Top 6 Machine Learning Classification Algorithms You Must Know
Oct 30, 2025 4 Min Read 2231 Views
(Last Updated)
Machines don’t have instincts. Or do they?
Every time the AI system removes hate speech, ranks up resumes, or anticipates a medical condition it is exercising something that feels very similar to instincts. This instinct stems from Machine Learning Classification Algorithms, the invisible engines that enable machines to distinguish, decide, and adapt.
In 2025, these algorithms are not just mathematical models; they’re the foundation of digital intelligence. Let’s dive into the six most powerful classification algorithms that give AI systems their uncanny ability to “know” what’s what.
Table of contents
- What is Classification in Machine Learning?
- Why Classification Algorithms Matter
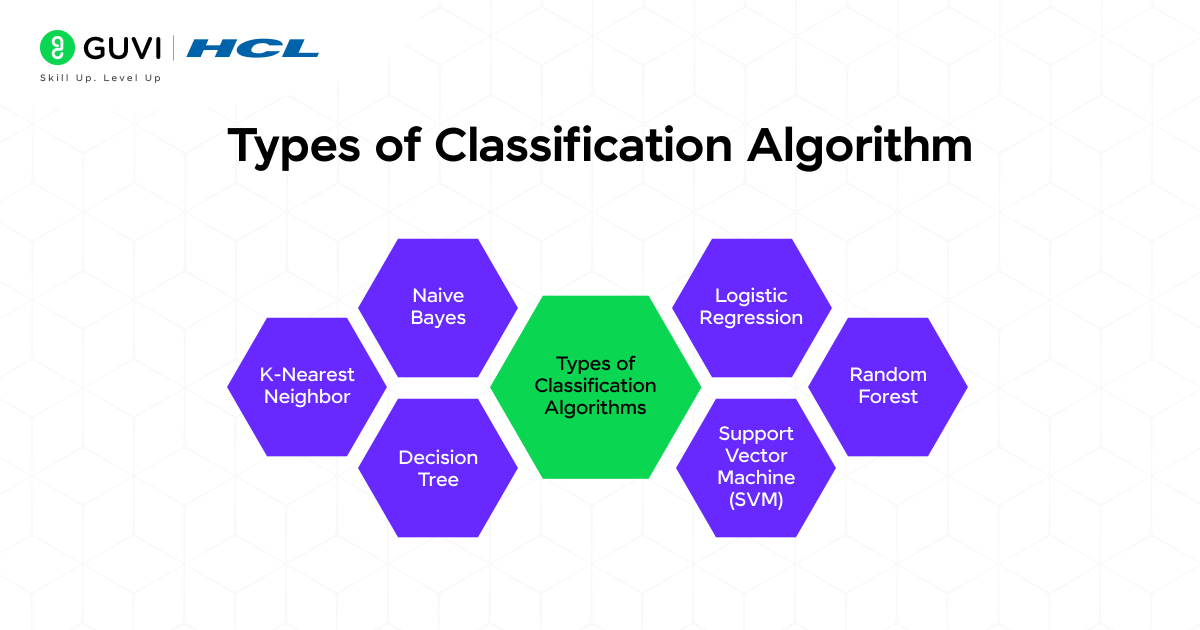
- Top 6 Machine Learning Classification Algorithms
- Logistic Regression
- k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
- Support Vector Machines (SVM)
- Naive Bayes
- Decision Trees
- Random Forest
- Comparison of Machine Learning Classification Algorithms
- How to Choose the Right Classification Algorithm?
- Wrapping It Up…
- FAQs
- What is the best algorithm for someone new to classification?
- Is it possible to use two algorithms at the same time?
- What is the best algorithm for text classification?
- Which libraries are the best to use for classification problems?
What is Classification in Machine Learning?
Classification is a type of supervised learning where a model learns from labeled data (input-output pairs) to predict discrete class labels for new, unseen data.
