
What is Software Development? A Beginner’s Guide
Oct 23, 2025 6 Min Read 2923 Views
(Last Updated)
Have you ever wondered how your favorite app or video game came to life? From the simple note-taking application on your phone to complex enterprise software running global businesses, they all exist thanks to software development.
But what exactly is software development, and how does it work? In this article, we’ll explore software development in a beginner-friendly way, covering its definition, importance, key processes, methodologies, and the roles involved.
By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of the foundations of software development and why it matters in today’s digital world.
Table of contents
- Understanding Software Development
- Types of Software
- Why Software Development Matters?
- The Software Development Process (SDLC)
- Planning & Requirements Analysis
- Design
- Development (Implementation)
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance & Updates
- Software Development Methodologies
- Roles in a Software Development Team
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is software development in simple words?
- What are the main types of software development?
- Which skills are required for software development?
- What is the difference between frontend and backend development?
- How long does it take to learn software development?
Understanding Software Development

At its core, software development is the process of creating computer programs or applications that perform specific tasks or solve particular problems. In simpler terms, it’s like building virtual tools or machines that tell a computer what to do.
This involves several activities – from designing the software’s structure, to coding it in a programming language, then testing it for bugs, and finally maintaining or updating it over time. Software itself is essentially a set of instructions (code) that directs hardware (the physical computer) to carry out tasks, making computers programmable and useful.
Types of Software
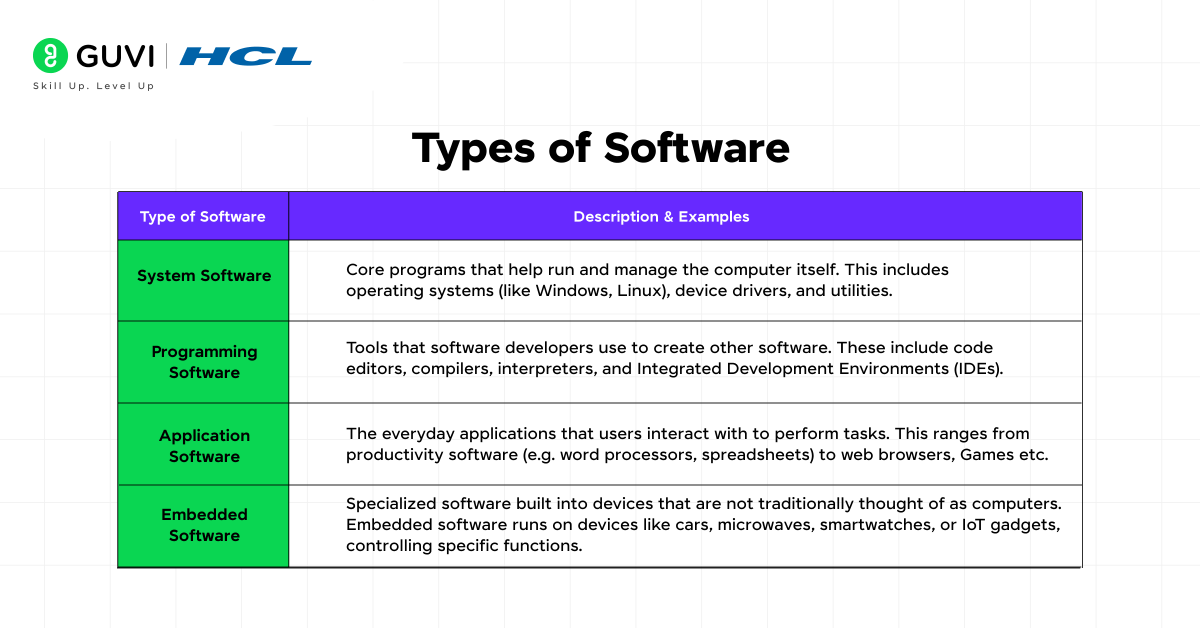
Not all software is the same. We can broadly categorize software into different types, each serving different purposes. Here are some major types of software:
| Type of Software | Description & Examples |
| System Software | Core programs that help run and manage the computer itself. This includes operating systems (like Windows, Linux), device drivers, and utilities. |
| Programming Software | Tools that software developers use to create other software. These include code editors, compilers, interpreters, and Integrated Development Environments (IDEs). |
| Application Software | Specialized software is built into devices that are not traditionally thought of as computers. Embedded software runs on devices like cars, microwaves, smartwatches, or IoT gadgets, controlling specific functions. |
| Embedded Software | Specialized software built into devices that are not traditionally thought of as computers. Embedded software runs on devices like cars, microwaves, smartwatches, or IoT gadgets, controlling specific functions. |
Understanding these categories helps clarify what software development can target – from developing a new mobile application to writing low-level code for an embedded device.
