
How to Learn DSA in 2026: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide
Feb 12, 2026 6 Min Read 3035 Views
(Last Updated)
Are you someone who has just started your coding journey? Then you must have heard about DSA, the short form of Data Structure and Algorithm. It might sound intimidating at first, but as you understand the basics, you can easily handle the hardest part in coding.
Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) enables you to think logically and organize data in-memory efficiently, both key skills for an effective programmer. In programming, whether you are building a simple application or a more complex framework like a search engine or social media application, you will have the ability to write more optimized code, quicker code, and more reliable code if you understand DSA.
In this blog, we will break down how to learn DSA, a step by step roadmap for you to get started and also why dsa is important and how you can build a strong foundation even if you are just a beginner.
Table of contents
- What is DSA and Why Should You Learn It?
- How to Learn DSA: A Step-by-Step Roadmap
- Step 1: Learn a Programming Language
- Step 2: Get Comfortable with Pseudo-Code
- Step 3: Understand Time and Space Complexity
- Step 4: Start with Basic Data Structures
- Step 5: Move to Advanced Data Structures
- Step 6: Learn the Algorithm
- Step 7: Visualize and Debug
- Step 8: Build Small Projects
- Step 9: Revise and Stay Consistent
- DSA Learning Resources You Shouldn’t Miss in 2026
- Book/Ebooks:
- YouTube Channels for Visual Learners
- Learn from Others (Bonus)
- Practice Problems Daily
- Courses to Master DSA
- Wrapping it up:
- FAQs
- What is the best way to learn DSA for beginners?
- Is it possible to learn DSA without coding knowledge?
- How much time should I dedicate to studying DSA every day?
- What is the best platform to learn DSA?
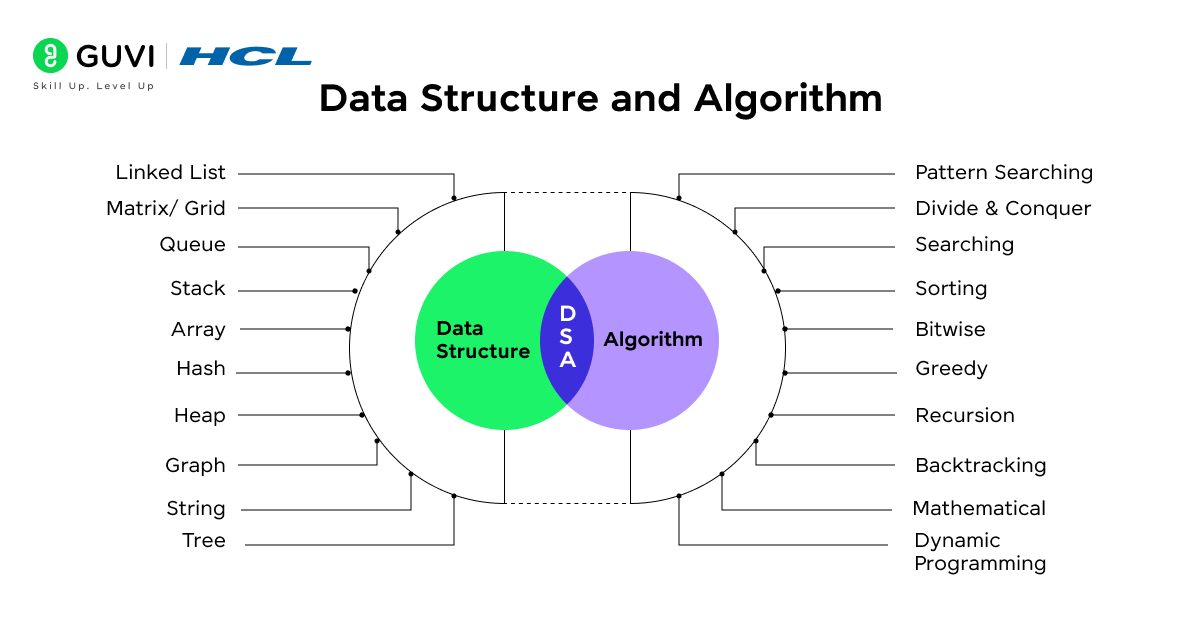
What is DSA and Why Should You Learn It?
“Data Structures” are the different types of storage containers or blueprints so that operations like searching, updating or deleting can be smooth and efficient. And you need different structures to contain unique types of data. Examples include Arrays, Linked Lists, Trees, and Graphs.
“Algorithms” are the step-by-step instructions for completing an operation on that data. Examples are sorting an array, finding a value in a list, or finding the route that takes the least distance between two points on a map.
Now, what makes learning DSA very important is that it:
- Enhances the ability to solve problems: You would learn to think logically and break larger problems into smaller, manageable pieces.
- Help you code better: If you have a decent grasp of DSA, you will be able to code more optimally.
