
How AI Works? A Comprehensive Guide
Sep 09, 2025 6 Min Read 28317 Views
(Last Updated)
AI is as big, if not bigger, than the internet, smartphones, cloud computing, and apps, according to Tim Cook, CEO of Apple.
This statement from a technology leader of his stature is enough to prove the dominance of AI. Also, according to PwC research, artificial intelligence could contribute up to 15.7 trillion dollars to the global economy by 2030, which shows how central AI has become in shaping technology and business.
Understanding how AI works helps in making sense of the process of AI and the way AI functions affects decision-making in many industries. Businesses and individuals benefit from understanding how data ingestion to prediction works, as well as the roles of model training and inference in improving outcomes.
Read the rest of this blog to see how sense–reason–act principles, algorithmic reasoning, and a feedback loop guide the process of AI from start to finish.
Approximately 42% of enterprise-scale organizations (with over 1,000 employees) have actively deployed AI in their operations, while 40% are exploring or experimenting with it.
Around 89% of small businesses use AI tools for tasks such as writing emails and analyzing data.
As of 2025, 78% of businesses report using AI in at least one function—up from 55% just a year earlier.
Table of contents
- The Process of AI: An Overview
- How Does Artificial Intelligence Work? A Step-by-Step Guide
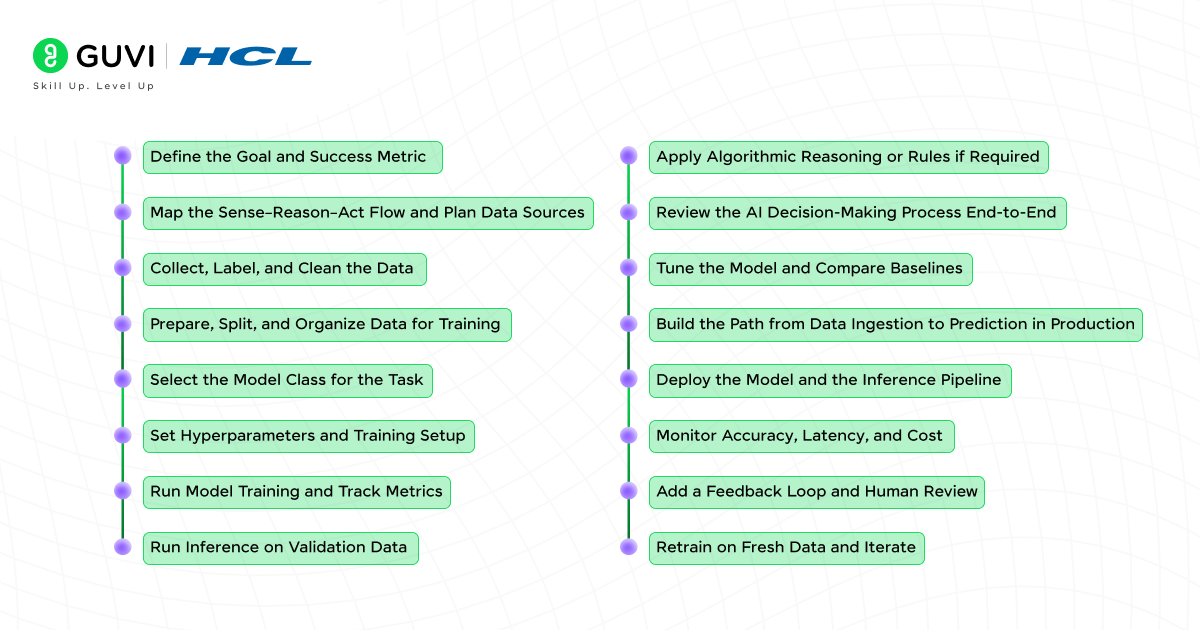
- Step 1: Define the Goal and Success Metric
- Step 2: Map the Sense–Reason–Act Flow and Plan Data Sources
- Step 3: Collect, Label, and Clean the Data
- Step 4: Prepare, Split, and Organize Data for Training
- Step 5: Select the model class for the task
- Step 6: Set hyperparameters and training setup
- Step 7: Run model training and track metrics
- Step 8: Run inference on validation data
- Step 9: Apply algorithmic reasoning or rules if required
- Step 10: Review the AI decision-making process end-to-end
- Step 11: Tune the model and compare baselines
- Step 12: Build the path from data ingestion to prediction in production
- Step 13: Deploy the model and the inference pipeline
- Step 14: Monitor accuracy, latency, and cost
- Step 15: Add a feedback loop and human review
- Step 16: Retrain on fresh data and iterate
- Quick Quiz: How Well Do You Understand AI?
- Answers
- Conclusion
- FAQs
The Process of AI: An Overview
The process of AI starts with data and ends with action. Understanding how AI works relies on structured steps, often powered by machine learning, that allow systems to sense their environment and reason about the information. This sense–reason–act sequence is the foundation of many AI applications.