Why Software Development Matters?

Software development isn’t just a technical exercise – it has a huge real-world impact. We live in a software-driven world where almost every aspect of life touches software. Software development plays an important role in our daily lives, empowering everything from smartphone apps to business operations worldwide.
Here are some key benefits and reasons why software development matters:
- Digital Transformation: Industries across the globe rely on software development to transform their services and operations into the digital realm. From online banking to telemedicine, software enables organizations to become more accessible, efficient, and globally connected.
- Automation and Efficiency: Software often automates repetitive tasks and complex processes, reducing the need for manual effort. This not only saves time but also minimizes human errors.
- Enhanced User Experience: Good software development focuses on creating intuitive, user-friendly interfaces and experiences. When developers build applications with a strong emphasis on usability and design, technology becomes more approachable and enjoyable for people of all skill levels.
- Problem Solving and Innovation: At its heart, each piece of software is a solution to a problem. Whether it’s an app that makes our lives more convenient or a complex system that addresses challenges in healthcare or education, software development drives innovation.
- High-Demand Careers: Because software is so integral to modern life, skilled software developers are in high demand. The tech industry offers abundant career opportunities. In fact, employment of software developers is projected to grow rapidly in the coming years.
In short, software development matters because it powers innovation, improves efficiency, enhances our daily experiences, and drives economic growth. Everything from the app you use to order food to the systems that run public transportation exists thanks to software development.
The Software Development Process (SDLC)
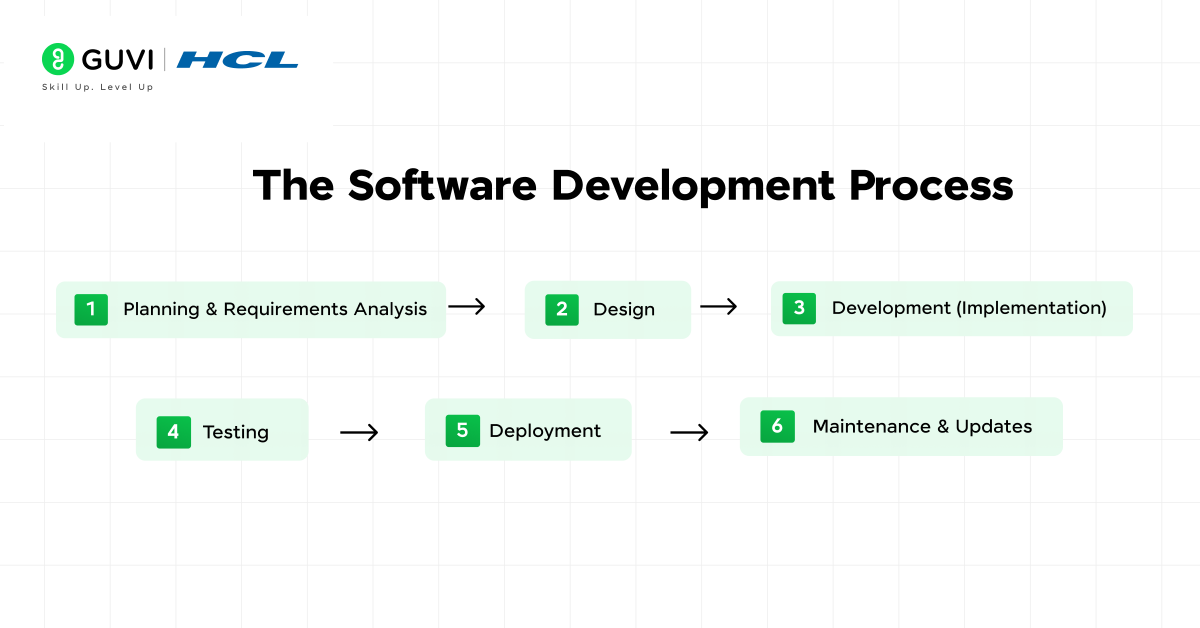
So, how do we develop software? Most software is built through a structured process known as the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). The SDLC breaks down the work into stages or steps that guide a project from an initial idea to a finished product.