- Is really important in interviews: The big tech companies like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft will evaluate you on your DSA skills.
- Is a basis for other topics: Most advanced concepts we discuss such as machine learning, databases, system design, can be based on efficient data manipulation, and are reliant on DSA.
Simply put, you cannot be a good programmer without learning DSA.
How to Learn DSA: A Step-by-Step Roadmap
Now lets start with the main part – how to learn DSA right away.
Going straight into learning DSA can be overwhelming; instead, you can just follow a structured roadmap to easily get started and not get confused.
Step 1: Learn a Programming Language
You can’t start learning DSA without knowing a programming language. You will need at least one programming language in which you must be proficient.
The most widely used programming languages for DSA are as follows:
- Python: Python is ideal for beginners because it’s a simple language. You will be able to concentrate on the logic of your implementation, and it is much less complex than Java or C++.
- Java/C++: Java and C++ are the preferred languages for competitive programming and systems-level interviews. These languages are faster and stronger in typing. This typing can benefit you when trying to understand concerns such as memory management.

Pro tip: Choose one language and become proficient in its fundamentals. Know how to implement basic structures like arrays, functions, loops, and classes/objects in that language. You should be able to write small programs without constantly looking up basic syntax.
Step 2: Get Comfortable with Pseudo-Code
DSA is all about logic. Before you touch the keyboard, you must be able to solve the problem on paper. This is where pseudo-code comes in, a plain-language description of the steps of an algorithm. Interviewers don’t test your language’s syntax; they test your logic, and pseudo-code is the best way to develop and express that logic clearly.
Also Explore: 5 Best Reasons to Learn Data Structures and Algorithms [DSA]
Step 3: Understand Time and Space Complexity
Before you go straight into data structures, you must first learnt learn how to measure your algorithm’s performance. This is where Time Complexity and Space Complexity come in.
- Time Complexity: What is the time it takes for your algorithm to run?
- Space Complexity: How much memory it takes your algorithm take to run?
You’ll likely come across terms such as O(n), O(log n), O(n²), all of which are part of Big O Notation, and it measures efficiency
Learning this part of the process early will set you up and help you analyze and improve your code later in the future, and is also an essential part of mastering how to learn DSA effectively.
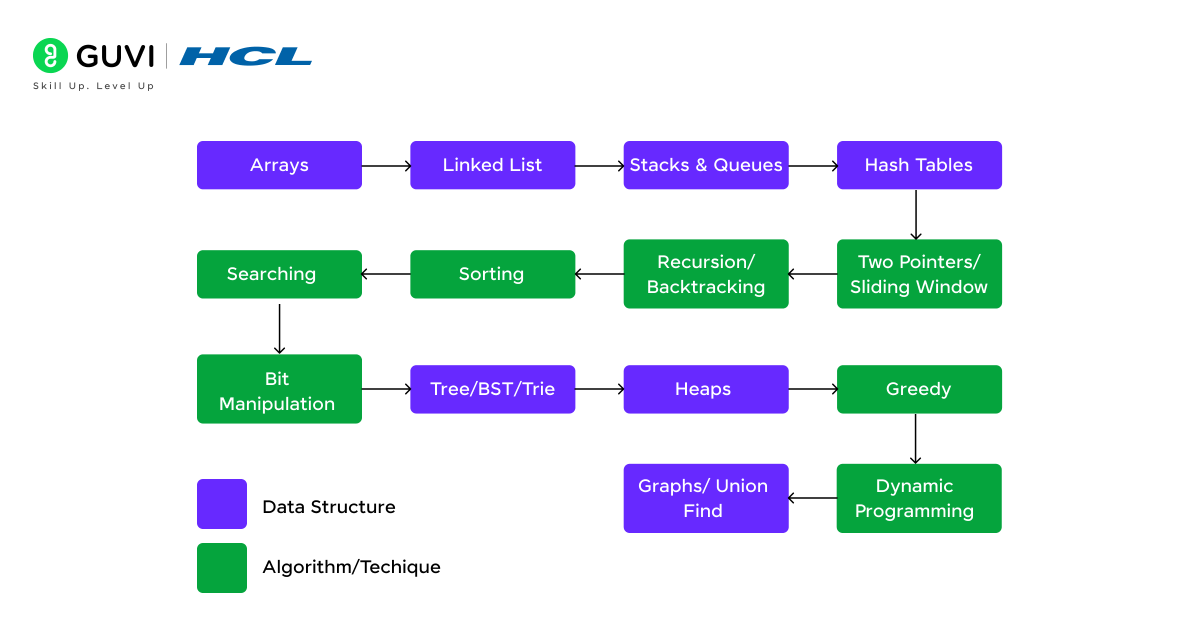
Step 4: Start with Basic Data Structures
Once you’re comfortable with the basics of programming, it’s time to start learning DSA and here are some basic topics you need to get started with:
1. Arrays
An array stores values or data of a single type in contiguous memory locations.
