
Top Mainframe Interview Questions and Answers
Oct 19, 2025 9 Min Read 1475 Views
(Last Updated)
Modern servers and cloud-based platforms are gradually replacing traditional technologies and systems, as they are cost-effective, scalable, highly secure, and enable companies to fine-tune their resources as needed. However, amid this new tech adoption, there are organizations, such as banks, government bodies, and other entities that rely heavily on maintaining records, which still have a dependence on Mainframe Systems.
But aren’t you curious why they are still depending on these old systems? The simple answer to this question is that the replacement cost is perilous, as the majority of their legacy software and applications are built on them and are a reliable and secure source of sensitive business data and information.
Remember, we are using the word “old” that doesn’t indicate that they are ineffective. And after understanding the criticality of these powerful data servers, it becomes highly crucial for the companies to conduct interviews based on the Mainframe and its fundamentals.
Since fewer candidates are preparing for Mainframes nowadays, there is a shortage in this domain. However, there is a massive opportunity for those who opt for gaining skills and expertise in this technology, as companies have a strong requirement for professionals who can extend their Mainframes by connecting them with modern technologies.
In this blog, we will lay a strong emphasis on the most genuine and effective Mainframe interview questions that are commonly asked in the core technical rounds. Based on the level of proficiency, we have segregated the level of questions into two distinct categories for freshers and for experienced ones. So, let’s get started.
Table of contents
- Mainframe Basic Interview Questions (For Freshers)
- Mainframe Advanced Interview Questions (For Experienced)
- Conclusion
Mainframe Basic Interview Questions (For Freshers)
- State the main characteristics of a Mainframe.

The most important characteristics of a Mainframe are:
- Reliability: Mainframes are particularly designed for running continuously for extended timeframes without any technical interruptions or outages.
- Scalability: Mainframe servers are highly efficient in handling heavy user concentration, specifically in managing the millions of transactions made per minute.
- Processing Power: They have a vast memory and storage capacity, which enables them to process and store massive amounts of data. The complex logic built into them allows they to perform complex calculations and analysis on the stored data.
- Security: These advanced computer systems also offer access control, encryption, and the best auditing features to protect the sensitive data from any kind of unauthorized access.
- What is COBOL?
COBOL (Common Business-Oriented Language) is an imperative and high-level language that was developed primarily for being implemented in mainframe systems.
It is implemented explicitly for processing high volumes of business data (for example, in banking and administrative systems). It is a language that is very easy to write, comprehend, and maintain due to its English-like syntax.
It is a self-documenting programming language that also resolves bugs and errors very effectively.
- Define JCL.
JCL stands for Job Control Language. This is a scripting language implemented on mainframes to direct the system in executing programs and managing data without any hindrances. In simple terms, a Job means a set of instructions.
When we submit a job to a mainframe source, JCL comes into action to suggest which programs to run. It consists of a bundle of control statements through which it connects the mainframe operating systems (OS) with the COBOL programs. JCL is also used for defining conditions, allocating memory storage, and resolving technical errors and malfunctions, due to which it becomes essential for batch processing.
- What is CICS, and what is its importance?
CICS (Customer Information Control System) is a transaction management and communication handling system. It is developed for handling large user requests in real-time, such as financial transactions, airline reservations, and core retail sales operations.
Its significance lies in various factors such as fast data processing, reliability, and security, even when thousands of users try to access the system simultaneously.
Due to its potential for managing sessions, user access, and supporting high-volume transactions, CICS is integrated into various critical enterprise applications and platforms.
- What is DB2 in the Mainframe?
It is a relational database management system (RDBMS) used extensively on mainframes to perform data manipulation like storage, management, and retrieval in an efficient manner.
Here, SQL queries are made for interacting with the database, and through the indexing process, the search tasks become very quick. DB2 is specially crafted for optimized performance and security. And business entities like banks, insurance companies, government software systems, and healthcare platforms, where data protection is prioritized, DB2 is the best system for handling these critical and large-scale enterprise databases.