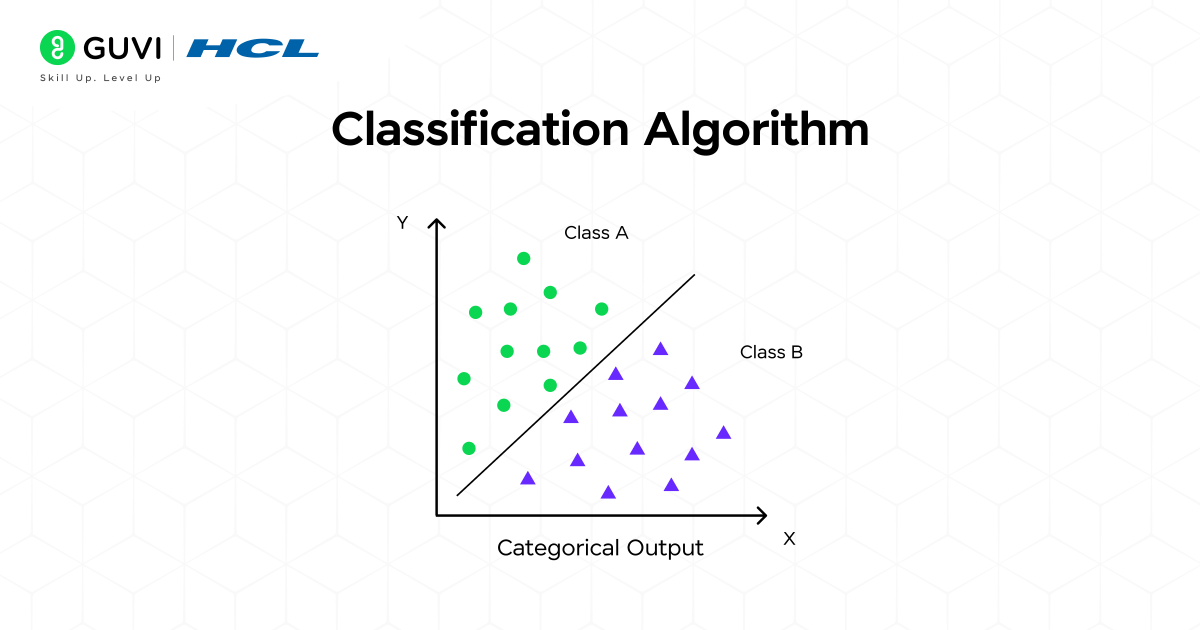
For example:
- Predicting if a tumor is malignant or benign
- Identifying if a customer will churn or stay
- Classifying reviews as positive, negative, or neutral
Essentially, classification helps machines make human-like decisions based on historical data.
Why Classification Algorithms Matter
Understanding Machine Learning Classification Algorithms helps data scientists and engineers automate predictions, improve accuracy, and make smarter business decisions. Classification algorithms form the foundation of intelligent systems. They:
- Simplify decision-making in complex systems
- Help automate tasks like email filtering or fraud detection
- Enhance personalization (e.g., recommendations, ads)
- Enable predictive analytics in finance, healthcare, and marketing
As data volumes explode, understanding how these algorithms work is crucial for anyone pursuing a career in AI or Data Science.
Top 6 Machine Learning Classification Algorithms
1. Logistic Regression
Don’t let the name confuse you; Logistic Regression is a classification algorithm, not a regression one. It’s one of the simplest, most interpretable, and widely-used algorithms for binary classification problems (e.g., Yes/No, Spam/Not Spam, 1/0).
