
Top 40 MEAN Stack Developer Interview Questions and Answers
Nov 27, 2025 6 Min Read 8474 Views
(Last Updated)
As a MEAN Stack developer, you’re working with four powerful tools: MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js. Together, these technologies help build dynamic, full-stack applications that are highly scalable.
If you’re preparing for a MEAN Stack developer interview questions and answers, you’re likely to encounter questions that gauge your understanding of each component, coding proficiency, and ability to apply MEAN Stack principles in real-world scenarios.
This article covers 40 MEAN stack developer interview questions and answers that are split into three levels – Fresher, Intermediate, Advanced and Scenario-based questions ,to help you prepare and excel. Let’s get started!
Quick Answer
MEAN Stack interviews mainly test how well you understand MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js, and how you use them together to build full-stack applications. You’ll be asked about REST APIs, authentication, schema design, Angular components, and handling backend logic in Node.
Table of contents
- MEAN Stack Developer Interview Questions and Answers
- Fresher Level
- Intermediate Level
- Advanced Level
- Scenario-Based Questions
- Conclusion
MEAN Stack Developer Interview Questions and Answers

Here are 30 MEAN stack developer interview questions and answers designed to equip you with the essentials.
Fresher Level
1. What is the MEAN Stack?
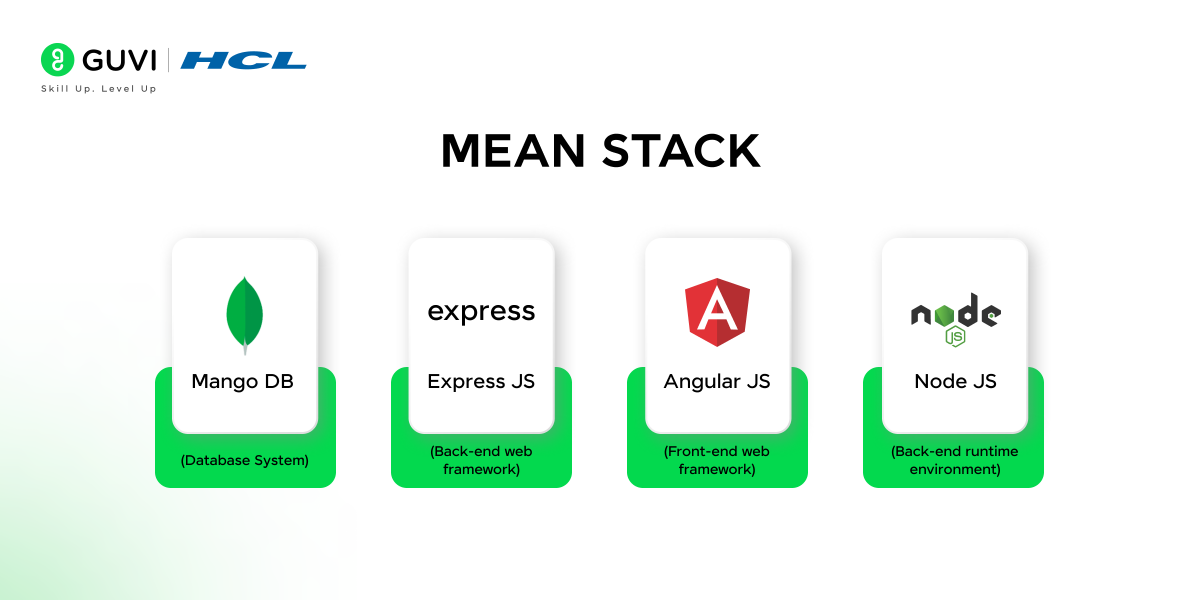
The MEAN Stack is a combination of four open-source technologies: MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js. Together, they enable developers to create dynamic end-to-end JavaScript applications. MongoDB serves as the database, Express.js as the backend framework, Angular as the frontend framework, and Node.js as the server environment.
2. Explain the role of each component in the MEAN Stack.
- MongoDB: A NoSQL database where data is stored in a JSON-like format.
- Express.js: A lightweight backend framework that helps manage routes and middleware.
- Angular: A frontend framework used for building the user interface and single-page applications.
