
In today’s data-driven world, understanding how to turn information into insight is a game-changer. From identifying customer behavior patterns to optimizing supply chains, statistical analysis plays a vital role in every decision-making process. It allows organizations to transform raw data into clear actionable conclusions, helping them predict outcomes, reduce risks, and make smarter business moves.
Before diving deeper, let’s first understand what statistical analysis actually means.
Statistical analysis is the process of collecting, organizing, interpreting, and presenting data to uncover meaningful patterns and relationships. It helps transform vast amounts of raw data into useful insights that guide informed decisions. In simple terms, it’s about using numbers to uncover the story hidden within data that highlights trends, confirms patterns, and drives logical conclusions.
Table of contents
- Why Is Statistical Analysis Important
- Key Concepts / Foundations To Know
- Population And Sample
- Variables
- Mean, Median And Mode
- Variance And Standard Deviation
- Correlation And Causation
- Types Of Statistical Analysis
- Descriptive Analysis
- Inferential Analysis
- Predictive Analysis
- Prescriptive Analysis
- Exploratory Analysis
- Casual Analysis
- Statistical Methods Used In Analysis
- Regression Analysis
- Hypothesis Testing
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)
- Correlation Analysis
- Time Series Analysis
- Steps In Applying Statistical Analysis
- Applications Of Statistical Analysis
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the main purpose of statistical analysis?
- Which industries use statistical analysis the most?
- Do I need strong math skills to learn statistical analysis?
- What are the most common statistical methods?
- 5 .Is statistical analysis part of data science?
Why Is Statistical Analysis Important
Every dataset tells a story, but only the right analytical approach can help you interpret it accurately. Statistical analysis is the approach that transforms raw data into meaningful insights, guiding smarter decisions, revealing hidden connections, and fueling innovation across industries. Here’s why it matters so much today:
- Improves Decision-Making
- Enhances Accuracy
- Reveals Relationships
- Supports Research and Innovation
Example – An airline company can analyze past flight data to forecast peak travel seasons, optimize seat pricing, and improve operational efficiency, all by applying statistical analysis effectively.
Kickstart your data journey with HCL GUVI’s 5-day free Data Science Email Series. Each day covers a new concept, from data collection and cleaning to visualization, machine learning, and real-world projects. Perfect for beginners who want quick, structured learning.
Key Concepts / Foundations To Know
Before diving into advanced tools and methods, it’s essential to learn the basic concepts that form the backbone of statistical analysis. These core ideas help you understand how data behaves and ensure you can interpret results accurately in any study.
1. Population And Sample
Every analysis starts with understanding what kind of data you are dealing with. You first decide who or what you want to study and then collect information from them.
A population is the entire group you want to learn about. For example, if a school wants to know the average height of all students, then every student in the school forms the population.
A sample is a smaller part of that population that you actually collect data from.If you only measure the height of 100 students and use that to estimate the average height of all, then that group of 100 is your sample.
2. Variables
Variables are the pieces of information you measure or observe in your data. They describe what you’re trying to study.
Quantitative variables are numbers like height, age, income, or temperature. They can be measured and used for calculations.
Qualitative variables describe qualities or categories like gender, city, color, or type of product.
Example – In a customer survey, age is a quantitative variable, while preferred payment method (cash or card) is qualitative.