Apart from these, it also supports concurrent access, meaning that at the same time, multiple users and programs from different sources can effortlessly perform CRUD (create, read, update, and delete) operations without any technical conflicts.
- What is VSAM?
VSAM (Virtual Storage Access Method) is a type of methodology mainly used on mainframe systems to store and access datasets efficiently. Unlike regular sequential files, VSAM enables users to retrieve required data much faster with the aid of keys and indexes.
Large datasets such as customer detail records, inventory information, and transaction logs can be effectively managed through this method. This particular method is highly versatile in nature due to its competency in both batch processing and online operations, where speed and security are the critical parameters to consider.
- What are the types of datasets in mainframes?
The following data types are:
- Sequential datasets: Where the data is stored in a sequential and systematic order, one after another.
- Partitioned datasets (PDS): A single dataset contains multiple files.
- VSAM datasets: These are datasets that are optimized for high-speed access.
- What is a deadlock in DB2?
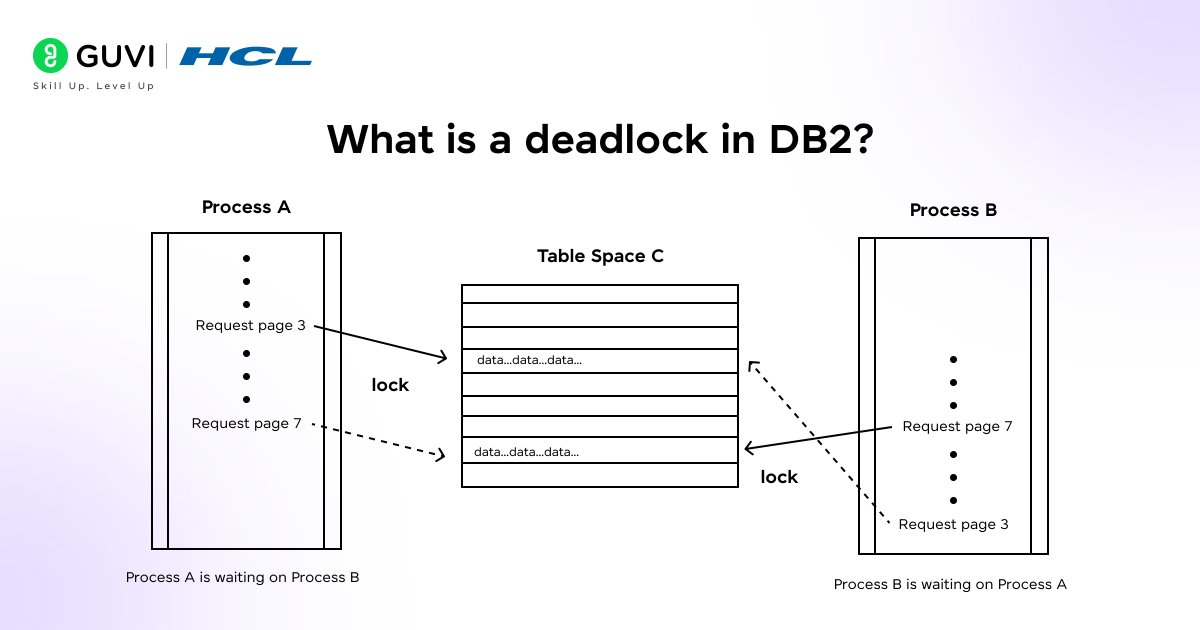
A deadlock in DB2 occurs when two or more functions are present in the queue waiting for each other to release the resources, such as rows and tables. This is an event when one program is occupying a row that belongs to another program, while simultaneously the second program has locked a different row that belongs to some other program.
So, this is a technical conflict that the DB2 identifies and resolves by choosing a process as the main issue and rolling it back, to ensure the other process can continue its operations.