- Node.js: A server-side platform that allows JavaScript to be used for server-side scripting.
3. How is MEAN Stack different from other stacks, like LAMP?
The main difference lies in the use of JavaScript across all parts of the application in the MEAN Stack. In contrast, the LAMP stack uses different languages, like PHP and MySQL. MEAN offers the advantage of a unified language (JavaScript) from client to server, which simplifies development and makes code more reusable.
4. What is Node.js, and why is it used in the MEAN Stack?
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 engine. It allows developers to run JavaScript code on the server, which is why it’s used in the MEAN Stack for backend operations.
5. Explain how MongoDB stores data.
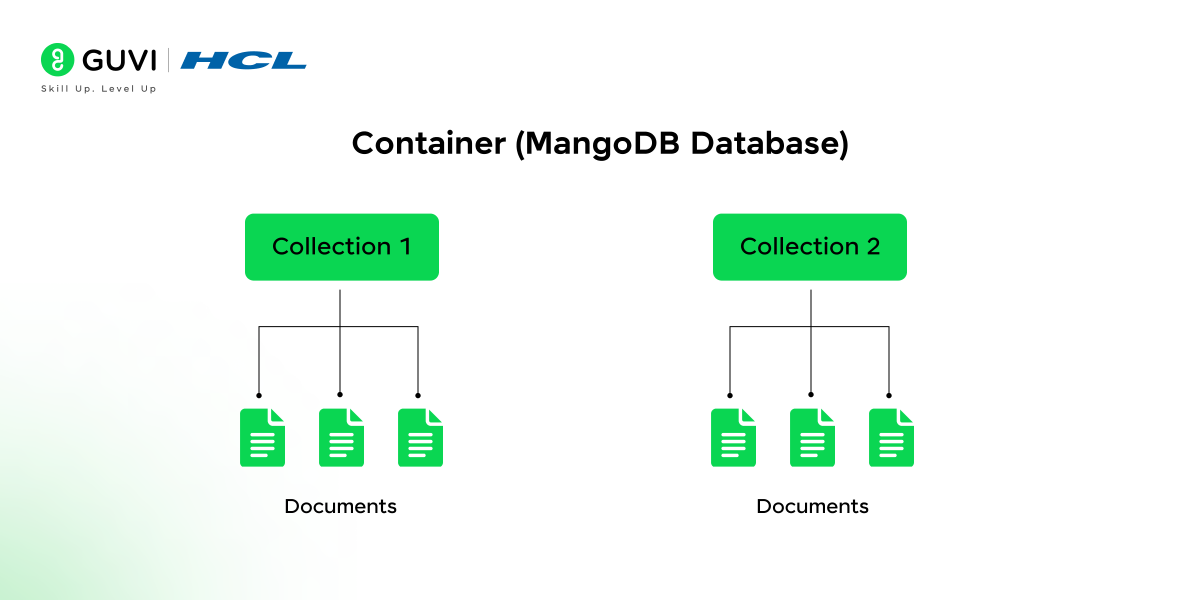
MongoDB stores data in collections of documents in a JSON-like format, making it a flexible, schema-less NoSQL database that easily scales horizontally.
6. Write a basic MongoDB query to retrieve all documents in a collection.
javascript
db.collectionName.find({})
This command fetches all documents from the specified collection.
7. What is a REST API, and how does Express help create one?
A REST API allows interaction with backend services through HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. Express simplifies creating REST APIs by providing a framework to handle routing, middleware, and request handling.
Intermediate Level
8. How do you handle errors in Express?
In Express, errors are typically managed by middleware. A custom error-handling middleware function can be written and used across routes to log and respond to errors consistently.
javascript
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.error(err.stack);
res.status(500).send('Something went wrong!');
});9. What is dependency injection in Angular, and why is it used?
Dependency Injection (DI) in Angular is a design pattern where services or dependencies are injected into components instead of being created within them. This improves modularity, testability, and flexibility by keeping components loosely coupled.
