What is a Double Ended Queue?
Introduction to Double Ended Queue
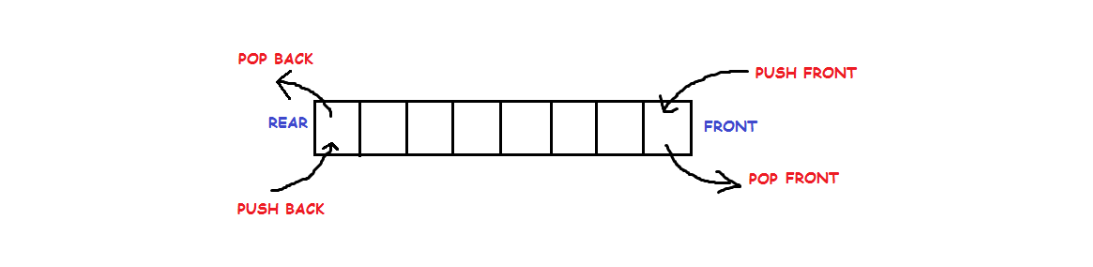
Double ended queue is a more generalized form of queue data structure which allows insertion and removal of elements from both the ends, i.e , front and back.
Implementation of Double ended Queue
Here we will implement a double ended queue using a circular array. It will have the following methods:
- push_back : inserts element at back
- push_front : inserts element at front
- pop_back : removes last element
- pop_front : removes first element
- get_back : returns last element
- get_front : returns first element
- empty : returns true if queue is empty
- full : returns true if queue is full
// Maximum size of array or Dequeue
#define SIZE 5
class Dequeue
{
//front and rear to store the head and tail pointers
int *arr;
int front, rear;
public :
Dequeue()
{
//Create the array
arr = new int[SIZE];
//Initialize front and rear with -1
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// Operations on Deque
void push_front(int );
void push_back(int );
void pop_front();
void pop_back();
int get_front();
int get_back();
bool full();
bool empty();
};Insert Elements at Front
First we check if the queue is full. If its not full we insert an element at front end by following the given conditions :
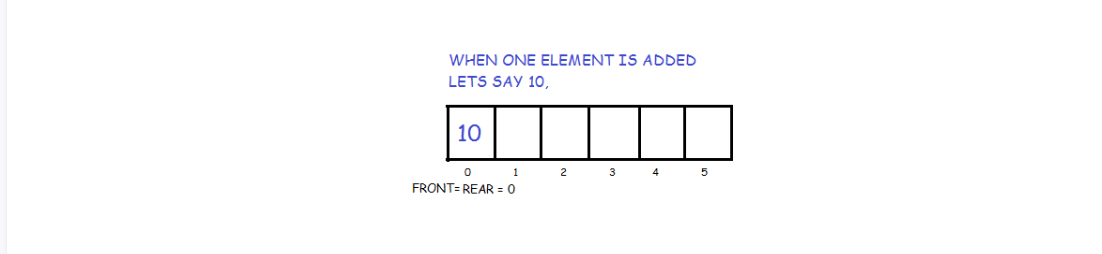
If the queue is empty then intialize front and rear to 0. Both will point to the first element
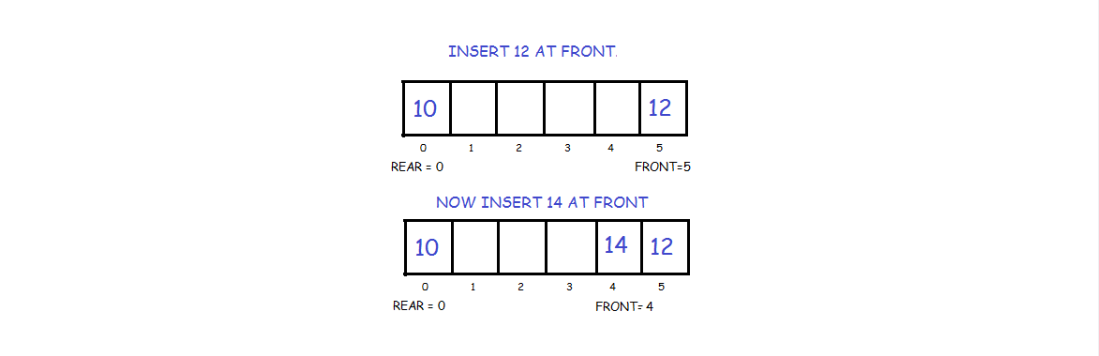
Else we decrement front and insert the element. Since we are using circular array, we have to keep in mind that if front is equal to 0 then instead of decreasing it by 1 we make it equal to SIZE-1.
void Dequeue :: push_front(int key)
{
if(full())
{
cout << "OVERFLOW\n";
}
else
{
//If queue is empty
if(front == -1)
front = rear = 0;
//If front points to the first position element
else if(front == 0)
front = SIZE-1;
else
--front;
arr[front] = key;
}
}Insert Elements at back
Again we check if the queue is full. If its not full we insert an element at back by following the given conditions:
- If the queue is empty then intialize front and rear to 0. Both will point to the first element.
