
Types of Learning in Machine Learning: A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Sep 15, 2025 4 Min Read 1722 Views
(Last Updated)
Modern technology now relies heavily on machine learning (ML), which powers almost everything from fraud detection systems and self-driving cars to voice assistants like Siri and Netflix recommendations. So what is machine learning? ML is all about teaching computers to learn from data to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed step by step.
But here’s the thing: machines do not “learn” in the same way as humans do. Rather, they rely on different forms of learning in machine learning that describe how the machine analyzes data, finds patterns, and improves over time. Each method of machine learning is designed for a specific problem.
Before getting started with machine learning, it’s necessary to first discuss the types of learning in machine learning.
This blog covers the types of machine learning, their approaches, real-world examples, real-world applications, and their advantages and disadvantages. At the end of this blog you will have a crystal clear understanding of machine learning types.
Table of contents
- Categories of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning in Machine Learning
- Unsupervised Learning in Machine Learning
- Difference between Supervised and Unsupervised Learning
- Semi-Supervised Learning in Machine Learning
- Reinforcement Learning in Machine Learning
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Types of Learning in Machine Learning
- Final thoughts..
- Why do we need machine learning?
- Which type of learning is best for beginners to start with?
- Do I need coding skills to learn machine learning?
- What are the advantages of machine learning approaches?
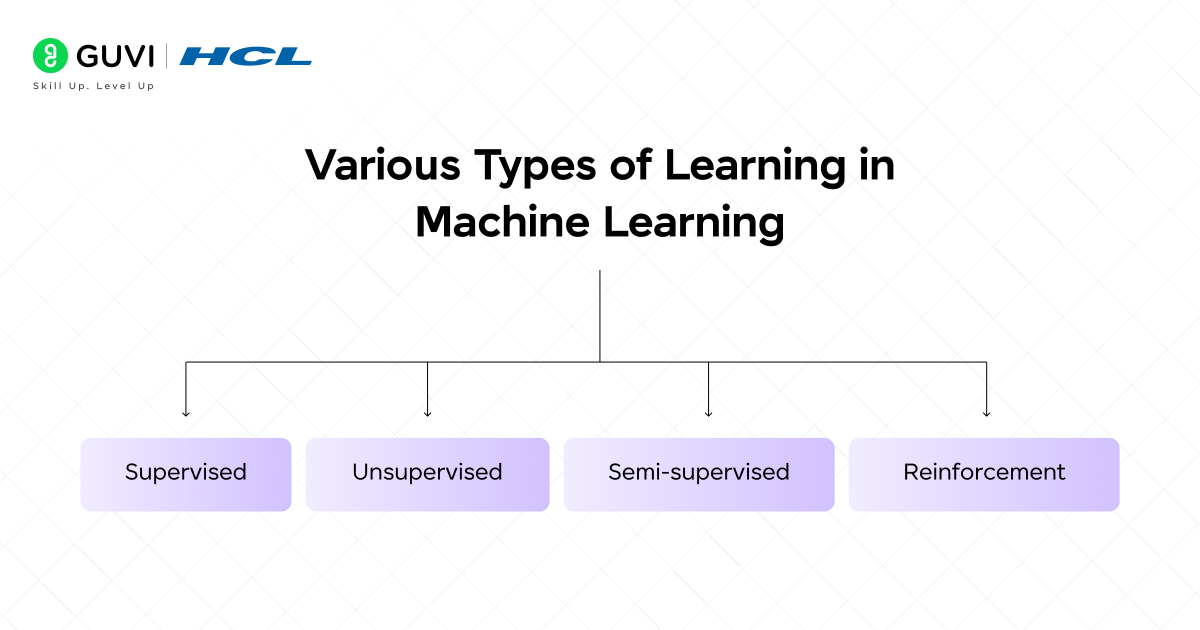
Categories of Machine Learning
Machine learning types are broadly categorized in several ways. Each of the methods has different characteristics and applications. Let’s explore the most common types known, one by one.