10. How do you create and export a module in Node.js?
To create and export a module in Node.js:
javascript
// File: myModule.js
module.exports = {
sayHello: function() {
console.log("Hello, MEAN Stack!");
}
};You can then import this module in another file:
javascript
const myModule = require('./myModule');
myModule.sayHello();11. What is the purpose of Mongoose in a MEAN application?
Mongoose is an Object Data Modeling (ODM) library that provides schema validation and a more straightforward way to interact with MongoDB from a Node.js application.
12. How do you handle CORS in a MEAN Stack application?
In a MEAN Stack application, Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) can be handled using the cors middleware in Express.
javascript
const cors = require('cors');
app.use(cors());This setup allows requests from different origins, which is essential for frontend-backend communication in MEAN Stack applications.
13. Explain the difference between AngularJS and Angular.
AngularJS (Angular 1.x) is the original version of Angular, using JavaScript. Angular (2+) is a complete rewrite using TypeScript, with improved performance, modularity, and tooling.
14. Write a sample Express route to handle a POST request.
javascript
app.post('/submit', (req, res) => {
const data = req.body;
// Process data here
res.send('Data received');
});This code defines a route that handles POST requests, typically used to send data to the server.
15. How do you define a schema in Mongoose?
javascript
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
email: String,
age: Number
});
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);This code defines a schema for users with name, email, and age fields.
Advanced Level
16. What are Promises and async/await in Node.js?
Promises are JavaScript objects that represent the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. async and await are syntactic sugars in Node.js that make asynchronous code look and behave more like synchronous code.
17. Explain the role of Angular services and how they facilitate data sharing.
Angular services are singleton objects that can store and manage data shared across multiple components. They are ideal for encapsulating business logic and making it reusable and maintainable.
18. How does MongoDB’s aggregation framework work?
The aggregation framework in MongoDB processes data records and returns computed results. It’s typically used for tasks like data transformation, filtering, and summarizing.
19. Write an example of an aggregation pipeline to group users by age.
javascript
db.users.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$age", count: { $sum: 1 } } }
]);This command groups users by their age and provides a count of each age group.
20. What is an Observable in Angular?
Observables are part of the Reactive Extensions for JavaScript (RxJS) library. They handle asynchronous data streams and enable reactive programming, which is fundamental for real-time applications in Angular.
21. Explain the difference between the PUT and PATCH methods.
- PUT is used to update a resource entirely.
- PATCH is used to make partial updates to a resource.
22. How do you optimize a MEAN Stack application for performance?
To optimize a MEAN Stack application:
- Use MongoDB indexing.
- Optimize middleware in Express.
- Minify and bundle Angular assets.
- Use caching techniques, such as Redis.
23. Write a middleware function to log requests in Express.
javascript
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(`Request URL: ${req.url}, Method: ${req.method}`);
next();
});This middleware logs the URL and HTTP method of each request.
24. What are Angular Guards, and how do they enhance security?
Angular Guards prevent unauthorized access to routes. Common guards include CanActivate, CanDeactivate, and Resolve, which are used to control access and navigation.
25. Explain JWT and how it is used in MEAN Stack applications.
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are used to securely transmit information between client and server. They are commonly used for user authentication, where the server generates a JWT on login, and the client includes it in subsequent requests.
26. Write code to generate and verify a JWT in Node.js.
javascript
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const secret = 'your_secret_key';
// Generating a JWT
const token = jwt.sign({ userId: 123 }, secret, { expiresIn: '1h' });
// Verifying a JWT
jwt.verify(token, secret, (err, decoded) => {
if (err) {
console.log("Token is invalid");
} else {
console.log("Token is valid", decoded);
}
});27. How do you handle environment variables in a MEAN application?
Environment variables can be managed with the dotenv package in Node.js:
javascript
require('dotenv').config();
const dbURL = process.env.DB_URL;28. Explain the purpose of Angular Interceptors.
Angular Interceptors allow you to modify HTTP requests and responses globally, often used for adding authentication headers or handling errors consistently.
29. How can you enable SSL in an Express.js server?
To enable SSL, you would use HTTPS with a server certificate:
javascript
const https = require('https');
const fs = require('fs');
const options = {
key: fs.readFileSync('server.key'),
cert: fs.readFileSync('server.cert')
};
https.createServer(options, app).listen(443);30. What is clustering in Node.js, and why is it used?
