
Top Generative AI Models 2026
Feb 12, 2026 6 Min Read 3082 Views
(Last Updated)
Generative AI models are revolutionizing businesses with tangible results. According to a recent Gartner survey, business owners using these innovations reported an average 16% revenue increase, 15% cost savings, and a 23% productivity improvement. As we step into 2026, these powerful technologies have not only reshaped creativity but also set new standards in automation across diverse industries.
You might be wondering what exactly a generative AI model is and which ones are leading the pack in 2026. Put simply, these models function by analyzing patterns in extensive datasets and using this understanding to create entirely new content.
In this beginner-friendly guide, you’ll discover the best generative AI models of 2026, how they work, and why they matter for your projects or business. Let’s get to work!
Table of contents
- What is a Generative AI Model?
- How it differs from discriminative models
- Why generative models matter in 2026
- How Generative AI Models Work
- 1) Training on large datasets
- 2) Learning patterns and generating new data
- Supervised vs unsupervised learning
- Top Generative AI Models in 2026
- GPT-4: Language generation and reasoning
- Gemini: Multimodal creativity and logic
- Claude 2: Conversational intelligence
- Mixtral: Mixture of Experts architecture
- DALL·E 3: Text-to-image generation
- Stable Diffusion XL: High-resolution image synthesis
- Gen2 by Runway: Text-to-video generation
- Deepseek Coder: Code generation and optimization
- Concluding Thoughts...
- FAQs
- Q1. What are the top generative AI models in 2026?
- Q2. How do generative AI models work?
- Q3. What are the main types of generative AI architectures?
- Q4. How are businesses benefiting from generative AI in 2026?
- Q5. What makes GPT-4 stand out among language models in 2026?
What is a Generative AI Model?
A generative AI model is artificial intelligence that can create original content rather than simply analyzing existing data. Unlike traditional AI systems that classify or predict outcomes, generative models produce entirely new text, images, videos, audio, code, or other data types that weren’t previously seen but resemble their training data.
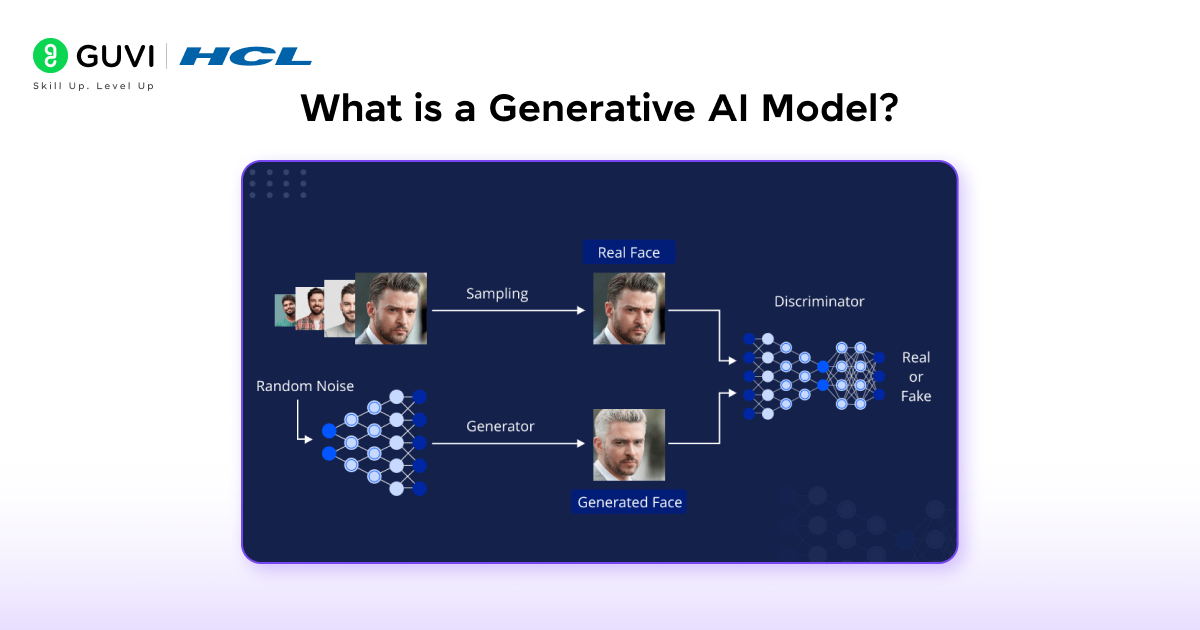
These models function as sophisticated neural networks that simulate the learning processes of the human brain. During training, they absorb terabytes of unstructured data—ranging from internet text to images—performing millions of “fill in the blank” exercises to predict what comes next in a sequence.