- In what way do mainframe computers handle tasks and users?
Mainframe computers are an interconnected network of multiple processors and memory.
Firstly, the system divides the processing resources into various components to allow millions of users to perform activities (checking balances, booking tickets, or managing CICS transactions) at the same time without any interruption.
While the users are interacting with the system, the mainframe in the backend is involved in switching tasks and allocating memory. In this way, the internal operations are executed with accuracy and precision and with minimal downtime.
- How do the global and external variables differ from each other?
Global and external variables are different based on their scope and accessibility. A global variable is declared within a program and can be accessed by all the functions or methods that are running inside that same program, whereas an external variable has a wider scope, as it can be shared across multiple distinct programs. In COBOL, global variables are used mainly for maintaining data consistency, but external variables are implemented only when different programs require the same data.
- What is the difference between an index and a subscript in a COBOL table?
In COBOL, both Index and Subscript have a common task to perform, which is to access the elements of a table, but the operational method is very different.
- Index (displacement) is a pointer that directly stores the memory address/location of a table element. In contrast, Subscript (numerical position) indicates the position of an element in the table.
- Another major difference is that Subscripts can be altered with normal arithmetic computations, while Indexes are more strict in nature, as they can be modified by using specific COBOL statements (like SET or PERFORM VARYING).
- Mention the different types of conditional statements present in COBOL.
These are the following conditional statements:
A. IF …ELSE statement
Example:
IF A = B
DISPLAY “Equal”
ELSE
DISPLAY “Not Equal”.
B. EVALUATE statement
Example:
EVALUATE TRUE
WHEN A > 100
DISPLAY “High”
WHEN A = 100
DISPLAY “Equal”
WHEN OTHER
DISPLAY “Low”
END-EVALUATE.
C. Nested IF statement
Example:
IF A > 0
IF B > 0
DISPLAY “Both Positive”.
D. SIGN condition
Example:
IF BALANCE IS POSITIVE
DISPLAY “Valid Balance”.
E. CLASS Condition
Example:
IF WS-VAR IS NUMERIC
DISPLAY “It is a number”.
F. Logical condition using AND / OR
Example:
IF A > 0 AND B > 0
DISPLAY “Both are Positive”.
- What is DRDA in the Mainframe?
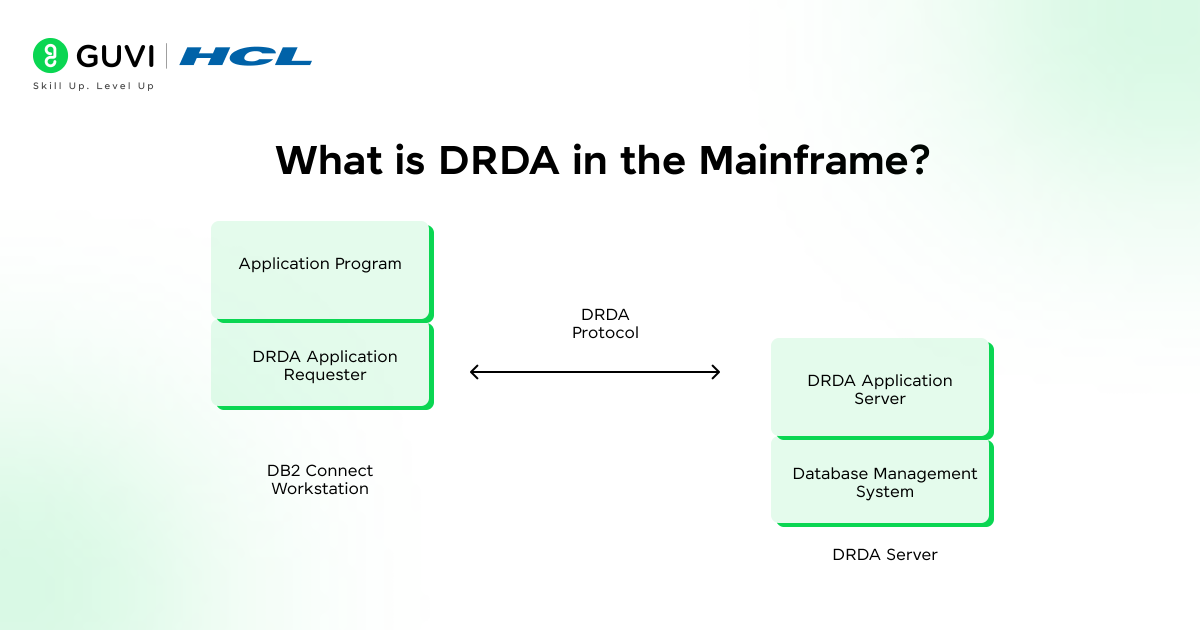
DRDA (Distributed Relational Database Architecture) is a type of protocol that was developed by IBM to allow programs and applications to share data across different systems.