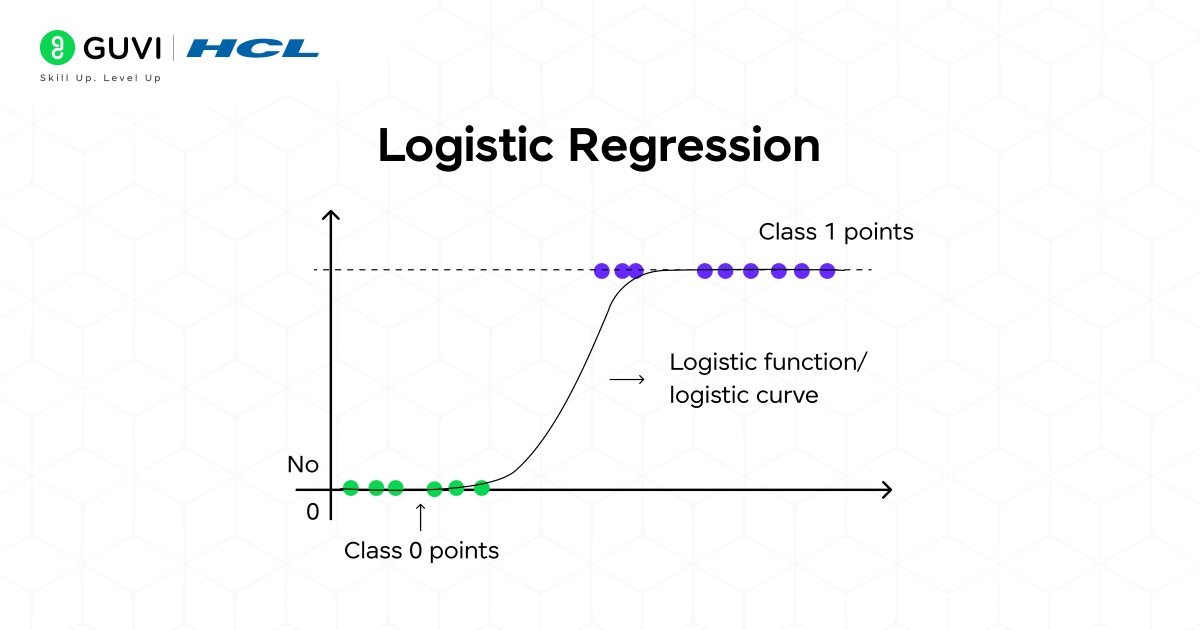
How does it work?
Rather than fitting a straight line to the data, as its name suggests, Logistic Regression instead uses a special type of curve called a sigmoid function, which is “S” shaped, to classify data values. The sigmoid function takes in any real-valued number and outputs a value between 0 and 1. This output is interpreted as the probability of an instance belonging to a class.
For example, suppose we are predicting whether an email is considered spam or not. The algorithm produces a probability, P(spam), and if P(spam) > 0.5, it classifies the email as “Spam” (and vice versa for not spam). It makes its decision by drawing a linear “decision boundary” in the feature space.
2. k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
k-Nearest Neighbors is an uncomplicated, intuitive, and non-parametric algorithm. k-Nearest Neighbors is often referred to as a “lazy learner,” which implies that the training algorithm does not generate a general internal model. k-Nearest Neighbors will store the entire training dataset.
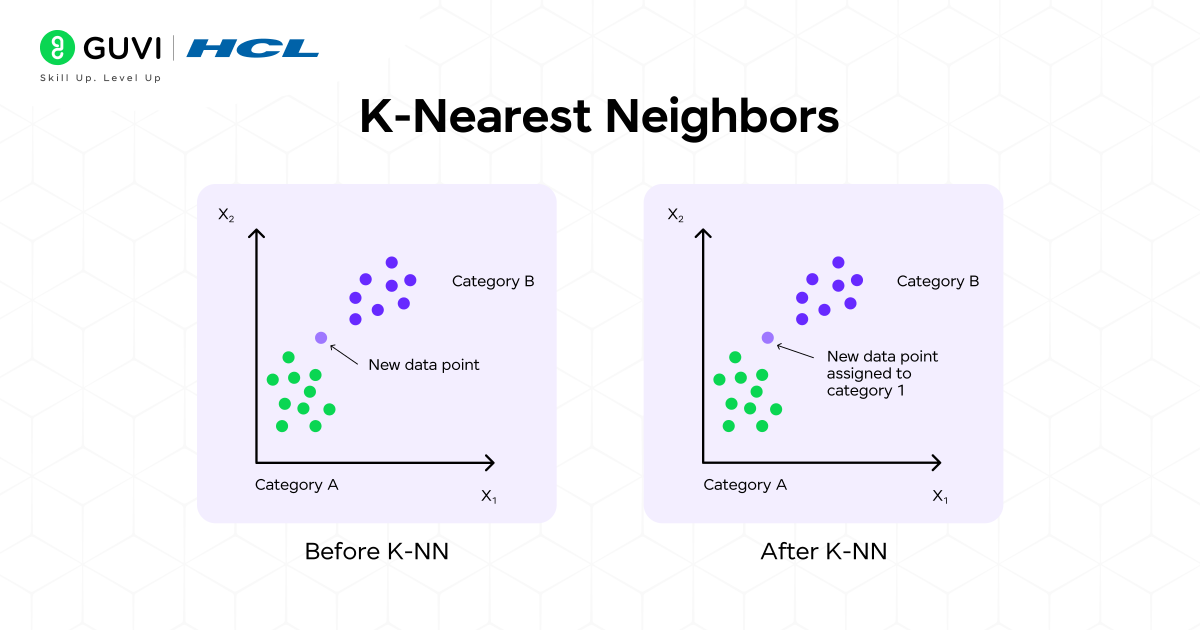
How does it work?