AI decision-making depends on data ingestion followed by model training and inference. Data ingestion to prediction is a chain of tasks where each step affects the accuracy of the outcome. Algorithmic reasoning further allows AI to evaluate patterns and select the most suitable action. Whether in healthcare, finance, or autonomous systems, this process of AI is applied to make accurate predictions and decisions in real-world scenarios.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Work? A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Define the Goal and Success Metric
Every AI project starts with a clear and measurable goal that directs the entire process. The goal should specify exactly what the AI system must achieve, such as “reduce delivery time to under two hours.” Alongside the goal, set a success metric that shows whether progress is being made.
Accuracy works well for classification, mean squared error for regression, and F1 score when precision and recall both matter. The goal shapes the process, and the metric measures its success.
Step 2: Map the Sense–Reason–Act Flow and Plan Data Sources
Once the goal is set, define how the AI will sense, reason, and act. This defining phase will play a pivotal part in the ultimate AI functioning.
- Sense is gathering inputs such as text, images, sensor readings, or historical records.
- Reason is algorithmic processing, where patterns are analyzed and decisions formed.
- An act is producing an output or action with real-world impact.
Planning data sources ensures the sensing stage runs smoothly. Decide whether data will be processed in real time or batches. Then, select reliable sensors or databases and design a storage approach for structured and unstructured data. Include validation checks so that only accurate and complete information enters the system.
Step 3: Collect, Label, and Clean the Data
Data collection should strictly follow the plan and focus on gathering the right type of information. Accurate labels are essential for supervised models.
During the data collection stage:
- Gather enough relevant data to support effective training.
- Apply precise labels that match real-world scenarios.
Step 4: Prepare, Split, and Organize Data for Training
Next, clean the dataset to remove duplicates and missing values, and standardize formats. Incomplete entries can be filled with calculated estimates or removed. Clean and consistent data strengthens model learning and supports better predictions.
After data cleaning, convert raw inputs into features or embeddings so the model can interpret them after cleaning.
- Select only features relevant to the goal.
- Encode categories into numbers.
- Create embeddings for text or image tasks.
Finally, split the data into training, validation, and test sets: often 70% for training, 15% for validation, and 15% for testing. Randomize the split, balance label distribution, and keep the test set hidden until final evaluation. This prevents overfitting and guarantees fair, unbiased performance measurement.
Also Read: Top 60+ AI Interview Questions and Answers
Step 5: Select the model class for the task
Once the data is ready, you choose the type of model that fits the problem. The choice depends on the goal and the nature of the data.
The most common options are:
- Decision trees for tasks where interpretability is important
- Neural networks for complex patterns in large datasets
- Support vector machines for smaller datasets with clear margins between classes
Choosing the right class is important because it defines the balance between accuracy and interpretability. This choice also impacts the training time and the resources needed.
Step 6: Set hyperparameters and training setup
The next stage is to configure how the model will learn. Hyperparameters are settings chosen before training starts. They control aspects such as learning speed and model depth.
To prepare for this step, you should:
- Decide the number of training iterations or epochs
- Choose the learning rate that controls weight updates
- Set the batch size, which decides how many samples are processed at once
A good setup makes deep learning model training and inference more stable and efficient. It also reduces the need for constant retraining in the feedback loop.
Also, Read: Highest Paying Jobs in Generative AI
Step 7: Run model training and track metrics
Training is the stage where the model learns patterns from the training set. Tracking metrics ensures that learning is moving in the right direction.
Useful actions during training are:
- Recording accuracy or loss at regular intervals
- Comparing validation results to training results
- Stopping training when the model stops improving
This step connects back to the success metric defined in step one. If results are below target, you can adjust hyperparameters or revisit earlier steps like feature creation.
Step 8: Run inference on validation data
Once training is complete, you need to see how the model performs on unseen examples. Validation data is separate from training data, so it gives an honest view of performance.
Running inference on this set helps you check if the AI decision-making process is stable and consistent. It also reveals whether the model generalizes well or memorizes training patterns.
When you run inference, you should:
- Compare predictions to the actual labels
- Record the chosen success metric
- Look for signs of overfitting, such as high training accuracy but low validation accuracy
Good validation results create confidence before moving into the reasoning and action stages in real use.
Step 9: Apply algorithmic reasoning or rules if required
Some AI systems combine learned models with fixed logic. This is called algorithmic reasoning. It allows the AI to follow strict rules alongside learned patterns.
You might add this step when:
- The goal requires compliance with regulations
- Certain outcomes must be blocked regardless of the model prediction
- Complex tasks need reasoning layers that use multiple model outputs
This stage blends the strengths of statistical learning and rule-based decision-making. It makes the process of AI more reliable in controlled environments.
Step 10: Review the AI decision-making process end-to-end
Before moving to deployment, you review the full flow from end to end. This ensures every part works as expected and reflects how AI works in practice.