This protocol connects the DB2 workstation with the DRDA server through which a centralized database system is created, as a result of which the security and consistency of data are maintained.
- What are the types of JCL statements, and why are they used?
There are three types of Job Control Language statements:
- JOB: Defines the start of the job, who submitted it, and how the system should manage it.
- EXEC: Specifies the program, utility, or procedure that needs to be executed in the job step.
- DD: Describes the datasets used, including the source of input and the destination for output.
- What is mainframe testing?
It is a process of testing applications and systems that runs in a mainframe environment. It is executed for checking whether the programs, databases, and other online processes are operating correctly or not.
Testers implement the advanced tools and JCL scripts to validate the input and output of data, assess COBOL programs, and verify the program’s capacity to handle heavy data loads while maintaining accuracy.
- What are the key components of mainframe computation?
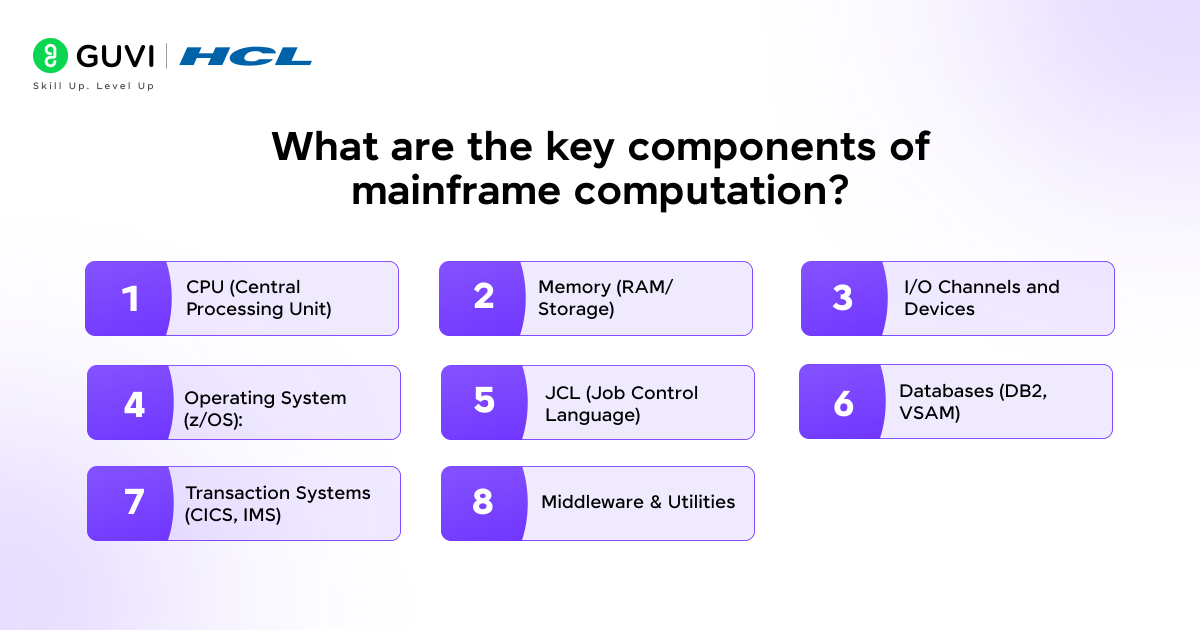
The key components or elements of mainframe computation are:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): Executes instructions and manages tasks.