Operations: Traversal, Insertion, Deletion, Searching, and Sorting.
2. Strings
A string is, in fact, an array of characters. That is, strings are character (data type) arrays that are treated as one object.
Operations: Concatenation, Substring, Reversal, Searching.
Also Explore: 5 Best Reasons to Learn Data Structures and Algorithms [DSA]
3. Linked Lists
A linked list is composed of nodes, where each node holds data and has a pointer to the next node.
A key difference with arrays is that linked lists do not need to have memory in a contiguous space and instead can take advantage of any available memory (linked lists are dynamic).
Types: Singly, Doubly, and Circular Linked Lists.
4. Stacks
A stack utilizes the LIFO (Last In, First Out) structure principle
Operations: Push, Pop, Peek.
5. Queues
A queue is organized based on FIFO (First In, First Out) logic.
Types: Circular Queue, Priority Queue, and Deque.
Pro Tip: Don’t just read about these structures – go on to practice coding them! Create a simple insert, delete, and search operation. This will help you understand how the structure works. Visualgo.net is a helpful online tool to visualize how these structures can work, step by step.
Step 5: Move to Advanced Data Structures
Once you’re comfortable with stacks, queues, arrays, and linked lists, you’re ready to take the next step. Advanced data structures help you work through more complex problems, such as searching, finding paths, or retrieving data efficiently, all of which are very useful for real-world problems and for technical interviews.
1. Trees (Binary Trees, BSTs, AVL Trees)
A Tree is a hierarchical configuration of nodes with one root node and many child nodes.
Trees are often used to represent structured relationships, such as a file system on your computer.
- Binary Tree: A tree where each node has no more than two children (left or right).
- Binary Search Tree (BST): Keeps the elements sorted, with smaller values going left and larger values right, enabling searching to be performed in O(log n) time.
- AVL Tree: A self-balancing binary search tree that allows for faster operations as data grows.
2. Heaps
A Heap is a special kind of binary tree that allows us to quickly extract the minimum or maximum value.
- Min-Heap: Parent node is smaller than the child node.
- Max-Heap: Parent node is larger than the child node.
Also Read: Is DSA Important for Placement in 2026?
3. Graphs
A Graph shows a relationship between objects (nodes, vertices) and their relationship (connections, edges). Graphs can be directed (one way) or undirected (two-way) and can be weighted or unweighted.
4. Hash Tables
A Hash Table (or Hash Map) stores data in key-value pairs and uses a hash function to access values instantly, usually in O(1) time.
Also read: Hashing in Data Structure: Definition, Working, and Types Explained
Step 6: Learn the Algorithm
Now that you understand data structures, it is time to take a look at algorithms.
To begin with, here is the list of essential types:
1. Sorting Algorithms
Sorting algorithms such as Bubble Sort, Selection Sort, Merge Sort, Quick Sort
Understand how they work, the time complexities (Best, Average, Worst) of each, and where (or when) the algorithm should be used.
2. Searching Algorithms
Linear Search, Binary Search are essential for efficiently searching for data.
3. Recursion
This is how we understand when a function calls itself. Recursion is typically used in tree traversals, backtracking, or divide-and-conquer problems.
4. Divide and Conquer
Divide and Conquer algorithms that break the problem down into smaller subproblems (this includes Merge Sort and Quick Sort).
5. Dynamic Programming
These algorithms solve overlapping subproblems efficiently using memorization or tabulation (bottom-up or top-down approaches).
6. Greedy Algorithms
Greedy algorithms make the best possible choice at each step (for example, Dijkstra’s algorithm).
7. Graph Algorithms
BFS, DFS, Shortest Path, Minimum Spanning Tree, etc.
Step 7: Visualize and Debug
Many beginners struggle because they can’t visualize how the algorithm works. Tools like:
- VisuAlgo
- AlgoExpert
This will help you see what is happening behind the code.
Step 8: Build Small Projects
Once you have the core DSA concepts covered, start using those concepts in smaller projects.
Example:
- A mini text editor (stacks are used for Undo/Redo)
- A social graph model (using adjacency lists)
- A task scheduler (priority queues are used)
- A spell checker (hashMaps are used).
Projects are a great way to help with real-world scenarios and to sharpen your logical thinking.
Step 9: Revise and Stay Consistent
Consistency is critical. DSA isn’t something you’ll learn overnight.
Create a routine:
- 1 Hour Daily for Theory or Revision
- 2 Hours for Practice
- Challenge / Contest on the Weekend
Revisit topics you’ve learned to deepen your learning.
DSA Learning Resources You Shouldn’t Miss in 2026
Here are some trusted learning sources:
Book/Ebooks:
- HCL GUVI’s Free DSA eBook: A perfect beginner-friendly resource with visuals, examples, and hands-on coding links that help you connect theory with real-world use cases.
