
What is MLOps? An Ultimate Beginner’s Guide
Sep 20, 2025 5 Min Read 1641 Views
(Last Updated)
We all know Machine learning is one of the fastest-growing technologies. It’s everywhere, yet despite its potential, research shows that out of 10, only 2 machine learning projects come into existence. The remaining 8 never make it past the experiment stage. The models work properly in the lab environment but stumble when it’s moved to the real world.
Why does it happen? It’s because the machine learning lifecycle lacks structure, automation, and collaboration. ML projects don’t have the same rigid structures found in traditional software because ML is constantly affected by changes in data, has complex workflows, and requires constant monitoring. Without a framework, it is nearly impossible for organizations to connect data science and operations.
This is exactly where MLOps comes in. Think of it as the missing link that transforms machine learning from an isolated experiment into a reliable, scalable business solution.
In this blog, we will go over what is MLOps, the MLOps process, MLOps workflow, MLOps pipeline, tools used in MLOps, the MLOps lifecycle, benefits of MLOps, best practices, and real-life examples to show how it helps solve one of the major challenges in AI today.
Table of contents
- What is MLOps?
- Why Do We Need MLOps?
- How MLOps works
- Data Collection/Preparation
- Model Experimentation and Development
- Validating and Staging
- Model Deployment
- Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
- Best Practices Checklist for Beginners in MLOps
- MLOps Tools
- MLOps vs DevOps
- Benefits of MLOps
- Beginner Roadmap to Learn MLOps
- Final words..
- What is MLOps in simple words?
- Is MLOps only for large companies?
- What are some popular MLOps tools?
- What's the future of MLOps?
What is MLOps?
MLOps, or Machine Learning Operations, is a collection of techniques that unites machine learning, DevOps, and data engineering to deploy and maintain a machine learning model in production consistently and reliably. The MLOps meaning encompasses the entire lifecycle of machine learning projects, from initial development to ongoing maintenance and monitoring.
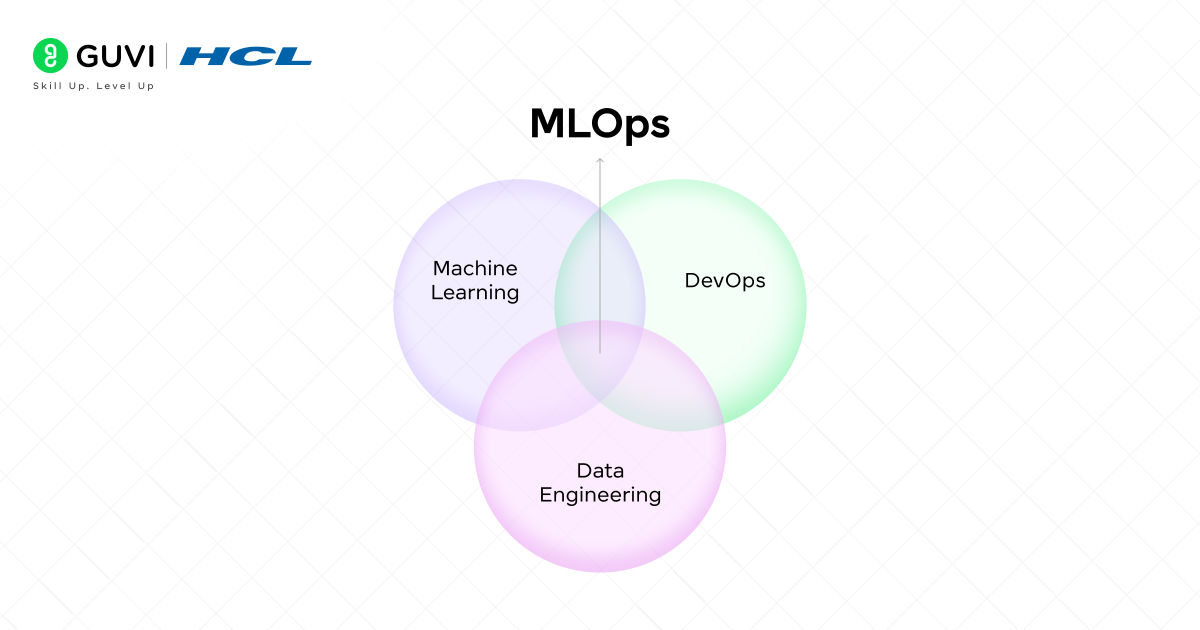
Visualize MLOps as the link between the experiment stage of machine learning and the production stage. Data Scientists are mostly be concerned with the pipeline to create an accurate model, whereas MLOps is more concerned with how the model can be deployed, scaled, and maintained in a production environment with a guarantee that the system will not collapse, nor will the outputs be unreasonable.