- Memory (RAM/Storage): Stores data and programs temporarily.
- I/O Channels and Devices: Handles both the input and output operations.
- Operating System (z/OS): Manages resources and job execution.
- JCL (Job Control Language): Provides instructions to run jobs (a set of program instructions).
- Databases (DB2, VSAM): Stores and retrieves structured data.
- Transaction Systems (CICS, IMS): Processes online requests in real-time (for example, Online UPI transactions and Flight Bookings).
- Middleware & Utilities: Connects applications and monitors performance.
- List some limitations of Mainframe Systems.
Some key limitations are:
- Expensive: These systems are very costly in terms of purchase as well as post-purchase, as they require regular maintenance and upgradation services.
- Bulky Infrastructure: Mainframes are extremely large in size, making them nearly impossible to transport. Due to their large dimensions, they require separate physical spaces, continuous power supply, and cooling systems to operate at peak efficiency level.
- Complexity: Managing an entire mainframe becomes challenging as it demands core competencies and hands-on experience in COBOL, JCL, CICS, and DB2, making it not at all beginner-friendly.
- What are the types of tables in COBOL?
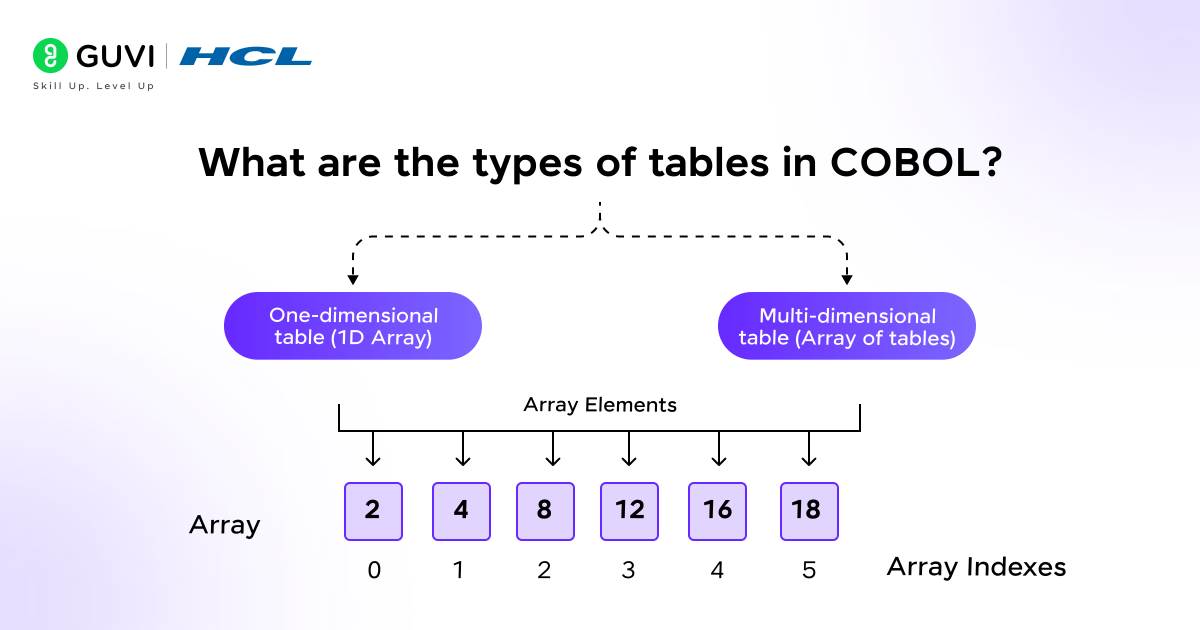
One-dimensional table (1D Array): It is a table where the variables are stored in a single row and are accessed by using a subscript or index. Example: A list of student IDs.