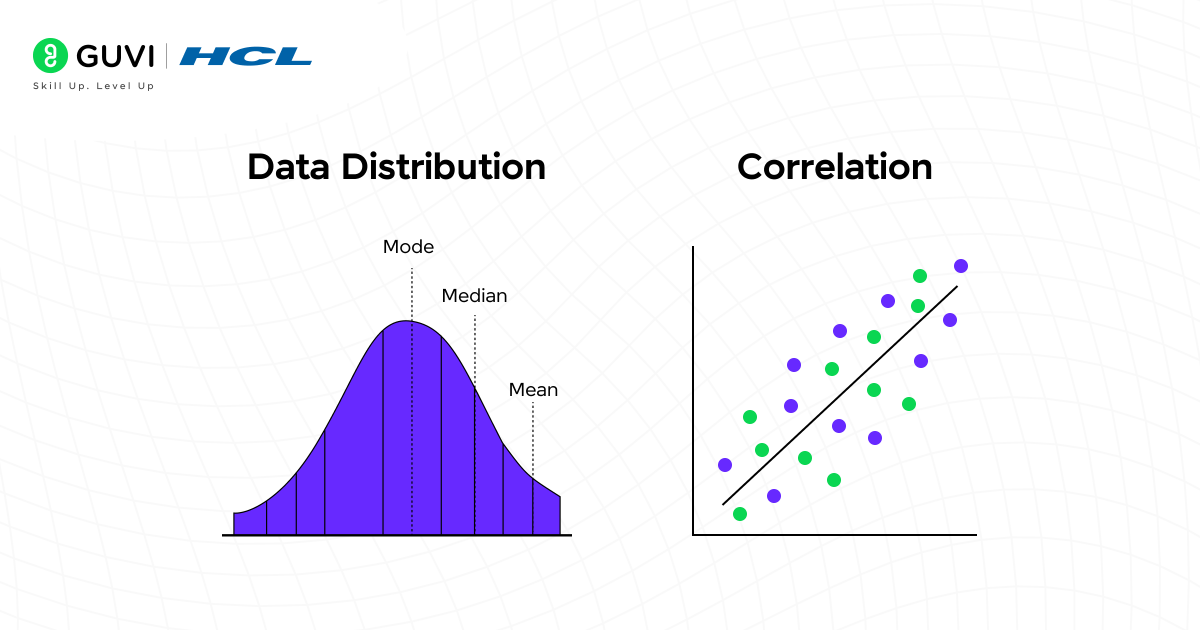
3. Mean, Median And Mode
These are three simple yet powerful ways to find the center or typical value in your data. They help you understand what’s normal in your dataset and help you summarize large sets of numbers in an easy-to-understand form.
Mean is the average. You add up all the numbers and divide by how many there are. For example, if five students score 70, 80, 90, 100, and 110, then the mean is 90.
Median is the middle value when numbers are arranged in order. In that same list, the median is also 90.
Mode is the number that appears most often. If most students scored 80, then 80 is the mode.
4. Variance And Standard Deviation
No two data points are always the same, and that variation tells an important story. Variance and standard deviation help you understand how far your data values are spread out from the average.
Variance shows how far the numbers are from the average.
Standard deviation is a simpler version of variance that’s easier to read and compare.
Example – If two classes have the same average score but one class’s marks vary a lot (some very high, some very low), then that class will have a higher standard deviation. It tells you how consistent or scattered the data is.
5. Correlation And Causation
These terms explain how things are related but are not the same.
Correlation means two things change together. For example, when ice cream sales go up, so does the weather temperature. That’s a correlation.
Causation means one thing actually causes the other to happen. For example, more practice directly improves test scores. That’s causation.
Types Of Statistical Analysis
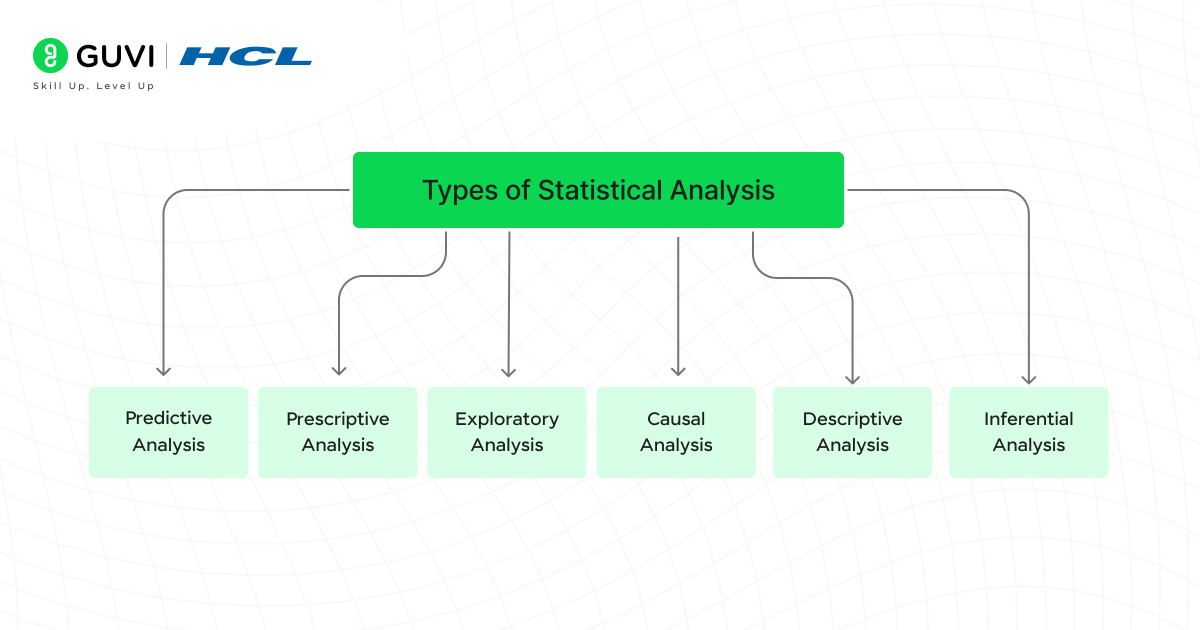
Each type of statistical analysis helps answer a different kind of question, from describing what happened to predicting what might happen next. Knowing which type to use depends on your goal, the data you have, and the insights you’re looking for. Here we’ll explore the different types of statistical analysis and the insights they provide.