While there are variations of this process, a typical software development process includes the following stages:
1. Planning & Requirements Analysis
Every successful software project starts with careful planning. In this stage, the goal is to understand what needs to be built and why. Developers and stakeholders gather and analyze requirements – essentially the features, functions, and constraints of the software.
This involves:
- Talking to end-users or clients to identify their needs and documenting what the software should achieve (often in a Requirements Specification).
- Planning also covers feasibility analysis, defining the project scope, and estimating resources (time, people, and budget) needed.
- A clear plan and requirement analysis set the foundation, ensuring the team knows the exact problem to solve before writing a single line of code.
2. Design
Once the requirements are clear, the next step is designing a solution. In the design phase, developers and architects outline how the software will work. This is like creating a blueprint for the application. It includes:
- Designing the overall software architecture (the high-level structure and components), the database schema if needed, and the user interface layouts.
- The team might create diagrams (using UML or other design tools) to map out components and how they interact. They also make decisions about technologies or frameworks to use.
- A good design phase results in detailed specifications that will guide the programmers in the next phase. Essentially, it translates the “what” from the requirements into the “how” of building the software.
3. Development (Implementation)
The development phase (also called implementation or coding) is where the design truly comes to life. Here, software developers write the actual code according to the design specifications. They choose appropriate programming languages (such as Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, etc., depending on the project) and start building the features.
This stage can be the longest, as it involves constructing all the functionality of the software and ensuring that different components work together. Developers often build and test small units of the software incrementally.
They also perform debugging during this phase – finding and fixing errors in the code to make sure each part behaves correctly. By the end of development, the team has a working software application ready for the next step.
4. Testing
Before any software is released, it must be tested thoroughly. The testing phase is all about quality assurance – verifying that the software does what it’s supposed to do and identifying any defects (bugs) that need fixing.
Testers run the application through various scenarios:
- They perform unit tests on individual functions
- Integration tests on how modules work together.
- System tests on the entire application.
They also check edge cases and ensure the software handles errors gracefully. In some projects, user acceptance testing is done, where actual users try the software to see if it meets their needs.
The term “debugging” (for fixing software bugs) originated in 1947 when engineers literally found a moth stuck in a Harvard Mark II computer, causing an error. This was jokingly logged as the first actual computer bug, and ever since, fixing errors in code has been called debugging!.
5. Deployment
Deployment is the stage where the software is released into the real world. After testing is complete and the product is deemed stable, it’s deployed to the production environment (for example, uploaded to an app store or installed on a server for users to access).
Deployment can involve setting up servers or cloud infrastructure, configuring databases, and ensuring everything is ready for users.
6. Maintenance & Updates
After deployment, the software enters the maintenance phase, which is an ongoing process. Real users may encounter bugs or request new features, so developers need to continuously maintain the software.
Maintenance involves monitoring performance, fixing any new issues that arise, and making improvements or enhancements over time. Think of all the updates you get for apps – those are part of maintenance, adding features, or patching security holes.
Good software development is iterative; even post-launch, the team remains involved to ensure the software stays useful, secure, and up-to-date. In many modern setups, maintenance is tightly coupled with deployment through continuous delivery practices (frequent small updates).
Software Development Methodologies
It’s worth noting that there are different methodologies or approaches to organizing the software development process. Methodologies provide a framework for how teams plan, structure, and execute the work.
Choosing a methodology can affect how flexible the process is to change and how quickly you can deliver software. Here are a few of the most common software development methodologies:
- Waterfall: The waterfall model is a traditional, linear approach to software development. It moves through each SDLC phase in sequence – first requirements, then design, then coding, and so on, without going back. Waterfall is straightforward to manage in terms of schedule, but it’s less flexible if requirements change mid-project.