Multi-dimensional table (Array of tables): This consists of multiple rows and columns (like a 2D matrix). And here the data is accessed using multiple subscripts or indexes. Example: A table containing monthly sales data for products, along with their respective categories.
- What are the different kinds of tablespaces in DB2?
The different kinds of tablespaces in DB2 are:
- System Managed Space (SMS) Tablespace: OS controls the storage allocation automatically.
- Database Managed Space (DMS) Tablespace: DB2 manages storage using pre-allocated containers.
- Automatic Storage Tablespace: Storage grows automatically without manual intervention.
- Partitioned Tablespace: Data is divided into multiple partitions for better performance.
- Universal Tablespace: Supports both segmented and partitioned storage in a single tablespace.
- What is the meaning of a CICS (Customer Information Control System) transaction?
It is a type of transactional process in which the mainframe system responds to the user’s requests. We can imagine a scenario where an individual is withdrawing money from an ATM or an admin who is updating the customer records. In every transaction, the data is processed quickly and securely without any conflict arising from multiple transaction procedures.
Mainframe Advanced Interview Questions (For Experienced)
- What is the difference between Static and Dynamic Calls in COBOL?
The key differences are:
- In the static call, the called program happens at compile time, whereas in a dynamic call, the called program is executed at run time.
- The program execution speed in static calling is faster, while in dynamic calling, it is slower.
- At the time of updates, the program requires recompilation in the case of a static call; however, in the case of a dynamic call, the program can be updated independently.
- The memory consumption in a static call is very high, whereas in a dynamic call it is less, as the program is rendered only when it is needed.
- What is the concept of referential integrity in DB2?
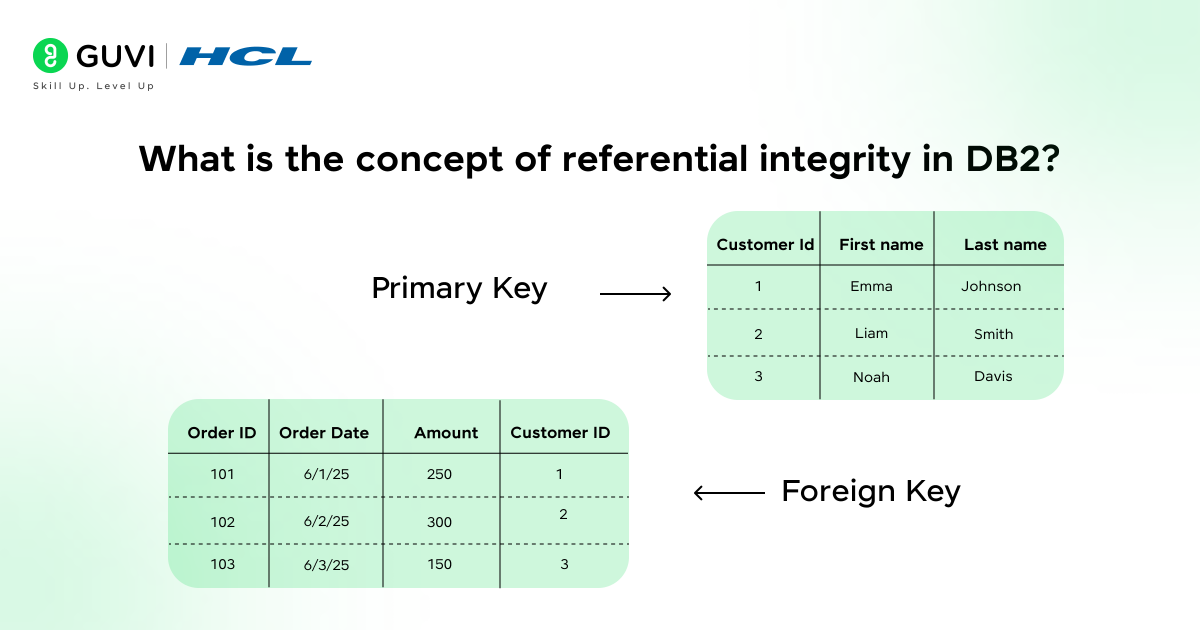
Referential integrity in DB2 is a protocol that is responsible for maintaining the right and consistent relationships between the data tables in the databases.