Why Do We Need MLOps?
Creating a machine learning model is fun, but putting it into production and maintaining it properly once it’s there is a different level of difficulty. Many organizations discover that while data scientists can train highly accurate models in a controlled environment, these models often fail to deliver consistent value once they are pushed to production. This gap between experimentation and real-world usage is exactly why we need MLOps.
Here are some of the common obstacles teams may experience without MLOps:
- Data drift (when new data differs from training data).
- Model degradation over time.
- Complex deployment pipelines.
- Lack of collaboration between teams.
MLOps solves these by ensuring models are not only trained but also deployed, monitored, updated, and governed.
How MLOps works
The MLOps process is continuous, iterative, and can be often visualized as an infinite loop. The MLOps lifecycle runs from data preparation to monitoring the model and back again. There are some very specific essential stages in the MLOps workflow. They are:
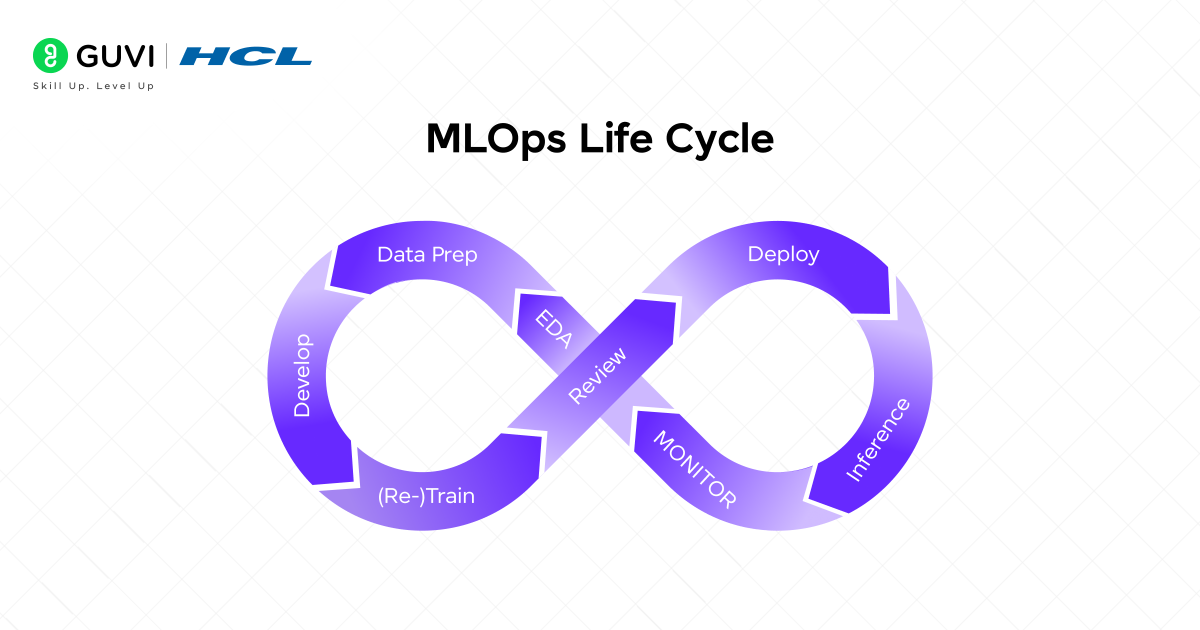
1. Data Collection/Preparation
This is the starting point. The adage “garbage in, garbage out’ holds even more true for ML. This stage includes the following steps:
- Data Ingestion: Collecting data from various sources (databases, data lakes, real-time streams)
- Data Cleaning: Dealing with missing values, errors, and outliers.
- Data Labelling: For supervised learning, helping to tag the data with correct answers.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Learning the data’s patterns, distributions and interdependencies.
The output at this stage is a clean, reliable dataset and is ready for experimentation.
2. Model Experimentation and Development
This is the part of the data science pipeline full of the excitement of exploration and learning. In this section, data scientists use the transformed data to:
- Feature Engineering: Generate new input variables (features) that would help the model find patterns.
- Model Training: Test multiple ML algorithms (e.g., linear regression, decision trees, neural networks) to identify the best model.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Adjust the knobs and dials on the selected algorithm to enhance the performance.
- Model Evaluation: Rigorously test the model on a dataset that was never used in the process for an unbiased estimate of the model’s performance.