The training process works in three phases:
- Foundation model creation – Training deep learning algorithms on huge volumes of raw data
- Fine-tuning – Adapting the model for specific tasks using labeled data
- Deployment – Using the model to generate new content based on prompts
This process encodes billions of parameters—mathematical representations of patterns and relationships—enabling the model to generate coherent, contextually relevant content autonomously.
How it differs from discriminative models
Generative models represent a significant shift from traditional discriminative approaches. While discriminative models focus on drawing boundaries between data categories (like determining if an image contains a dog or a cat), generative models learn the entire data distribution.
The key differences include:
- Mathematical approach: Generative models calculate the joint probability of features and labels occurring together, while discriminative models directly estimate the probability of labels given features
- Complexity: Generative models are typically more complex as they must model the entire data distribution rather than just decision boundaries
- Capabilities: Discriminative models excel at classification tasks, whereas generative models can both classify existing data and create entirely new content
Essentially, discriminative models try to draw boundaries in the data space, while generative models attempt to understand how data is distributed throughout the entire space.
Why generative models matter in 2026
The significance of generative AI in 2026 extends far beyond novelty. These technologies now drive substantial business impact, with the potential to increase global GDP by approximately 7% (USD 7 trillion) and boost productivity growth by 1.5 percentage points over a decade.
Generative AI has matured beyond simple text generation into a versatile technology with applications across industries:
- Content creation – Generating everything from marketing copy to technical documentation
- Visual design – Creating unique artwork, design elements, and special effects
- Research and development – Generating synthetic molecular structures for drug discovery
- Software development – Producing functional code and optimizing existing programs
By understanding patterns in existing data and generating novel outputs, generative AI models have become powerful tools for businesses seeking to automate creative processes, enhance productivity, and discover new possibilities across virtually every sector of the economy.
How Generative AI Models Work
Behind the magic of generative AI models lies a sophisticated process of data ingestion, pattern recognition, and content creation. Let’s explore how these remarkable systems actually function.
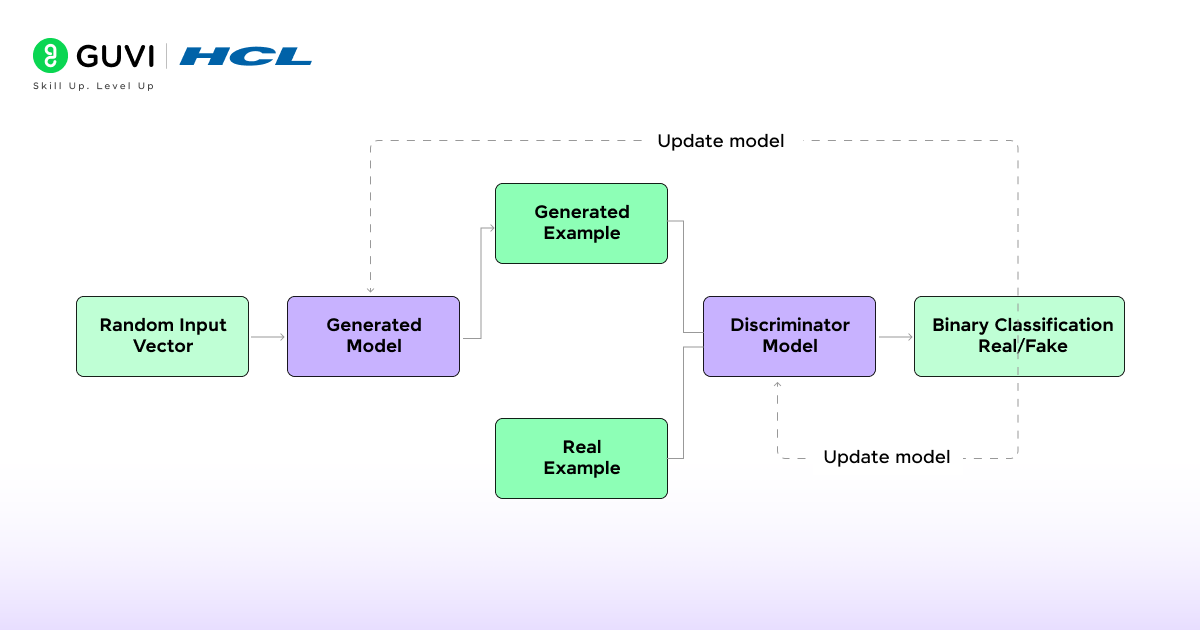
1) Training on large datasets
Creating powerful generative models requires enormous amounts of data. For instance, GPT-3 was trained on approximately 45 terabytes of text data—equivalent to roughly a quarter of the Library of Congress—at an estimated cost of several million dollars. This immense scale is necessary because the model must encounter countless examples to learn language patterns effectively.