The “k” in KNN is the key. Among the simplest Machine Learning Classification Algorithms, KNN relies on distance measures to classify new data points. When a new, unlabeled data point needs to be categorized, the k-NN algorithm determines the ‘k’ data points in the training data that are “nearest neighbors” to the unknown data point. The new data point is assigned a class label corresponding to the most common class among its k nearest “neighbors.”
For example, if k=5 and three of the new point’s five nearest “neighbors” have class label “Cat” and two have class label “Dog,” then the new point will be assigned the class label “Cat.” Distance is usually identified with Euclidean distance.
Don’t just read about Machine Learning, start building with it! Join HCL GUVI’s Free 5-Day AI & Machine Learning Email Course, understand real-world applications of algorithms like Logistic Regression and Random Forest and get guided exercises and mini projects to strengthen your ML foundation
3. Support Vector Machines (SVM)
Support Vector Machines are powerful and versatile algorithms known for their robustness, especially in high-dimensional spaces. Their primary goal is to find the optimal “decision boundary” that separates classes.
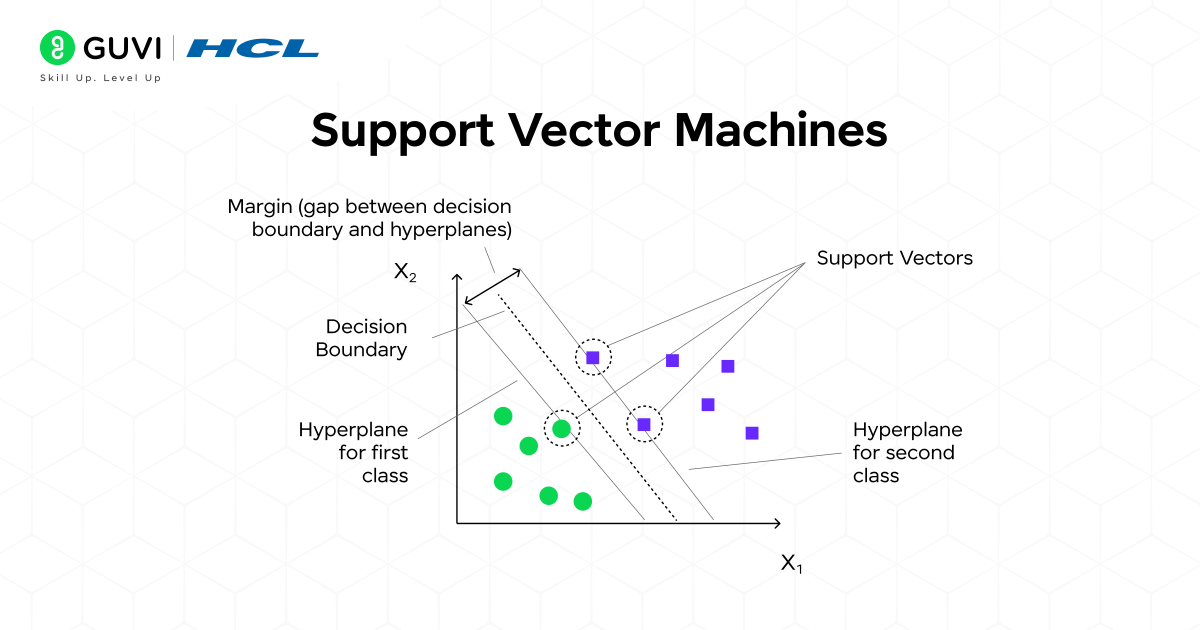
How does it work?
An SVM doesn’t just look for any separating line; it looks for the best one. It seeks the hyperplane (a line in 2D, a plane in 3D, etc.) that has the maximum margin. The margin is the distance between the hyperplane and the closest data points from each class, which are called support vectors.
By focusing only on these critical support vectors, SVMs become very robust. They also employ a brilliant trick called the “kernel trick,” which allows them to implicitly transform data into a higher dimension where a linear separation becomes possible, even if the data is not linearly separable in its original space.