MLOps for this phase is to document each experiment and what code, data, and parameterization went into generating a result. Full reproducibility is obtained in this stage.
3. Validating and Staging
Before a model can be made available to users, it must be assessed.
- Validation: Assessed against the business’s metrics and compared to the current champion model for improvements.
- Packaging: The model with its dependencies and lightweight inference code is put into a container (e.g., a Docker container), which eliminates the “works on my machine” issue by providing the same environment no matter where the container is executed.
- Staging: The model is deployed to a pre-production, or staging, environment that simulates the live system to finalize integration testing as well as load testing.
4. Model Deployment
This phase is the process of releasing the validated model into one or more live/production environments for the model to make real predictions for end users. Deployment can be:
- Canary Deployment: Here the model may be deployed to a small portion of users to measure its impact on performance before fully going live.
- A/B Testing: This involves running the new model (challenger)p, alongside the old model (champion) for some time to observe their impacts on the business metrics directly.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
Deployment is not the end; it is the beginning. This is the most important stage of the MLOps lifecycle.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the prediction accuracy of the model and real-time latency.
- Data Drift Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the production incoming data to determine if its statistical characteristics are drifting from the data used to train the model.
- Model Decay Monitoring: Setting up alerts for when the model’s performance falls below a specified threshold.
- Trigger Retraining: A monitoring that triggers a new cycle of the MLOps lifecycle: Collect new data, retrain the model, redeploy the model. The “continuous” loop central to MLOps is now established.
Best Practices Checklist for Beginners in MLOps
If you are new to MLOps, here is a short checklist to consider:
- Begin small with one model, then scale.
- Version control both code and data.
- Automate models from the beginning to enable re-use, e.g. model training or testing, etc.
- Continuous monitoring for data drift and model decay.
- Document all experiments (parameters, data, & results).
- Use containers (Docker) from the beginning for reproducibility.
- Work with DevOps and data engineering teams from the outside.
- Test everything in a staging environment before passing over to production.
MLOps Tools
There are several tools that make MLOps possible. Some popular categories include:
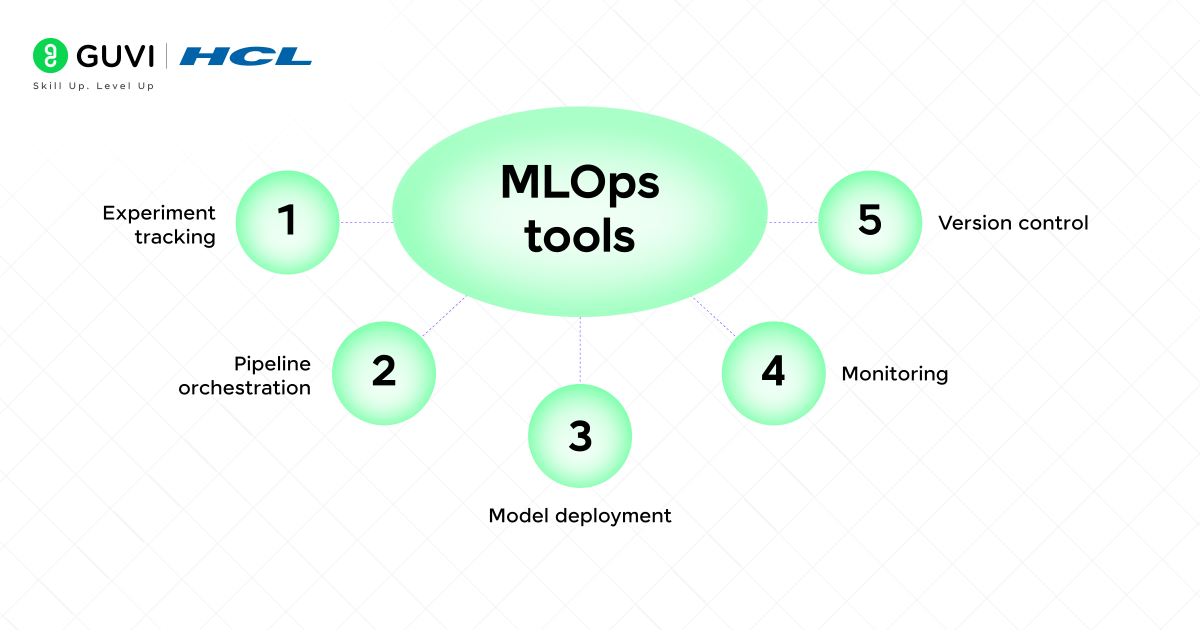
- Experiment tracking: MLflow, Weights & Biases.
