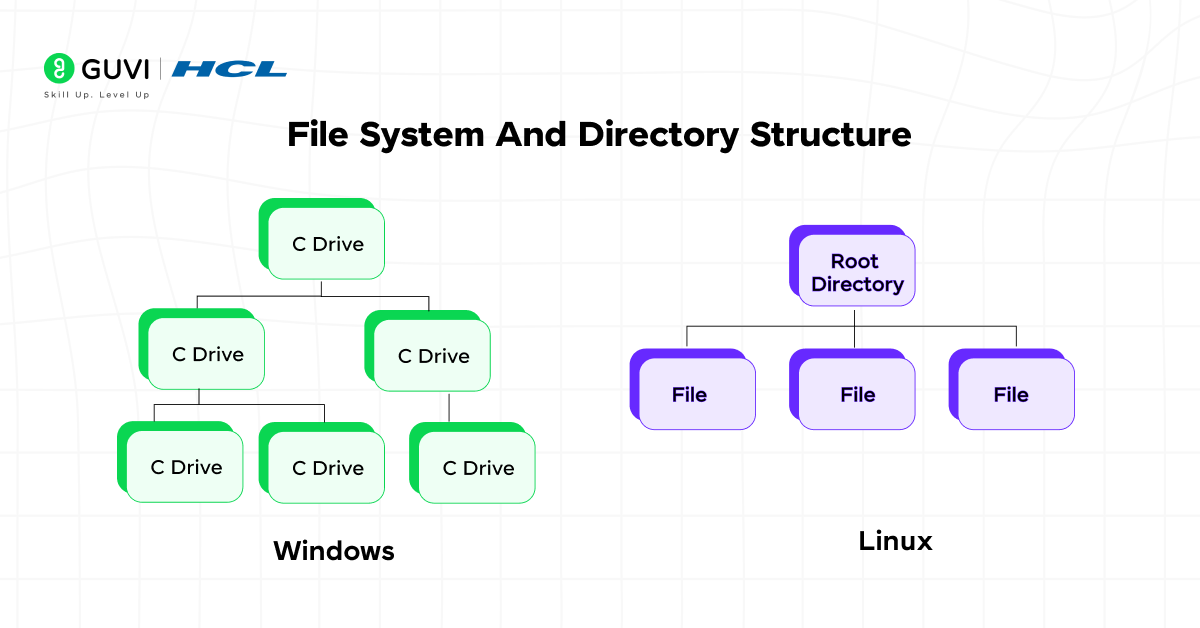
File management plays a major role in the difference between Unix and Windows OS, as both handle data organization differently.
Unix:
Unix uses a hierarchical file system starting from the root directory (/). Everything, including hardware and processes, is treated as a file, allowing a unified and efficient management system.
Windows:
Windows employs a drive-based file system with partitions labeled as C:, D:, and so on. It organizes data under directories like “Program Files” and “Users,” separating system and user data for clarity.
In short, Unix follows a unified root structure, while Windows organizes files under drive-based partitions.
4. Command Line And Shell Usage
The difference between Unix and Windows OS becomes evident when comparing how commands and shells are used.
Unix:
Unix provides multiple shell environments like Bash, Korn, and C shell, each supporting scripting and automation. Users can perform advanced tasks efficiently with simple command-line inputs.
Windows:
Windows offers Command Prompt and PowerShell. While PowerShell enhances automation with scripts, it remains less versatile compared to Unix shells in terms of system control.
In short, Unix shells offer greater flexibility and scripting power, while Windows commands focus on accessibility and integration.