The working principle is based on linking the primary key in the parent table through a foreign key that is present in the child table; in this way, a systematic and sequential data flow is maintained.
Due to this structure, the admin users are not allowed to insert row data in the child table with the help of a foreign key that doesn’t belong to the parent table.
To understand this better, one can’t create an order for a customer who doesn’t exist in the system. For the creation of an order, a valid customer must exist in the parent source table. By enforcing referential integrity, DB2 avoids the orphan (unlinked) records and preserves data integrity.
- What is quasi-reentrancy in CICS (Customer Information Control System)? Explain it.
Quasi-reentrancy in CICS is an important concept because mainframes are designed to handle thousands of users at the same time. Imagine if every user needed a separate copy of the same program — the system would waste a lot of memory and run very slowly. Instead, in CICS, a program is written in such a way that one copy of it can be shared by many users simultaneously. This is what we call quasi-reentrant. The word “quasi” means “almost” — so the program is not 100% reentrant, but CICS manages it carefully so that each user gets their own private area for storing personal data, like COMMAREA or the Task Control Area (TCA).
Think of it like a busy bank counter: the banker (program) is the same person helping many customers (users), but each customer has their own form and details (private storage). When one customer is waiting (like waiting for approval), the banker can immediately serve the next customer without getting confused. Similarly, CICS pauses one task and switches to another, all while keeping each user’s data separate. This system prevents errors like mixing up two users’ transactions and makes the mainframe extremely reliable. Without quasi-reentrancy, programs would clash with each other, users’ data could be overwritten, and the whole system would become unstable.
- What is the role of Coupling Facilities in Parallel Sysplex?
In Parallel Sysplex, the Coupling Facility acts like a centralized authority source that regulates the multiple mainframe systems to work in a synchronized way.
In Parallel Sysplex, it is possible to interconnect various mainframes with each other to form a unified computer. Here, the Coupling Facility ensures that each component of this system effectively shares data, coordinates tasks, and avoids technical conflicts.
Essentially, the primary role of the Coupling Facility is to facilitate rapid communication and data flow among the interconnected web of mainframe systems.
It also manages lock structures, cache structures, and list structures to prevent deadlock situations, to perform constructive memory caching, and to manage data queues and workloads.
- What approach does CICS follow for handling multi-threading?
For handling and managing the multi-threading and task control program (TCP), CICS treats every single request or transaction as a separate modular component. The components are like independent tasks that work simultaneously without any hindrances, and that is possible due to the task control program (TCP).
The TCP ensures each small task is assigned a proportion of CPU time (the amount of time the CPU invests in executing a program or function) and runs in the proper order without any interference with other tasks. And in this way, thousands of transactional processes can be executed without any glitches.
- Give an example of COBOL table handling by searching for an employee in a table using INDEX.
This example highlights the difference between INDEX and SUBSCRIPT:
// COBOLE Code
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 EMP-TABLE.
05 EMP-ID OCCURS 1000 TIMES
INDEXED BY EMP-IDX.