1. Descriptive Analysis
Sometimes, you just need to understand what’s going on in your data, not predict or test anything. That’s where descriptive analysis comes in.
It focuses on summarizing data using numbers, tables, charts, and averages to show patterns and trends.
- It explains what has happened in the past.
- Common tools include percentages, frequency tables, and graphs.
Example- A retail store reviews last month’s sales data to see which product categories sold the most. The goal isn’t to predict, just to describe existing trends.
2. Inferential Analysis
When studying a small sample but needing to make conclusions about a larger group, inferential analysis is key.It helps you draw conclusions and make generalizations about an entire population based on sample data.
- It uses techniques like hypothesis testing and confidence intervals.
- Useful when it’s not possible or practical to study an entire population.
Example – A survey of 500 voters is used to predict the preferences of 5 million voters in an election – this is an inferential approach.
3. Predictive Analysis
If you want to look into the future using past data, predictive analysis is your go-to. It uses statistical models and machine learning to forecast what might happen next based on existing patterns.
- Commonly used in finance, marketing, and weather forecasting.
- Helps anticipate risks, demands, or outcomes before they occur.
Example – An e-commerce company analyzes past purchase data to predict which products customers are most likely to buy during the next sale.
4. Prescriptive Analysis
Once you know what’s likely to happen, prescriptive analysis takes things one step further and helps us decide what actions to take next.This type of analysis recommends solutions or strategies using data-driven simulations and optimization models.
- It focuses on “what should be done” rather than just “what will happen.”
- Often powered by artificial intelligence and scenario analysis.
Example: A delivery company uses route optimization algorithms to find the most fuel-efficient paths, saving both time and cost.
5. Exploratory Analysis
When you’re not sure what you’re looking for, exploratory analysis helps you discover patterns, trends, or relationships hidden within the data. It’s often the first step in analysis, guiding where deeper investigations should go.
- It involves visualizing data in different ways to spot new insights.
- Common in research and data discovery projects.
Example: A healthcare analyst studies hospital records without a fixed question, uncovering that certain symptoms often appear together before a diagnosis.
6. Casual Analysis
Causal analysis digs deeper to find why something happened. It’s all about uncovering cause-and-effect relationships rather than mere correlations.
- Commonly used in scientific and experimental research.
- Helps validate if one factor directly influences another.
Example: Researchers test whether a new drug actually improves patient recovery compared to existing treatments, establishing a true cause-and-effect link.