Clustering allows Node.js to utilize multiple CPU cores by creating worker processes. This enhances performance and ensures requests are managed efficiently by balancing load across multiple instances.
If you want to learn more about these popular MEAN stack frameworks and how they enhance your full-stack project, consider enrolling for HCL GUVI’s Certified Full Stack Development Course which teaches everything you need and will also provide an industry-grade certificate!
Scenario-Based Questions
31. Your API Built With Node.js Has Suddenly Slowed Down After Deployment. How Would You Diagnose And Fix It?
I would start by checking server logs, monitoring CPU/memory usage, and identifying any recent code changes. Then I’d use tools like Node.js Profiler or PM2 monitoring to detect bottlenecks. I would also test API response times using Postman or Load Testing tools, optimize slow database queries, and ensure no blocking functions freeze the event loop.
32. A User Complains That Their Changes Aren’t Reflecting On The Angular Frontend Even Though The API Works Fine. What Would You Check?
I’d check whether the Angular component is correctly subscribed to the API response, ensure change detection is triggered, confirm caching isn’t causing old data to display, and verify that the correct environment file (dev/prod) is being used. I’d also inspect the console for errors that might be preventing UI updates.
33. Your MongoDB Collection Is Growing Extremely Fast, And Some Queries Have Become Slow. What Would You Do?
I’d analyze which fields are queried frequently and add proper indexes. I’d also consider schema redesign if documents are becoming too large, archive old data into separate collections, and review query patterns to avoid full collection scans.
34. During Deployment, Your Angular App Shows A Blank Screen. What Steps Would You Take?
I’d check for path issues in angular.jsonVerify the production build was generated correctly, ensure that environment variables are set properly, inspect the browser console for 404 or TypeError messages, and confirm that the backend API URLs are correct in the production environment file.
35. Your Node.js Server Crashes Randomly Without Showing Clear Errors. How Would You Handle It?
I’d enable detailed logging, wrap risky operations in try–catch blocks, use process.on('uncaughtException') for diagnostics, and run the app under PM2 to track crash reports. Then I’d analyze logs to identify memory leaks, infinite loops, or unhandled promises causing the crash.
36. The Frontend Is Sending Data Correctly, But The Backend Receives Null Values. What Would You Investigate?
I’d confirm that the request body parser (like express.json()) is correctly configured, make sure headers like Content-Type: application/json are set, verify Angular’s form binding, and inspect whether the API expects a different field name from what the frontend sends.
37. Two Developers Pushed Conflicting Code That Broke A Feature. How Would You Resolve This?
I’d pull the latest code, run the app to reproduce the issue, check Git logs to identify the conflicting commits, merge them manually, test the feature end-to-end, and push a clean fix. I’d also suggest improving the branch strategy or PR reviews to avoid similar issues.
38. Your MongoDB Aggregation Pipeline Is Giving Incorrect Output. What Steps Would You Take To Debug It?
I’d run each stage individually in MongoDB Compass, review field names for consistency, inspect data types, and check whether $lookup or $group stages are using the correct keys. I’d also ensure the collection has the expected data before running the pipeline.
39. A Feature Works On Localhost But Breaks On The Production Server. What Would You Check?
I’d compare environment variables, API endpoints, MongoDB connection details, and build configurations. I’d check browser console errors, inspect network requests, and ensure production security settings (CORS, HTTPS, rate limiters) aren’t blocking functionality
40. Your Angular Form Works, But Validation Messages Are Not Appearing. What Would You Do?
I’d ensure form controls are correctly linked, validators are applied, and the template conditions are used touched, dirty, or invalid checks. I’d also verify whether error messages are inside the correct form group and if change detection is updating the UI.
Conclusion
In conclusion, preparing for MEAN Stack developer interviews requires a solid grasp of each component in the stack, as well as practical coding skills.
By reviewing these questions across fresher, intermediate, advanced, and scenario-based levels, you’re ready to tackle a wide range of topics that showcase your knowledge and technical proficiency. Good luck!
































Did you enjoy this article?