- Agile: Agile is a modern approach that breaks the development process into smaller cycles or “sprints.” Instead of one big project delivered at the end, an agile team delivers in incremental pieces continuously. Agile methodologies (like Scrum or Kanban) embrace change – there’s a constant feedback loop, and the team can adjust the software as they go based on testing and user feedback.
- DevOps: DevOps is not just a methodology but a culture shift that combines development and IT operations. In DevOps, the same team (or closely collaborating teams) handles both writing the software and deploying/operating it. This approach emphasizes automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery (CI/CD) of software updates.
Roles in a Software Development Team

Software development is rarely a solo endeavor – it typically involves a team of professionals, each with specific roles and expertise to ensure the project’s success. Here are some of the common roles in a software development team:
- Software Developers / Programmers: These are the folks who write the code. They take the requirements or design and implement the actual software by programming. Developers need to be proficient in programming languages and are responsible for building features and fixing bugs.
- Quality Assurance (QA) / Testers: QA engineers or testers focus on the testing phase we discussed earlier. Their job is to catch issues in the software before it reaches users. They design test cases, run the software through various scenarios, and report bugs to the developers.
- UI/UX Designers: Not every software team has dedicated designers, but for user-facing applications, this role is crucial. UI (User Interface) designers decide how the software looks – the layout of screens, color schemes, buttons, and icons. UX (User Experience) designers ensure the software is intuitive and satisfying to use.
- Project Managers / Product Managers: These members oversee the project’s progress and alignment with goals. A project manager coordinates tasks, timelines, and communication among the team. They make sure the project stays on schedule and within scope, and they often serve as a liaison between the development team and other stakeholders (like the client or management).
- DevOps Engineers: In teams adopting DevOps practices, DevOps specialists manage the infrastructure and deployment processes. They create automated pipelines for building, testing, and deploying code to production. They are responsible for things like configuring cloud services, monitoring applications in production, and ensuring the system is reliable and scalable.
All these roles collaborate closely. If you’re just getting into software development, you’ll likely start as a programmer/developer, but it’s good to understand the bigger team picture in which software is built.
If you’re serious about mastering software development and want to apply it in real-world scenarios, don’t miss the chance to enroll in HCL GUVI’s IITM Pravartak and MongoDB Certified Online AI Software Development Course. Endorsed with NSDC certification, this course adds a globally recognized credential to your resume, a powerful edge that sets you apart in the competitive job market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, software development is a vast, exciting field that serves as the backbone of our modern digital world. For beginners, the key takeaway is that software development is a blend of creative problem-solving and a systematic process. It’s about understanding people’s needs and crafting software solutions to meet those needs.
If you’re intrigued by this process, there’s a lot more to explore – from learning programming languages and algorithms, to experimenting with building your simple projects. The world of software development is continually evolving, but the foundational concepts you’ve read about here will remain relevant throughout your learning journey.
Now that you have a grasp of the basics, you can appreciate the software around you with new eyes – and perhaps even take the first steps towards developing software yourself. Happy coding!
FAQs
1. What is software development in simple words?
Software development is the process of creating computer programs or applications that perform specific tasks. It involves planning, designing, coding, testing, and maintaining software to meet a user’s needs.
2. What are the main types of software development?
The main types include:
– Web development
– Mobile app development
– Desktop software development
– Embedded systems development
– Game development
– Cloud and DevOps development
3. Which skills are required for software development?
Key skills include knowledge of programming languages (like Python, Java, C++), problem-solving, understanding of algorithms and data structures, version control (Git), and familiarity with databases, software testing, and development methodologies.
4. What is the difference between frontend and backend development?
Frontend development deals with the part of the software users see and interact with (UI/UX).
Backend development focuses on the server-side logic, databases, and application infrastructure that make the frontend work.
5. How long does it take to learn software development?
The timeline varies depending on your learning pace and goals. Basic coding skills can be learned in 3–6 months, while mastering full software development (including multiple technologies and frameworks) can take 1–2 years or more.



































Did you enjoy this article?