The training process typically uses datasets such as:
- Common Crawl: Terabytes of text from billions of web pages
- The Pile: An 800 GB corpus from 22 diverse academic and professional sources
- RefinedWeb: A filtered collection with over 5 trillion tokens
- Wikipedia: Nearly 20 GB of comprehensive articles
These massive datasets expose the model to diverse writing styles, vocabulary, and subject matter. Consequently, high-performance GPUs or TPUs are often needed to accelerate the computationally intensive training process.
2) Learning patterns and generating new data
- Once fed with data, generative AI doesn’t simply memorize content—it identifies statistical patterns and relationships. The model works by trying to predict the next word (or “token”) in a sequence based on what came before. Through exposure to billions of examples, it gradually learns grammar, facts, and even develops reasoning abilities of a sort.
- During training, the model adjusts its parameters—numerical values that control how it learns and generates content. These parameters act like knobs that determine the model’s behavior. The process focuses on minimizing the difference between generated content and actual data, measured through what’s called a loss function.
- After training, the model can create synthetic data—artificial information that mimics the statistical properties of real-world data. This capability proves valuable for:
- Data augmentation (expanding training datasets)
- Testing and validation without needing real-world data
- Creating diverse and representative synthetic datasets
Supervised vs unsupervised learning
Generative AI employs two fundamental learning approaches with distinct characteristics:
- Unsupervised learning occurs when algorithms analyze unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns without human intervention. This resembles how a toddler absorbs language by hearing countless conversations before understanding rules. In generative AI, unsupervised learning typically happens during “pretraining,” when the model is exposed to vast internet-scraped text to learn basic patterns.
- Supervised learning, alternatively, uses labeled input-output pairs to train models. The algorithm makes predictions on data and adjusts based on correct answers. For generative AI, this often occurs during “finetuning,” when researchers create carefully crafted examples of prompts paired with ideal responses.
Top Generative AI Models in 2026
In 2026, the generative AI landscape boasts several powerful models, each specializing in different creative tasks. These top performers have established themselves through exceptional capabilities and consistent results across various applications.
1. GPT-4: Language generation and reasoning
GPT-4 represents OpenAI’s most advanced language model, exhibiting human-level performance across professional and academic benchmarks. It outperforms previous versions by scoring in the top 10% on simulated bar exams, compared to GPT-3.5’s bottom 10% performance.
- Features: Accepts both text and image inputs, producing text-based outputs for a wide range of applications — from essays to code explanations.
- Company: Developed by OpenAI, a pioneer in large-scale language modeling.