- Else we increment rear and insert the element. Since we are using circular array, we have to keep in mind that if rear is equal to SIZE-1 then instead of increasing it by 1 we make it equal to 0.
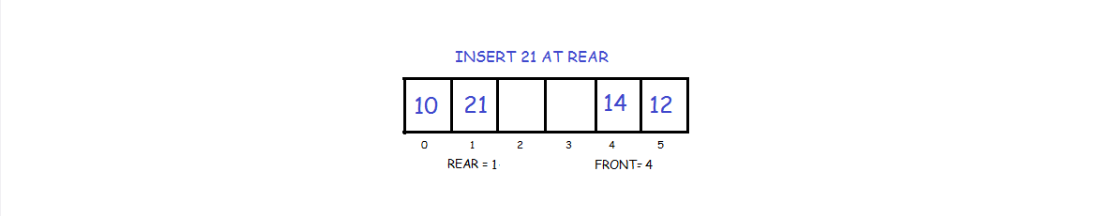
void Dequeue :: push_back(int key)
{
if(full())
{
cout << "OVERFLOW\n";
}
else
{
//If queue is empty
if(front == -1)
front = rear = 0;
//If rear points to the last element
else if(rear == SIZE-1)
rear = 0;
else
++rear;
arr[rear] = key;
}
}Delete First Element
In order to do this, we first check if the queue is empty. If its not then delete the front element by following the given conditions :
- If only one element is present we once again make front and rear equal to -1.
- Else we increment front. But we have to keep in mind that if front is equal to SIZE-1 then instead of increasing it by 1 we make it equal to 0.
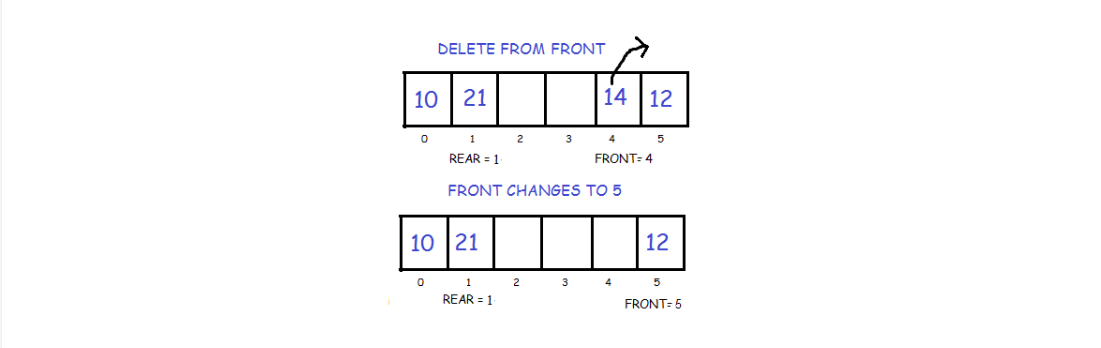
void Dequeue :: pop_front()
{
if(empty())
{
cout << "UNDERFLOW\n";
}
else
{
//If only one element is present
if(front == rear)
front = rear = -1;
//If front points to the last element
else if(front == SIZE-1)
front = 0;
else
++front;
}
}Delete Last Element
Inorder to do this, we again first check if the queue is empty. If its not then we delete the last element by following the given conditions :
- If only one element is present we make front and rear equal to -1.
- Else we decrement rear. But we have to keep in mind that if rear is equal to 0 then instead of decreasing it by 1 we make it equal to SIZE-1.
void Dequeue :: pop_back()
{
if(empty())
{
cout << "UNDERFLOW\n";
}
else
{
//If only one element is present
if(front == rear)
front = rear = -1;
//If rear points to the first position element
else if(rear == 0)
rear = SIZE-1;
else
--rear;
}
}Check if Queue is empty
It can be simply checked by looking where front points to. If front is still intialized with -1, the queue is empty.
bool Dequeue :: empty()
{
if(front == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}Check if Queue is full
Since we are using circular array, we check for following conditions as shown in code to check if queue is full.
bool Dequeue :: full()
{
if((front == 0 && rear == SIZE-1) ||
(front == rear + 1))
return true;
else
return false;
}Return First Element
If the queue is not empty then we simply return the value stored in the position which front points.
int Dequeue :: get_front()
{
if(empty())
{ cout << "f=" <<front << endl;
cout << "UNDERFLOW\n";
return -1;
}
else
{
return arr[front];
}
}Return Last Element
If the queue is not empty then we simply return the value stored in the position which rear points.
int Dequeue :: get_back()
{
if(empty())
{
cout << "UNDERFLOW\n";
return -1;
}
else
{
return arr[rear];
}
}