- “Introduction to Algorithms” by Cormen: This is a go-to book for all programmers out there. It offers rigorous mathematical explanations of algorithms, ideal if you want to truly understand the “why” behind every concept.
- “Data Structures & Algorithms Made Easy” by Narasimha Karumanchi: Simplifies complex topics and gives you a structured way to prepare for coding interviews.
Also, check out the roadmap.sh DSA Guide, a visual roadmap that helps you understand what to learn next and how every DSA topic fits into your learning path.
YouTube Channels for Visual Learners
If you prefer to learn by watching, then these creators’ channels are a must-watch to learn DSA in simpler and unique ways.
- HCL GUVI YouTube Channel: HCL Guvi has a playlist for DSA, where you can find practical examples, concepts in animations, and the best part is you can learn in your regional language, and if you prefer English you can switch to English as well.
- CodeWithHarry: If you are starting out, then you must have heard of CodeWithHarry. One of the most loved coding educators for beginners. His DSA tutorials (in Hindi and English) blend practical coding, humor, and clarity. Perfect if you enjoy learning in a conversational tone.
- Abdul Bari: This channel is very famous for crystal clear visualization of DSA, not just dsa but many computer science-related concepts.
- Striver’s A2Z DSA Playlist: A complete, structured roadmap covering everything from arrays to advanced graph algorithms. Is ideal for interview prep.
You can also refer to GDSC-KIIT DSA Resources Repository on GitHub, a collection of DSA problem sets, learning materials, and structured practice paths designed by the Google Developer Student Club at KIIT.
Learn from Others (Bonus)
Participate in:
- Coding contests (Codeforces, HackerEarth)
- Online forums (Reddit, Stack Overflow)
- Study groups and Discord communities
Discussing problems and analyzing multiple approaches helps you think differently, a vital step in mastering how to learn DSA efficiently.
Practice Problems Daily
You cannot learn DSA just by giving it a read and then just leave. You need to practice it daily in order to truly understand it. You can practice with easy problems then graulaay move to medium and then to the hard problems. Here are some of the platform you can start you practice with:
- HCL Guvi’s CodeKata: Practice DSA in your preferred language, track your progress, and get instant feedback. Be consistent for better learning.
- LeetCode: The go-to platform for coding interviews. Offers categorized problems, contests, and detailed solutions to learn multiple approaches.
- HackerRank: Great for beginners who want guided learning with topic-wise exercises and tutorial
- CodeChef: Perfect for building competitive programming skills and participating in timed contests to test your speed and accuracy.
Courses to Master DSA
If you like to learn in structured lessons and explanations, then taking a course can be useful. Here are some of the best online courses by Top Universities you can take to help you with learning DSA.
- Easy to Advanced Data Structures: This course is perfect for complete beginners to learn DSA fundamentals step by step, starting with arrays and stacks, working towards trees, graphs and the like. It is the perfect entry point if you want to learn how to code.
- Algorithms I: Princeton University (Coursera): In this course, you’ll learn essential algorithmic concepts for sorting, searching and graph processing delivered by Professor Robert Sedgewick on Coursera with real-world examples.
- Algorithms II: Princeton University (Coursera): This is a continuation of Algorithms I. You will learn more advanced topics, such as network flows, string processing, and advanced graph algorithms.
Every great coder starts somewhere. Why not start today?
Take your first real step into mastering DSA with HCL GUVI’s hands-on Artificial Intelligence & Software Development, co-created with IIT-M Pravartak. Learn by doing, get guided by mentors, and build the confidence to crack interviews like a pro.
Wrapping it up:
Don’t just learn DSA to just crack the interview. Remember, DSA helps you think logically as a program, so take your time and learn DSA clearly to help you throughout your coding journey. I hope this blog, “How to learn DSA,” helps you to figure out where you can start to get on with DSA. Stay consistent with practice, and apply what you learn; you’ll transform from a beginner coder into a confident problem-solver. Happy learning!!
FAQs
1. What is the best way to learn DSA for beginners?
Choose one language to start with, familiarize yourself with a few data structures, then do some practice questions every day. And simply follow a roadmap, like the one above.
2. Is it possible to learn DSA without coding knowledge?
Definitely! Just familiarize yourself with the basic fundamentals of a programming language, then start with DSA topics that are geared towards beginners.
3. How much time should I dedicate to studying DSA every day?
Ideally, you should spend 2 – 3 hours a day studying. Perhaps an hour on theory work, and two dedicated to solving practice problems.
4. What is the best platform to learn DSA?
HCL GUVI, or LeetCode are all terrific options to learn the topic in a structured manner and get plenty of practice.
























Did you enjoy this article?