1. Supervised Learning in Machine Learning
Supervised learning is the most used machine learning approach, and it is usually the first introduction many people have to machine learning. In simple terms, supervised learning is learning with a teacher. The algorithm learns using a labeled dataset, which means that for every input, there is a known output. The model uses these examples to “learn” the relationship between inputs and outputs, and once trained, it can use this relationship to predict the output for new, unseen data.
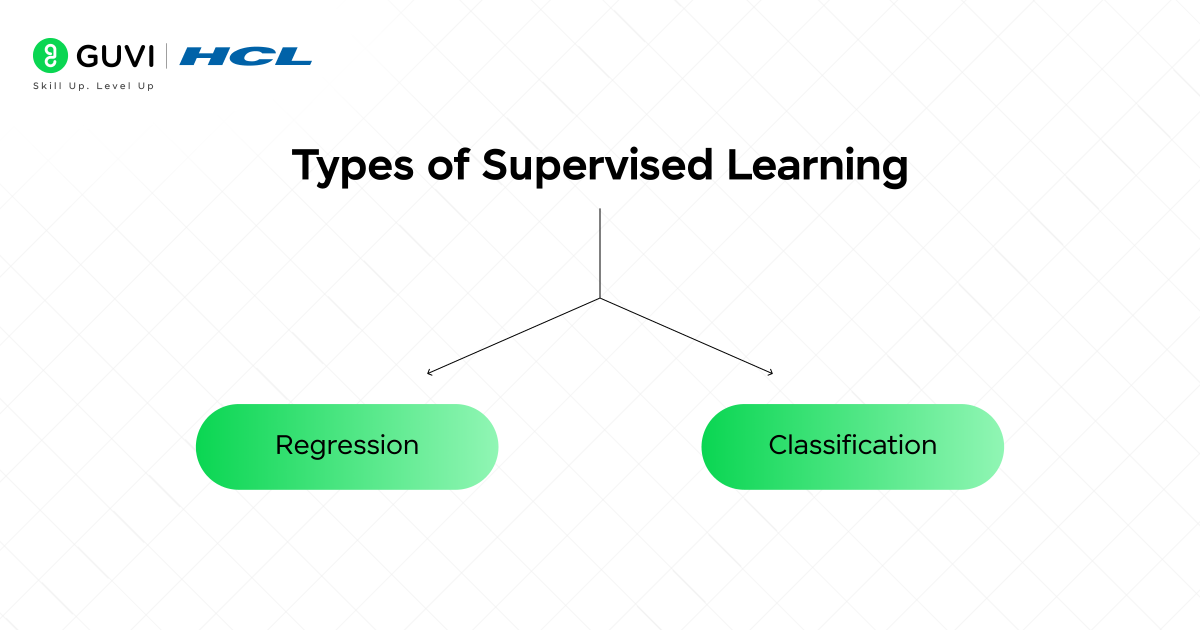
1.1 Regression:
Regression aims to predict a continuous numeric value. Rather than putting data into a class, a model tries to look for a trend or relationship between some input features and a number-based output.
Some examples of regression are:
- Guessing how much a house will cost depending on its area, location, and number of rooms.
- Guessing how much electricity will be used next month.
- Figuring out how much an employee will make based on their skills and experience.
Widely Used Regression Algorithms:
- Linear Regression
- Polynomial Regression
- Ridge Regression
- Lasso Regression
- Decision Tree Regressor
- Random Forest Regressor
1.2 Classification
Classification is used when, instead of predicting numbers, we are trying to predict categories or labels. The output can belong to a finite or discrete class. In other words, the algorithm learns patterns from the input data and predicts which class the new data point falls into.
Some examples of Classification are:
- Determining if an email is spam or not.
- Predicting if a student will pass or fail an exam.
- Recognizing if an image includes a cat or a dog.