A complete review should:
- Check that each stage follows the original plan
- Verify that data quality stays high throughout the pipeline
- Confirm that outputs meet the success metric
This review connects the technical steps to the business or project goal. It is the final chance to fix gaps before real-world operation.
Step 11: Tune the model and compare baselines
Even well-trained models can improve with careful adjustments. Tuning means making small changes to settings or training data to boost performance.
When tuning, you can:
- Adjust hyperparameters such as learning rate or depth
- Add new features or remove ones that add noise
- Compare current results to a baseline model to measure gains
Tuning creates a stronger link between training results and production readiness. It also reduces errors during live predictions.
Step 12: Build the path from data ingestion to prediction in production
Once the model performs well, you prepare the system for real-world use. This stage connects raw inputs to live predictions in a stable and repeatable way, ensuring the final step of how AI works is reliable.
Your production path should:
- Collect and process incoming data in the same way as during training
- Feed inputs into the trained model without delays
- Return predictions to the application or user in the expected format
A strong production path keeps AI functioning consistently over time. It also prepares the system for the next stages, like deployment and monitoring.
Step 13: Deploy the model and the inference pipeline
Deployment is the point where the AI leaves the testing environment and starts working in real conditions. The inference pipeline is the set of processes that take new data, send it through the model, and return predictions.
A successful deployment includes:
- Placing the model on servers or devices that can handle the expected workload
- Ensuring the pipeline processes inputs in the same way as during training
- Returning predictions in a format that is ready for use by the application or end user
Deployment marks the moment when the process of AI begins to deliver value to real operations.
Step 14: Monitor accuracy, latency, and cost
Once deployed, the model needs ongoing monitoring. Without it performance can drop over time as data changes or systems slow down.
Key areas to monitor include:
- Accuracy of predictions compared to the success metric
- Latency, which measures the time between input and output
- Cost of running the model in terms of computation and storage
Consistent monitoring keeps AI functioning at a level that supports the original goal. It also helps identify when adjustments are needed.
Step 15: Add a feedback loop and human review
A feedback loop authorizes the AI to learn from its real-world performance. Human review adds another layer of quality control, especially in tasks that carry high risk.
An effective feedback loop might:
- Capture cases where predictions are incorrect
- Label new data created during live use
- Feed the new labeled data back into the training set
This process connects deployment with ongoing improvement. It also prepares the system for retraining.
Step 16: Retrain on fresh data and iterate
Retraining is necessary when the model starts to lose accuracy due to changes in the data. Fresh data preparation and implementation reflects current conditions better than older records.
Retraining steps can include:
- Adding recent data to the original training set
- Adjusting features to reflect new patterns
- Running updated training and validation cycles
This step strengthens the link between the AI decision-making process and its real-world context. This final step also closes the loop and makes the system easier to explain to stakeholders or new team members.
Want to go beyond just understanding AI?
Turn your knowledge into career-ready skills with our Intel®-certified AI–ML course. Learn the core mathematics that power AI—linear algebra, calculus, optimization—and apply them through real-world projects. Join 80,000+ learners mastering an industry-aligned curriculum, hands-on training, and native language support. In 2025 and beyond, this is the most practical path from knowing how AI works to building it yourself.
Quick Quiz: How Well Do You Understand AI?
- What does the “sense” stage in AI refer to?
a) Storing data
b) Gathering inputs from the environment
c) Deploying a model
d) Tuning hyperparameters
- Which metric is best when both precision and recall are equally important?
a) Mean Squared Error
b) Accuracy
c) F1 Score
d) Latency
- What’s the primary role of the inference stage in AI?
a) Training the model
b) Making predictions on unseen data
c) Collecting new datasets
d) Encoding features
- True or False: Algorithmic reasoning combines rule-based logic with learned patterns from models
- Which AI model type is typically used for complex pattern recognition in very large datasets?
a) Decision Trees
b) Support Vector Machines
c) Neural Networks
d) K-Means Clustering
Answers
- b) Gathering inputs from the environment
- c) F1 Score
- b) Making predictions on unseen data
- True
- c) Neural Networks
Conclusion
The process of AI moves through a clear sequence that starts with setting a goal and ends with ongoing improvement. Each stage in AI functioning connects to the next, so the system can sense, reason, and act in a way that meets its purpose.
Clean data and a strong feedback loop keep the AI decision-making process reliable over time. When these steps are followed, the path from data ingestion to prediction becomes predictable and repeatable.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between model training and inference?
Model training teaches the AI patterns from historical data. Inference applies that knowledge to make predictions on new data.
Q2: How often should an AI model be retrained?
Retraining should happen when accuracy drops or when new patterns appear in the data.
Q3: What is algorithmic reasoning in AI?
Algorithmic reasoning is when AI uses fixed rules alongside learned patterns to make decisions.




























Did you enjoy this article?