4. Naive Bayes
Naive Bayes is a group of algorithms that apply Bayes’ Theorem with a strong (and “naive”) assumption: that all features are independent of one another given the class label. For many situations, this assumption is a simplification, and in fact, it is very rarely true in real life; however, it works surprisingly well.
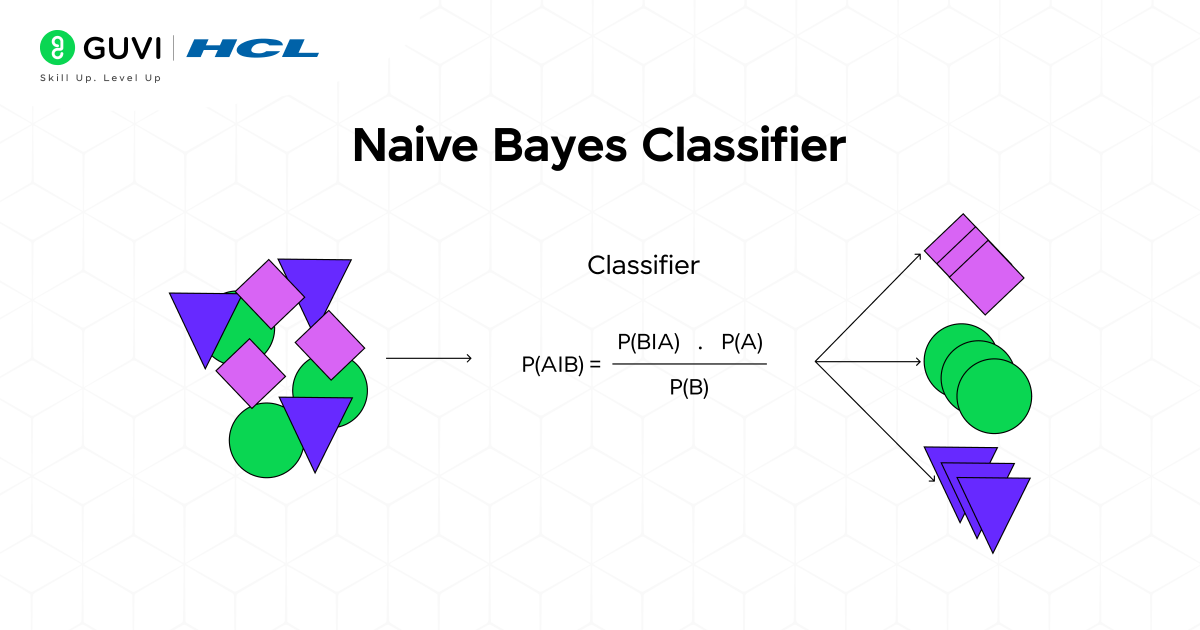
How does it work?
The algorithm computes the probability of a data point belonging to each class label. Bayes’ Theorem is used to assess the probability of an event based on prior knowledge of conditions that may be related to that same event.
The “naive” comes from the concept that the presence (or absence) of one feature does not influence the presence of any other feature. For example, a Naive Bayes classifier for classifying fruits could be based on the features red, round, and 3 inches in diameter for class membership to apple, in spite of these features being dependent.
5. Decision Trees
A Decision Tree is a flowchart-like model that mimics human decision-making. It asks a series of questions about the features of the data to arrive at a final classification. Its structure is white-box and highly intuitive.