Widely Used Classification Algorithms:
- Logistic Regression
- Decision Tree
- Random Forest
- K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
- Support Vector Machines (SVM)
- Naive Bayes
2. Unsupervised Learning in Machine Learning
In supervised learning, you always have data with labels (answers), but in unsupervised learning, you have data that are not labeled. This means the algorithm is never given the “correct output.” Instead, it tries to find the pattern, groupings, or even structures that are hidden in the given data.
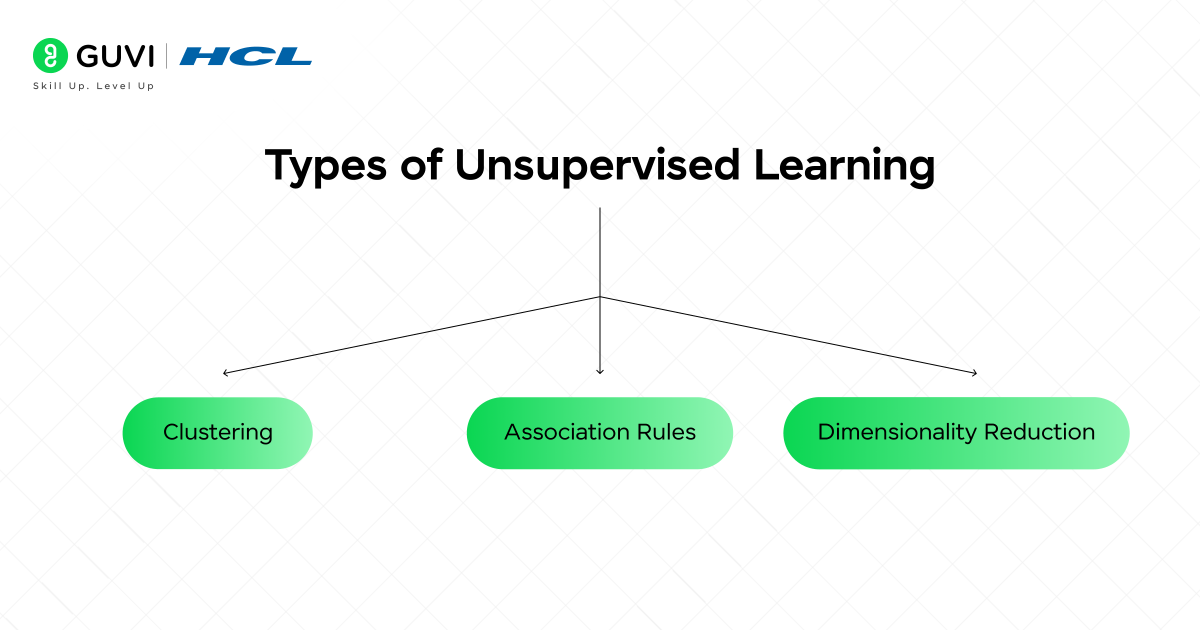
2.1 Clustering
Clustering is grouping similar data points to form groups or clusters, such that the items in the same cluster share common characteristics and are different from the items in the other clusters.
Some examples of Clustering are:
- Grouping customers into different segments for targeted marketing.
- Organizing articles or news stories into topics.
- Detecting communities in social networks.
Widely Used Clustering Algorithms:
- K-Means Clustering
- Hierarchical Clustering
- DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering)
- Mean Shift
2.2 Association
Association Rule Learning identifies the hidden relationships, correlations or patterns among variables within large datasets. It does not predict outcomes. Instead, it discovers if–then rules that depict how items or actions are associated with each other.
Think of it like this: “If event A occurs, what is the probability that event B also occurs?”
Some examples of Association Rule Learning are:
- Finding that customers who buy bread also often buy butter.
- Recommending movies based on what other users with similar tastes watched.
- Suggesting additional products on e-commerce websites.