- Paid/Free: Available through ChatGPT Plus (paid) and the OpenAI API.
- Unique Use: Excels at deep reasoning, structured content generation, and complex analysis — even scoring in the top 10% on simulated bar exams.
2. Gemini: Multimodal creativity and logic
Google DeepMind’s Gemini 2.5 stands out with its native multimodal capabilities and extensive context window. The model comes in three variants: Pro (for complex reasoning), Flash (for balanced performance), and Flash-Lite (optimized for cost-efficiency).
- Features: Native multimodal intelligence that processes text, images, audio, and code seamlessly.
- Company: Created by Google DeepMind.
- Paid/Free: Available via Google AI Studio and Vertex AI (freemium model).
- Unique Use: Comes in three optimized versions — Pro, Flash, and Flash-Lite — for tasks ranging from reasoning to cost-efficient automation.
- Extra Edge: Offers a 1,048,576-token context window, enabling AI agents to tackle complex, multi-step workflows.
3. Claude 2: Conversational intelligence
Anthropic’s Claude 2 excels in maintaining context over extended conversations, producing natural-sounding responses that rival ChatGPT. Its advanced context understanding allows it to process up to 100,000 tokens—enough to read an entire short book.
- Features: Can handle up to 100,000 tokens in a single conversation — enough to summarize an entire book or report.
- Company: Developed by Anthropic, known for its ethical AI framework.
- Paid/Free: Available in Claude.ai (free) and Claude Pro (paid).
- Unique Use: Exceptional at reading, summarizing, and analyzing large documents while maintaining accuracy and tone.
- Bonus Feature: Prioritizes transparency and safety through its constitutional AI design.
4. Mixtral: Mixture of Experts architecture
Mixtral 8x7B introduces an innovative Sparse Mixture of Experts (SMoE) architecture that achieves remarkable efficiency. Although it contains 46.7 billion total parameters, it only uses 12.9 billion per token, making it 6x faster than Llama 2 70B while outperforming it on most benchmarks.
- Features: Uses a Sparse Mixture of Experts (SMoE) architecture — activating only select model experts per task.
- Company: Created by Mistral AI, a leader in open and efficient LLM development.
- Paid/Free: Fully open-source and free to use.
- Unique Use: With 46.7B total parameters (12.9B active), it’s 6x faster than Llama 2 70B and excels in multilingual reasoning.
- Supported Languages: English, French, Italian, German, and Spanish.
Generative AI might seem like a recent breakthrough, but its roots go back several decades. Here are some surprising insights into how it all began:
The Birth of Generative Models: The foundation for generative AI was laid in the 1950s with the creation of the first neural networks—long before modern computers could even process large datasets.
GANs Changed Everything: The modern era of generative AI began in 2014 when Ian Goodfellow introduced Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), a system where two neural networks “compete” to create realistic data. This concept revolutionized image and video synthesis.
Text-to-Anything Revolution: Today’s models like GPT-4 and DALL·E use transformer architectures—a design inspired by how humans pay “attention” to context—enabling AI to generate text, images, and even videos with astonishing accuracy.
From mathematical theories in the mid-20th century to today’s multimodal powerhouses, generative AI’s journey reflects decades of innovation built on human creativity and computational brilliance.
5. DALL·E 3: Text-to-image generation
OpenAI’s DALL·E 3 represents a significant advancement in text-to-image generation with its exceptional prompt-following capabilities. When integrated with ChatGPT, it automatically generates tailored, detailed prompts that bring user ideas to life.
- Features: Generates highly detailed images that perfectly match your prompt intent.
- Company: Developed by OpenAI.
- Paid/Free: Available within ChatGPT Plus (paid) and Bing Image Creator (free).
- Unique Use: Integrates with ChatGPT to auto-enhance your prompts and bring ideas to life effortlessly.
- Bonus Feature: Provides full commercial rights for generated artwork and includes robust content safety filters.