Statistical Methods Used In Analysis
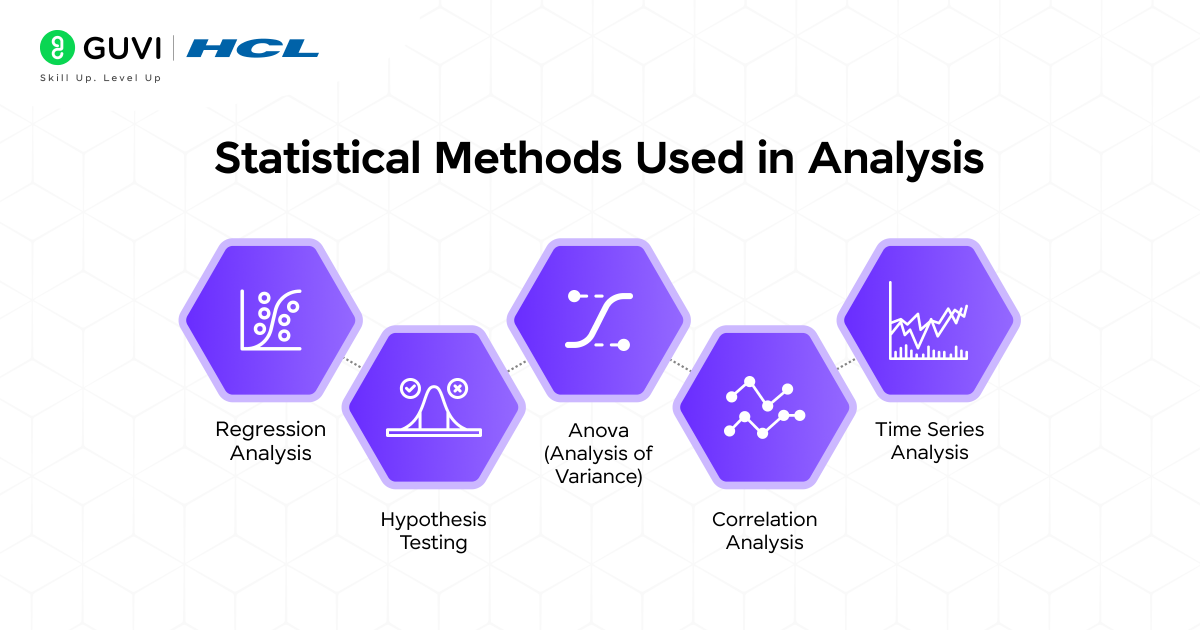
Once you understand the different types of analysis, the next step is learning about the methods that make them work. These statistical methods help analysts test ideas, identify relationships, and make reliable predictions based on data.
1. Regression Analysis
Ever wondered how one factor affects another, like how marketing influences sales? That’s where regression analysis comes in. It studies the relationship between a dependent variable (what you want to predict) and one or more independent variables (factors that might influence it).
- Helps identify trends and make predictions.
- Commonly used in business forecasting and research.
Example – A retail brand analyzes how changes in advertising spend impact monthly sales revenue.
2. Hypothesis Testing
Before making decisions, businesses and researchers often start with assumptions, and hypothesis testing helps check if those assumptions hold. It uses statistical tests such as the t-test, z-test, or chi-square test to confirm whether observed results are meaningful or just due to chance.
- Helps validate claims or ideas with real data.
- Widely used in product testing, clinical trials, and business decisions.
Example: A company tests whether a new training program truly improves employee performance compared to the old one.
3. ANOVA (Analysis of Variance)
When you need to compare results across multiple groups, ANOVA is your go-to method. It checks whether the mean (average) values of three or more groups are significantly different from each other.
- Useful when comparing multiple strategies, campaigns, or samples.
- Helps determine which factors have the greatest effect on results.
Example: A marketer uses ANOVA to identify which social media platform – Instagram, Facebook, or YouTube – drives the most engagement for a new campaign.
4. Correlation Analysis
Correlation helps measure how closely two variables move together. It doesn’t prove cause and effect, but it reveals how strongly they are connected.
- Positive correlation: both values increase together.
- Negative correlation: one increases while the other decreases.
Example: A researcher studies how the number of study hours relates to exam scores—students who study more tend to score higher, showing a positive correlation.
5. Time Series Analysis
When data is collected over time, time series analysis helps identify trends, patterns, and cycles. It’s especially useful for forecasting future outcomes based on historical data.
- Common in economics, weather forecasting, and digital analytics.
- Helps detect seasonality and long-term trends.
Example: A company analyzes website traffic from the past two years to predict monthly visitor numbers for the upcoming year.