Widely Used Association Algorithms:
- Apriori Algorithm
- Eclat Algorithm
- FP-Growth Algorithm
2.3 Dimensionality Reduction
Dimensionality reduction is used to make complex datasets with numerous features less complex. It reduces input variables but also maintains important information intact. Dimensionality reduction makes it easier to visualize, speeds up computation, and removes noise in the data.
Some examples of Dimensionality Reduction are:
- Compressing images without losing important details.
- Visualizing high-dimensional data in 2D or 3D for easier understanding.
- Speeding up machine learning models by removing redundant features.
Widely Used Dimensionality Reduction Algorithms:
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
In most machine learning projects, nearly 80% of the time is spent on cleaning and preparing data, not building models. Raw data often has missing values, errors, or duplicates that can mislead algorithms. Data scientists work on removing noise, labeling datasets, and formatting features so models can perform accurately. This is why experts say: “Better data beats better algorithms.”
Difference between Supervised and Unsupervised Learning
| Aspect | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
| Data | Uses labeled data (input + output). | Uses unlabeled data (only input). |
| Goal | Predict outcomes (values or categories). | Find hidden patterns or groups. |
| Examples | Spam email detection, house price prediction. | Customer segmentation, market basket analysis. |
| Algorithms | Linear Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest, SVM. | K-Means, Hierarchical Clustering, PCA, Apriori. |
| Output | Known results (categories/numbers). | Unknown structures (clusters/associations). |
3. Semi-Supervised Learning in Machine Learning
As the name suggests, semi-supervised learning is a mix of both supervised and unsupervised learning; that is, it uses both labeled and unlabeled data. Since labeling data can be expensive and time-consuming, this method helps when you have only a small amount of labeled data.
Example:
Suppose a hospital is creating an AI that can identify medical diseases based on scans of X-ray images. However, labeling medical images requires expert doctors and is time-consuming and expensive. The hospital can get a minimal set of X-rays labeled as “disease” and “healthy” and has a lot of unlabeled X-rays.
In semi-supervised learning, the model initially learns from a limited set of labeled X-rays and subsequently leverages a large volume of unlabeled X-rays to enhance its understanding. By integrating the unlabeled data with the labeled data, the AI can increase its accuracy without the need for every X-ray to be labeled by a doctor.
Some of the Common Approaches are:
- Self-training
- Graph-based Models
- Label propagation
4. Reinforcement Learning in Machine Learning
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a type of machine learning where an agent learns by interacting with an environment. Instead of being given correct answers like in supervised learning, the agent learns from feedback in the form of rewards or penalties.
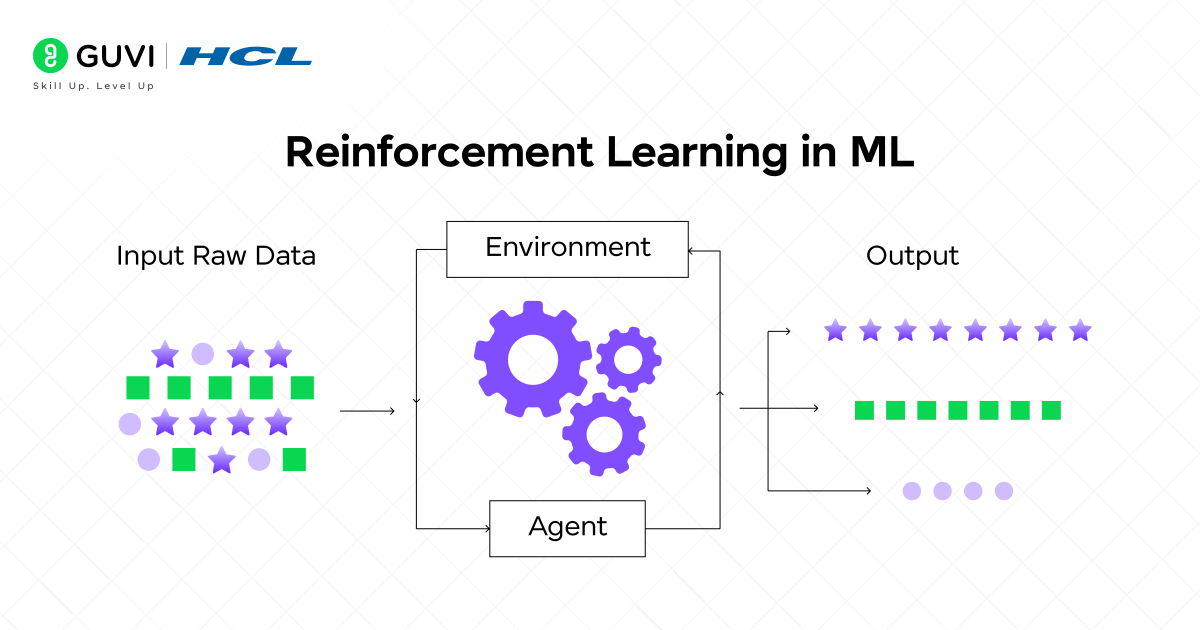
Example:
Think of a self-driving car. The car is the agent, and the road serves as the environment. When the car follows traffic rules, for example, it stops at a red light, then it gets a reward of some sort. If the car violates traffic rules, for example, it runs a red light, then it receives a penalty. Eventually, the car learns how to drive most safely and effectively.