- Pipeline orchestration: Kubeflow, Apache Airflow.
- Model deployment: Seldon, BentoML, TorchServe.
- Monitoring: Evidently AI, WhyLabs.
- Version control: DVC (Data Version Control), Git.
Choosing the right MLOps tools depends on project size, data complexity, and team expertise.
MLOps vs DevOps
| Aspect | DevOps | MLOps |
| Primary Focus | Software development and deployment | Machine learning model development, deployment, and monitoring |
| Key Components | Code, infrastructure, CI/CD pipelines | Code, data, features, models, pipelines, monitoring |
| Data Handling | Limited focus on data (mainly configuration files and databases) | Strong emphasis on data collection, preprocessing, versioning, and validation |
| Version Control | Source code and infrastructure | Source code, datasets, model artifacts, and experiment tracking |
| Monitoring Needs | System uptime, performance metrics, and errors | Model accuracy, drift detection, fairness, explainability, as well as system performance |
| Iteration Speed | Faster software releases through CI/CD | Continuous retraining and redeployment of models as data and business needs evolve |
| Collaboration | Developers + Operations teams | Data scientists + ML engineers + Operations teams |
| Tools | Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, GitHub Actions | MLflow, Kubeflow, DVC, Airflow, Seldon, Weights & Biases |
Benefits of MLOps
- Increased Speed: The manual steps can be automated, and teams can create and release new models and updates more quickly and more often.
- Increased Reliability & Reproducibility: Identify and trace every model version back to the code and data used to create it, so that audits and de-bugging can occur.
- Scalability: Automate pipelines to deal with thousands of models seamlessly, while this would be impossible to do manually.
- Decreased Risk: Continuous monitoring identifies the decay of models and drift of data, so that early interventions can prevent actual business damage from broken models.
- Increased Productivity: It enables highly-skilled data scientists to get out of the plumbing and deployment work, allowing them to focus on the most valuable work within the organization, which is research and innovation.
Beginner Roadmap to Learn MLOps
Here’s a step-by-step path you can follow if you want to learn MLOps effectively:
1. Build ML Foundations
- Learn Python, ML libraries (Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch).
- Understand ML workflows (data prep → training → evaluation).
2. Get Comfortable with DevOps Basics
- Git & GitHub for version control.
- Docker for containerization.
- CI/CD concepts.
3. Learn MLOps Tools
- MLflow or Weights & Biases (experiment tracking).
- Kubeflow or Airflow (pipeline orchestration).
- Seldon or BentoML (deployment).
4. Practice Monitoring & Automation
- Use tools like Evidently AI for drift detection.
- Set up automated retraining pipelines.
5. Work on Projects
- Start with a personal ML project → deploy it with MLOps tools.
- Contribute to open-source MLOps projects.
6. Stay Updated
- Follow MLOps communities (Reddit r/MLOps, Slack groups).
- Take beginner-friendly courses (like HCL GUVI’s AI & ML program).
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Do you want to take your AI capabilities to the next level? Then check out HCL GUVI’s Advanced AI & Machine Learning Course, co-designed with Intel and IITM Pravartak. You’ll master hands-on skills in Python, Deep Learning, NLP, Generative AI, and MLOps and a globally recognized Intel certification to turn your learning into a career advantage.
Final words..
MLOps in machine learning is fundamental for all organizations that want to move beyond random ML projects and build a valuable and sustainable AI capability. It is the engineering discipline that turns machine learning from an opaque, academic practice into a dependable, systematic, and meaningful industrial practice.
Becoming familiar with MLOps meaning, lifecycle, and best practices is the first step toward unlocking the true potential of your machine learning investments. It is the road that creates the bridge from promising prototypes to compelling products. Hope you find this blog useful. Happy learning!
1. What is MLOps in simple words?
MLOps is like DevOps but for machine learning. MLOps make sure that ML models are build, deployed, monitored and update.
2. Is MLOps only for large companies?
No, not at all. While the platform can be complex, there are many open source tools that can used by smaller companies who only have a single model.
3. What are some popular MLOps tools?
Kubeflow, MLflow, Airflow, DVC, and Seldon are widely used tools.
4. What’s the future of MLOps?
The future of MLOps includes increased automation, better integration with AI development workflows, enhanced monitoring capabilities for complex AI systems, and stronger focus on responsible AI practices.





























Did you enjoy this article?