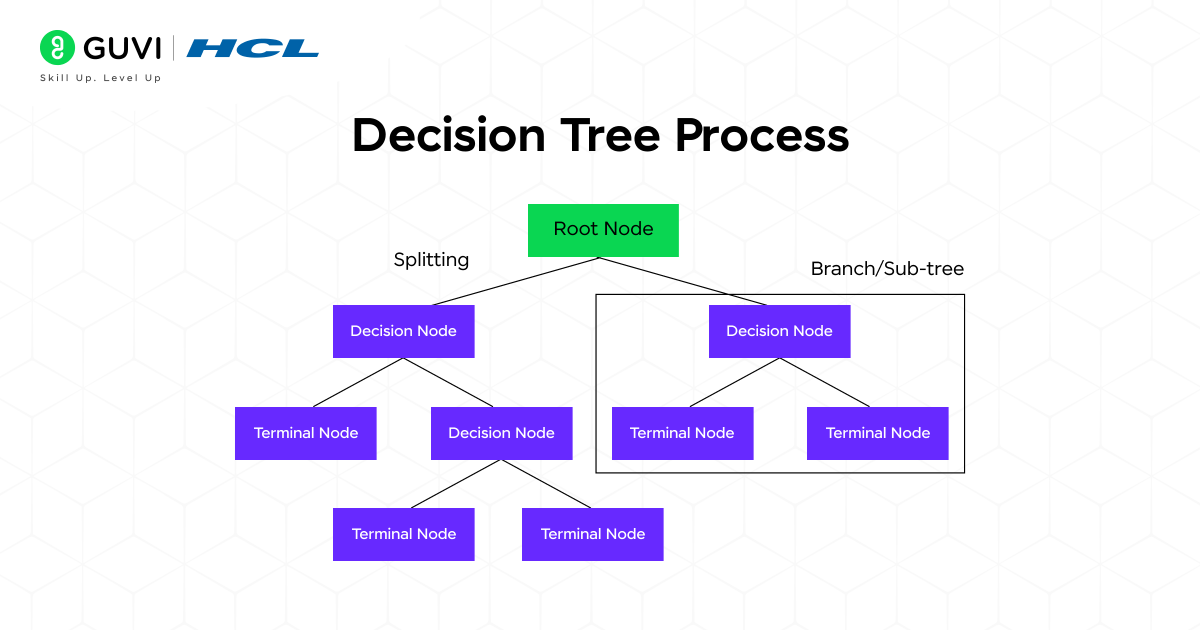
How does it work?
The algorithm builds the tree by selecting the “best” feature to split the data at each node, based on criteria like Gini Impurity or Information Gain (which relies on entropy). The goal is to create subsets of data that are as “pure” as possible (i.e., containing instances of mostly one class).
The process is recursive: it starts at the root, makes a split, and continues splitting the resulting subsets until a stopping criterion is met (e.g., a maximum depth is reached, or a node is 100% pure). The final nodes, called “leaves,” provide the classification decision.
6. Random Forest
Random Forest is an ensemble method that builds upon the simplicity of Decision Trees to create a vastly superior model. The core idea is “the wisdom of the crowd.” Instead of relying on a single, fragile Decision Tree, it builds a “forest” of them and combines their predictions.
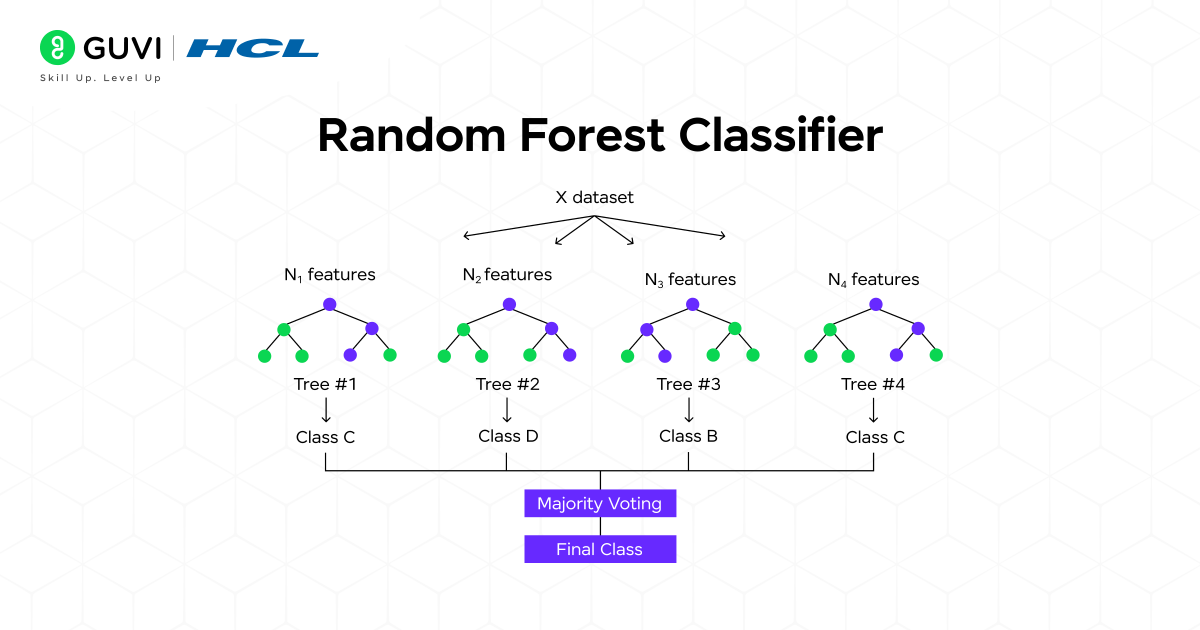
How does it work?