Widely Used RL Algorithms:
- Q-learning
- Deep Q-learning
- SARSA (State–Action–Reward–State–Action)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Types of Learning in Machine Learning
| Learning Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Supervised Learning | – Produces accurate results with enough labeled data. – Easy to understand and implement. – Works well for classification and regression tasks. | – Requires a large amount of labeled data (time-consuming & costly). – Struggles with unseen or noisy data. |
| Unsupervised Learning | – Can discover hidden patterns and relationships in data. – Useful when labeled data is not available. – Good for clustering and dimensionality reduction. | – Results may be less accurate. – Harder to interpret outcomes.- May group data incorrectly without context. |
| Reinforcement Learning | – Learn from interaction with the environment. – Useful for decision-making and automation. – Improves performance with experience. | – Training takes a long time. – Requires lots of trial and error. – May need high computational resources. |
| Semi-Supervised Learning | – Reduces the need for large labeled datasets. – Combines strengths of supervised and unsupervised learning. – Improves accuracy over unsupervised learning. | – Still requires some labeled data. – More complex than supervised/unsupervised methods. |
Check out GUVI’s Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Course, certified by Intel and IIT-M Pravartak. Designed by industry experts, this course will help you gain real-world skills, build hands-on projects, and prepare for top tech jobs.
Final thoughts..
Hope this blog has helped you gain a better understanding of the different ways of learning in machine learning. If you are just starting out, don’t worry. Stay focused on the basic concepts such as supervised and unsupervised learning, and then proceed to advanced methods such as reinforcement or self-supervised learning.
It may seem overwhelming at first and that is understandable. However, with practice and a lot of curiosity, you will quickly see that machine learning is not as complicated as it appears. Remember, experts were once beginners just like you are now. So keep experimenting, keep learning and you will soon be building smart applications!
1. Why do we need machine learning?
Machine learning is crucial, as it enables computers to learn directly from data, make predictions, and adapt their processes without the need for explicit programming. It is utilized in practical applications such as recommendation systems, fraud detection, and voice assistants.
2. Which type of learning is best for beginners to start with?
Beginners often start with Supervised Learning because it is easy to understand, has practical applications, and is frequently used in areas like spam detection and house price prediction.
3. Do I need coding skills to learn machine learning?
Basic knowledge in Python will get you started. However, there are many tools and platforms that provide no-code ML solutions, so you can learn the concepts without needing to learn deep coding skills.
4. What are the advantages of machine learning approaches?
Automates repetitive tasks.
Handles large and complex datasets.
Improves decision-making with better accuracy.
Learns and adapts from new data.




























Did you enjoy this article?