Cloud Computing: The Backbone of Modern Digital Transformation
Aug 06, 2025 2 Min Read 2051 Views
(Last Updated)
What’s powering your favorite apps, online games, virtual classrooms, and global businesses behind the scenes? The answer is cloud computing.
In the last decade, cloud computing has revolutionized the way we store, process, and manage data. It is no longer a buzzword; it’s a foundational technology that powers everything from small startups to global enterprises.
So, how did it become the backbone of modern innovation, and what exactly makes it so powerful? Let us learn the answers to these questions in this article!
Table of contents
- What is Cloud Computing?
- Cloud Computing Service Models
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Deployment Models in Cloud Computing
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- Real-World Applications of Cloud Computing
- Media & Entertainment
- E-Commerce
- Healthcare
- Education
- Enterprises
- Challenges in Cloud Computing
- The Future of Cloud Computing
- Conclusion
What is Cloud Computing?

Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing resources over the Internet. These resources include storage, servers, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, available on demand, typically on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Instead of maintaining physical infrastructure and data centers, organizations can access scalable and flexible resources through cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Cloud Computing Service Models
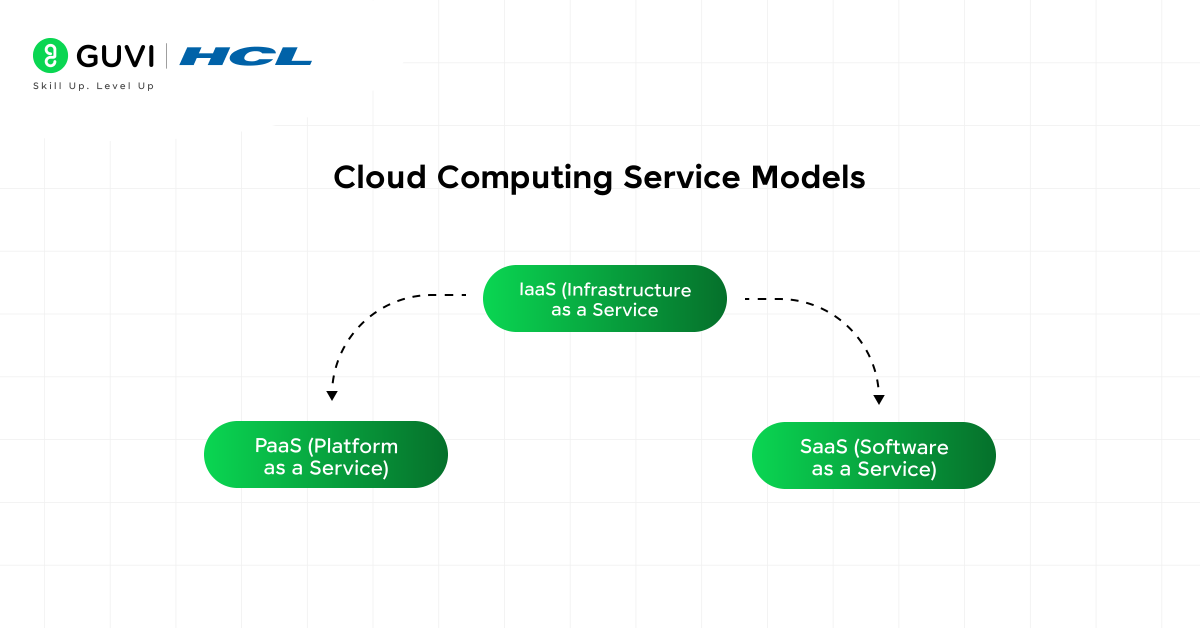
Cloud computing offers various service models, each serving different purposes:
1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- Definition: Provides virtualized computing resources via the internet.
- Examples: AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine, Azure Virtual Machines.
- Use Case: Suitable for system administrators and developers who want full control over infrastructure without investing in physical hardware.
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- Definition: Provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of maintaining infrastructure.
- Examples: Google App Engine, Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Services.
- Use Case: Ideal for developers focused on coding and application logic, not managing servers.
3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Definition: Delivers software applications over the internet, on a subscription basis.
- Examples: Microsoft 365, Salesforce, Dropbox, Gmail.
- Use Case: Best for end users needing ready-to-use applications without technical maintenance.
Deployment Models in Cloud Computing

There are different ways cloud services can be deployed depending on business needs:
Public Cloud
- Managed by third-party providers.
- Accessible by multiple users via the internet.
- Cost-effective but shared resources.
Private Cloud
- Used exclusively by a single organization.
- Offers more control and security.
- Hosted on-premises or by third-party vendors.
Hybrid Cloud
- Combining public and private clouds.
- Enables data and applications to move between environments.
- Balances flexibility with control and security.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- Scalability: Instantly scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Flexibility: Access services from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for what you use—no need for capital expenditure.
- High Availability: Services are designed for 24/7 uptime and reliability.
- Security: Advanced data encryption, compliance, and security features are standard.
Real-World Applications of Cloud Computing
Here is a list of real-world applications of cloud computing:
Media & Entertainment
- Netflix uses AWS to stream content globally.
- Spotify leverages Google Cloud for real-time analytics.
E-Commerce
- Amazon and Alibaba rely on the cloud to scale during massive sales events.
Healthcare
- Hospitals store patient data in secure cloud environments.
- AI diagnostics and health analytics run on cloud-based platforms.
Education
- Platforms like Coursera, Google Classroom, and Zoom use the cloud to enable remote learning.
Enterprises
- Salesforce, Oracle Cloud, and SAP provide cloud-based enterprise software.
Challenges in Cloud Computing
Despite its benefits, cloud computing comes with certain challenges:
- Security & Privacy Risks: Cloud data is vulnerable to cyber threats without proper measures.
- Downtime & Outages: Dependence on the internet and service provider uptime.
- Compliance: Meeting international data regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, etc.
- Vendor Lock-In: Switching providers can be technically and financially difficult.
The Future of Cloud Computing
The cloud is continuously evolving. Here are the key future trends:
- Edge Computing: Bringing computing power closer to data sources for low-latency processing.
- Serverless Architecture: Developers deploy code without managing servers (e.g., AWS Lambda).
- AI & ML in the Cloud: Cloud platforms now provide powerful AI/ML services to build intelligent applications.
- Sustainable Cloud: Providers are focusing on green energy and carbon-neutral infrastructures.
If you want to learn Cloud Computing deeply through Azure, consider enrolling in GUVI’s
Cloud Computing with Azure Course, which will arm you with the skills and knowledge to engage with the power of Microsoft Azure’s cloud services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud computing isn’t just reshaping the tech landscape; it’s redefining how we work, connect, and grow. From startups building the next big thing to enterprises optimizing global operations, the cloud offers a level of speed, scale, and intelligence that traditional systems simply can’t match.
As the world moves toward edge computing, AI-driven services, and greener infrastructure, one thing is clear: the future of digital transformation will continue to live in the cloud.































Did you enjoy this article?