5. Security And Permissions
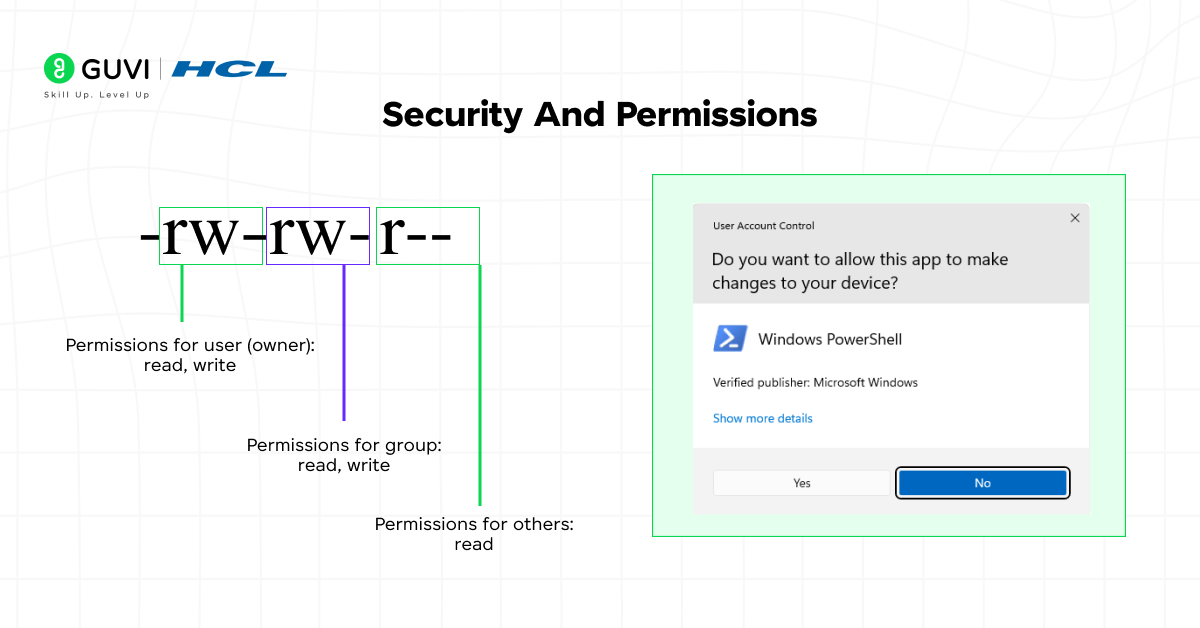
Security is one of the most critical factors defining the difference between Unix and Windows OS.
Unix:
Unix is built with a permission-based security model. Each file and process has specific access rights assigned to users, groups, and others, reducing the chances of unauthorized access.
Windows:
Windows provides user account control (UAC) and built-in security tools like Windows Defender. While it offers strong protection, its large user base makes it a common target for malware.
In short, Unix prioritizes built-in permission security, whereas Windows combines user control with frequent updates and protection tools.
6. Performance And Stability
Performance and reliability are central to the difference between Unix and Windows OS.
Unix:
Unix systems are known for their stability and efficiency, capable of running for months or years without rebooting. They are optimized for servers and multiuser environments.
Windows:
Windows focuses on performance for desktop users, with regular updates and support for extensive hardware and software. However, it may require occasional restarts and maintenance.
In short, Unix delivers long-term stability and performance, while Windows offers user-focused speed and compatibility.
7. Application And Software Support
Software availability highlights another difference between Unix and Windows OS in real-world usability.
Unix:
Unix supports open-source software, developer tools, and server applications. However, it has limited compatibility with commercial desktop software like Adobe or MS Office.
Windows:
Windows dominates the desktop application market, supporting a vast range of business, gaming, and productivity software, making it the preferred choice for general users.
In short, Unix excels in open-source and development tools, while Windows leads in commercial and user-centric applications.
8. Networking Capabilities
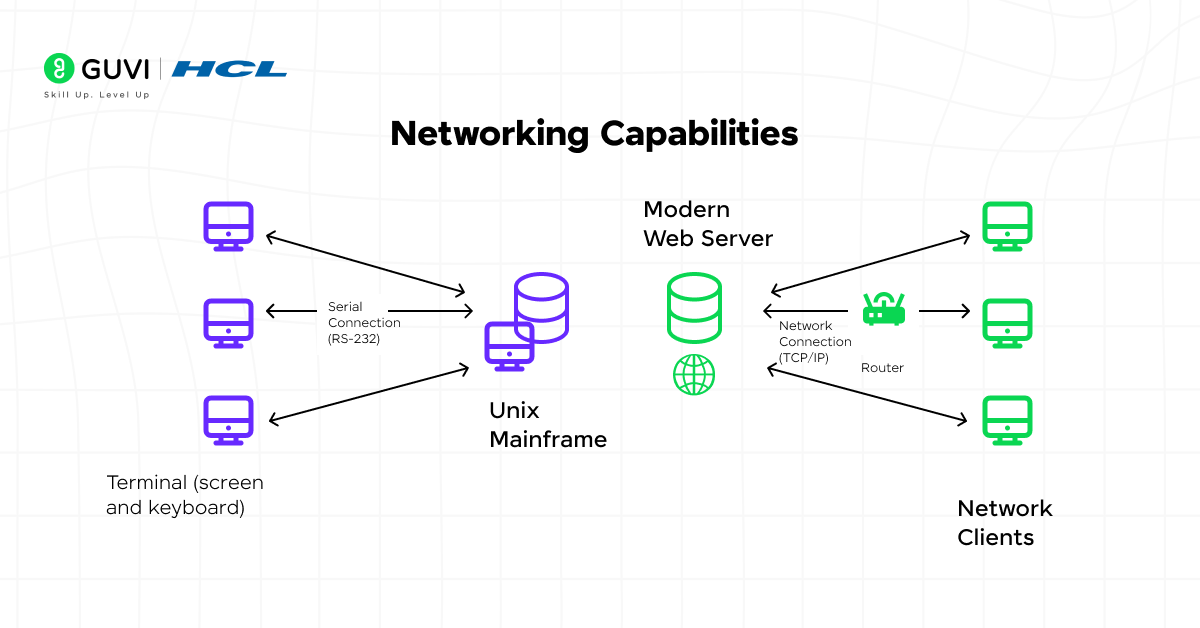
Networking strength defines the difference between Unix and Windows OS in connectivity and communication.