Steps In Applying Statistical Analysis

Once you understand the methods, the next step is to apply them in a structured way to ensure accurate, consistent, and meaningful results from your data analysis. Here is a structured way to apply the statistical analysis ;
- Define the Objective
- Collect the Data
- Clean and Organize Data
- Choose the Right Method
- Analyze the Data
- Interpret the Results
- Visualize and Communicate Findings
Applications Of Statistical Analysis
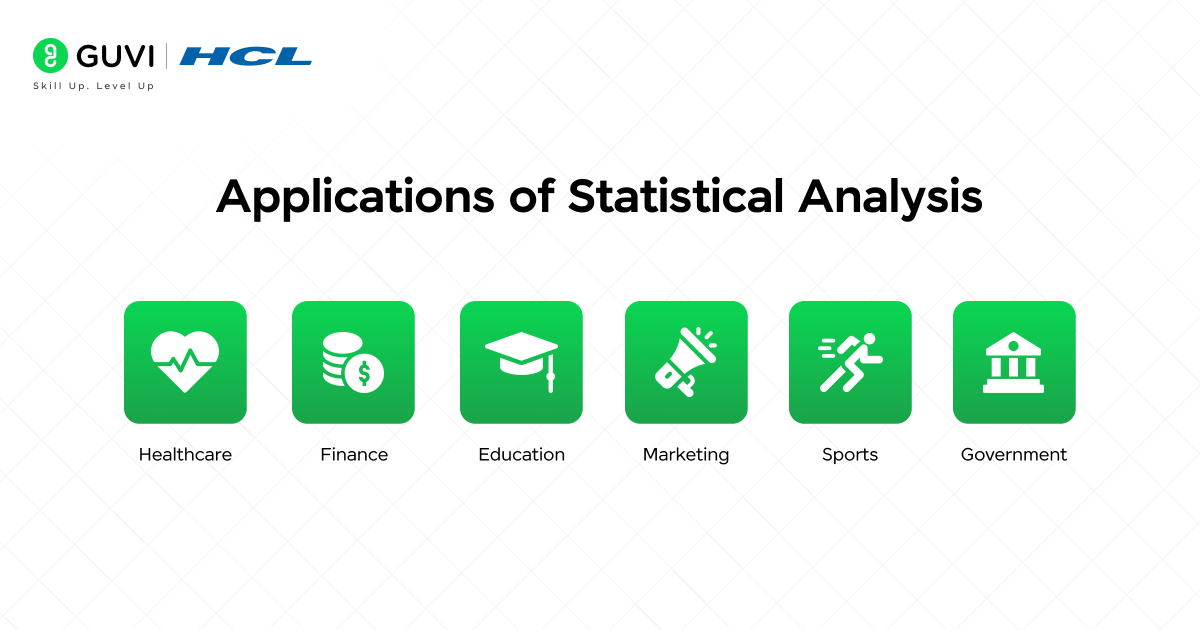
- Healthcare – Doctors and researchers use statistical analysis to track patient recovery rates, test treatment effectiveness, and predict disease outbreaks
- Finance – In finance, numbers tell powerful stories. Statistical tools help detect fraud, assess risks, and forecast investment returns.
- Education – Educators rely on data to measure student performance, identify learning gaps, and improve teaching strategies.
- Marketing – Marketers use statistical analysis to understand what customers like, track buying behavior, and measure campaign success.
- Sports – Coaches and analysts use data to evaluate player performance, design training plans, and predict match results.
- Government – Public departments depend on data to plan better policies, allocate resources, and manage large populations.
Your step-by-step intro to the world of analytics – HCL GUVI’s Data Science eBook Series is designed for self-paced learners eager to strengthen their fundamentals.It covers Python programming, data analysis, visualization, and real-world machine learning projects, helping you learn at your own pace and build practical expertise.
Conclusion
Statistical analysis bridges the gap between raw information and decision-making. In a world where data defines success, mastering this skill allows you to turn insights into action. Whether you’re working with business, science, or social data, statistical analysis helps uncover patterns that shape the future.
Data analysis forms the foundation of data science, powering everything from prediction models to intelligent decision-making. To explore this field in depth, check out HCL GUVI’s Zen Class Data Science Course—a placement-driven course that covers everything from Python, statistics, and SQL to machine learning, data visualization, and real-world project building. The program is designed to give you hands-on experience and job-ready skills guided by expert mentors.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of statistical analysis?
It helps summarize, interpret, and draw insights from large datasets to support decision-making.
2. Which industries use statistical analysis the most?
It’s widely used in finance, healthcare, education, marketing, and research sectors
3. Do I need strong math skills to learn statistical analysis?
Basic math helps, but practical tools like Python and Excel make learning much easier.
4. What are the most common statistical methods?
Regression, hypothesis testing, correlation, ANOVA, and time series analysis are the most used.
5 .Is statistical analysis part of data science?
Yes, it forms the foundation of data science, powering prediction models and insights



























Did you enjoy this article?