10 EMP-NUM PIC 9(5).
01 WS-SEARCH-ID PIC 9(5) VALUE 12345.
01 WS-FOUND PIC X VALUE ‘N’.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
SET EMP-IDX TO 1
SEARCH EMP-ID
AT END
DISPLAY “EMPLOYEE NOT FOUND”
WHEN EMP-NUM(EMP-IDX) = WS-SEARCH-ID
MOVE ‘Y’ TO WS-FOUND
DISPLAY “EMPLOYEE FOUND AT INDEX ” EMP-IDX
END-SEARCH.
- How significant is the DD statement in JCL?
A DD (data definition) statement in JCL is utilized to instruct the system about which files or datasets a program needs to print during execution. Each time a COBOL or other mainframe program gets executed, there is a requirement for input files that analyze and decode the data and output files for storing the results.
In this case, DD statements act like a bridge by linking these files to the program. With the help of DD, you can establish an identity for the dataset by assigning it a unique name and memory location.
- How does z/OS Workload Manager (WLM) control system performance in a multi-LPAR environment, and how would you tune WLM policies for critical online workloads?
The z/OS Workload Manager (WLM) is like the “traffic controller” of system performance in a multi-LPAR (Logical Partition) environment. Its main job is to decide how system resources like CPU and memory are shared among competing workloads. Instead of assigning fixed priorities, WLM works with service classes and goals (like response time or throughput) defined by the system administrator.
Each workload is classified into a service class, and WLM constantly monitors performance against the goals. If one workload is falling behind its goal, WLM can dynamically adjust priorities, allocate more CPU cycles, or rebalance resources across LPARs using technologies like PR/SM (Processor Resource/System Manager).
For tuning critical online workloads, you would typically:
- Define service classes with higher importance for online transaction systems (like CICS or IMS).
- Set goals based on response time instead of throughput, since users expect quick responses.
- Ensure that batch jobs or lower-priority work are given less importance so they don’t starve critical online transactions.
- Monitor performance reports (SMF/RMF) and fine-tune service class weights or goals to make sure WLM adapts correctly during peak loads.
- How are buffer pools in DB2 tuned to optimize the I/O performance?
The buffer pool is a portion of the main RAM (memory) that stores data temporarily and indexes information read from the disk. For tuning them for better I/O results, we can :
- Increase the buffer pool size to achieve the optimum hit ratio.
- Distribute the objects across pools to prevent contention and balance memory consumption.
- Implement the DB2 performance optimization tools like DB2 Statistics and SMF (system management facilities) to detect the I/O concentrated areas and tune in accordance with that.
- Is it possible to redefine a field defined as X(50) with another field of X(100)? If yes, how can it be done in COBOL?
Yes, it is possible in COBOL. You can use the REDEFINES clause to let one field share the same memory area as another.
For example:
01 FIELD-A PIC X(50).
01 FIELD-B REDEFINES FIELD-A PIC X(100).
Here, FIELD-B uses the same memory as FIELD-A, but it can be interpreted as a longer string.
Note: When redefining with a larger size, make sure that it does not overwrite adjacent memory or other variables; typically, the redefined field should fit safely within the allocated storage.
If you want to become job-ready in this highly competitive software industry, then why not learn from the best mentors and build real-world projects that add value to your portfolio? Unlock the path to a thriving tech career by enrolling in HCL GUVI’s IIT-M Pravartak certified Data Science Course. And if you want to delve deep into the fundamentals of Mainframe Architecture, then join our Mainframe Course and create real-time applications.
Conclusion
We hope this blog on the most essential Mainframe interview questions has been a valuable resource to enhance your technical knowledge. Mainframe systems are very crucial in industries like banking, cloud-based tech organizations, and digital security provider agencies.
So that’s why, individuals or professionals who acquire the necessary skills and knowledge in mainframe components, such as COBOL, JCL, CICS, DB2, and VSAM, can establish themselves as competent software engineers and remain in demand by companies.



































Did you enjoy this article?