Unix:
Unix was designed with networking in mind, offering built-in tools for communication, remote access, and file sharing. It remains the backbone of most web servers worldwide.
Windows:
Windows provides easy network setup and sharing for home and office environments. While robust, it’s more suited to local and enterprise-level connectivity than large-scale servers.
In short, Unix dominates networked server environments, while Windows focuses on user-friendly local and business networks.
9. Cost And Licensing

Cost and ownership are practical aspects influencing the difference between Unix and Windows OS.
Unix:
Most Unix-based systems, such as Linux, are open source and free. Even enterprise editions are more affordable compared to commercial OS models.
Windows:
Windows requires purchasing licenses for personal and professional versions, and additional costs may apply for updates or enterprise features.
In short, Unix offers cost-effective freedom, while Windows involves paid licensing for consistent support and features.
Real-World Applications
The difference between Unix and Windows OS is most visible in how they’re applied in real-world situations. While Unix powers large-scale infrastructure and development environments, Windows is built for personal, educational, and business use.
Unix
Unix is widely used for tasks that demand reliability, security, and multitasking. Its open-source nature and stability make it ideal for enterprise and technical environments.
- Cloud Hosting: Powers most cloud servers and web services (used by Google, AWS, Facebook).
- Data Centers: Handles large-scale computing operations in research and enterprise setups.
- Cybersecurity: Used in ethical hacking and digital forensics (e.g., Kali Linux).
- IoT Devices: Runs lightweight, efficient versions for routers, smart devices, and controllers.
In short, Unix supports the world’s digital infrastructure, focusing on performance, security, and scalability.
Windows
Windows dominates everyday and enterprise computing with its user-friendly design and wide software compatibility.
- Gaming: Preferred OS for gamers, supporting advanced graphics and DirectX.
- Office Productivity: Used in businesses for tools like MS Office, Teams, and Outlook.
- Education: Common in schools and colleges for its simple interface and learning software.
- Personal Use: Ideal for home users due to broad device and app support.
In short, Windows is designed for convenience and accessibility, making it the go-to system for gaming, business, and education.
Challenges Faced by Both Systems
Despite their strengths, both systems face challenges:
- Unix: Steeper learning curve and less commercial software support.
- Windows: Frequent updates, higher vulnerability, and more resource usage.
Still, both continue to evolve — Unix through open-source innovation and Windows through AI and cloud integration.
Conclusion
The difference between Unix and Windows OS highlights how each system shapes the way we use technology. Unix is known for its stability, reliability, and power in managing complex environments, while Windows focuses on user experience, application support, and accessibility for all types of users.
Understanding both systems helps you appreciate how operating systems function at different levels — from servers and data centers to desktops and classrooms. Whether you’re a student, developer, or IT professional, learning about Unix and Windows equips you with the knowledge to work confidently across diverse computing platforms.
Explore HCL GUVI’s Basics of Computer Course. It helps you understand how computers and operating systems work, offering an easy and interactive learning experience for beginners eager to grasp real-world system concepts.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between Unix and Windows OS?
Unix is open-source, command-based, and highly secure, while Windows is proprietary, GUI-based, and beginner-friendly.
2. Which operating system is more secure?
Unix is generally more secure due to its permission-based model and lower exposure to malware.
3. Can Unix run Windows software?
Not directly. However, tools like Wine or virtual machines can help emulate Windows applications on Unix systems.
4. Why do developers prefer Unix?
Developers prefer Unix for its stability, scripting capabilities, and control over system resources.
5. Which is better for beginners – Unix or Windows?
Windows is easier for beginners due to its GUI, while Unix suits those who want to learn programming or system administration.



































Did you enjoy this article?