6. Stable Diffusion XL: High-resolution image synthesis
Stability AI’s Stable Diffusion XL delivers impressive high-resolution image synthesis at up to 1024×1024 pixels—a substantial improvement over previous 512×512 capabilities. The model employs a three times larger UNet backbone with 3.5 billion parameters, enabling extraordinary detail and realism.
- Features: Creates images up to 1024×1024 pixels, delivering outstanding detail and realism.
- Company: Built by Stability AI.
- Paid/Free: Free and open-source, with optional paid enterprise support.
- Unique Use: Employs a larger 3.5B parameter UNet backbone, producing fine-grained textures and photorealistic visuals.
- Bonus Feature: Its open licensing allows integration into countless third-party creative tools.
7. Gen2 by Runway: Text-to-video generation
Runway’s Gen-2 transforms text prompts into dynamic videos with remarkable fidelity. Unlike earlier models requiring structural conditioning, Gen-2 can handle direct text-guided video generation.
- Features: Converts text, image, or video prompts into fully animated video clips.
- Company: Developed by Runway, a creative AI platform.
- Paid/Free: Paid plans with limited free trials.
- Unique Use: Offers creative modes like Text-to-Video, Image-to-Video, and Stylization for effortless storytelling.
- Bonus Feature: Doesn’t require any motion conditioning — it directly understands your text cues.
8. Deepseek Coder: Code generation and optimization
DeepSeek Coder specializes in programming tasks across 338 languages with performance comparable to proprietary models. Trained on 2 trillion tokens (87% code, 13% natural language), it achieves state-of-the-art results on benchmarks like HumanEval and MBPP.
- Features: Trained on 2 trillion tokens (87% code, 13% text), making it exceptionally fluent in logic and syntax.
- Company: Built by DeepSeek AI, a Chinese AI research firm.
- Paid/Free: Open-source and freely accessible.
- Unique Use: Handles 338 programming languages and supports 128K context length — ideal for large project-level completions.
- Bonus Feature: Achieves state-of-the-art results on benchmarks like HumanEval and MBPP.
Step into 2026’s AI boom with HCL GUVI’s Intel-backed Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Course— a hands-on, industry-aligned program covering Generative AI, agentic systems, deep learning, prompt engineering, and more to equip learners with real skills and job readiness.
Concluding Thoughts…
Generative AI has rapidly evolved from an emerging technology to an essential business tool in 2026. Throughout this guide, you’ve learned how these systems work by analyzing patterns in massive datasets to create entirely new content.
After all, the true value of generative AI lies not just in its technical capabilities but in how you apply it. As generative AI continues to mature, early adopters who understand these technologies will undoubtedly gain significant competitive advantages in their respective fields.
FAQs
Q1. What are the top generative AI models in 2026?
Some of the leading generative AI models in 2026 include GPT-4 for language generation and reasoning, Gemini for multimodal creativity, DALL·E 3 for text-to-image generation, Stable Diffusion XL for high-resolution image synthesis, and Gen2 by Runway for text-to-video generation.
Q2. How do generative AI models work?
Generative AI models work by training on large datasets to learn patterns and relationships. They then use this knowledge to generate new content. The process involves foundation model creation, fine-tuning for specific tasks, and deployment to generate content based on prompts.
Q3. What are the main types of generative AI architectures?
The main types of generative AI architectures include transformer-based models, diffusion models, GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), VAEs (Variational Autoencoders), autoregressive models, and flow-based models. Each type has unique strengths for different applications.
Q4. How are businesses benefiting from generative AI in 2026?
Businesses using generative AI in 2026 are seeing significant benefits, including an average 16% increase in revenue, 15% cost savings, and 23% improvement in productivity. These models are being applied across various industries for tasks like content creation, visual design, and software development.
Q5. What makes GPT-4 stand out among language models in 2026?
GPT-4 distinguishes itself by exhibiting human-level performance across professional and academic benchmarks. It’s a multimodal model that can accept both text and image inputs while outputting text, making it versatile for a wide range of tasks from content creation to complex reasoning.




























Did you enjoy this article?