It introduces two key sources of randomness:
- Bagging (Bootstrap Aggregating): It trains each tree on a random subset of the original training data (sampled with replacement).
- Feature Randomness: When splitting a node, it only considers a random subset of the features.
This randomness ensures that the individual trees are diverse and uncorrelated. When it’s time to make a prediction, each tree in the forest “votes” for a class, and the class with the most votes becomes the model’s final prediction (this is called majority voting).
- The term “Machine Learning” was coined way back in 1959 by Arthur Samuel — decades before modern AI took off!
- The Naïve Bayes classifier is one of the oldest algorithms (from the 1700s!) yet it still powers spam filters and sentiment analysis today.
- Support Vector Machines once powered the top handwriting recognition systems, including early postal automation!
- Random Forest got its name because it’s literally a “forest” of decision trees — each one trained on random subsets of data.
- Classification models aren’t just for AI — they’re used in finance, medicine, marketing, cybersecurity, and even astronomy to detect galaxies!
Comparison of Machine Learning Classification Algorithms
| Algorithm | Strengths | Weaknesses | Use Cases |
| Logistic Regression | Simple, interpretable, works well with linear data | Struggles with non-linear data, sensitive to outliers | Credit scoring, churn prediction, medical diagnosis |
| K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) | Easy to implement, no training phase, handles non-linear data | Slow with large data, sensitive to noise | Recommender systems, image classification |
| Decision Tree | Highly interpretable, handles categorical & numerical data | Prone to overfitting, unstable to small data changes | Risk assessment, fraud detection, segmentation |
| Random Forest | High accuracy, reduces overfitting, handles large datasets | Less interpretable, slower training | Loan approvals, healthcare analytics, stock prediction |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | Great for high-dimensional data, flexible with kernels | Fast, efficient, and performs well on text data | Text classification, image recognition, bioinformatics |
| Naïve Bayes | Fast, efficient, performs well on text data | Assumes feature independence, limited for correlated data | Spam detection, sentiment analysis, document categorization |
How to Choose the Right Classification Algorithm?
The choice between different Machine Learning Classification Algorithms depends on your data size, complexity, and interpretability needs.
Here’s a quick guide:
| Scenario | Best Algorithm |
| Small dataset, linearly separable | Logistic Regression |
| Large dataset with complex boundaries | Random Forest or SVM |
| Text classification | Naive Bayes |
| When interpretability is key | Decision Tree |
| When data is small and simple | KNN |
If this topic sparked your curiosity, it’s time to go beyond theory and build real-world ML projects. Join HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak Certified Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Course, designed by industry experts and backed by NSDC. Learn hands-on with expert mentorship, live projects, and job-ready skills.
Wrapping It Up…
Classification is the foundation of intelligent decision-making in AI. Classification Algorithms in Machine Learning convert your data into useful and actionable information, whether you’re making predictions about health-related outcomes, or securing financial transactions.
Your level of machine learning skills will definitely improve by seeing and understanding these common six algorithms, and you will also have learnt to identify the best model for the problem you are trying to solve, which is an important strength for any data scientist to possess.
FAQs
1. What is the best algorithm for someone new to classification?
Logistic Regression is the best place to start. It is simple and intuitive, and serves as a foundation for many more advanced methods.
2. Is it possible to use two algorithms at the same time?
Absolutely! Using ensemble methods like bagging or boosting (Random Forest/XGBoost) often improves accuracy.
3. What is the best algorithm for text classification?
Naive Bayes works extremely well on text data (e.g., spam detection/sentiment analysis).
4. Which libraries are the best to use for classification problems?
Use Scikit-learn for simplicity and for deep learning (TensorFlow/PyTorch) in more complicated applications.




























Did you enjoy this article?